1. MVC架构
MVC属于苹果推荐的架构模式,包含几个明显的特征: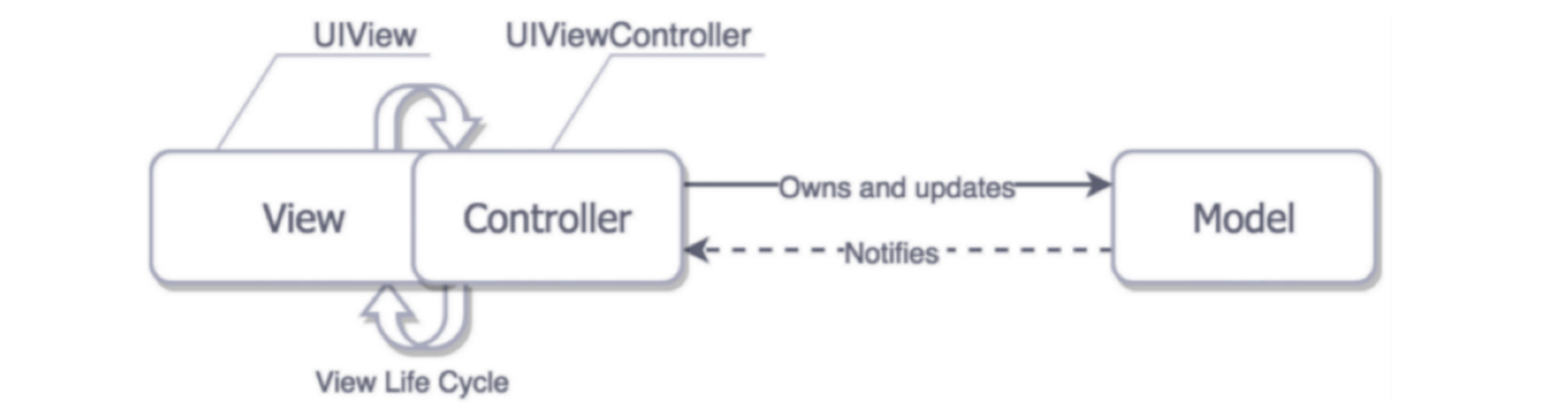
Model:模型层,封装了应用程序的数据,并定义操控和处理该数据的逻辑和运算View:视图层,用于视图控件的渲染,并且对用户的操作作出响应Controller:程序的视图对象和模型对象之间的交互和通讯,由控制器充当媒介,负责二者的执行设置和协调任务,并管理它们的生命周期
这种方式在实际开发中,会产生两个常见的问题:
Controller中存在大量的代理、逻辑、UI和内部方法,导致VC层过重View和Model之间很容易产生依赖,导致耦合度过高
开发中,非常典型的View和Model产生依赖的代码: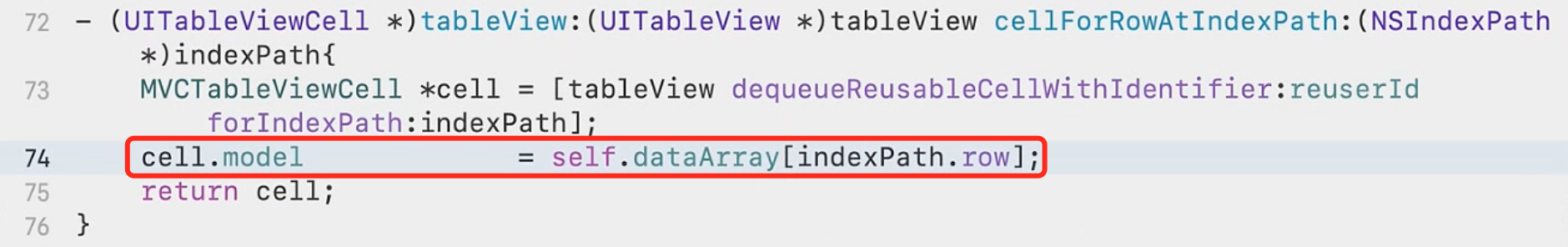
一个好的架构,应该做到高内聚,低耦合。让代码的复用性提高,模块之间的依赖程度降低。简单来说,应该谁的事情谁做,模块之间各负其职,持续保持项目的生命周期
2. 轻量化VC
VC的实际意义,只是建立模块之间的依赖关系。但开发中,我们在VC中还会加入一些繁重的UI代码、啰嗦的业务逻辑、很长的网络层代码、难受的代理功能
这些原本不属于VC的业务代码,全部堆积在VC中,导致VC愈发笨重,难以维护
构建轻量级VC,把不属于VC的业务代码全部分散。例如:将常见的UITableView相关代理,使用自定义DataSource进行封装。将繁重的UI代码,使用自定义View进行封装
自定义DataSource封装UITableView相关代理,这个类对整个项目来说都可以被复用
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>#import <UIKit/UIKit.h>typedef void (^CellConfigureBefore)(id cell, id model, NSIndexPath * indexPath);@interface LMDataSource : NSObject<UITableViewDataSource,UICollectionViewDataSource>@property (nonatomic, weak) NSArray *dataArray;- (id)initWithIdentifier:(NSString *)identifier configureBlock:(CellConfigureBefore)before;@property (nonatomic, strong) IBInspectable NSString *cellIdentifier;@property (nonatomic, copy) CellConfigureBefore cellConfigureBefore;- (id)modelsAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath;@end@implementation LMDataSource- (id)initWithIdentifier:(NSString *)identifier configureBlock:(CellConfigureBefore)before {if(self = [super init]) {_cellIdentifier = identifier;_cellConfigureBefore = [before copy];}return self;}- (id)modelsAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {return self.dataArray.count > indexPath.row ? self.dataArray[indexPath.row] : nil;}#pragma mark UITableViewDataSource- (NSInteger)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section{return !self.dataArray ? 0: self.dataArray.count;}- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath{UITableViewCell *cell = [tableView dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:self.cellIdentifier forIndexPath:indexPath];id model = [self modelsAtIndexPath:indexPath];if(self.cellConfigureBefore) {self.cellConfigureBefore(cell, model,indexPath);}return cell;}#pragma mark UICollectionViewDataSource- (NSInteger)collectionView:(UICollectionView *)collectionView numberOfItemsInSection:(NSInteger)section{return !self.dataArray ? 0: self.dataArray.count;}- (UICollectionViewCell *)collectionView:(UICollectionView *)collectionView cellForItemAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath{UICollectionViewCell *cell = [collectionView dequeueReusableCellWithReuseIdentifier:self.cellIdentifier forIndexPath:indexPath];id model = [self modelsAtIndexPath:indexPath];if(self.cellConfigureBefore) {self.cellConfigureBefore(cell, model,indexPath);}return cell;}- (NSMutableArray *)dataArray{if (!_dataArray) {_dataArray = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:5];}return _dataArray;}@end
自定义View封装繁重的UI代码
