1. 内存布局
当程序运行时,系统会开辟内核区、程序使用的内存五大区和保留区
1.1 内核区
操作系统分为两种运行级别,分别是内核态与用户态。当程序运行,系统会分配出4G虚拟内存,其中内核区占用1G,用于进行内核处理操作的区域。剩余3G,会预留给程序使用的内存五大区和保留区
1.2 内存五大区
内存主要分为栈区、堆区、全局区、常量区、代码区五大区域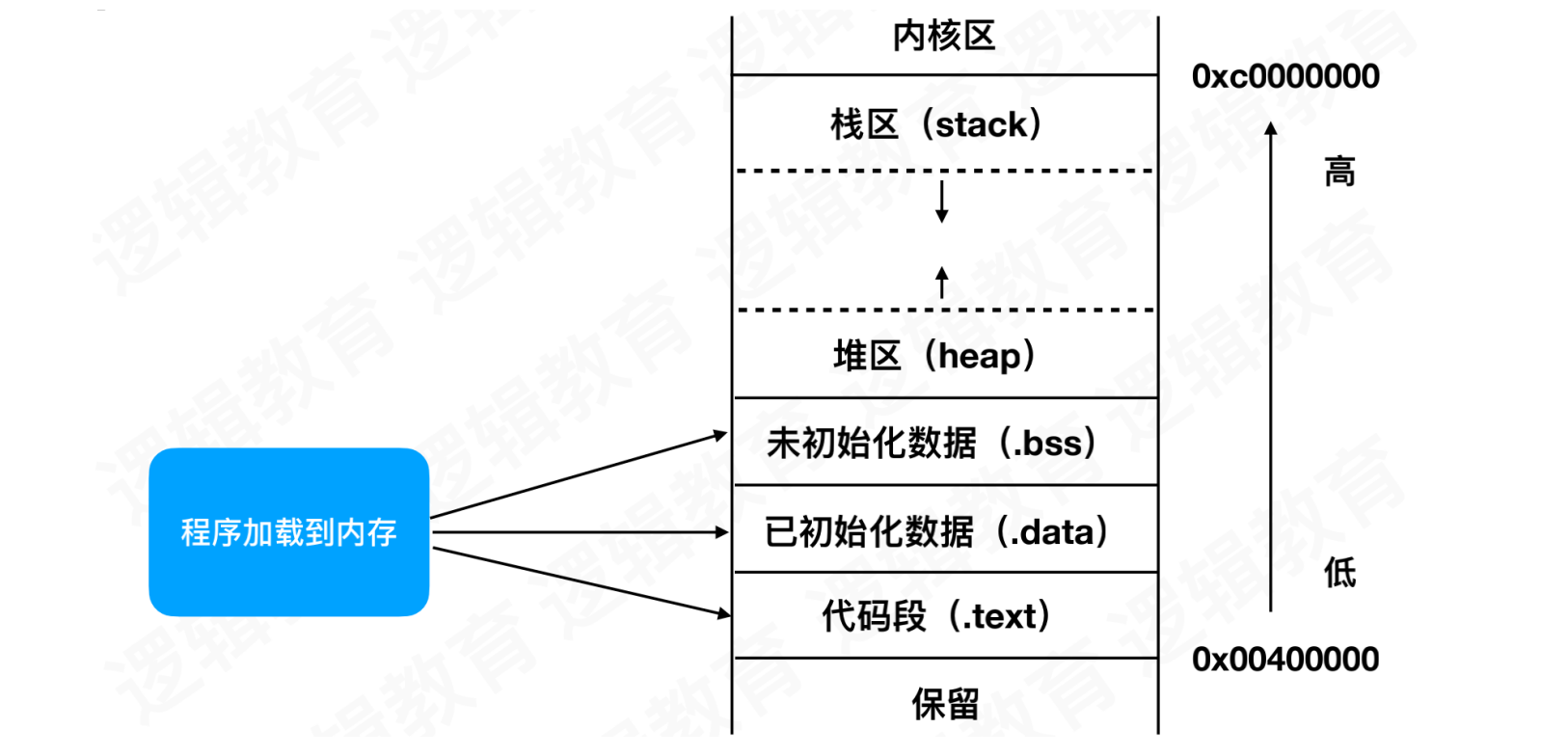
1.2.1 栈区(Stack)
栈是系统数据结构,栈所对应的进程或线程是唯一的
ARM64系统下,栈的地址由高到底,向下拉伸栈是一块连续的内存区域,遵循先进后出(
FILO)原则栈区在运行时分配空间,
iOS中栈的地址一般以0X7开头栈区由系统负责分配和销毁,效率更高,速度更快
栈区中存储局部变量和方法/函数的参数
栈区的内存昂贵,大小有限制
iOS的主线程栈大小为1MB,其他线程为512KB
1.2.2 堆区(Heap)
堆区的内存空间是不连续的,利于增删,不利于查询
堆区在运行时分配空间,
iOS中堆区的地址一般以0X6开头堆区由开发者负责申请开辟和销毁,效率不如栈
堆区的存储
OC中,使用alloc或new创建的对象,在ARC模式下,由系统回收释放C语言中,使用malloc、calloc、realloc开辟的空间,需要手动调用free函数对其释放
堆区的内存空间较大,可以存储整个结构体以及成员变量。而栈区适合存储结构体指针
1.2.3 全局静态区(.bss & .data)
全局区在编译时分配内存空间,在
iOS中一般以0x1开头全局区的数据一直存在,程序结束后由系统释放
全局区存储全局变量和
static修饰的静态变量,其中静态变量分为全局静态变量和静态局部变量未初始化的变量存储在
BSS区(.bss),已初始化的变量存储在数据区(.data)
1.2.4 常量区(.rodata)
常量区在编译时分配内存空间
常量区的数据一直存在,程序结束后由系统释放
常量区存储了程序中定义的死值,例如:
int a = 10;
1.2.5 代码区(.text)
代码区在编译时分配内存空间
代码区存储程序运行时的代码,会被编译成二进制存进内存
1.3 保留区
在ARM64系统中,内存五大区的低地址从0x00400000开始。其主要原因是0x00000000表示nil,我们不能直接用nil表示一个段,故此系统单独预留一段内存用于处理nil等情况
1.4 面试题
1.4.1 栈区的内存是如何定位的?
通过sp寄存器定位,sp为栈顶
1.4.2 全局变量和局部变量的区别?
