前置知识
凸多边形
凸多边形是指所有内角大小都在 [0, Π] 范围内的 简单多边形。
凸包
在平面上能包含所有给定点的最小凸多边形叫做凸包。
其定义为:对于给定集合X,所有包含 X的凸集的交集 S 被称为 X 的 凸包。
实际上可以理解为用一个橡皮筋包含住所有给定点的形态。
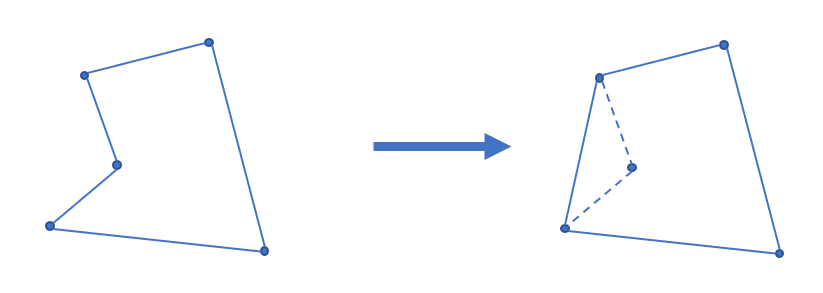
凸包用最小的周长围住了给定的所有点。如果一个凹多边形围住了所有的点,它的周长一定不是最小,如下图。根据三角不等式,凸多边形在周长上一定是最优的。
向量点乘:a · b = |a||b|cosθ = x1x2 + y1y2 ,表示数量积,内积
向量叉乘:a × b = |a||b|sinθ = x1y2 - x2y1 ,表示向量积,外积
Andrew算法
步骤:
- 双关键字排序:第一关键字
x从小到大,第二关键字y从小到大
显然排序后最小的元素和最大的元素一定在凸包上。 - 用栈维护凸包,先扫上半边,再扫下半边
- 若栈中只有一个元素,直接入栈即可
- 正着扫描,若栈中元素数大于等于两个,假设栈顶元素为
b,栈顶第二个元素为a,待考虑点为c,若ab × ac < 0,说明是顺时针方向,将c入栈,若ab × ac > 0,说明是逆时针方放,将b出栈,迭代考虑栈顶元素,最后将c入栈
同时记得记录栈中元素st,避免反着扫描时再次用到 - 栈底元素记为没有被使用过,保证最后闭合
- 反着扫描,同步骤4
时间复杂度: O(nlogn)
Graham算法
类似Anbdrew算法
找到最低点,以该点为基准对所有点按极角进行排序,极角相同的按极值从小到大排序。
一次遍历就可以求出凸包上的点
Jarvis 算法
相较于Graham算法,没有前置的排序,每次暴力寻找当前最右侧点,使得其余点均在其左侧
时间复杂度:O(n2)
例题
587. 安装栅栏
难度困难126收藏分享切换为英文接收动态反馈
在一个二维的花园中,有一些用 (x, y) 坐标表示的树。由于安装费用十分昂贵,你的任务是先用最短的绳子围起所有的树。只有当所有的树都被绳子包围时,花园才能围好栅栏。你需要找到正好位于栅栏边界上的树的坐标。
示例 1:
输入: [[1,1],[2,2],[2,0],[2,4],[3,3],[4,2]]
输出: [[1,1],[2,0],[4,2],[3,3],[2,4]]
解释: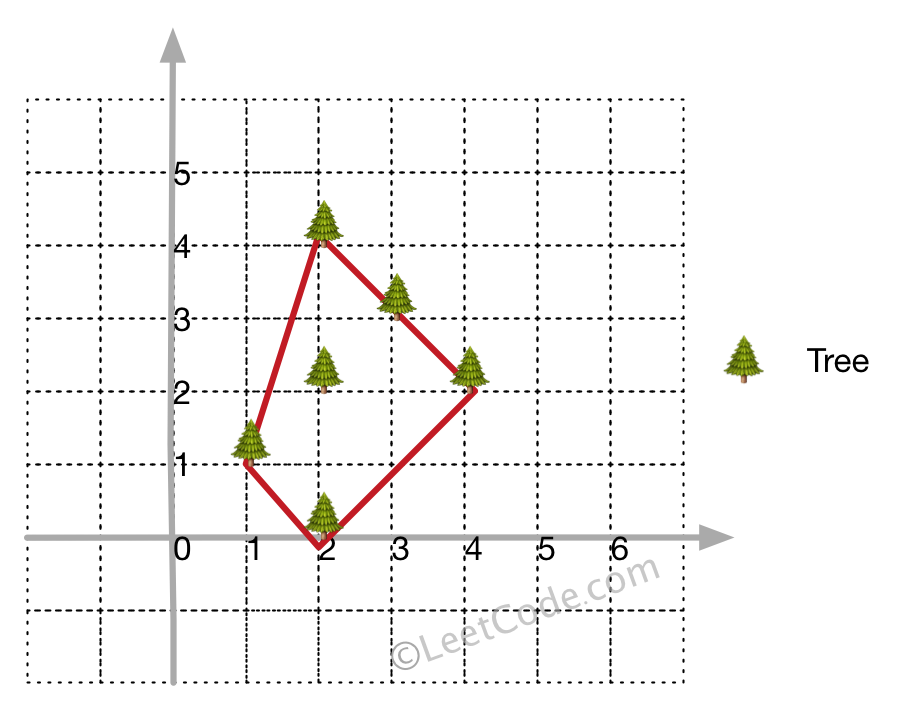
示例 2:
输入: [[1,2],[2,2],[4,2]]
输出: [[1,2],[2,2],[4,2]]
解释: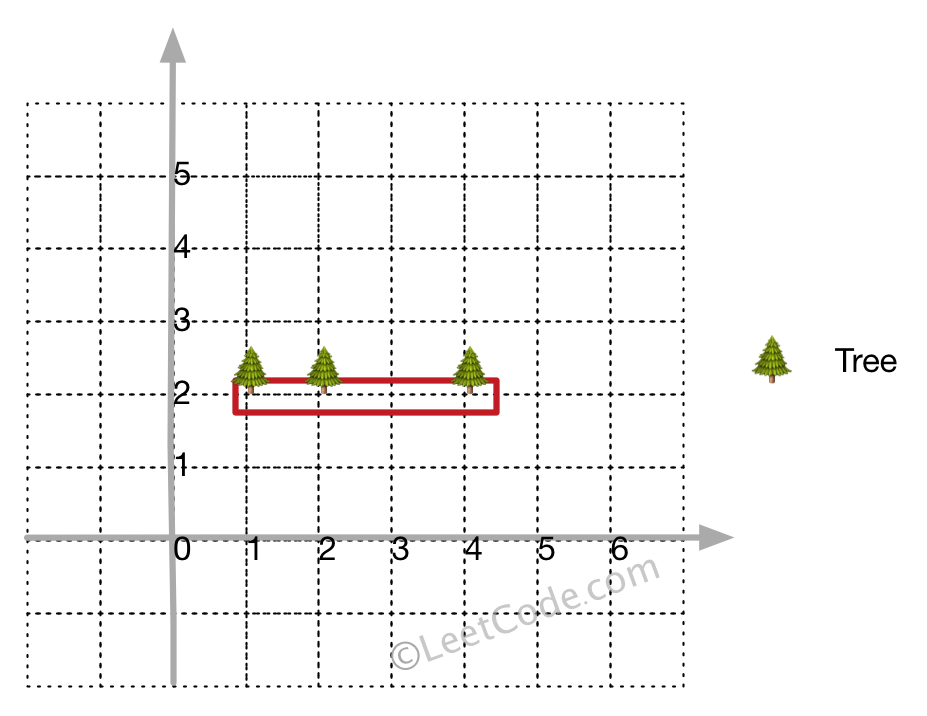
即使树都在一条直线上,你也需要先用绳子包围它们。
注意:
- 所有的树应当被围在一起。你不能剪断绳子来包围树或者把树分成一组以上。
- 输入的整数在 0 到 100 之间。
- 花园至少有一棵树。
- 所有树的坐标都是不同的。
- 输入的点没有顺序。输出顺序也没有要求。
思路:
Andrew算法求凸包