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h>#import "MVCTableViewCell.h"@interface LGView : UIView@property (nonatomic, strong) UITableView *tableView;- (void)setDataSource:(id<UITableViewDataSource>)dataSource;@end@implementation LGView- (instancetype)initWithFrame:(CGRect)frame{self = [super initWithFrame:frame];if (self) {[self addSubview:self.tableView];}return self;}- (void)setDataSource:(id<UITableViewDataSource>)dataSource{self.tableView.dataSource = dataSource;}- (UITableView *)tableView{if (!_tableView) {_tableView = [[UITableView alloc] initWithFrame:self.frame style:UITableViewStylePlain];_tableView.tableFooterView = [UIView new];_tableView.backgroundColor = [UIColor whiteColor];[_tableView registerClass:[MVCTableViewCell class] forCellReuseIdentifier:[MVCTableViewCell reuserId]];}return _tableView;}@end
轻量级VC中的代码
#import "MVCViewController.h"#import "LMDataSource.h"#import "MVCTableViewCell.h"#import "Present.h"#import "Model.h"#import "LGView.h"@interface MVCViewController ()@property (nonatomic, strong) LGView *lgView;@property (nonatomic, strong) LMDataSource *dataSource;@property (nonatomic, strong) Present *pt;@end@implementation MVCViewController- (void)viewDidLoad {[super viewDidLoad];// 建立关系self.view = self.lgView;[self.dataSource setDataArray:self.pt.dataArray];[self.lgView setDataSource:self.dataSource];}#pragma mark - lazy// UI布局代码- (LGView *)lgView{if(!_lgView){_lgView = [[LGView alloc] initWithFrame:self.view.bounds];}return _lgView;}// 数据提供层- (Present *)pt{if(!_pt){_pt = [[Present alloc] init];}return _pt;}// 数据代理层- (LMDataSource *)dataSource{if(!_dataSource){_dataSource = [[LMDataSource alloc] initWithIdentifier:[MVCTableViewCell reuserId] configureBlock:^(MVCTableViewCell *cell, Model *model, NSIndexPath *indexPath) {cell.model = model;}];}return _dataSource;}@end
3. MVP架构
上述案例中,还存在UI与Model之间的强依赖关系
在Cell中,UI的展示需要使用Model
- (void)setModel:(Model *)model{_model = model;self.numLabel.text = model.num;self.nameLabel.text = model.name;}
当用户点击Cell上的某个按钮发生交互,同样需要修改Model
- (void)didClickAddBtn:(UIButton *)sender{self.num++;}- (void)setNum:(int)num{_num = num;self.numLabel.text = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%d",self.num];self.model.num = self.numLabel.text;}
对于UI和Model层的解耦处理,可以采用MVP面向协议编程,即Model View Presenter(模型 视图 协调器)
3.1 特征
任务均摊:将最主要的任务划分到
Presenter和Model,而View的功能较少可测试性:由于一个功能简单的
View层,所以测试数业务逻辑变得简单易用性:比使用
MVC模式的代码量更多,但MVP模式具备非常清晰的结构
所以,MVC与MVP的区别就是,在MVP中Model和View没有直接通信
3.2 设计模式
Model层不仅仅是创建一个数据对象,还应该包含网络请求,以及数据Cache的操作View层就是一些封装、重用Presenter层并不涉及数据的网络请求和Cache操作,只是搭建Model层和View层的一个桥梁
3.3 优势
模型与视图完全分离,修改视图而不影响模型
可以更高效地使用模型,因为所有交互都在
Presenter中把逻辑放在
Presenter中,可以脱离用户接口进行单元测试可以将一个
Presener用于多个视图,而不需要改变Presenter的逻辑。这个特性非常的有用,因为视图的变化总是比模型的变化频繁
3.4 UI与Model解耦
创建LGProtocol,实现Cell中按钮点击的事件接口
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>@protocol LGProtocol <NSObject>- (void)didClickNum:(NSString *)num indexpath:(NSIndexPath *)indexpath;@end
