1. 元类
将实例对象isa进行&运算,可得到类对象地址。同样类也是一个对象,也有自己的数据结构,如果将类对象的isa & ISA_MASK,会得到什么?
1.1 对象isa
打开main.m文件,写入以下代码:
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {@autoreleasepool {LGPerson *p = [LGPerson alloc];NSLog(@"%@",p);}return 0;}
打印实例对象的数据结构
x/4g p-------------------------0x100547b50: 0x011d800100008365 0x00000000000000000x100547b60: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
isa:0x011d800100008365
得到类对象地址
p/x 0x011d800100008365 & 0x00007ffffffffff8ULL-------------------------0x0000000100008360
将地址进行po打印
po 0x0000000100008360-------------------------LGPerson
- 实例对象
p的isa,指向LGPerson类
1.2 类的isa
打印LGPerson的数据结构
x/4g 0x0000000100008360-------------------------0x100008360: 0x0000000100008338 0x00007fff806700080x100008370: 0x0000000100712880 0x0002802c00000003
isa:0x0000000100008338
类对象isa进行&运算
p/x 0x0000000100008338 & 0x00007ffffffffff8ULL-------------------------0x0000000100008338
- 得到相同的地址
将地址进行po打印
po 0x0000000100008338-------------------------LGPerson
分别使用实例对象和类对象的isa & ISA_MASK,得到的地址完全不同,但打印结果同样是LGPerson
0x100008360 = LGPerson = 0x100008338
此时我们有一个大胆的设想,同一个类在内存中不止有一个,它可能和对象一样,可以无限开辟
1.3 元类初探
Class class1 = [LGPerson class];Class class2 = [LGPerson alloc].class;Class class3 = object_getClass([LGPerson alloc]);NSLog(@"class1:%p", class1);NSLog(@"class2:%p", class2);NSLog(@"class3:%p", class3);-------------------------//输出结果:class1:0x100008360class2:0x100008360class3:0x100008360
- 测试结果很明显,真正的
LGPerson类,地址为0x100008360
所以0x100008338又是什么?
在OC中,类也是一个对象。既然是对象,也会存在isa指针,指向它所属的类。就是我们所说的元类 (MetaClass)
在代码中,我们无法找到元类的代码。它是由系统生成和编译的,可使用MachOView查看
0x100008338:就是LGPerson类所属的元类
结论:
- 实例对象
isa→类isa→元类
扩展内容
为什么对象isa进行&运算,得到的地址不同。但类isa进行&运算,得到的地址相同?
- 对象的
isa为nonpointer类型,除了类对象地址,isa中包含了类信息、对象的引⽤计数等,所以对象isa进行&运算,得到的地址不同 - 类的
isa为非nonpointer类型,属于纯isa指针,只存储类对象的地址。我们很少听说一个类有引⽤计数、弱引用、是否释放等信息,所以类isa进行&运算,得到的地址相同
2. isa走位 & 继承链
2.1 isa走位
一个类的isa指向它的元类,那元类的isa又会指向谁?
2.1.1 LGPerson的isa
上述案例中,LGPerson的isa,指向元类0x100008338,那元类isa又会指向哪里?
打印元类的数据结构
x/4g 0x0000000100008338-------------------------0x100008338: 0x00007fff8066ffe0 0x00007fff8066ffe00x100008348: 0x00007fff20261aa0 0x0000e03500000000
- 元类
isa:0x00007fff8066ffe0
元类isa进行&运算
p/x 0x00007fff8066ffe0 & 0x00007ffffffffff8ULL-------------------------0x00007fff8066ffe0
- 得到相同的地址
将地址进行po打印
po 0x00007fff8066ffe0-------------------------NSObject
- 元类的
isa指向NSObject
查看NSObject类的地址
p/x NSObject.class-------------------------0x00007fff80670008 NSObject
NSObject地址和LGPerson元类isa指向的NSObject地址不同
疑问:
- 元类
isa指向的地址到底是什么?
2.1.2 NSObject的isa
打印NSObject类的数据结构
x/4g 0x00007fff80670008-------------------------0x7fff80670008: 0x00007fff8066ffe0 0x00000000000000000x7fff80670018: 0x00000001005605a0 0x0001801000000003
NSObject作为根类,它的isa指向的元类,称之为根元类- 根元类的地址和
LGPerson元类isa指向的地址相同 LGPerson的元类isa,指向的并不是NSObject,而是根元类(NSObject的元类)
打印根元类的数据结构
x/4g 0x00007fff8066ffe0-------------------------0x7fff8066ffe0: 0x00007fff8066ffe0 0x00007fff806700080x7fff8066fff0: 0x0000000100562a90 0x0005e03100000007
- 根元类
isa指向自己
结论:
LGPerson的元类isa,指向根元类(NSObject的元类)NSObject作为根类,isa走位只有两层- 根类
isa→根元类isa→自己
2.1.3 isa走位图
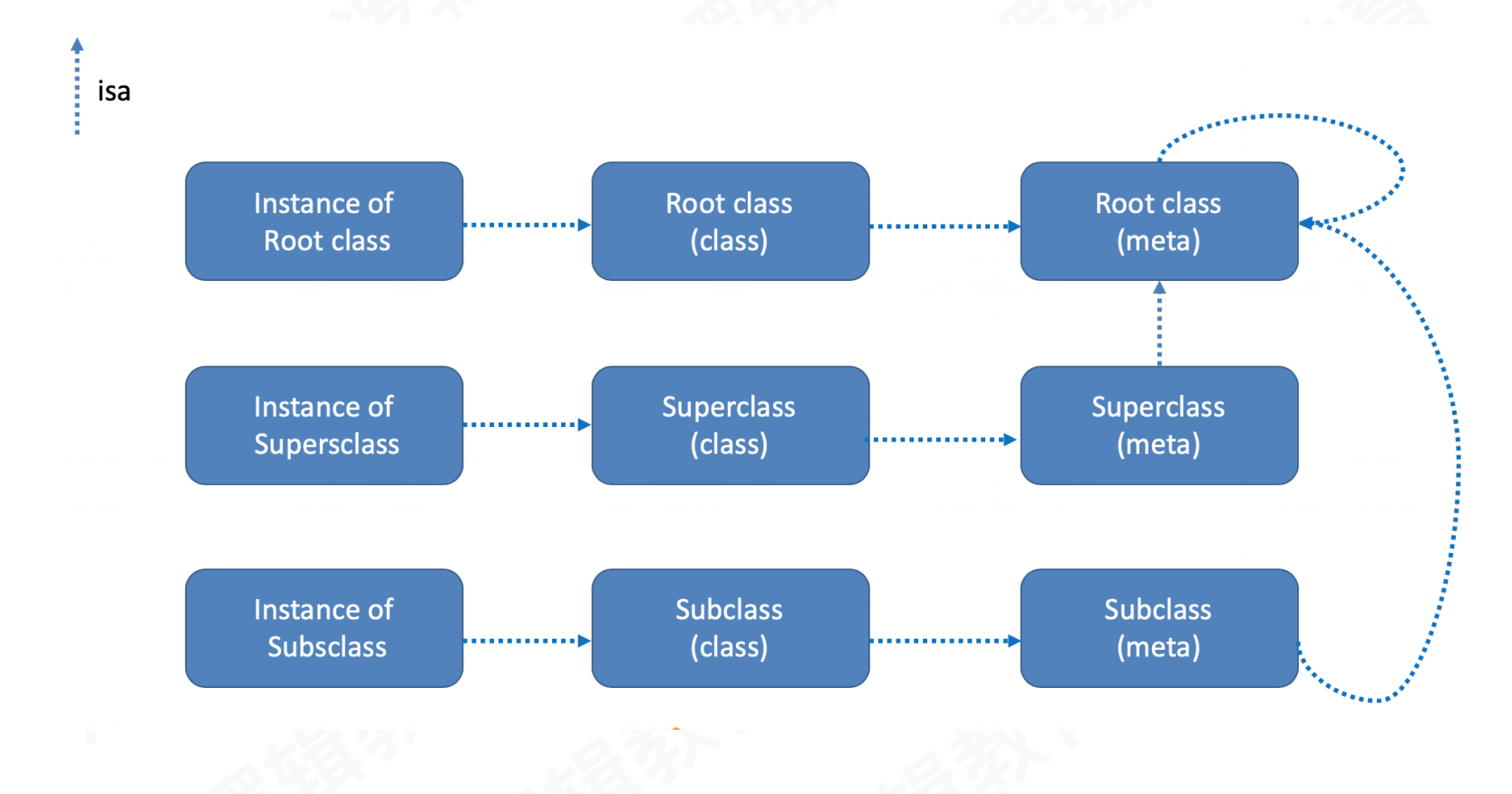
- 实例对象
isa→类isa→元类isa→根元类isa→自己 - 根类的实例对象
isa→根类isa→根元类isa→自己
2.2 继承链
任何一个类,都会有它的继承关系。那元类继承于谁,它的父类又会是谁?