class Solution {public int[][] outerTrees(int[][] trees) {int n = trees.length;Arrays.sort(trees, (o1, o2) -> (o1[0] == o2[0] ? o1[1] - o2[1] : o1[0] - o2[0]));int[] stk = new int[n + 1];boolean[] st = new boolean[n];int p = -1;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {while (p >= 1 && cross(trees, stk[p - 1], stk[p], i) > 0) {st[stk[p]] = false;p--;}stk[++p] = i;st[i] = true;}st[0] = false;for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {if (st[i]) continue;while (p >= 1 && cross(trees, stk[p - 1], stk[p], i) > 0) {p--;}stk[++p] = i;}int[][] res = new int[p][];for (int i = 0; i < p; i++) {res[i] = trees[stk[i]];}return res;}int cross(int[][] t, int a, int b, int c) {int x1 = t[b][0] - t[a][0], y1 = t[b][1] - t[a][1];int x2 = t[c][0] - t[a][0], y2 = t[c][1] - t[a][1];return x1 * y2 - x2 * y1;}}
方法2:Graham算法 :::danger 注意本题需要求出凸包上的所有点,纯粹Graham算法最后存在共线情况时只能求出两端的点,所以需要稍加改进,对最后共线的点按照距离从大到小排序 :::
class Solution {public int[][] outerTrees(int[][] trees) {int n = trees.length;if (n < 4) {return trees;}int bottom = 0;/* 找到 y 最小的点 bottom*/for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {if (trees[i][1] < trees[bottom][1]) {bottom = i;}}swap(trees, bottom, 0);/* 以 bottom 原点,按照极坐标的角度大小进行排序 */Arrays.sort(trees, 1, n, (a, b) -> {int diff = cross(trees[0], a, b) - cross(trees[0], b, a);if (diff == 