在Present中,实现LGProtocol协议的didClickNum方法
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>#import "Model.h"#import "LGProtocol.h"#import <YYKit.h>@interface Present : NSObject<LGProtocol>@property (nonatomic, strong) NSMutableArray *dataArray;@property (nonatomic, weak) id<LGProtocol> delegate;@end@implementation Present- (instancetype)init{if (self = [super init]) {[self loadData];}return self;}- (void)loadData{NSArray *temArray =@[@{@"name":@"HK",@"imageUrl":@"http://HK",@"num":@"99"},@{@"name":@"KD",@"imageUrl":@"http://KD",@"num":@"99"},@{@"name":@"CC",@"imageUrl":@"http://CC",@"num":@"99"},@{@"name":@"KC",@"imageUrl":@"http://KC",@"num":@"59"},@{@"name":@"LA",@"imageUrl":@"http://LA",@"num":@"24"}];for (int i = 0; i<temArray.count; i++) {Model *m = [Model modelWithDictionary:temArray[i]];[self.dataArray addObject:m];}}#pragma mark -LGProtocol- (void)didClickNum:(NSString *)num indexpath:(NSIndexPath *)indexpath{@synchronized (self) {if (indexpath.row < self.dataArray.count) {Model *model = self.dataArray[indexpath.row];model.num = num;}}}#pragma mark - lazy- (NSMutableArray *)dataArray{if (!_dataArray) {_dataArray = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:10];}return _dataArray;}@end
在MVCTableViewCell中,删除UI对Model的数据绑定。在按钮点击的交互方法中,调用delegate的didClickNum方法
- (void)didClickAddBtn:(UIButton *)sender{self.num++;}- (void)setNum:(int)num{_num = num;self.numLabel.text = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%d",self.num];// 发出响应 model delegate UIif (self.delegate && [self.delegate respondsToSelector:@selector(didClickNum:indexpath:)]) {[self.delegate didClickNum:self.numLabel.text indexpath:self.indexPath];}}// 删除UI对Model的数据绑定//- (void)setModel:(Model *)model{// _model = model;// self.numLabel.text = model.num;// self.nameLabel.text = model.name;//}
来到VC代码中LMDataSource的Block,完成Cell中UI对Model的数据绑定,以及delegate和indexPath的设置
#import "MVCViewController.h"#import "LMDataSource.h"#import "MVCTableViewCell.h"#import "Present.h"#import "Model.h"#import "LGView.h"@interface MVCViewController ()@property (nonatomic, strong) LGView *lgView;@property (nonatomic, strong) LMDataSource *dataSource;@property (nonatomic, strong) Present *pt;@end@implementation MVCViewController- (void)viewDidLoad {[super viewDidLoad];// 建立关系self.view = self.lgView;[self.dataSource setDataArray:self.pt.dataArray];[self.lgView setDataSource:self.dataSource];}#pragma mark - lazy// UI布局代码- (LGView *)lgView{if(!_lgView){_lgView = [[LGView alloc] initWithFrame:self.view.bounds];}return _lgView;}// 数据提供层- (Present *)pt{if(!_pt){_pt = [[Present alloc] init];}return _pt;}// 数据代理层- (LMDataSource *)dataSource{if(!_dataSource){__weak typeof(self) weakSelf = self;_dataSource = [[LMDataSource alloc] initWithIdentifier:[MVCTableViewCell reuserId] configureBlock:^(MVCTableViewCell *cell, Model *model, NSIndexPath *indexPath) {__strong __typeof(weakSelf)strongSelf = weakSelf;cell.numLabel.text = model.num;cell.nameLabel.text = model.name;cell.delegate = strongSelf.pt;cell.indexPath = indexPath;}];}return _dataSource;}@end