2.2.1 LGPerson的继承链
LGPerson继承于NSObject,LGPerson元类的父类又会是谁?
打印NSObject的isa走位
NSObject *obj = [NSObject alloc];Class metaClass = object_getClass(class);Class rootMetaClass = object_getClass(rootClass);NSLog(@"根类的实例对象:%p", obj);NSLog(@"根类:%p", rootClass);NSLog(@"根元类:%p", rootMetaClass);-------------------------//输出结果:根类的实例对象:0x100571310根类:0x7fff80670008根元类:0x7fff8066ffe0
打印LGPerson元类的父类
Class pMetaClass = object_getClass(LGPerson.class);Class pSuperClass = class_getSuperclass(pMetaClass);NSLog(@"LGPerson元类的父类:%@ - %p",pSuperClass,pSuperClass);-------------------------LGPerson元类的父类:NSObject - 0x7fff8066ffe0
- 通过地址可以看出,
LGPerson元类的父类并不是NSObject,而是NSObject的元类,即:根元类
元类的父类是根元类,这个结论正确吗?我们需要用层级更深的继承链去验证
2.2.2 LGTeacher的继承链
LGTeacher继承于LGPerson,LGPerson继承于NSObject,打印LGTeacher的继承链
打印LGPerson的isa走位
Class pMetaClass = object_getClass(LGPerson.class);Class pRootMetaClass = object_getClass(pMetaClass);NSLog(@"LGPerson元类:%p", pMetaClass);NSLog(@"LGPerson根元类:%p", pRootMetaClass);-------------------------//输出结果:LGPerson元类:0x100008338LGPerson根元类:0x7fff8066ffe0
打印LGTeacher元类的父类
Class tMetaClass = object_getClass(LGTeacher.class);Class tSuperClass = class_getSuperclass(tMetaClass);NSLog(@"LGTeacher元类的父类:%@ - %p",tSuperClass,tSuperClass);-------------------------LGTeacher元类的父类:LGPerson - 0x100008338
LGTeacher元类的父类,指向其父类LGPerson的元类
结论:
- 元类的父类是根元类,结论显然是错误的
- 元类→父类的元类→根元类
2.2.3 NSObject的继承链
NSObject作为根类,它的继承链有些特殊
打印根类和根元类
Class rootClass = NSObject.class;Class rootMetaClass = object_getClass(rootClass);NSLog(@"根类:%p", rootClass);NSLog(@"根元类:%p", rootMetaClass);-------------------------//输出结果:根类:0x7fff80670008根元类:0x7fff8066ffe0
打印根类的父类和根元类的父类