全局变量保存在内存的全局区,
bss+data段,占用静态的存储单元局部变量保存在栈中,当函数被调用时,才会动态为变量分配存储单元
1.4.3 Block是否可以直接修改全局变量?
可以直接修改,因为全局变量、全局静态变量,都存储在全局区,它们的作用域更广泛,可以在Block中直接修改
局部变量被Block捕获,成为Block结构体的成员变量。它会以值的形式传递,而非地址,所以不能直接修改,需要使用__block修饰
而局部静态变量,可以在Block中直接修改,因为Block中直接捕获的是指针
2. 内存管理方案
iOS中内存管理方法,分为手动管理MRC和自动管理ARC
2.1 MRC
对象通过引用计数判断是否销毁,需要手动调用对象的retain、release、autorelease等方法,维护对象引用计数
对象被创建时,引用计数为
1调用对象的
retain方法,引用计数+1调用对象的
release方法,引用计数-1autorelease是一个特殊的release,有用延后释放。调用对象的autorelease方法,对象会加入到自动释放池中,最迟会在主循环结束前释放,依赖于Runloop当对象引用计数为
0,系统将销毁此对象
2.2 ARC
ARC为自动引用计数管理,属于编译器的一种特性,在WWDC2011和iOS5时代被引入
引用计数的规则和
MRC手动管理一致无需手动调用
retain、release、autorelease等方法维护对象引用计数编译器会在适当的地方自动插入
retain、release方法
3. Tagged Pointer
除了上述的ARC和MRC,内存管理方法中还包括几个重要的内容:
Tagged Pointer:专门用于存储小的对象,例如:NSNumber、NSIndexPath、NSDate、NSStringNonpointerISA:非纯指针类型的isa,isa中包含了类信息、对象的引⽤计数等SideTables:散列表,主要包含引用计数表和弱引用表
3.1 概述
以NSString为例,读取一个常规的NSString,通过栈区存储的指针地址,找到堆区空间,然后从堆区读取到字符串的值,整个读取流程效率较低
所以,系统对其进行优化,如果NSString存储的字符串长度较短,会使用Tagged Pointer存储
Tagged Pointer也是一个指针,指针中包含Tagged标记,用于区分存储的数据类型。同时将值也存储在指针中,通过位运算将其编码成一个指针格式
Tagged Pointer的读取,只需要将指针解码,通过tagget标记按不同类型规则进行读取即可,这样即节省内存空间,同时提升读取效率
案例:
- (void)viewDidLoad {[super viewDidLoad];NSString *str = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"kc"];NSLog(@"%p-%@-%@",str,str,str.class);}-------------------------//输出以下内容:0x800000000031b592-kc-NSTaggedPointerString
上述案例字符串的所属为
NSTaggedPointerString系统对字符串进行优化,当字符串是由数字、英文字母组合且长度
<= 9,会自动成为NSTaggedPointerString类型,存储在常量区当字符串中包含中文或者其他特殊符号,会直接成为
__NSCFString类型,存储在堆区
NSString内存管理的三种类型:
__NSCFConstantString:字符串常量,是一种编译时常量,retainCount值很大,对其操作不会引起引用计数变化,存储在字符串常量区__NSCFString:运行时创建的NSString子类,创建后引用计数默认为1,存储在堆区NSTaggedPointerString:字符串符合优化条件,自动成为NSTaggedPointerString类型,存储在常量区
3.2 结构
3.2.1 模拟器
在objc4-818.2源码中,找到Tagged Pointer的解码方法
进入_objc_decodeTaggedPointer函数
#if __arm64__// ARM64 uses a new tagged pointer scheme where normal tags are in// the low bits, extended tags are in the high bits, and half of the// extended tag space is reserved for unobfuscated payloads.# define OBJC_SPLIT_TAGGED_POINTERS 1#else# define OBJC_SPLIT_TAGGED_POINTERS 0#endifstatic inline uintptr_t_objc_decodeTaggedPointer(const void * _Nullable ptr){uintptr_t value = _objc_decodeTaggedPointer_noPermute(ptr);#if OBJC_SPLIT_TAGGED_POINTERSuintptr_t basicTag = (value >> _OBJC_TAG_INDEX_SHIFT) & _OBJC_TAG_INDEX_MASK;value &= ~(_OBJC_TAG_INDEX_MASK << _OBJC_TAG_INDEX_SHIFT);value |= _objc_obfuscatedTagToBasicTag(basicTag) << _OBJC_TAG_INDEX_SHIFT;#endifreturn value;}
- 调用
_objc_decodeTaggedPointer_noPermute函数,返回指针 - 判断
OBJC_SPLIT_TAGGED_POINTERS,符合条件进行位运算
进入_objc_decodeTaggedPointer_noPermute函数
static inline uintptr_t_objc_decodeTaggedPointer_noPermute(const void * _Nullable ptr){uintptr_t value = (uintptr_t)ptr;#if OBJC_SPLIT_TAGGED_POINTERSif ((value & _OBJC_TAG_NO_OBFUSCATION_MASK) == _OBJC_TAG_NO_OBFUSCATION_MASK)return value;#endifreturn value ^ objc_debug_taggedpointer_obfuscator;}
- 和
objc_debug_taggedpointer_obfuscator进行按位异或 objc_debug_taggedpointer_obfuscator,可以理解为随机数
objc_debug_taggedpointer_obfuscator的赋值:在dyld读取image时,调用_read_images函数。里面包含对initializeTaggedPointerObfuscator函数的调用,对Tagged Pointer进行初始化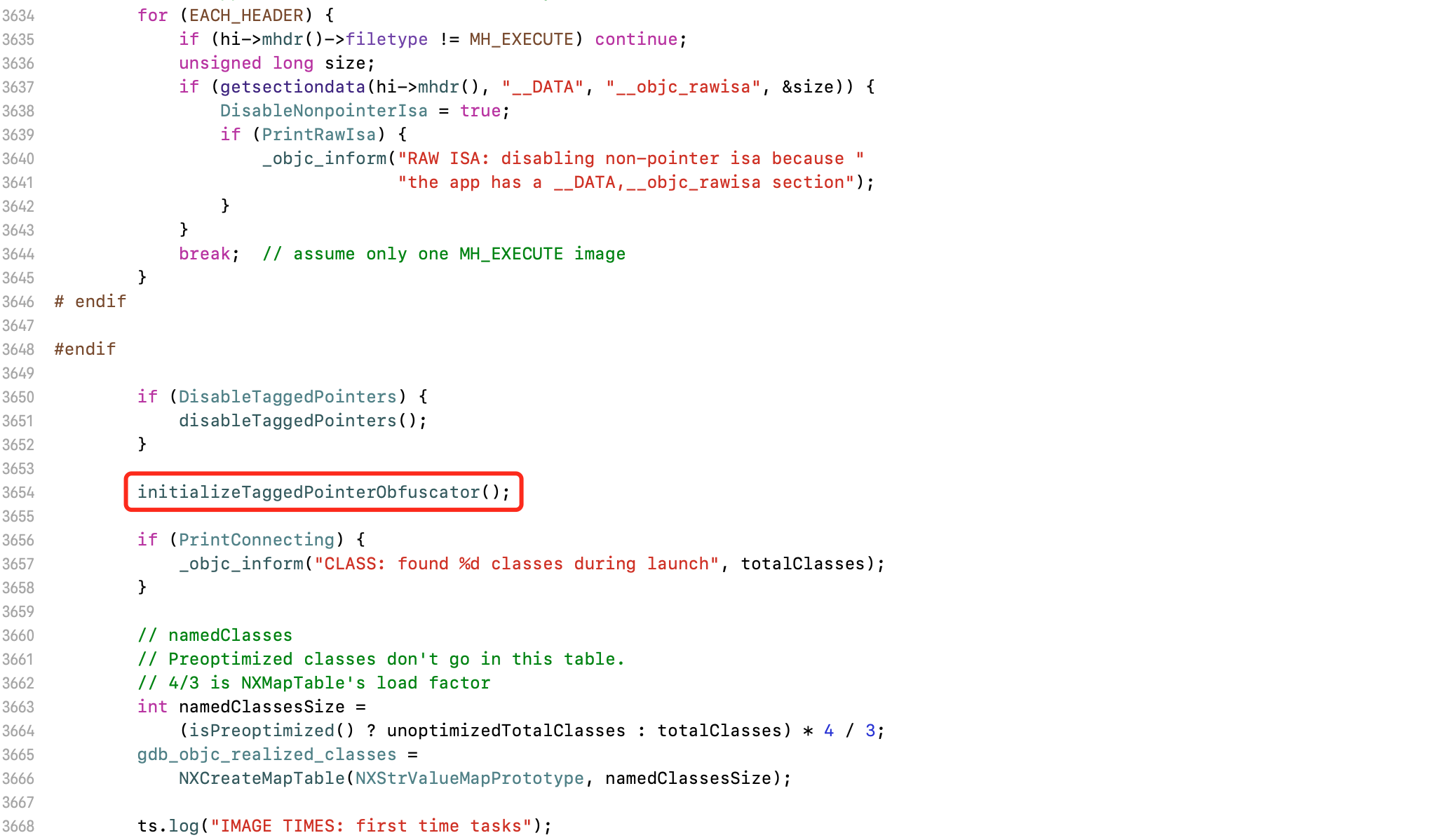
进入initializeTaggedPointerObfuscator函数
