1206. 设计跳表
难度困难218收藏分享切换为英文接收动态反馈
不使用任何库函数,设计一个 跳表 。
跳表 是在 O(log(n)) 时间内完成增加、删除、搜索操作的数据结构。跳表相比于树堆与红黑树,其功能与性能相当,并且跳表的代码长度相较下更短,其设计思想与链表相似。
例如,一个跳表包含 [30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 90] ,然后增加 80、45 到跳表中,以下图的方式操作: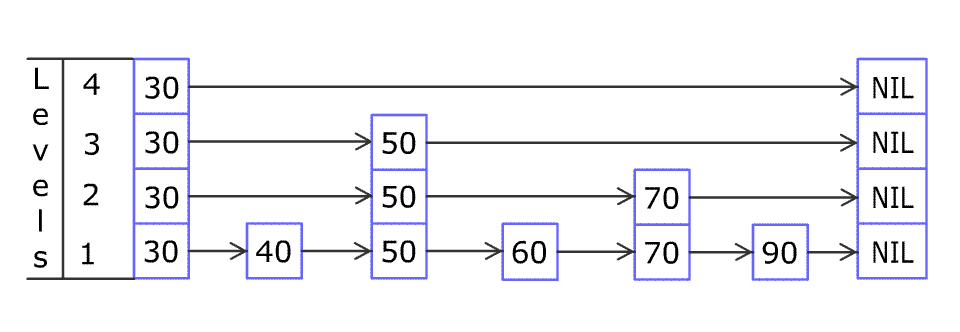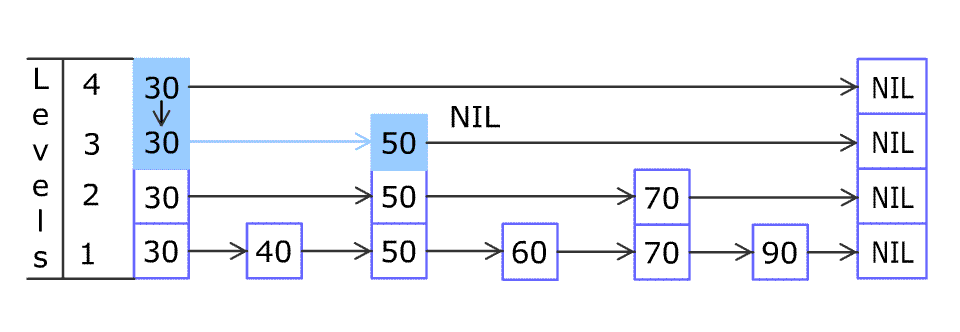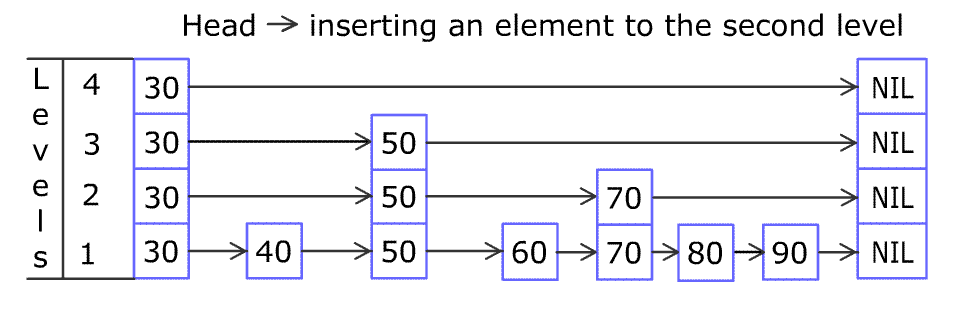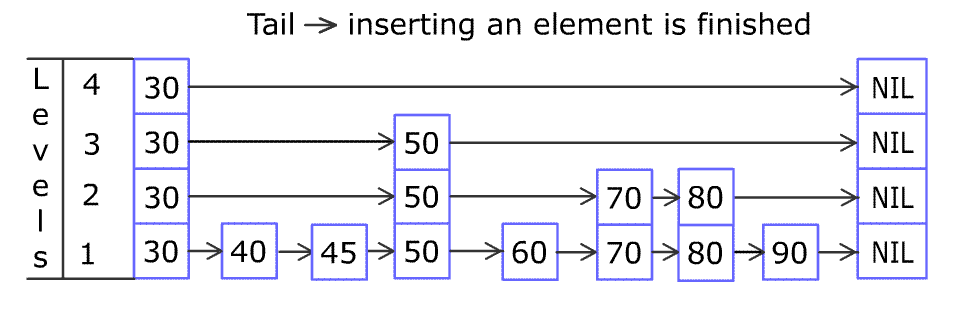
Artyom Kalinin [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons
跳表中有很多层,每一层是一个短的链表。在第一层的作用下,增加、删除和搜索操作的时间复杂度不超过 O(n)。跳表的每一个操作的平均时间复杂度是 O(log(n)),空间复杂度是 O(n)。
了解更多 : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Skip_list
在本题中,你的设计应该要包含这些函数:
- bool search(int target) : 返回target是否存在于跳表中。
- void add(int num): 插入一个元素到跳表。
- bool erase(int num): 在跳表中删除一个值,如果 num 不存在,直接返回false. 如果存在多个 num ,删除其中任意一个即可。
注意,跳表中可能存在多个相同的值,你的代码需要处理这种情况。
示例 1:
输入 [“Skiplist”, “add”, “add”, “add”, “search”, “add”, “search”, “erase”, “erase”, “search”] [[], [1], [2], [3], [0], [4], [1], [0], [1], [1]] 输出 [null, null, null, null, false, null, true, false, true, false] 解释 Skiplist skiplist = new Skiplist(); skiplist.add(1); skiplist.add(2); skiplist.add(3); skiplist.search(0); // 返回 false skiplist.add(4); skiplist.search(1); // 返回 true skiplist.erase(0); // 返回 false,0 不在跳表中 skiplist.erase(1); // 返回 true skiplist.search(1); // 返回 false,1 已被擦除
提示:
- 0 <= num, target <= 2 * 104
- 调用search, add, erase操作次数不大于 5 * 104
思路:
使用多层有序链表
时间复杂度:插入,查询,删除都是O(logn)
空间复杂度:O(n)
class Skiplist {static final int level = 10;class Node {int val;Node[] ne;Node(int val) {this.val = val;ne = new Node[level];}}void find(int target, Node[] res) {Node p = head;for (int i = level - 1; i >= 0; i--) {while(p.ne[i] != null && p.ne[i].val < target)p = p.ne[i];res[i] = p;}}Node head = new Node(-1);Node[] pre = new Node[level];Random r = new Random();public Skiplist() {}public boolean search(int target) {find(target, pre);if (pre[0].ne[0] == null || pre[0].ne[0].val != target) return false;return true;}public void add(int target) {find(target, pre);Node node = new Node(target);for (int i = 0; i < level; i++) {node.ne[i] = pre[i].ne[i];pre[i].ne[i] = node;if (r.nextInt(2) == 0) break;}}public boolean erase(int target) {find(target, pre);if (pre[0].ne[0] == null || pre[0].ne[0].val != target) return false;for (int i = 0; i < level; i++) {if (pre[i].ne[i] != null && pre[i].ne[i].val == target)pre[i].ne[i] = pre[i].ne[i].ne[i];}return true;}}/*** Your Skiplist object will be instantiated and called as such:* Skiplist obj = new Skiplist();* boolean param_1 = obj.search(target);* obj.add(num);* boolean param_3 = obj.erase(num);*/