3.5 双向绑定
开发中遇到以下需求时,需要UI和Model进行双向绑定。例如:触发Cell的didClickAddBtn事件,当num++大于5,UI层只展示前两条数据
修改LGProtocol,增加UI刷新的事件接口
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>@protocol LGProtocol <NSObject>- (void)didClickNum:(NSString *)num indexpath:(NSIndexPath *)indexpath;- (void)reloadUI;@end
修改Present中的didClickNum方法,增加num大于5,只保留前两条数据,并调用delegate的reloadUI方法刷新UI
- (void)didClickNum:(NSString *)num indexpath:(NSIndexPath *)indexpath{@synchronized (self) {if (indexpath.row < self.dataArray.count) {Model *model = self.dataArray[indexpath.row];model.num = num;if ([num intValue] > 5) {[self.dataArray removeAllObjects];NSArray *temArray =@[@{@"name":@"HK",@"imageUrl":@"http://HK",@"num":@"99"},@{@"name":@"KC",@"imageUrl":@"http://KC",@"num":@"99"}];for (int i = 0; i<temArray.count; i++) {Model *m = [Model modelWithDictionary:temArray[i]];[self.dataArray addObject:m];}if (self.delegate && [self.delegate respondsToSelector:@selector(reloadUI)]) {[self.delegate reloadUI];}}}}}
修改LGView,实现LGProtocol协议的刷新UI方法
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h>#import "MVCTableViewCell.h"#import "LGProtocol.h"@interface LGView : UIView<LGProtocol>@property (nonatomic, strong) UITableView *tableView;- (void)setDataSource:(id<UITableViewDataSource>)dataSource;@end@implementation LGView- (instancetype)initWithFrame:(CGRect)frame{self = [super initWithFrame:frame];if (self) {[self addSubview:self.tableView];}return self;}- (void)setDataSource:(id<UITableViewDataSource>)dataSource{self.tableView.dataSource = dataSource;}- (void)reloadUI{[self.tableView reloadData];}- (UITableView *)tableView{if (!_tableView) {_tableView = [[UITableView alloc] initWithFrame:self.frame style:UITableViewStylePlain];_tableView.tableFooterView = [UIView new];_tableView.backgroundColor = [UIColor whiteColor];[_tableView registerClass:[MVCTableViewCell class] forCellReuseIdentifier:[MVCTableViewCell reuserId]];}return _tableView;}@end
修改MVCViewController,将UI和Model建立关系
- (void)viewDidLoad {[super viewDidLoad];// 建立关系self.view = self.lgView;[self.dataSource setDataArray:self.pt.dataArray];[self.lgView setDataSource:self.dataSource];//将UI和Model建立关系self.pt.delegate = self.lgView;}
3.6 案例总结
对于上述MVP的简单案例,其实还存在很多缺陷。这种简陋的代码,连开发中常见的需求都难以满足
例如以下一些情况:
遇到更复杂的
Cell形态使用过多的
delegate等胶水代码当遇到模块层次更深的情况,相互之间难以通讯
所以,针对上述的问题,还要介绍一下MVP的真正使用方式
4. 适配器设计
当一个列表中出现多种Cell形态,可以使用适配器设计方式
创建KCBaseAdapter基类,基于UITableView的代理,实现基础方法
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>#import <UIKit/UIKit.h>NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_BEGIN@protocol KCBaseAdapterDelegate <NSObject>@optional- (void)didSelectCellData:(id)cellData;- (void)deleteCellData:(id)cellData;- (void)willDisplayCell:(UITableViewCell *)cell forRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath;@end@protocol KCBaseAdapterScrollDelegate <NSObject>- (void)scrollViewWillBeginDragging:(UIScrollView *)scrollView ;- (void)scrollViewDidScroll:(UIScrollView *)scrollView ;- (void)scrollViewDidEndDragging:(UIScrollView *)scrollView;@end@protocol KCBaseAdapterPullUpDelegate <NSObject>- (void)beginToRefresh;@end@interface KCBaseAdapter : NSObject<UITableViewDataSource, UITableViewDelegate>{}@property (nonatomic, weak) id<KCBaseAdapterDelegate> adapterDelegate;@property (nonatomic, weak) id<KCBaseAdapterScrollDelegate> adapterScrollDelegate;@property (nonatomic, weak) id<KCBaseAdapterPullUpDelegate> adapterPullUpDelegate;@property (nonatomic, strong) NSMutableArray *arr;- (float)getTableContentHeight;- (void)refreshCellByData:(id)data tableView:(UITableView*)tableView;- (NSArray*)getAdapterArray;- (void)setAdapterArray:(NSArray*)arr;@end@implementation KCBaseAdapter- (instancetype)init{self = [super init];if (self) {_arr = [NSMutableArray new];}return self;}- (NSArray*)getAdapterArray{return _arr;}- (void)setAdapterArray:(NSArray*)arr{[_arr removeAllObjects];[_arr addObjectsFromArray:arr];}- (float)getTableContentHeight{return 0;}#pragma mark - 抽象方法- (void)refreshCellByData:(id)data tableView:(UITableView*)tableView{}#pragma mark UITableView DataSource- (NSInteger)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section{return _arr.count;}- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath{if (indexPath.row > self.getAdapterArray.count-1) {return [UITableViewCell new];}id cellData = [self.arr objectAtIndex:indexPath.row];UITableViewCell* cell = NULL;CCSuppressPerformSelectorLeakWarning(cell = [self performSelector:NSSelectorFromString([NSString stringWithFormat:@"tableView:cellFor%@:", [cellData class]]) withObject:tableView withObject:cellData];);return cell;}#pragma mark - UITableView Delegate- (CGFloat)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView heightForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath{return 0;}- (void)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView didSelectRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath{if (indexPath.row > self.getAdapterArray.count-1) {return;}[tableView deselectRowAtIndexPath:indexPath animated:false];id cellData = [self.arr objectAtIndex:indexPath.row];if (self.adapterDelegate) {if ([_adapterDelegate respondsToSelector:@selector(didSelectCellData:)]) {[_adapterDelegate didSelectCellData:cellData];}}}- (void)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView willDisplayCell:(UITableViewCell *)cell forRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath{if (indexPath.row > self.getAdapterArray.count-1) {return;}if (self.adapterPullUpDelegate && [self.adapterPullUpDelegate respondsToSelector:@selector(beginToRefresh)]) {//倒数第三个 发送请求if (tableView.style == UITableViewStyleGrouped) {if (self.getAdapterArray.count >1) {NSArray *dataArray = [self.getAdapterArray objectAtIndex:0];if (dataArray.count > 4 && dataArray.count - 4 == indexPath.row) {[self.adapterPullUpDelegate