static voidinitializeTaggedPointerObfuscator(void){// && dyld_program_sdk_at_least(dyld_fall_2018_os_versions)if (!DisableTaggedPointerObfuscation) {// Pull random data into the variable, then shift away all non-payload bits.arc4random_buf(&objc_debug_taggedpointer_obfuscator,sizeof(objc_debug_taggedpointer_obfuscator));objc_debug_taggedpointer_obfuscator &= ~_OBJC_TAG_MASK;#if OBJC_SPLIT_TAGGED_POINTERS// The obfuscator doesn't apply to any of the extended tag mask or the no-obfuscation bit.objc_debug_taggedpointer_obfuscator &= ~(_OBJC_TAG_EXT_MASK | _OBJC_TAG_NO_OBFUSCATION_MASK);// Shuffle the first seven entries of the tag permutator.int max = 7;for (int i = max - 1; i >= 0; i--) {int target = arc4random_uniform(i + 1);swap(objc_debug_tag60_permutations[i],objc_debug_tag60_permutations[target]);}#endif} else {// Set the obfuscator to zero for apps linked against older SDKs,// in case they're relying on the tagged pointer representation.objc_debug_taggedpointer_obfuscator = 0;}}
- 判断是否开启混淆,开启将
objc_debug_taggedpointer_obfuscator赋值随机数,否则赋值为0
系统生成的Tagged Pointer是编码后的,我们要想了解它的结构,需要对其进行解码
objc_debug_taggedpointer_obfuscator为全局静态变量,我们可以在程序中,使用extern修饰,将其导出,自己实现一个解码函数,使用相同的值,将指针再次按位异或即可还原
extern uintptr_t objc_debug_taggedpointer_obfuscator;uintptr_tkc_objc_decodeTaggedPointer(id ptr){return (uintptr_t)ptr ^ objc_debug_taggedpointer_obfuscator;}
案例:
- (void)viewDidLoad {[super viewDidLoad];NSString *str = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"kc"];NSLog(@"%p-%@-%@ - 0x%lx",str,str,str.class,kc_objc_decodeTaggedPointer(str));}-------------------------//输出以下内容:0xa0000000000636b2-kc-NSTaggedPointerString - 0xa0000000000636b2
- 使用模拟器运行程序,解码后的指针地址:
0xa0000000000636b2
在lldb中,使用p/t命令,查看二进制形式
(lldb) p/t 0xa0000000000636b2(unsigned long) $0 = 0b1010000000000000000000000000000000000000000001100011011010110010
0b表示二进制- 高地址第一位
1,表示该isa为Tagged Pointer类型
通过位运算,获取有效负载
(lldb) p/t $0 >> 4(unsigned long) $1 = 0b0000101000000000000000000000000000000000000000000110001101101011
低地址最后16位,每8位进行一次打印
(lldb) po 0b01101011107(lldb) po 0b0110001199
里面存储的内容,其实就是字符的assic码
(lldb) po (char)107'k'(lldb) po (char)99'c'
将isa转为二进制,高地址的前4位,第一位表示该isa为Tagged Pointer类型,后面三位010表示Tagged Pointer所存储的类型
(lldb) po 0b0102
对应objc源码中的类型
// 60-bit payloadsOBJC_TAG_NSAtom = 0,OBJC_TAG_1 = 1,OBJC_TAG_NSString = 2,OBJC_TAG_NSNumber = 3,OBJC_TAG_NSIndexPath = 4,OBJC_TAG_NSManagedObjectID = 5,OBJC_TAG_NSDate = 6,...
3.2.2 真机
Tagged Pointer结构,在真机上更为复杂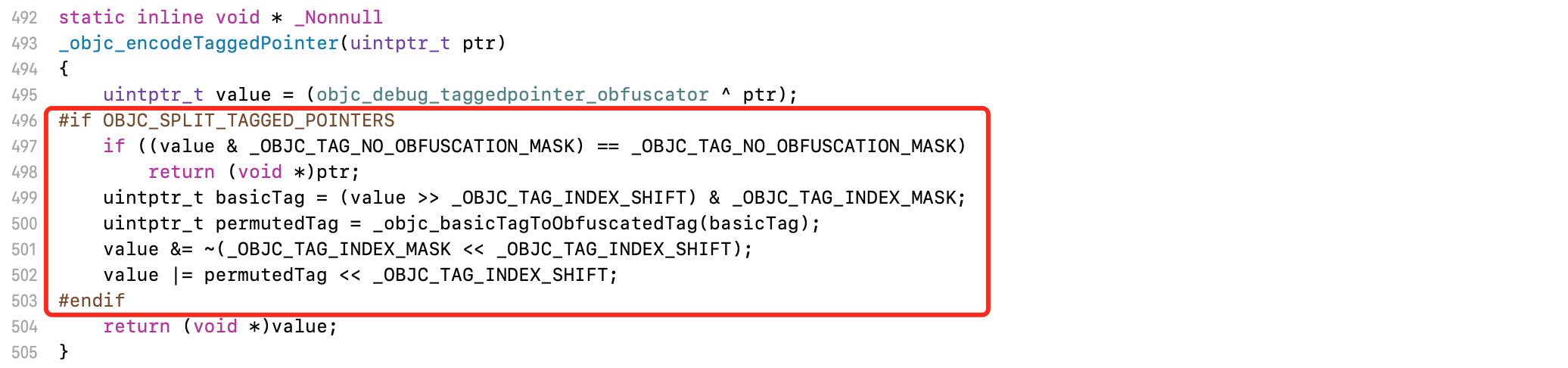
实现真机环境解码函数
#define kc_OBJC_TAG_INDEX_MASK 0x7UL#define kc_OBJC_TAG_INDEX_SHIFT 0extern uint8_t objc_debug_tag60_permutations[8];uintptr_t kc_objc_obfuscatedTagToBasicTag(uintptr_t tag) {for (unsigned i = 0; i < 7; i++)if (objc_debug_tag60_permutations[i] == tag)return i;return 7;}uintptr_tkc_objc_decodeTaggedPointer(id ptr){uintptr_t value = (uintptr_t)ptr ^ objc_debug_taggedpointer_obfuscator;uintptr_t basicTag = (value >> kc_OBJC_TAG_INDEX_SHIFT) & kc_OBJC_TAG_INDEX_MASK;value &= ~(kc_OBJC_TAG_INDEX_MASK << kc_OBJC_TAG_INDEX_SHIFT);value |= kc_objc_obfuscatedTagToBasicTag(basicTag) << kc_OBJC_TAG_INDEX_SHIFT;return value;}static inline uintptr_t kc_objc_basicTagToObfuscatedTag(uintptr_t tag) {return objc_debug_tag60_permutations[tag];}void *kc_objc_encodeTaggedPointer(uintptr_t ptr){uintptr_t value = (objc_debug_taggedpointer_obfuscator ^ ptr);uintptr_t basicTag = (value >> kc_OBJC_TAG_INDEX_SHIFT) & kc_OBJC_TAG_INDEX_MASK;uintptr_t permutedTag = kc_objc_basicTagToObfuscatedTag(basicTag);value &= ~(kc_OBJC_TAG_INDEX_MASK << kc_OBJC_TAG_INDEX_SHIFT);value |= permutedTag << kc_OBJC_TAG_INDEX_SHIFT;return (void *)value;}