Class nSuperClass = class_getSuperclass(rootClass);Class rnSuperClass = class_getSuperclass(rootMetaClass);NSLog(@"NSObject的父类:%@ - %p",nSuperClass,nSuperClass);NSLog(@"根元类的父类:%@ - %p",rnSuperClass,rnSuperClass);-------------------------//输出结果:根类的父类:(null) - 0x0根元类的父类:NSObject - 0x7fff80670008
NSObject作为根类,没有父类- 根元类的父类,指向根类,即:
NSObject
总结:
- 根类的继承链:根类→
nil - 根元类的继承链:根元类→根类→
nil
2.2.4 继承链流程图
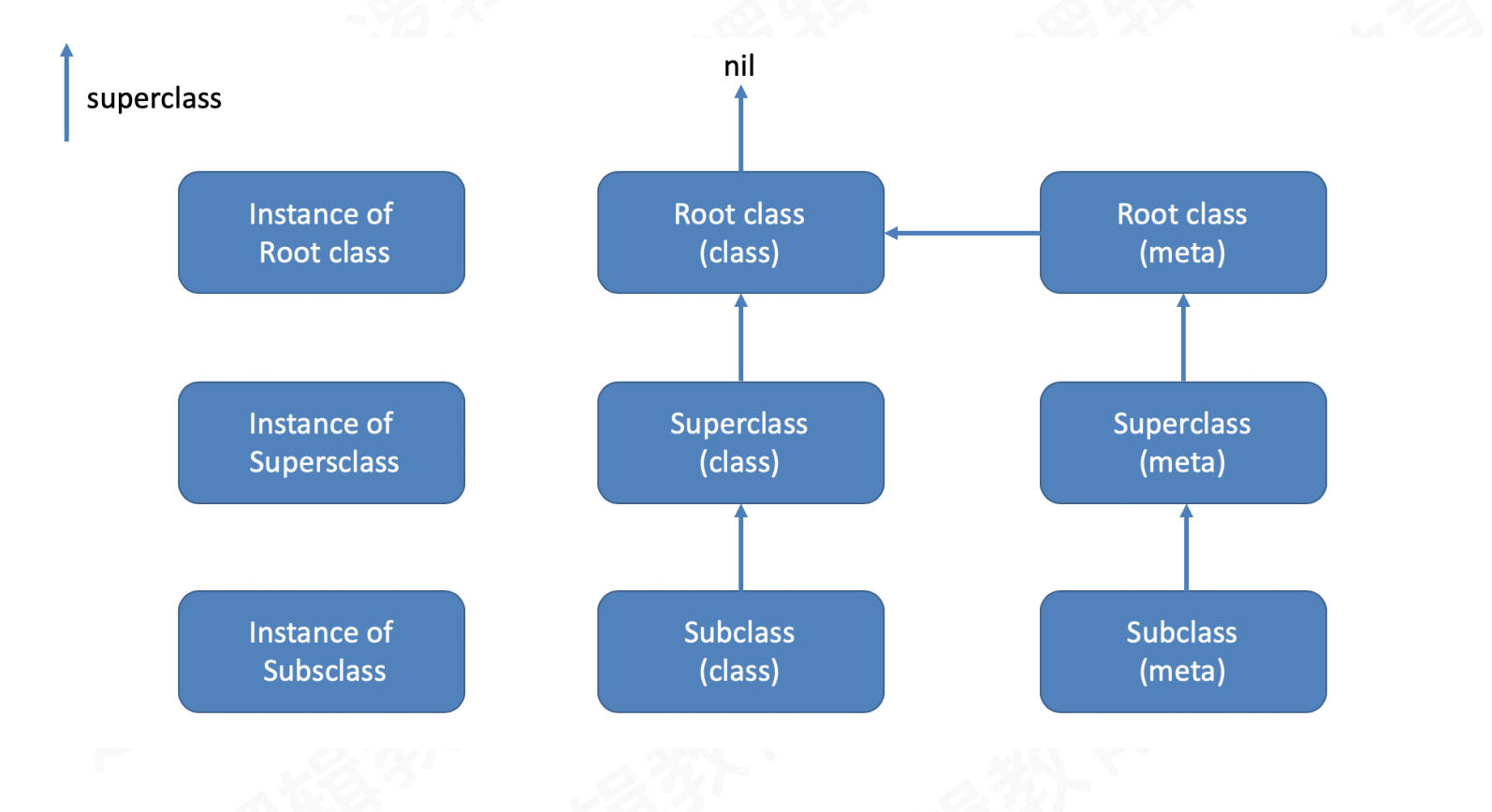
- 类的继承链:类→父类→根类→
nil - 元类的继承链:元类→父类的元类→根元类→根类→
nil - 继承关系只来自于类,对象之间没有这层关系
NSObject作为根类,它才是真正的万物之主,所有类都源于NSObject
2.3 官方流程图
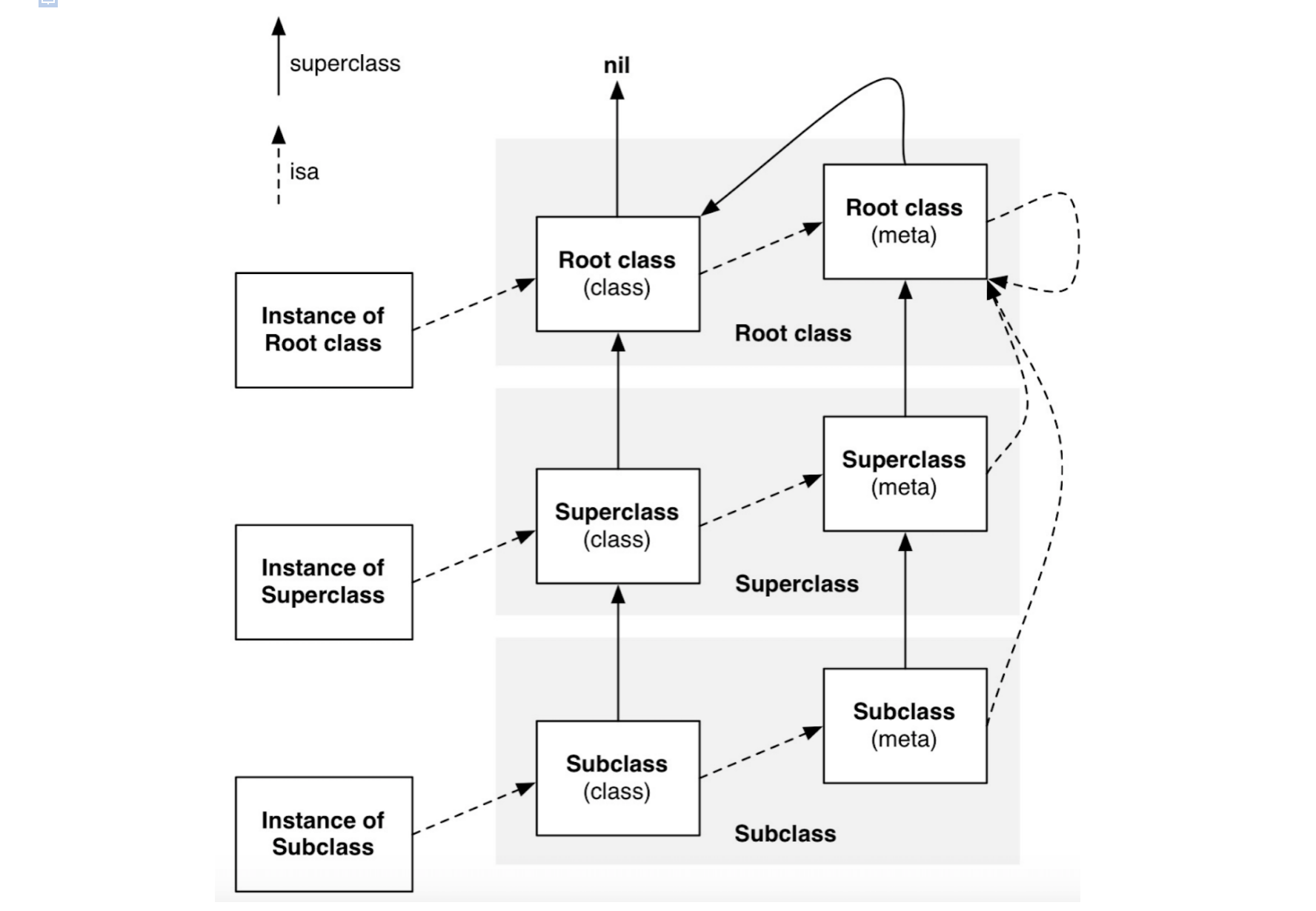
- isa走位:实例对象
isa→类isa→元类isa→根元类isa→自己 - 类的继承链:类→父类→根类→
nil - 元类的继承链:元类→父类的元类→根元类→根类→
nil
3. 类的结构
类也是一个对象,有自己的数据结构,而类的底层来自objc_class结构体,可通过源码分析类的结构
3.1 源码分析
在objc4-818.2源码中,搜索struct objc_class关键字,跳过一些过时的代码。例如:objc-runtime-old.h中的定义,以及runtime.h中的老旧代码
在objc-runtime-new.h中,找到objc_class结构体的定义:
struct objc_class : objc_object {objc_class(const objc_class&) = delete;objc_class(objc_class&&) = delete;void operator=(const objc_class&) = delete;void operator=(objc_class&&) = delete;// Class ISA;Class superclass;cache_t cache; // formerly cache pointer and vtableclass_data_bits_t bits; // class_rw_t * plus custom rr/alloc flags...};
objc_class继承自objc_object
结构体objc_class下,除objc_object的isa之外,还包含自身的superclass、cache和bits三个成员变量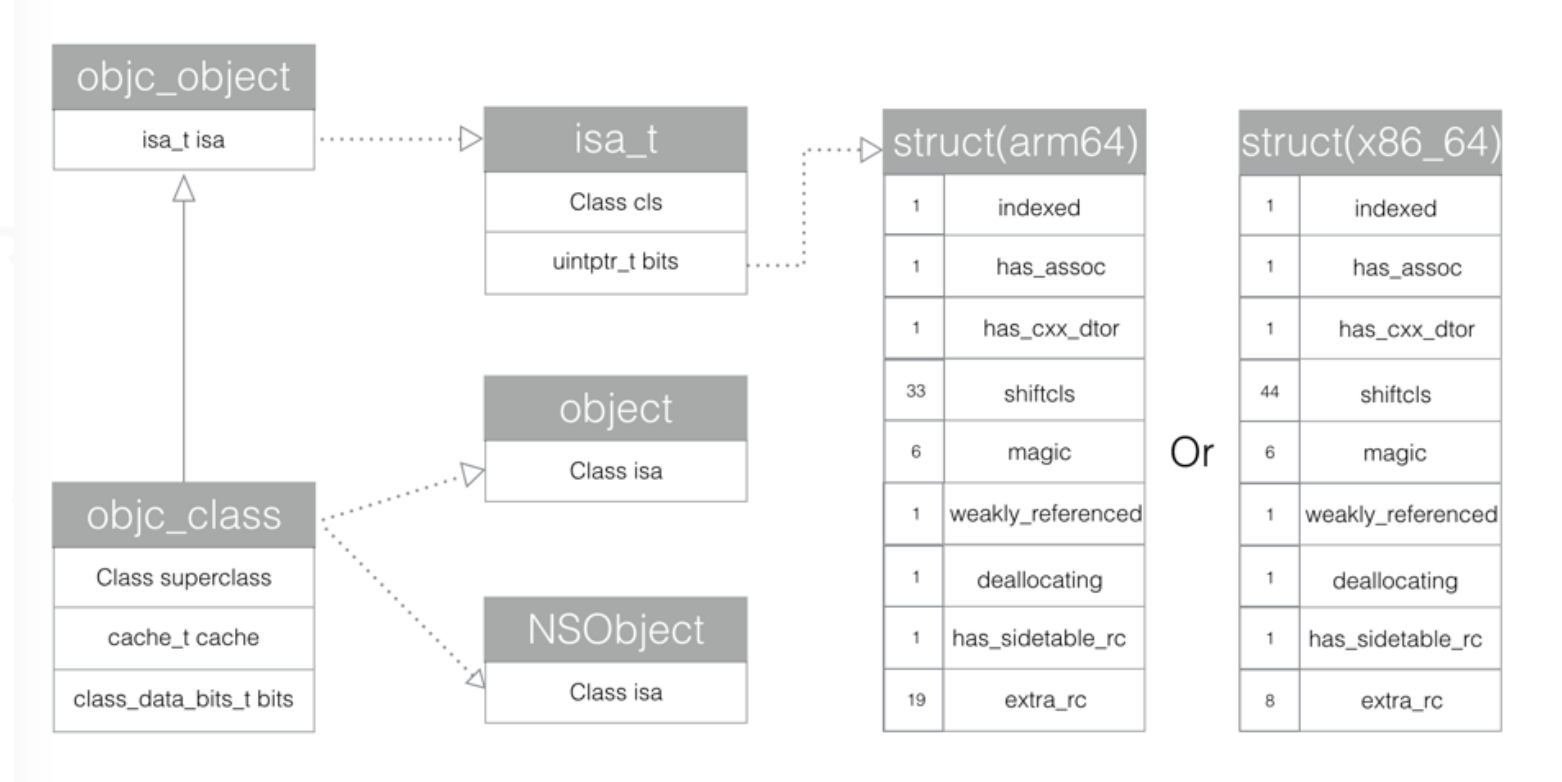
superclass为结构体指针,存储父类cache为cache_t结构体,存储方法缓存bits为class_data_bits_t结构体,存储方法、属性、协议列表等
疑问:
- 在
objc_class结构体中,如何获取到bits的数据?
3.2 内存平移
内存中读取数据,可以使用内存平移的方式。在首地址的基础上,偏移出数据的大小,即可将其完整读取
3.2.1 普通指针
int a = 10;int b = 10;NSLog(@"a:%d,%p", a, &a);NSLog(@"b:%d,%p", b, &b);-------------------------//输出结果:a:10,0x7ffeefbff3acb:10,0x7ffeefbff3a8
&a和&b的地址不同,但都指向相同的值10。这就是我们常说的值拷贝,即:深拷贝&a和&b的地址是连续的,由于是int类型,它们相差4字节
3.2.2 对象指针