beginToRefresh];}}}else if (tableView.style == UITableViewStylePlain){if (self.getAdapterArray.count > 4 && self.getAdapterArray.count - 4 == indexPath.row) {[self.adapterPullUpDelegate beginToRefresh];}}}if (self.adapterDelegate) {if ([_adapterDelegate respondsToSelector:@selector(willDisplayCell:forRowAtIndexPath:)]) {[_adapterDelegate willDisplayCell:cell forRowAtIndexPath:indexPath];}}}#pragma mark - UIScrollViewDelegate- (void)scrollViewWillBeginDragging:(UIScrollView *)scrollView {if (self.adapterScrollDelegate && [self.adapterScrollDelegate respondsToSelector:@selector(scrollViewWillBeginDragging:)]) {[self.adapterScrollDelegate scrollViewWillBeginDragging:scrollView];}}- (void)scrollViewDidScroll:(UIScrollView *)scrollView {if (self.adapterScrollDelegate && [self.adapterScrollDelegate respondsToSelector:@selector(scrollViewDidScroll:)]) {[self.adapterScrollDelegate scrollViewDidScroll:scrollView];}}- (void)scrollViewDidEndDragging:(UIScrollView *)scrollView willDecelerate:(BOOL)decelerate {if (self.adapterScrollDelegate && [self.adapterScrollDelegate respondsToSelector:@selector(scrollViewDidEndDragging:)]) {[self.adapterScrollDelegate scrollViewDidEndDragging:scrollView];}}@end
创建KCHomeAdapter,继承于KCBaseAdapter,实现针对首页的业务逻辑
#import "KCHomeAdapter.h"#import "KCHomeTableViewCell.h"#import "KCChannelProfile.h"@implementation KCHomeAdapter- (CGFloat)getCellHeight:(NSInteger)row{CGFloat height = SCREEN_WIDTH*608/1080 + 54;KCChannelProfile *model = [self.getAdapterArray objectAtIndex:row];if (model.title.length > 0) {CGSize titleSize = [model.title sizeWithAttributes:@{NSFontAttributeName:[UIFont systemFontOfSize:14]}];if (titleSize.width > SCREEN_WIDTH - 35) {// 两行height +=67;}else{height +=50;}}else{height += 8;}return height;}- (CGFloat)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView heightForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {return [self getCellHeight:indexPath.row];}- (NSInteger)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section {return self.getAdapterArray.count;}- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {KCChannelProfile* liveModel = self.getAdapterArray[indexPath.row];UITableViewCell *cell = nil;CCSuppressPerformSelectorLeakWarning (cell = [self performSelector:NSSelectorFromString([NSString stringWithFormat:@"tableView:cellForKCChannelProfile:"]) withObject:tableView withObject:liveModel];);return cell;}- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForKCChannelProfile:(id)model {NSString *cellIdentifier = NSStringFromSelector(_cmd);KCHomeTableViewCell *cell = (KCHomeTableViewCell *)[tableView dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:cellIdentifier];if (!cell) {cell = [[KCHomeTableViewCell alloc] initWithStyle:UITableViewCellStyleDefault reuseIdentifier:cellIdentifier];}KCChannelProfile* liveModel = model;[cell setCellContent:liveModel];return cell;}- (void)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView didSelectRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {[tableView deselectRowAtIndexPath:indexPath animated:NO];id model = self.getAdapterArray[indexPath.row];if (self.adapterDelegate && [self.adapterDelegate respondsToSelector:@selector(didSelectCellData:)]) {[self.adapterDelegate didSelectCellData:model];}}@end