上述案例,使用真机运行
0x800000000031b592-kc-NSTaggedPointerString - 0x800000000031b592
在lldb中,使用p/t命令,查看二进制形式
(lldb) p/t 0x800000000031b592(unsigned long) $0 = 0b1000000000000000000000000000000000000000001100011011010110010010
- 和模拟器的区别,高地址第一位,没有变化,表示该
isa为Tagged Pointer类型 - 但类型的位置发生变化,存储在低地址最后三位
低地址4~7位0010,表示字符串长度
(lldb) po 0b00102
查看NSNumber类型
number:0x8000000000000313-6 -__NSCFNumber- 0x8000000000000313number1:0x800000000000032b-6 -__NSCFNumber- 0x800000000000032b
在lldb中,使用p/t命令,查看二进制形式
(lldb) p/t 0x8000000000000313(unsigned long) $0 = 0b1000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001100010011(lldb) p/t 0x800000000000032b(unsigned long) $1 = 0b1000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001100101011
- 低地址最后三位
011表示NSNumber的类型 - 低地址
4~7位,分别存储0010和0101,表示存储的基本数据类型。例如:int、long、double、float等
该枚举值在objc源码中未定义,只能通过代码测试类型所对应的枚举值:
char:0short:1int:2long:3float:4double:5
3.3 关闭混淆
在真机环境,探索结构需要我们自己实现解码的代码。其实这里还有更简单的方式
通过源码发现,在初始化时,如果不符合混淆条件,objc_debug_taggedpointer_obfuscator会被设置为0
搜索DisableTaggedPointerObfuscation
OPTION( DisableTaggedPointerObfuscation, OBJC_DISABLE_TAG_OBFUSCATION, "disable obfuscation of tagged pointers")
- 它的值取决于
OBJC_DISABLE_TAG_OBFUSCATION环境变量的设置
在测试项目中,添加OBJC_DISABLE_TAG_OBFUSCATION环境变量,将其设置为YES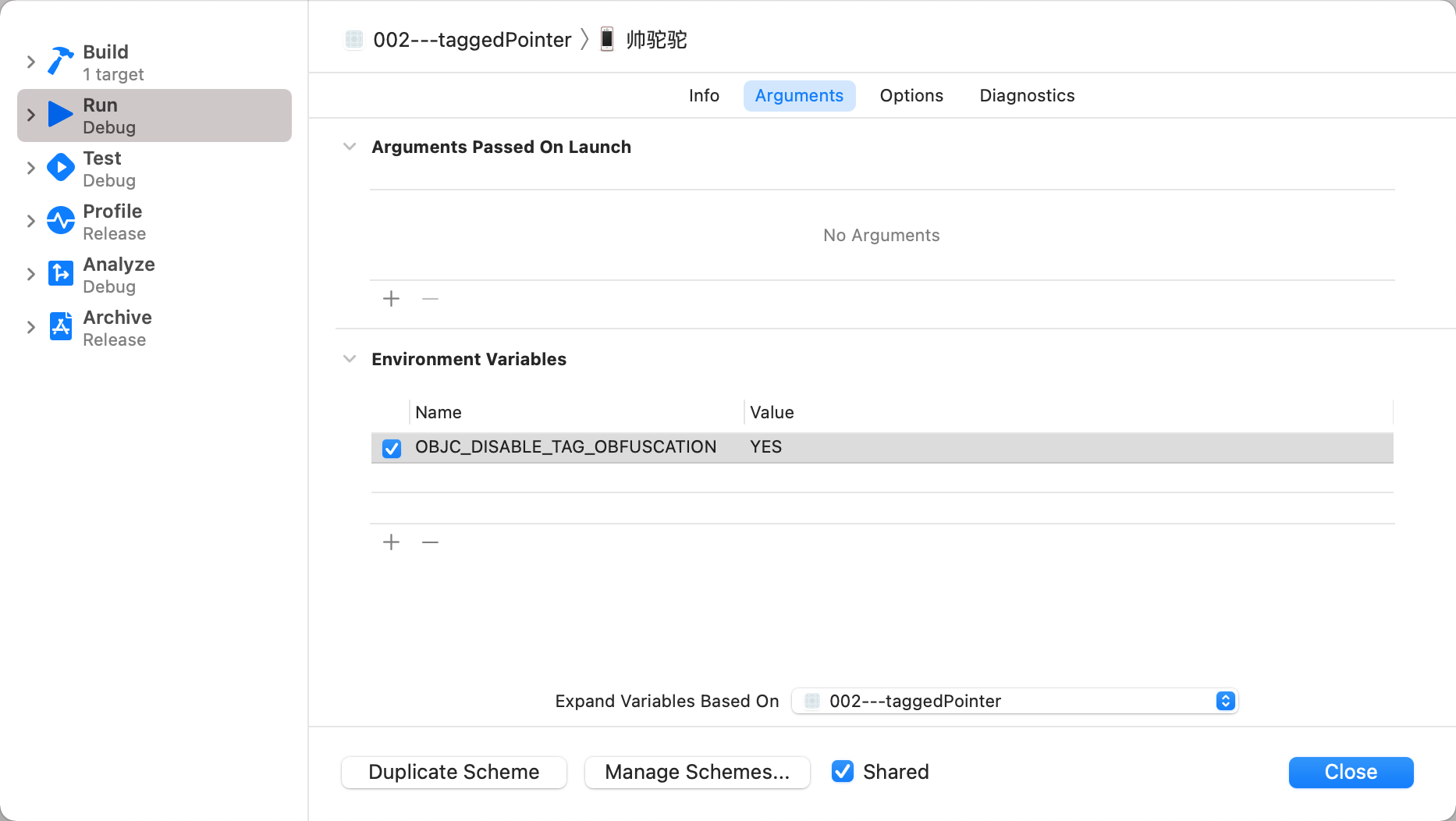
运行项目:
- (void)viewDidLoad {[super viewDidLoad];NSNumber *number = @6;NSLog(@"number:%p-%@ -%@- 0x%lx",number,number,number.class,(uintptr_t)number);}-------------------------//输出以下内容:number:0x8000000000000313-6 -__NSCFNumber- 0x8000000000000313
- 此时,直接获得未编码的
isa
3.4 内存管理
案例:
- (void)taggedPointerDemo {self.queue = dispatch_queue_create("com.lg.cn", DISPATCH_QUEUE_CONCURRENT);for (int i = 0; i<10000; i++) {dispatch_async(self.queue, ^{self.nameStr = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"kc"];NSLog(@"%@",self.nameStr);});}}- (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event{for (int i = 0; i<100000; i++) {dispatch_async(self.queue, ^{self.nameStr = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"kc_和谐学习不急不躁"];NSLog(@"%@",self.nameStr);});}}
taggedPointerDemo的运行,不会出现任何问题。因为字符串kc会被优化成NSTaggedPointerString类型touchesBegan的运行,会导致程序崩溃。因为字符串中包含中文,所以使用__NSCFString类型。它的值存储在堆区,赋值的过程本质上对旧值release,对新值retain。当多线程执行时,可能出现多次release造成过度释放,一些野指针的操作导致程序崩溃
上述案例中,NSTaggedPointerString类型多线程执行不会崩溃,主要在于它的内存管理机制
在objc源码中,找到rootRetain函数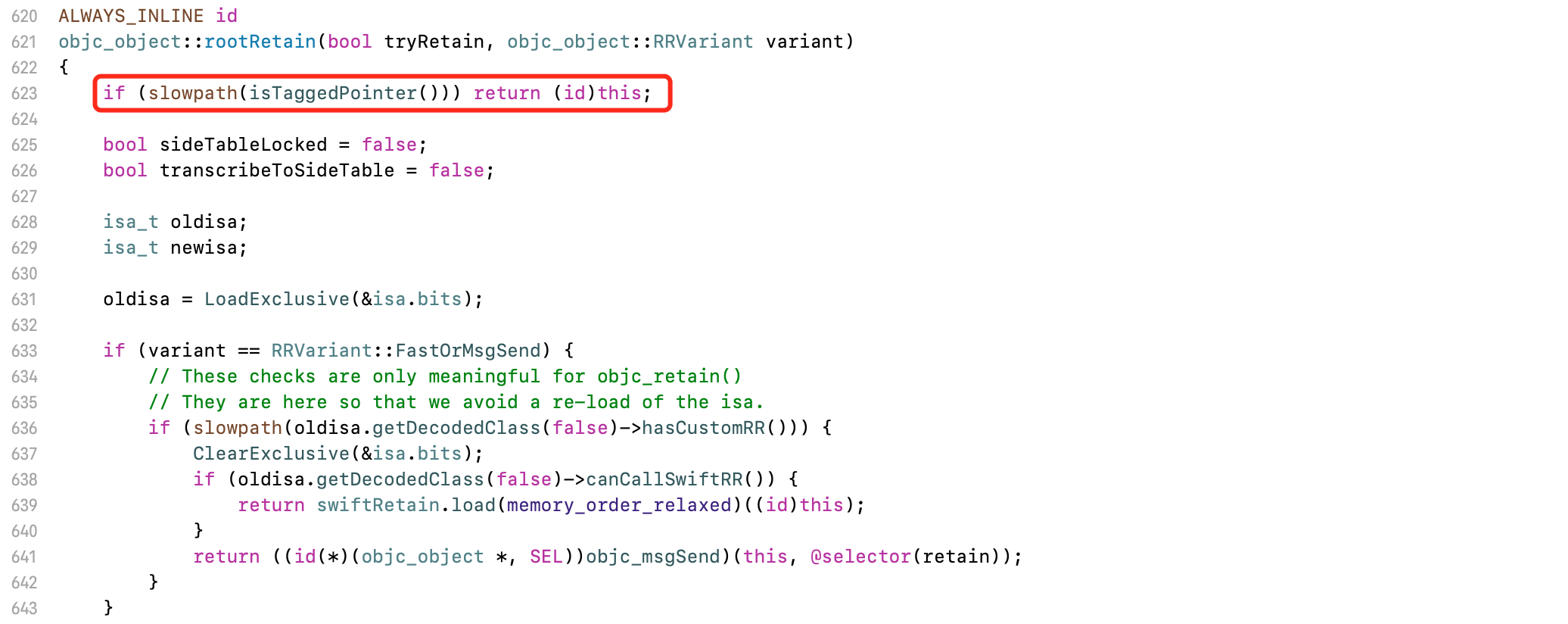
- 判断如果是
TaggedPointer的isa,直接返回。不用进行后面的新旧值的retain和release
进入rootRelease函数
- 同样,判断如果是
TaggedPointer的isa,直接返回false
Tagged Pointer触发retain和release,什么都不处理直接返回。这意味着它不需要ARC进行管理,而是直接被系统回收释放
3.5 总结
Tagged Pointer专门用于存储小的对象,例如:NSNumber、NSIndexPath、NSDate、NSString指针由
标志+值+扩展+类型组成,通过混淆编码成指针地址使用
Tagged Pointer类型的好处,节省内存空间,提升读取效率Tagged Pointer触发retain和release,什么都不处理直接返回。这意味着它不需要ARC进行管理,而是直接被系统回收释放Tagged Pointer的内存并不存储在堆中,而是在常量区中,所以不需要malloc和free。它的读取速度,相比存储在堆区的数据读取,效率上快了3倍左右。创建的效率相比堆区快了近100倍左右Tagged Pointer结构,在ARM64架构下:高地址第一位,标志位,表示该
isa为Tagged Pointer类型低地址最后三位,表示存储的类型,例如:
NSNumber、NSIndexPath、NSDate、NSString低地址
4~7位,记录扩展信息,例如:存储NSString记录字符串长度、存储NSNumber记录基本数据类型的枚举值其余
56位,用于存储值
4. SideTables
NonpointerISA表示它不⽌是类对象地址,isa中包含了类信息、对象的引⽤计数等
以ARM64架构为例,引⽤计数存储在NonpointerISA位域的extra_rc中,高位的前19位
extra_rc表示该对象的引⽤计数值,实际上是引⽤计数值-1。例如,如果对象的引⽤计数为10,那么extra_rc为9。如果引⽤计数⼤于 10,则需要使⽤到下⾯的has_sidetable_rc
has_sidetable_rc当对象引⽤计数⼤于10时,则借⽤该变量存储进位。此时会配合散列表SideTables进行存储
4.1 retain
在objc源码中,进入rootRetain函数
ALWAYS_INLINE idobjc_object::rootRetain(bool tryRetain, objc_object::RRVariant variant){//1、判断如果是TaggedPointer,什么都不处理,直接返回if (slowpath(isTaggedPointer())) return (id)this;bool sideTableLocked = false;bool transcribeToSideTable = false;isa_t oldisa;isa_t newisa;oldisa = LoadExclusive(&isa.bits);if (variant == RRVariant::FastOrMsgSend) {// These checks are only meaningful for objc_retain()// They are here so that we avoid a re-load of the isa.if (slowpath(oldisa.getDecodedClass(false)->hasCustomRR())) {ClearExclusive(&isa.bits);if (oldisa.getDecodedClass(false)->canCallSwiftRR()) {return swiftRetain.load(memory_order_relaxed)((id)this);}return ((id(*)(objc_object *, SEL))objc_msgSend)(this, @selector(retain));}}if (slowpath(!oldisa.nonpointer)) {// a Class is a Class forever, so we can perform this check once// outside of the CAS loop//2、如果是纯isa,判断如果是一个类,也不需要Retain操作if (oldisa.getDecodedClass(false)->isMetaClass()) {ClearExclusive(&isa.bits);return (id)this;}}do {transcribeToSideTable = false;newisa = oldisa;if (slowpath(!newisa.nonpointer)) {//3、如果是纯isa,使用散列表,进行Retain操作ClearExclusive(&isa.bits);if (tryRetain) return sidetable_tryRetain() ? (id)this : nil;else return sidetable_retain(sideTableLocked);}// don't check newisa.fast_rr; we already called any RR overridesif (slowpath(newisa.isDeallocating())) {//4、如果当前isa正在释放,不需要Retain操作ClearExclusive(&isa.bits);if (sideTableLocked) {ASSERT(variant == RRVariant::Full);sidetable_unlock();}if (slowpath(tryRetain)) {return nil;} else {return (id)this;}}//5、通过bits对RC_ONE进行Retain操作,引用计数+1,将状态赋值carryuintptr_t carry;newisa.bits = addc(newisa.bits, RC_ONE, 0, &carry); // extra_rc++if (slowpath(carry)) {// newisa.extra_rc++ overflowedif (variant != RRVariant::Full) {ClearExclusive(&isa.bits);return rootRetain_overflow(tryRetain);}// Leave half of the retain counts inline and// prepare to copy the other half to the side table.if (!tryRetain && !sideTableLocked) sidetable_lock();//6、存储已满,修改一些标记,设置isa的extra_rc和has_sidetable_rc//RC_HALF表示砍半,将一半存储在extra_rcsideTableLocked = true;transcribeToSideTable = true;newisa.extra_rc = RC_HALF;newisa.has_sidetable_rc = true;}} while (slowpath(!StoreExclusive(&isa.bits, &oldisa.bits, newisa.bits)));if (variant == RRVariant::Full) {if (slowpath(transcribeToSideTable)) {// Copy the other half of the retain counts to the side table.//7、将另一半存储到散列表SideTable中sidetable_addExtraRC_nolock(RC_HALF);}if (slowpath(!tryRetain && sideTableLocked)) sidetable_unlock();} else {ASSERT(!transcribeToSideTable);ASSERT(!sideTableLocked);}return (id)this;}
retain流程:
【步骤一】判断如果是
TaggedPointer是,什么都不处理,直接返回
不是,进入【第二步】
【第二步】判断是纯
isa,并且是一个类是,不需要
Retain操作,直接返回不是,进入【第三步】
【第三步】如果是纯
isa,但不是类是,使用散列表,进行
Retain操作不是,进入【第四步】
【第四步】判断当前
isa正在释放是,不需要
Retain操作,直接返回不是,进入【第五步】
【第五步】通过
bits对RC_ONE进行Retain操作,引用计数+1,将状态赋值carry,进入【第六步】【第六步】判断
extra_rc是否存储已满存储已满,修改一些标记,设置
isa的extra_rc和has_sidetable_rc,进入【第七步】RC_HALF表示砍半,将一半存储在extra_rc