LGPerson *p1 = [LGPerson alloc];LGPerson *p2 = [LGPerson alloc];NSLog(@"p1:%@,%p", p1, &p1);NSLog(@"p2:%@,%p", p2, &p2);-------------------------//输出结果:p1:<LGPerson: 0x101088280>,0x7ffeefbff3a8p2:<LGPerson: 0x101088450>,0x7ffeefbff3a0
p1和p2是指针,指向堆区开辟的内存空间&p1和&p2是指向p1和p2对象指针的地址,俗称:二级指针
对象指针和普通指针的区别: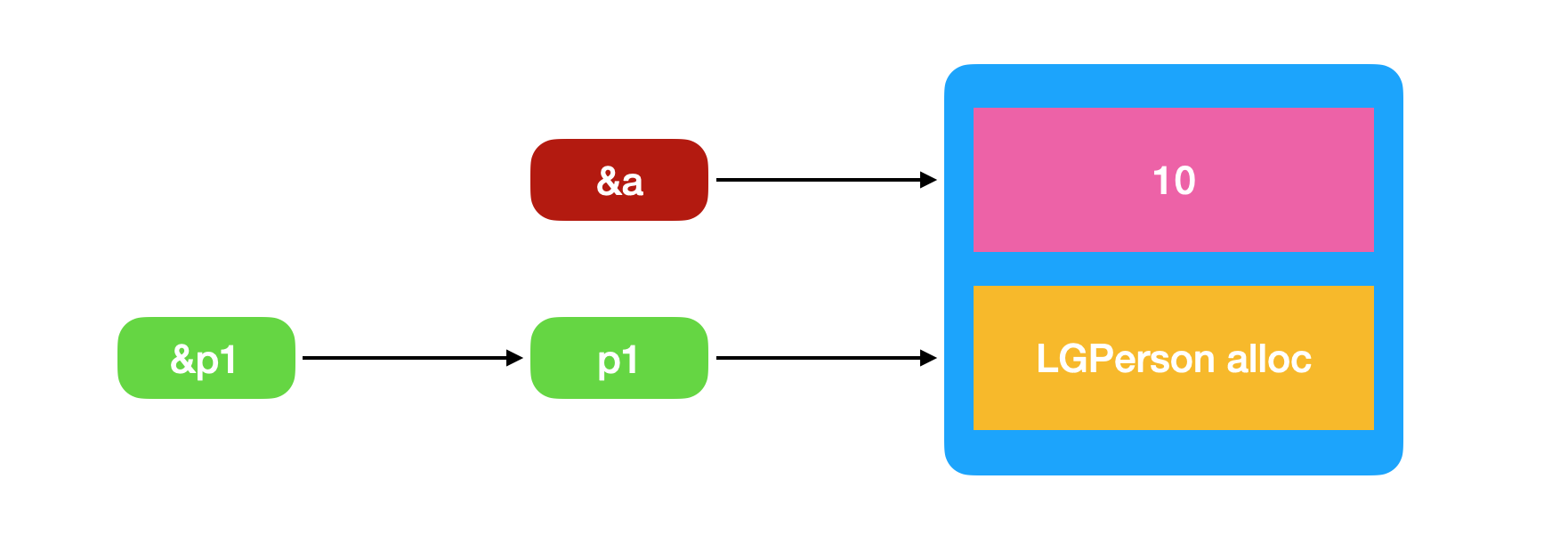
3.2.3 数组指针
int c[4] = {1,2,3,4};int *d = c;NSLog(@"c:%p,%p,%p,%p", &c, &c[0], &c[1], &c[2]);NSLog(@"d:%p,%p,%p,%p", d, d+0, d+1, d+2);-------------------------//输出结果:c:0x7ffeefbff3c0,0x7ffeefbff3c0,0x7ffeefbff3c4,0x7ffeefbff3c8d:0x7ffeefbff3c0,0x7ffeefbff3c0,0x7ffeefbff3c4,0x7ffeefbff3c8
- 数组中
索引0元素的地址,即是数组的首地址 - 数组中元素的地址是连续的,由于是
int类型数组,每个元素的地址之间相差4字节 - 读取元素的方式,也可以使用内存平移的方式。在首地址上,移动指定步长即可
数组中的元素指向: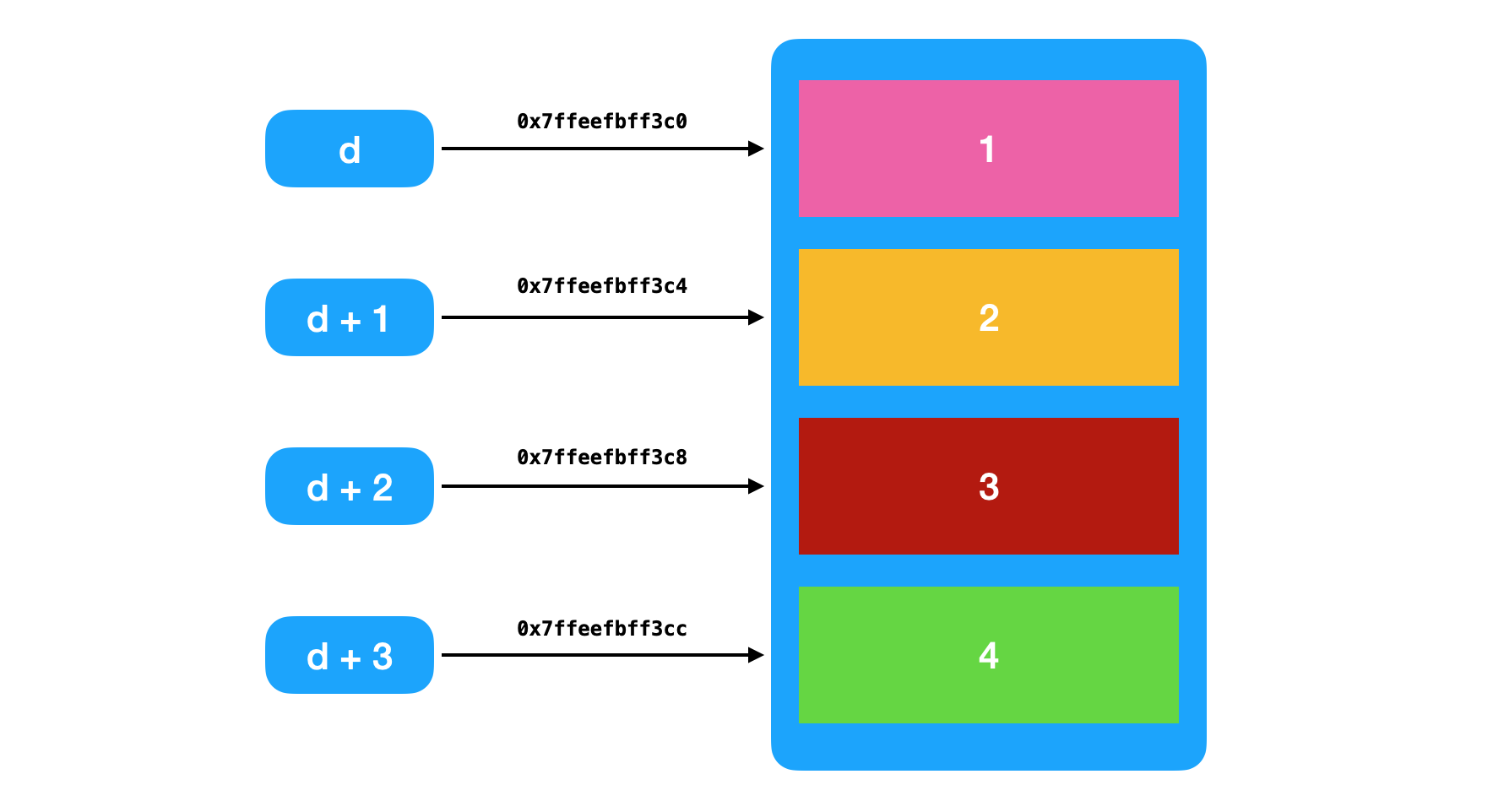
使用内存平移的方式,遍历数组中的元素
for (int i = 0; i<4; i++) {int value = *(d+i);NSLog(@"索引%d:%d", i, value);}-------------------------//输出结果:索引0:1索引1:2索引2:3索引3:4
3.3 内存计算
按照内存平移的原理,从objc_class中获取bits数据,需要跨过isa、superclass和cache三个成员变量的大小之和
3.3.1 superclass
isa和superclass都是Class类型,本质是结构体指针,占8字节。其中superclass,从字面上看,应该存储的是其父类
验证superclass存储的数据:
LGPerson继承自NSObject
@interface LGPerson : NSObject@end
打印LGPerson类的数据结构
x/4g LGPerson.class-------------------------0x100008330: 0x0000000100008358 0x000000010036a1400x100008340: 0x0000000100362390 0x0000803400000000
打印第二个8字节数据
po 0x000000010036a140-------------------------NSObject
打印NSObject地址进行对比
p/x NSObject.class-------------------------0x000000010036a140 NSObject
- 从打印结果来看,
superclass和NSObject地址一致,说明superclass存储的的确是其父类
3.3.2 cache
cache为cache_t结构体类型,存储方法缓存,它在内存中占用多少空间呢?
找到cache_t结构体的定义
struct cache_t {private:explicit_atomic<uintptr_t> _bucketsAndMaybeMask;union {struct {explicit_atomic<mask_t> _maybeMask;#if __LP64__uint16_t _flags;#endifuint16_t _occupied;};explicit_atomic<preopt_cache_t *> _originalPreoptCache;};...};