因为在项目中,针对不同业务的实现代码逻辑各不相同。我们在基类中只实现基础代码,通过继承或分类的形式,完成业务代码,以此方式做到去中心化,增强代码的复用性
5. context设计
创建宏定义,实现代理方法的万能调用
#define KC(instance, protocol, message) [(id<protocol>)(instance) message]
创建KCBaseViewController作为VC层的基类,内部实现UI层和Model层都依赖的Context上下文
#import "KCBaseViewController.h"@interface KCBaseViewController ()@property (nonatomic, strong) NSMutableDictionary *eventMap;@property (nonatomic, assign) BOOL mvpEnabled;@end@implementation KCBaseViewController- (void)configMVP:(NSString*)name{self.mvpEnabled = true;self.rootContext = [[CDDContext alloc] init]; //strongself.context = self.rootContext; //weak//presentorClass presenterClass = NSClassFromString([NSString stringWithFormat:@"KC%@Presenter", name]);if (presenterClass != NULL) { // 缓存self.context.presenter = [presenterClass new];self.context.presenter.context = self.context;}//interactorClass interactorClass = NSClassFromString([NSString stringWithFormat:@"KC%@Interactor", name]);if (interactorClass != NULL) {self.context.interactor = [interactorClass new];self.context.interactor.context = self.context;}//viewClass viewClass = NSClassFromString([NSString stringWithFormat:@"KC%@View", name]);if (viewClass != NULL) {self.context.view = [viewClass new];self.context.view.context = self.context;}//build relationself.context.presenter.view = self.context.view;self.context.presenter.baseController = self;self.context.interactor.baseController = self;self.context.view.presenter = self.context.presenter;self.context.view.interactor = self.context.interactor;}- (void)viewDidLoad{[super viewDidLoad];if (self.mvpEnabled) {self.context.view.frame = self.view.bounds;self.view = self.context.view;}KCLog(@"\n\nDid Load ViewController: %@\n\n", [self class]);}- (void)dealloc{KCLog(@"\n\nReleasing ViewController: %@\n\n", [self class]);[Notif removeObserver:self];}@end
VC下的context为rootContextrootContext下包含presenter、interactor、view的创建,并对各层级下的context进行赋值- 文件的命名,必须和代码规则一致
找到CDDContext、CDDPresenter、CDDInteractor、CDDView的定义:
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>#import "NSObject+CDD.h"@class CDDContext;@class CDDView;@interface CDDPresenter : NSObject@property (nonatomic, weak) UIViewController* baseController;@property (nonatomic, weak) CDDView* view;@property (nonatomic, weak) id adapter; //for tableview adapter@end@interface CDDInteractor : NSObject@property (nonatomic, weak) UIViewController* baseController;@end@interface CDDView : UIView@property (nonatomic, weak) CDDPresenter* presenter;@property (nonatomic, weak) CDDInteractor* interactor;@end//Context bridges everything automatically, no need to pass it around