未存满,进入【第八步】
【第七步】将另一半存储到散列表
SideTable中【第八步】返回,
retain流程结束
4.2 release
进入rootRetain函数
ALWAYS_INLINE boolobjc_object::rootRelease(bool performDealloc, objc_object::RRVariant variant){//1、判断如果是TaggedPointer,什么都不处理,直接返回if (slowpath(isTaggedPointer())) return false;bool sideTableLocked = false;isa_t newisa, oldisa;oldisa = LoadExclusive(&isa.bits);if (variant == RRVariant::FastOrMsgSend) {// These checks are only meaningful for objc_release()// They are here so that we avoid a re-load of the isa.if (slowpath(oldisa.getDecodedClass(false)->hasCustomRR())) {ClearExclusive(&isa.bits);if (oldisa.getDecodedClass(false)->canCallSwiftRR()) {swiftRelease.load(memory_order_relaxed)((id)this);return true;}((void(*)(objc_object *, SEL))objc_msgSend)(this, @selector(release));return true;}}if (slowpath(!oldisa.nonpointer)) {// a Class is a Class forever, so we can perform this check once// outside of the CAS loop//2、如果是纯isa,判断如果是一个类,也不需要Release操作if (oldisa.getDecodedClass(false)->isMetaClass()) {ClearExclusive(&isa.bits);return false;}}retry:do {newisa = oldisa;if (slowpath(!newisa.nonpointer)) {//3、如果是纯isa,使用散列表,进行Release操作ClearExclusive(&isa.bits);return sidetable_release(sideTableLocked, performDealloc);}if (slowpath(newisa.isDeallocating())) {//4、如果当前isa正在释放,不需要Release操作ClearExclusive(&isa.bits);if (sideTableLocked) {ASSERT(variant == RRVariant::Full);sidetable_unlock();}return false;}// don't check newisa.fast_rr; we already called any RR overrides//5、通过bits对RC_ONE进行Release操作,引用计数-1,将状态赋值carryuintptr_t carry;newisa.bits = subc(newisa.bits, RC_ONE, 0, &carry); // extra_rc--if (slowpath(carry)) {// don't ClearExclusive()//6、如果extra_rc减空,进入underflow代码流程goto underflow;}} while (slowpath(!StoreReleaseExclusive(&isa.bits, &oldisa.bits, newisa.bits)));if (slowpath(newisa.isDeallocating()))goto deallocate;if (variant == RRVariant::Full) {if (slowpath(sideTableLocked)) sidetable_unlock();} else {ASSERT(!sideTableLocked);}return false;underflow:// newisa.extra_rc-- underflowed: borrow from side table or deallocate// abandon newisa to undo the decrementnewisa = oldisa;if (slowpath(newisa.has_sidetable_rc)) {//7、判断当前已使用散列表存储if (variant != RRVariant::Full) {ClearExclusive(&isa.bits);return rootRelease_underflow(performDealloc);}// Transfer retain count from side table to inline storage.if (!sideTableLocked) {ClearExclusive(&isa.bits);sidetable_lock();sideTableLocked = true;// Need to start over to avoid a race against// the nonpointer -> raw pointer transition.oldisa = LoadExclusive(&isa.bits);goto retry;}// Try to remove some retain counts from the side table.//从散列表中取出一半auto borrow = sidetable_subExtraRC_nolock(RC_HALF);//如果散列表中取空了,标记emptySideTablebool emptySideTable = borrow.remaining == 0; // we'll clear the side table if no refcounts remain there//判断从散列表中取出内容if (borrow.borrowed > 0) {// Side table retain count decreased.// Try to add them to the inline count.bool didTransitionToDeallocating = false;//进行-1操作,赋值extra_rc//通过emptySideTable标记,修改has_sidetable_rcnewisa.extra_rc = borrow.borrowed - 1; // redo the original decrement toonewisa.has_sidetable_rc = !emptySideTable;//存储到isa的bits中bool stored = StoreReleaseExclusive(&isa.bits, &oldisa.bits, newisa.bits);if (!stored && oldisa.nonpointer) {// Inline update failed.