0) {return distance(trees[0], a) - distance(trees[0], b);} else {return -diff;}});/* 对于凸包最后且在同一条直线的元素按照距离从大到小进行排序 */int r = n - 1;while (r >= 0 && cross(trees[0], trees[n - 1], trees[r]) == 0) {r--;}System.out.println(trees[0][0] + " " + trees[0][1]);for (int i = r + 1; i < n; i++) {System.out.println(trees[i][0] + " " + trees[i][1]);}for (int l = r + 1, h = n - 1; l < h; l++, h--) {swap(trees, l, h);}Deque<Integer> stack = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();stack.push(0);stack.push(1);for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) {int top = stack.pop();/* 如果当前元素与栈顶的两个元素构成的向量顺时针旋转,则弹出栈顶元素 */while (!stack.isEmpty() && cross(trees[stack.peek()], trees[top], trees[i]) < 0) {top = stack.pop();}stack.push(top);stack.push(i);}int size = stack.size();int[][] res = new int[size][2];for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {res[i] = trees[stack.pop()];}return res;}public int cross(int[] p, int[] q, int[] r) {return (q[0] - p[0]) * (r[1] - q[1]) - (q[1] - p[1]) * (r[0] - q[0]);}public int distance(int[] p, int[] q) {return (p[0] - q[0]) * (p[0] - q[0]) + (p[1] - q[1]) * (p[1] - q[1]);}public void swap(int[][] trees, int i, int j) {int temp0 = trees[i][0], temp1 = trees[i][1];trees[i][0] = trees[j][0];trees[i][1] = trees[j][1];trees[j][0] = temp0;trees[j][1] = temp1;}}