- 影响结构体大小,只有
_bucketsAndMaybeMask和union - 方法和函数,不影响结构体大小
static成员,存储在MachO的全局区,也不影响结构体大小
_bucketsAndMaybeMask:
- 泛型,大小取决于传入的数据类型
uintptr_t类型,无符号整数,能够存储指针,占8字节
union:
struct:
◦ _maybeMask:泛型,传入的mask_t为uint32_t类型,占4字节
◦ _flags:uint16_t类型,占2字节
◦ _occupied:uint16_t类型,占2字节
◦ struct,共计8字节
_originalPreoptCache:结构体指针,占8字节
struct中的mask_t定义
typedef uint32_t mask_t; // x86_64 & arm64 asm are less efficient with 16-bits
联合体特性,成员之间内存共用,大小为最大成员变量的大小。故此,union大小,占8字节
结论:
cache_t结构体的大小:uintptr_t(8字节) +union(8字节) =16字节
3.4 结构分析
得到isa、superclass和cache的大小,使用内存平移,可获取bits成员变量
bits为class_data_bits_t结构体类型,通过定义不难看出,核心方法存储在class_rw_t结构体中
struct class_data_bits_t {friend objc_class;// Values are the FAST_ flags above.uintptr_t bits;...class_rw_t* data() const {return (class_rw_t *)(bits & FAST_DATA_MASK);}...};
- 使用
friend定义objc_class为友元,内部的私钥方法也可使用
3.4.1 准备工作
以下探索过程,必须在可编译的objc源码中进行
打开LGPerson.h文件,写入以下代码:
@interface LGPerson : NSObject{NSString *desc;}@property (strong,nonatomic) NSString *name;@property (strong,nonatomic) NSString *nick;-(void)sayNB;+(void)good;@end
- 一个成员变量
desc - 两个属性
name和nick - 一个实例方法
sayNB - 一个类方法
good
打开LGPerson.m文件,写入以下代码:
@implementation LGPerson- (instancetype)init{self = [super init];if (self) {}return self;}-(void)sayNB{}+(void)good{}@end
3.4.2 class_rw_t
找到class_rw_t中的核心方法
打印LGPerson的首地址
p/x LGPerson.class-------------------------0x0000000100008330 LGPerson
内存平移:首地址 + 32字节
p/x 0x0000000100008330 + 0x20-------------------------0x0000000100008350
得到bits地址,但我们并不能直接打印地址中的数据结构,需将其转为结构体指针
p (class_data_bits_t *)0x0000000100008350-------------------------(class_data_bits_t *) $12 = 0x0000000100008350
获取class_rw_t,来自于class_data_bits_t的data函数。因为是结构体指针,使用->指向。如果是结构体,可以直接使用.