// Try it again right now. This prevents livelock on LL/SC// architectures where the side table access itself may have// dropped the reservation.//存储失败的补救处理uintptr_t overflow;newisa.bits =addc(oldisa.bits, RC_ONE * (borrow.borrowed-1), 0, &overflow);newisa.has_sidetable_rc = !emptySideTable;if (!overflow) {stored = StoreReleaseExclusive(&isa.bits, &oldisa.bits, newisa.bits);if (stored) {didTransitionToDeallocating = newisa.isDeallocating();}}}if (!stored) {// Inline update failed.// Put the retains back in the side table.ClearExclusive(&isa.bits);sidetable_addExtraRC_nolock(borrow.borrowed);oldisa = LoadExclusive(&isa.bits);goto retry;}// Decrement successful after borrowing from side table.if (emptySideTable)sidetable_clearExtraRC_nolock();if (!didTransitionToDeallocating) {if (slowpath(sideTableLocked)) sidetable_unlock();return false;}}else {// Side table is empty after all. Fall-through to the dealloc path.}}deallocate:// Really deallocate.//8、进入deallocate代码流程ASSERT(newisa.isDeallocating());ASSERT(isa.isDeallocating());if (slowpath(sideTableLocked)) sidetable_unlock();__c11_atomic_thread_fence(__ATOMIC_ACQUIRE);if (performDealloc) {//调用对象的dealloc方法((void(*)(objc_object *, SEL))objc_msgSend)(this, @selector(dealloc));}return true;}
release流程:
【第一步】判断如果是
TaggedPointer是,什么都不处理,直接返回
不是,进入【第二步】
【第二步】判断是纯
isa,并且是一个类是,不需要
Release操作,直接返回不是,进入【第三步】
【第三步】如果是纯
isa,但不是类是,使用散列表,进行
Release操作不是,进入【第四步】
【第四步】判断当前
isa正在释放是,不需要
Release操作,直接返回不是,进入【第五步】
【第五步】通过
bits对RC_ONE进行Release操作,引用计数-1,将状态赋值carry,进入【第六步】【第六步】判断
extra_rc是否减空是,进入【第七步】
不是,进入【第八步】
【第七步】进入
underflow代码流程,判断当前已使用散列表存储是,从散列表中取出一半
如果散列表中取空了,标记
emptySideTable如果从散列表中取出内容,进行
-1操作,赋值extra_rc通过
emptySideTable标记,修改has_sidetable_rc存储到
isa的bits中如果存储失败,进行补救处理
不是,进入【第八步】
【第八步】进入
deallocate代码流程调用对象的
dealloc方法返回,
release流程结束
4.3 SideTable的结构
散列表本质就是一张哈希表
当retain操作使用SideTable进行存储时,会进入sidetable_retain函数
idobjc_object::sidetable_retain(bool locked){#if SUPPORT_NONPOINTER_ISAASSERT(!isa.nonpointer);#endifSideTable& table = SideTables()[this];if (!locked) table.lock();size_t& refcntStorage = table.refcnts[this];if (! (refcntStorage & SIDE_TABLE_RC_PINNED)) {refcntStorage += SIDE_TABLE_RC_ONE;}table.unlock();return (id)this;}
- 本质上操作的是
SideTable结构,在SideTables中,找到当前对象对应的一张散列表
这说明散列表不止只有一张,它的底层使用StripedMap
template<typename T>class StripedMap {#if TARGET_OS_IPHONE && !TARGET_OS_SIMULATORenum { StripeCount = 8 };#elseenum { StripeCount = 64 };#endif...}
- 根据不同系统架构,可创建
8或64张SideTable。在iOS设置上,只能创建8张
查看SideTable的结构
struct SideTable {spinlock_t slock;RefcountMap refcnts;weak_table_t weak_table;SideTable() {memset(&weak_table, 0, sizeof(weak_table));}~SideTable() {_objc_fatal("Do not delete SideTable.");}void lock() { slock.lock(); }void unlock() { slock.unlock(); }void forceReset() { slock.forceReset(); }// Address-ordered lock discipline for a pair of side tables.template<HaveOld, HaveNew>static void lockTwo(SideTable *lock1, SideTable *lock2);template<HaveOld, HaveNew>static void unlockTwo(SideTable *lock1, SideTable *lock2);};
- 包含一把锁、一张引用计数表和一张弱引用表
- 对
SideTable的存取,会牵扯加锁和解锁的耗时操作,为了线程安全。所以当多个对象同时操作SideTable时,为了保证效率,采用多张SideTable表分散压力 - 当对象分散使用多张表时,当表中的对象全部释放后,该表也可以释放,这样可以及时回收内存
- 由于开表所消耗的内存过大,如果针对每个对象都开一张表,会造成很大程度的内存浪费
所以SideTable的核心作用,对引用计数表和弱引用表进行处理
4.4 SideTable的存取
当extra_rc存满后,只会分出一半存储到SideTable中