manually@interface CDDContext : NSObject@property (nonatomic, strong) CDDPresenter* presenter;@property (nonatomic, strong) CDDInteractor* interactor;@property (nonatomic, strong) CDDView* view; //view holds strong reference back to context@end@implementation CDDPresenter@end@implementation CDDInteractor@end@implementation CDDView- (void)dealloc{self.context = nil;}@end@implementation CDDContext- (void)dealloc{NSLog(@"context being released");}@end
- 对于
Context上下文,它只负责信息的综合管理,不负责业务细节的实现,所以并不存在臃肿的现象
6. context分发
无论自定义View的层级有多深,都可以调用到context上下文
例如:直播页面中弹出的礼物列表弹窗,点击发送礼物的事件
- (void)buttonSendClicked:(id)sender{if (_selectedItem) {KC(self.context.presenter, KCLiveStreamPresenterDeleagte, sendGiftWithIndex:(int)_selectedItem.tag);}}
子View中的context上下文的构建方式,通过VC层对context进行设置,而context实际上是基于NSObject创建的CDD分类,在分类中使用关联对象的方式进行设置
#import "NSObject+CDD.h"#import "CDDContext.h"#import <objc/runtime.h>@implementation NSObject (CDD)@dynamic context;- (void)setContext:(CDDContext*)object {objc_setAssociatedObject(self, @selector(context), object, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_ASSIGN);}- (CDDContext*)context {id curContext = objc_getAssociatedObject(self, @selector(context));if (curContext == nil && [self isKindOfClass:[UIView class]]) {//try get from superview, lazy getUIView* view = (UIView*)self;UIView* sprView = view.superview;while (sprView != nil) {if (sprView.context != nil) {curContext = sprView.context;break;}sprView = sprView.superview;}if (curContext != nil) {[self setContext:curContext];}}return curContext;}+ (void)swizzleInstanceSelector:(SEL)oldSel withSelector:(SEL)newSel{Method oldMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(self, oldSel);Method newMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(self, newSel);if (!oldMethod || !newMethod){return;}class_addMethod(self,oldSel,class_getMethodImplementation(self, oldSel),method_getTypeEncoding(oldMethod));class_addMethod(self,newSel,class_getMethodImplementation(self, newSel),method_getTypeEncoding(newMethod));method_exchangeImplementations(class_getInstanceMethod(self, oldSel),class_getInstanceMethod(self, newSel));}@end
如果当前对象为UIView的实例对象,并且context上下文不存在,会遍历当前对象的父容器,找到可用的context,并对当前对象的context进行赋值
这样就保证了在VC下的所有子View,都能找到可用上下文,从而解决模块之间的通讯问题
总结
MVC架构:
设计模式
Model:模型层,封装了应用程序的数据,并定义操控和处理该数据的逻辑和运算View:视图层,用于视图控件的渲染,并且对用户的操作作出响应Controller:程序的视图对象和模型对象之间的交互和通讯,由控制器充当媒介,负责二者的执行设置和协调任务,并管理它们的生命周期
常见问题
Controller中存在大量的代理、逻辑、UI和内部方法,导致VC层过重View和Model之间很容易产生依赖,导致耦合度过高
轻量化VC:
VC的实际意义,只是建立模块之间的依赖关系避免在
VC中加入繁重的UI代码、啰嗦的业务逻辑、很长的网络层代码、难受的代理功能
MVP架构:
特征
任务均摊:将最主要的任务划分到
Presenter和Model,而View的功能较少可测试性:由于一个功能简单的
View层,所以测试数业务逻辑变得简单易用性:比使用
MVC模式的代码量更多,但MVP模式具备非常清晰的结构
设计模式
Model层不仅仅是创建一个数据对象,还应该包含网络请求,以及数据Cache的操作View层就是一些封装、重用Presenter层并不涉及数据的网络请求和Cache操作,只是搭建Model层和View层的一个桥梁
优势
模型与视图完全分离,修改视图而不影响模型
可以更高效地使用模型,因为所有交互都在
Presenter中把逻辑放在
Presenter中,可以脱离用户接口进行单元测试可以将一个
Presener用于多个视图,而不需要改变Presenter的逻辑。这个特性非常的有用,因为视图的变化总是比模型的变化频繁