p $12->data()-------------------------(class_rw_t *) $15 = 0x0000000100627860
使用*取值,打印class_rw_t的数据结构
p *$15-------------------------(class_rw_t) $16 = {flags = 2148007936witness = 0ro_or_rw_ext = {std::__1::atomic<unsigned long> = {Value = 4295000120}}firstSubclass = nilnextSiblingClass = NSUUID}
通过打印,我们看不出class_rw_t中的数据结构。这种情况,只能从源码分析入手
找到class_rw_t的定义
struct class_rw_t {...const method_array_t methods() const {auto v = get_ro_or_rwe();if (v.is<class_rw_ext_t *>()) {return v.get<class_rw_ext_t *>(&ro_or_rw_ext)->methods;} else {return method_array_t{v.get<const class_ro_t *>(&ro_or_rw_ext)->baseMethods()};}}const property_array_t properties() const {auto v = get_ro_or_rwe();if (v.is<class_rw_ext_t *>()) {return v.get<class_rw_ext_t *>(&ro_or_rw_ext)->properties;} else {return property_array_t{v.get<const class_ro_t *>(&ro_or_rw_ext)->baseProperties};}}const protocol_array_t protocols() const {auto v = get_ro_or_rwe();if (v.is<class_rw_ext_t *>()) {return v.get<class_rw_ext_t *>(&ro_or_rw_ext)->protocols;} else {return protocol_array_t{v.get<const class_ro_t *>(&ro_or_rw_ext)->baseProtocols};}}};
- 找到了存储方法、属性、协议列表的三个核心方法
3.4.3 properties
获取LGPerson类中的属性列表
p $1->properties()-------------------------(const property_array_t) $2 = {list_array_tt<property_t, property_list_t, RawPtr> = {= {list = {ptr = 0x0000000100008160}arrayAndFlag = 4295000416}}}
$1:结构体指针class_rw_t *
找到property_array_t的定义
class property_array_t :public list_array_tt<property_t, property_list_t, RawPtr>{typedef list_array_tt<property_t, property_list_t, RawPtr> Super;public:property_array_t() : Super() { }property_array_t(property_list_t *l) : Super(l) { }};
- 继承自
list_array_tt
找到list_array_tt的定义
template <typename Element, typename List, template<typename> class Ptr>class list_array_tt {struct array_t {uint32_t count;Ptr<List> lists[0];...};protected:class iterator {const Ptr<List> *lists;const Ptr<List> *listsEnd;typename List::iterator m, mEnd;...};...};
list_array_tt<Element, List, Ptr>为模板类- 包含迭代器(
iterate)的方法,具有遍历特性
打印property_array_t下的list
p $2.list-------------------------(const RawPtr<property_list_t>) $3 = {ptr = 0x0000000100008160}
打印ptr
p $3.ptr-------------------------(property_list_t *const) $4 = 0x0000000100008160
使用*取值,打印property_list_t的数据结构
p *$4-------------------------(property_list_t) $5 = {entsize_list_tt<property_t, property_list_t, 0, PointerModifierNop> = (entsizeAndFlags = 16, count = 2)}
找到property_list_t的定义
struct property_list_t : entsize_list_tt<property_t, property_list_t, 0> {};
- 继承自
entsize_list_tt结构体
找到entsize_list_tt的定义
template <typename Element, typename List, uint32_t FlagMask, typename PointerModifier = PointerModifierNop>struct entsize_list_tt {uint32_t entsizeAndFlags;uint32_t count;...Element& get(uint32_t i) const {ASSERT(i < count);return getOrEnd(i);}...};
- 成员变量
count,可获取属性总数 get函数,传入索引,可获取指定属性
打印属性总数
p $5.count-------------------------(uint32_t) $6 = 2
- 共计两个属性
打印属性1
p $5.get(0)-------------------------(property_t) $7 = (name = "name", attributes = "T@\"NSString\",&,N,V_name")
打印属性2
p $5.get(1)-------------------------(property_t) $8 = (name = "nick", attributes = "T@\"NSString\",&,N,V_nick")
找到property_t的定义
struct property_t {const char *name;const char *attributes;};
- 结构体中定义了
name和attributes成员变量,可直接打印
疑问:
LGPerson中的desc成员变量在哪里?
3.4.4 methods
获取LGPerson类中的方法列表
p $1->methods()-------------------------(const method_array_t) $2 = {list_array_tt<method_t, method_list_t, method_list_t_authed_ptr> = {= {list = {ptr = 0x0000000100008080}arrayAndFlag = 4295000192}}}
打印method_array_t下的list.ptr
p $2.list.ptr-------------------------(method_list_t *const) $3 = 0x0000000100008080
使用*取值,打印method_list_t的数据结构
p *$3-------------------------(method_list_t) $4 = {entsize_list_tt<method_t, method_list_t, 4294901763, method_t::pointer_modifier> = (entsizeAndFlags = 27, count = 6)}
找到method_list_t的定义
struct method_list_t : entsize_list_tt<method_t, method_list_t, 0xffff0003, method_t::pointer_modifier> {...};
- 继承自
entsize_list_tt结构体
打印方法总数
p $4.count-------------------------(uint32_t) $5 = 7
- 共计七个方法
打印方法1
p $4.get(0)-------------------------(method_t) $6 = {}
- 遇到小问题,打印结果为空
找到method_t的定义
struct method_t {...struct big {SEL name;const char *types;MethodListIMP imp;};...big &big() const {ASSERT(!isSmall());return *(struct big *)this;}...objc_method_description *getDescription() const {return isSmall() ? getSmallDescription() : (struct objc_method_description *)this;}...};
- 结构体内没有定义成员变量,故此打印结果为空
- 通过
big()或getDescription()打印方法信息
打印LGPerson下的所有方法
p *($4.get(0).getDescription())p *($4.get(1).getDescription())p *($4.get(2).getDescription())p *($4.get(3).getDescription())p *($4.get(4).getDescription())p *($4.get(5).getDescription())p *($4.get(6).getDescription())-------------------------//打印结果:(objc_method_description) $7 = (name = "sayNB", types = "v16@0:8")(objc_method_description) $8 = (name = "nick", types = "@16@0:8")(objc_method_description) $9 = (name = "setNick:", types = "v24@0:8@16")(objc_method_description) $10 = (name = "init", types = "@16@0:8")(objc_method_description) $11 = (name = "name", types = "@16@0:8")(objc_method_description) $12 = (name = ".cxx_destruct", types = "v16@0:8")(objc_method_description) $13 = (name = "setName:", types = "v24@0:8@16")
方法1:sayNB实例方法方法2:nick属性的getter方法方法3:nick属性的setter方法方法4:init方法方法5:name属性的getter方法方法6:C++的析构方法方法7:name属性的setter方法
疑问:
LGPerson中的good类方法在哪里?
3.4.5 protocols
定义LGPersonProtocol协议
@protocol LGPersonProtocol-(void)lalala;@end
LGPerson遵循协议
@interface LGPerson : NSObject<LGPersonProtocol>@end
获取LGPerson类中的协议列表
p $17->protocols()-------------------------(const protocol_array_t) $18 = {list_array_tt<unsigned long, protocol_list_t, RawPtr> = {= {list = {ptr = 0x00000001000080c8}arrayAndFlag = 4295000264}}}
打印protocol_array_t下的list.ptr
p $18.list.ptr-------------------------(protocol_list_t *const) $19 = 0x00000001000080c8
使用*取值,打印protocol_list_t的数据结构
p *$19-------------------------(protocol_list_t) $20 = (count = 1, list = protocol_ref_t [] @ 0x00007fac118979e8)
找到protocol_list_t的定义
struct protocol_list_t {// count is pointer-sized by accident.uintptr_t count;protocol_ref_t list[0]; // variable-size...};
找到protocol_ref_t的定义
typedef uintptr_t protocol_ref_t; // protocol_t *, but unremapped
疑问:
在protocol_list_t结构体中,只有count和protocol_ref_t类型的list,其中也没有任何获取协议信息的方法。而protocol_ref_t结构体,我们在源码中,只找到了它的定义。此时问题来了,我们怎么才能输出协议信息?
在源码中,搜索protocol_ref_t关键字
找到这样一个方法,传入protocol_ref_t结构体,返回protocol_t结构体指针
static ALWAYS_INLINE protocol_t *remapProtocol(protocol_ref_t proto){runtimeLock.assertLocked();// Protocols in shared cache images have a canonical bit to mark that they// are the definition we should useif (((protocol_t *)proto)->isCanonical())return (protocol_t *)proto;protocol_t *newproto = (protocol_t *)getProtocol(((protocol_t *)proto)->mangledName);return newproto ? newproto : (protocol_t *)proto;}
- 核心代码:直接将
protocol_ref_t强转为protocol_t结构体指针
找到protocol_t的定义
struct protocol_t : objc_object {const char *mangledName;struct protocol_list_t *protocols;method_list_t *instanceMethods;method_list_t *classMethods;method_list_t *optionalInstanceMethods;method_list_t *optionalClassMethods;property_list_t *instanceProperties;...};
- 所有协议信息都在里面
继续lldb调试
将protocol_list_t强转为protocol_t结构体指针
p (protocol_t *)$20.list[0]-------------------------(protocol_t *) $21 = 0x0000000100008398
使用*取值,打印protocol_t的数据结构
p *$21-------------------------(protocol_t) $22 = {objc_object = {isa = {bits = 4298547400cls = Protocol= {nonpointer = 0has_assoc = 0has_cxx_dtor = 0shiftcls = 537318425magic = 0weakly_referenced = 0unused = 0has_sidetable_rc = 0extra_rc = 0}}}mangledName = 0x0000000100003ed0 "LGPersonProtocol"protocols = 0x0000000000000000instanceMethods = 0x0000000100008038classMethods = 0x0000000000000000optionalInstanceMethods = 0x0000000000000000optionalClassMethods = 0x0000000000000000instanceProperties = 0x0000000000000000size = 96flags = 0_extendedMethodTypes = 0x0000000100008058_demangledName = 0x0000000000000000_classProperties = 0x0000000000000000}
- 成功打印协议信息
协议中的instanceMethods为method_list_t结构体指针类型,打印其中的方法
p ((method_list_t *)0x0000000100008038).get(0).big()-------------------------(method_t::big) $31 = {name = "lalala"types = 0x0000000100003eec "v16@0:8"imp = 0x0000000000000000}
4. 成员变量
使用properties获取LGPerson的属性列表,但是desc成员变量存储在哪里呢?
在WWDC曾经提到过,成员变量Ivars存储在class_ro_t中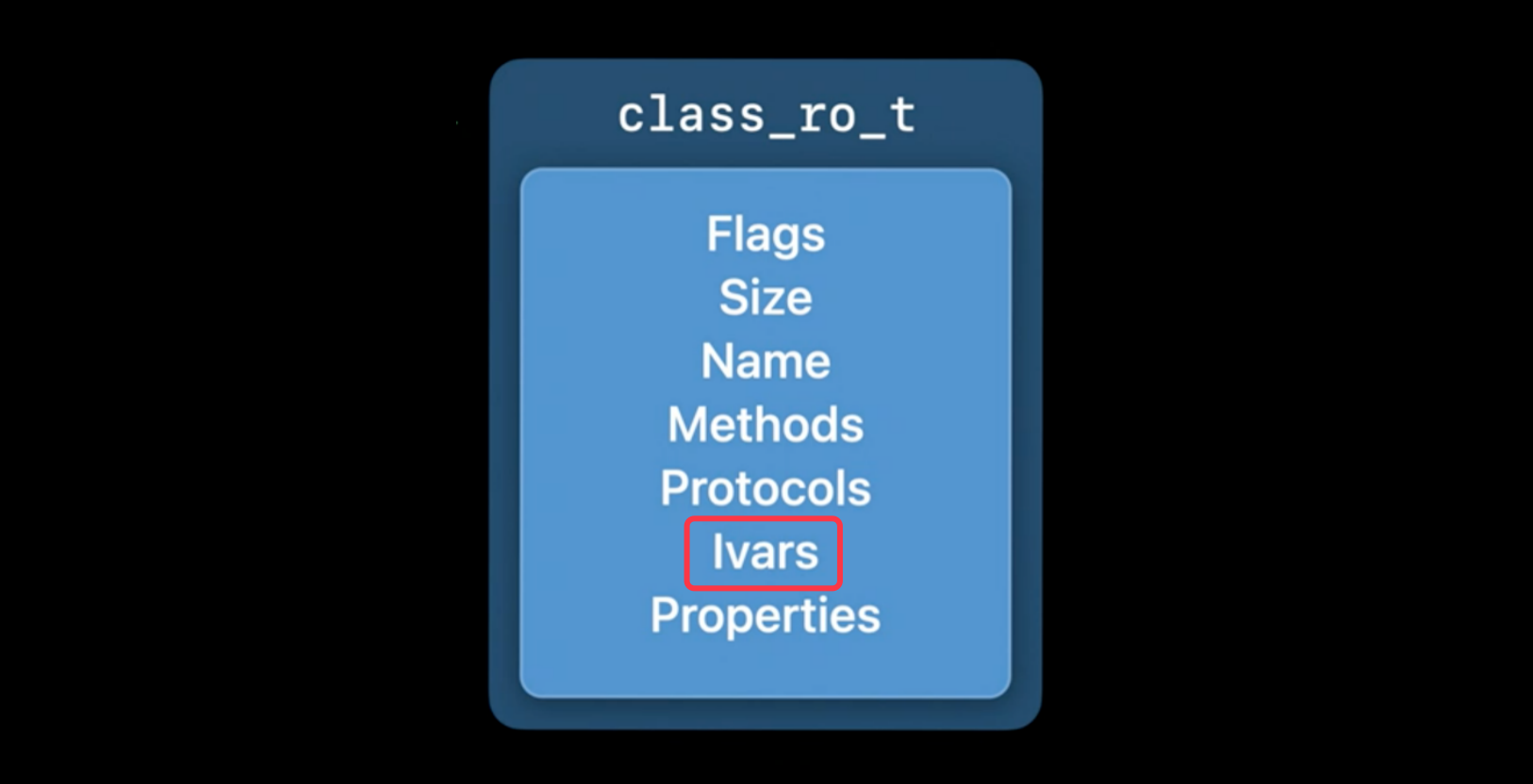
4.1 class_ro_t
找到class_rw_t的定义
struct class_rw_t {...const class_ro_t *ro() const {auto v = get_ro_or_rwe();if (slowpath(v.is<class_rw_ext_t *>())) {return v.get<class_rw_ext_t *>(&ro_or_rw_ext)->ro;}return v.get<const class_ro_t *>(&ro_or_rw_ext);}...};
- 通过
ro函数,得到class_ro_t
4.2 Ivars
获取LGPerson类中的class_ro_t
p $1->ro()-------------------------(const class_ro_t *) $2 = 0x0000000100008038
使用*取值,打印class_ro_t的数据结构
p *$2-------------------------(const class_ro_t) $3 = {flags = 388instanceStart = 8instanceSize = 32reserved = 0= {ivarLayout = 0x0000000100003f22 "\x03"nonMetaclass = 0x0000000100003f22}name = {std::__1::atomic<const char *> = "LGPerson" {Value = 0x0000000100003f24 "LGPerson"}}baseMethodList = 0x0000000100008080baseProtocols = 0x0000000000000000ivars = 0x0000000100008130weakIvarLayout = 0x0000000000000000baseProperties = 0x0000000100008198_swiftMetadataInitializer_NEVER_USE = {}}
ivars:成员变量列表
将ivars转为结构体指针
p (ivar_list_t *)0x0000000100008130-------------------------(ivar_list_t *) $4 = 0x0000000100008130
使用*取值,打印ivar_list_t的数据结构
p *$4-------------------------(ivar_list_t) $5 = {entsize_list_tt<ivar_t, ivar_list_t, 0, PointerModifierNop> = (entsizeAndFlags = 32, count = 3)}
找到ivar_list_t的定义
struct ivar_list_t : entsize_list_tt<ivar_t, ivar_list_t, 0> {bool containsIvar(Ivar ivar) const {return (ivar >= (Ivar)&*begin() && ivar < (Ivar)&*end());}};
- 继承自
entsize_list_tt结构体
打印成员变量总数
p $5.count-------------------------(uint32_t) $6 = 3
- 共计三个成员变量
打印成员变量1
p $5.get(0)-------------------------(ivar_t) $7 = {offset = 0x0000000100008240name = 0x0000000100003f2d "desc"type = 0x0000000100003f78 "@\"NSString\""alignment_raw = 3size = 8}
打印成员变量2
p $5.get(1)-------------------------(ivar_t) $8 = {offset = 0x0000000100008248name = 0x0000000100003f32 "_name"type = 0x0000000100003f78 "@\"NSString\""alignment_raw = 3size = 8}
打印成员变量3
p $5.get(2)-------------------------(ivar_t) $9 = {offset = 0x0000000100008250name = 0x0000000100003f38 "_nick"type = 0x0000000100003f78 "@\"NSString\""alignment_raw = 3size = 8}
总结:
- 成员变量存储在
class_ro_t结构体中
5. 类方法
使用methods获取LGPerson的方法列表,但是good类方法存储在哪里呢?
5.1 思考
实例方法也称为对象方法,它存储在实例对象所属的类中。这种设计方式,可以避免多个对象之间存储相同的方法列表,导致内存空间的浪费
如果类方法,也存储在类对象中,这样合理吗?
在OC中,实例方法和类方法,在底层的实现都函数。同一个类中,允许出现同名的实例方法和类方法。如果它们都存储在类对象中,底层该如何区分这些同名方法呢?
所以,类方法存储在类对象中,显然是不合理的
我们都知道,类的本质也是对象。故此,类方法存储在类对象所属的元类中,这样设计更为合理
这也是系统提供元类的原因之一
5.2 探索
打印LGPerson的数据结构
x/4g LGPerson.class-------------------------0x100008290: 0x00000001000082b8 0x000000010036a1400x1000082a0: 0x0000000100362390 0x0000803400000000
isa:0x00000001000082b8
打印类的isa指向的元类
p/x 0x00000001000082b8 & 0x00007ffffffffff8ULL-------------------------0x00000001000082b8
打印元类的bits地址
p (class_data_bits_t *)(0x00000001000082b8 + 0x20)-------------------------(class_data_bits_t *) $17 = 0x00000001000082d8
打印元类的class_rw_t
p $17->data()-------------------------(class_rw_t *) $18 = 0x000000010062c250
获取元类的方法列表
p $18->methods()-------------------------(const method_array_t) $19 = {list_array_tt<method_t, method_list_t, method_list_t_authed_ptr> = {= {list = {ptr = 0x0000000100008238}arrayAndFlag = 4295000632}}}
打印method_array_t下的list.ptr
p $19.list.ptr-------------------------(method_list_t *const) $20 = 0x0000000100008238
使用*取值,打印method_list_t的数据结构
p *$20-------------------------(method_list_t) $21 = {entsize_list_tt<method_t, method_list_t, 4294901763, method_t::pointer_modifier> = (entsizeAndFlags = 27, count = 1)}
打印方法总数
p $21.count-------------------------(uint32_t) $22 = 1
- 只有一个方法
打印方法1
p $21.get(0).big()-------------------------(method_t::big) $23 = {name = "good"types = 0x0000000100003f8c "v16@0:8"imp = 0x0000000100003e10 (KCObjcBuild`+[LGPerson good])}
总结:
- 在
OC中,实例方法和类方法,在底层的实现都函数 - 类方法存储在类对象所属的元类中
总结
元类
- 类也是一个对象,也存在
isa指针,指向它所属的类。即:元类 (MetaClass) - 元类初探:实例对象
isa→类isa→元类 - 对象的
isa为nonpointer类型,除了类对象地址,isa中包含类信息,所以&运算后地址不同 - 类的
isa为非nonpointer类型,属于纯isa指针,只存储类对象的地址,所以&运算后地址相同
isa走位图
NSObject为根类,NSObject的元类为根元类- 实例对象
isa→类isa→元类isa→根元类isa→自己 - 根类的实例对象
isa→根类isa→根元类isa→自己
继承链
- 继承关系只来自于类,对象之间没有这层关系
- 类和元类都存在继承链
- 元类的父类是父类的元类
- 类的继承链:类→父类→根类→nil
- 元类的继承链:元类→父类的元类→根元类→根类→nil
NSObject作为根类,它才是真正的万物之主,所有类都源于NSObject
类的结构
objc_class继承自objc_object- 除
objc_object的isa之外,还包含superclass、cache、bits superclass存储父类cache存储方法缓存bits存储方法、属性、协议列表等
内存平移
- 普通指针
◦ &a和&b的地址不同,但都指向相同的值,即:值拷贝(深拷贝)
◦ &a和&b的地址是连续的,由于是int类型,它们相差4字节
- 对象指针
◦ p1和p2是指针,指向堆区开辟的内存空间
◦ &p1和&p2是指向p1和p2对象指针的地址,俗称:二级指针
- 数组指针
◦ 数组中索引0元素的地址,即是数组的首地址
◦ 数组中元素的地址是连续的,由于是int类型数组,每个元素的地址之间相差4字节
◦ 读取元素的方式,也可以使用内存平移的方式。在首地址上,移动指定步长即可
内存计算
isa和superclass本质是结构体指针,占8字节cache为cache_t结构体类型cache_t结构体的大小,uintptr_t(8字节) +union(8字节) =16字节
类的结构分析
bits为class_data_bits_t结构体,存储方法、属性、协议列表等- 核心方法在
class_rw_t结构体中
◦ properties:可获取属性列表,但不包含成员变量
◦ methods:可获取方法列表,但不包含类方法
◦ protocols:可获取协议列表
成员变量
- 成员变量存储在
class_ro_t结构体中
类方法
- 在
OC中,实例方法和类方法,在底层的实现都函数 - 类方法存储在类对象所属的元类中