因为对SideTable的操作,需要经过加锁、解锁保证线程安全,相对耗时。如果extra_rc存满后全部导入SideTable中,在引用计数-1的时候,需要频繁对SideTable进行操作,效率太低
相比extra_rc的操作,它通过isa的位运算得到,可以直接进行+1、-1的操作,效率要比SideTable高很多
下面对散列表SideTable中引用计数的存取进行底层分析
4.4.1 sidetable_retain
对散列表中的引用计数+1
idobjc_object::sidetable_retain(bool locked){#if SUPPORT_NONPOINTER_ISAASSERT(!isa.nonpointer);#endifSideTable& table = SideTables()[this];if (!locked) table.lock();size_t& refcntStorage = table.refcnts[this];if (! (refcntStorage & SIDE_TABLE_RC_PINNED)) {refcntStorage += SIDE_TABLE_RC_ONE;}table.unlock();return (id)this;}
- 通过当前对象,找到所属的
SideTable - 通过当前对象,找到在引用计数表的所属空间
- 所属空间中并不是直接存储引用计数,而是使用位域存储很多信息
- 核心代码:
refcntStorage += SIDE_TABLE_RC_ONE
找到SIDE_TABLE_RC_ONE的定义
#define SIDE_TABLE_WEAKLY_REFERENCED (1UL<<0)#define SIDE_TABLE_DEALLOCATING (1UL<<1) // MSB-ward of weak bit#define SIDE_TABLE_RC_ONE (1UL<<2) // MSB-ward of deallocating bit#define SIDE_TABLE_RC_PINNED (1UL<<(WORD_BITS-1))
1左移2位,结果为4,转为十六进制为100- 因为真正的
refcnt在位域中的第2位上存储,+100的目的就是不影响前面两位,实则引用计数+1 SIDE_TABLE_WEAKLY_REFERENCED:弱引用标记SIDE_TABLE_DEALLOCATING:是否正在析构SIDE_TABLE_RC_ONE:引用计数SIDE_TABLE_RC_PINNED:标记引用计数是否越界
4.4.2 sidetable_addExtraRC_nolock
当extra_rc存储已满,将一半存储到散列表中
boolobjc_object::sidetable_addExtraRC_nolock(size_t delta_rc){ASSERT(isa.nonpointer);SideTable& table = SideTables()[this];size_t& refcntStorage = table.refcnts[this];size_t oldRefcnt = refcntStorage;// isa-side bits should not be set hereASSERT((oldRefcnt & SIDE_TABLE_DEALLOCATING) == 0);ASSERT((oldRefcnt & SIDE_TABLE_WEAKLY_REFERENCED) == 0);if (oldRefcnt & SIDE_TABLE_RC_PINNED) return true;uintptr_t carry;size_t newRefcnt =addc(oldRefcnt, delta_rc << SIDE_TABLE_RC_SHIFT, 0, &carry);if (carry) {refcntStorage =SIDE_TABLE_RC_PINNED | (oldRefcnt & SIDE_TABLE_FLAG_MASK);return true;}else {refcntStorage = newRefcnt;return false;}}
- 同样对
delta_rc进行左移SIDE_TABLE_RC_SHIFT位
找到SIDE_TABLE_RC_SHIFT的定义
#define SIDE_TABLE_RC_SHIFT 2
- 进行左移
2位
4.4.3 sidetable_subExtraRC_nolock
当extra_rc减空,从散列表中读取一半
objc_object::SidetableBorrowobjc_object::sidetable_subExtraRC_nolock(size_t delta_rc){ASSERT(isa.nonpointer);SideTable& table = SideTables()[this];RefcountMap::iterator it = table.refcnts.find(this);if (it == table.refcnts.end() || it->second == 0) {// Side table retain count is zero. Can't borrow.return { 0, 0 };}size_t oldRefcnt = it->second;// isa-side bits should not be set hereASSERT((oldRefcnt & SIDE_TABLE_DEALLOCATING) == 0);ASSERT((oldRefcnt & SIDE_TABLE_WEAKLY_REFERENCED) == 0);size_t newRefcnt = oldRefcnt - (delta_rc << SIDE_TABLE_RC_SHIFT);ASSERT(oldRefcnt > newRefcnt); // shouldn't underflowit->second = newRefcnt;return { delta_rc, newRefcnt >> SIDE_TABLE_RC_SHIFT };}
- 对散列表中的
refcnt砍半,同样先经过左移2位的操作 - 将剩余的
refcnt返回给上层函数,需要先右移2位,恢复为正常的引用计数
5. WeakTable
5.1 rootRetainCount
打印对象的引用计数
- (void)viewDidLoad {[super viewDidLoad];NSObject *objc = [[NSObject alloc] init];NSLog(@"objc:%ld",CFGetRetainCount((__bridge CFTypeRef)objc));}-------------------------//输出以下内容:objc:1
在老版本的objc源码中,对象alloc默认为0。为了避免它的释放,在rootRetainCount方法中,系统对引用计数默认+1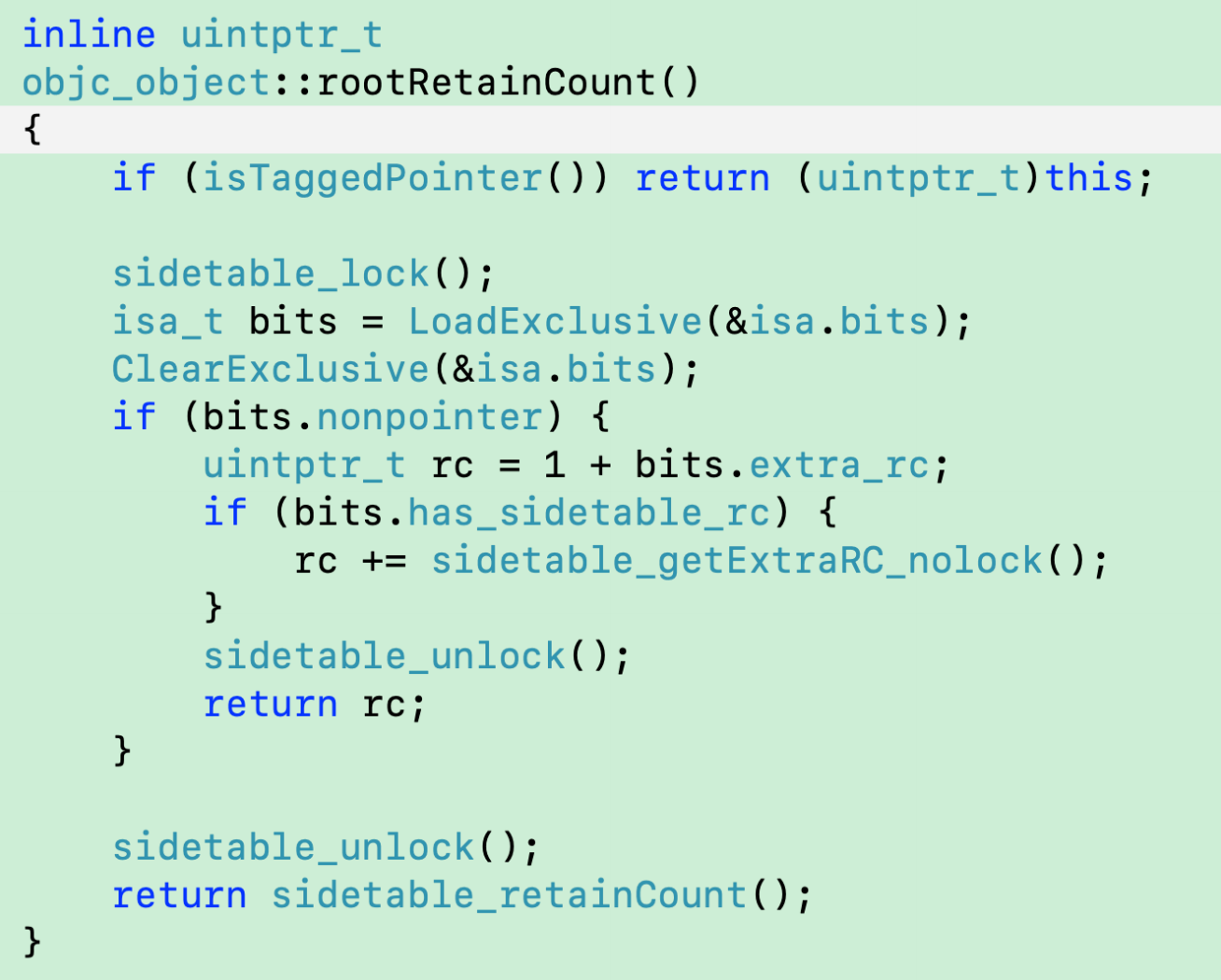
- 仅在读取时对引用计数
+1 - 实际上
extra_rc中的引用计数仍然为0
在最新版本的objc4-818.2源码中,对rootRetainCount函数进行了修改
inline uintptr_tobjc_object::rootRetainCount(){if (isTaggedPointer()) return (uintptr_t)this;sidetable_lock();isa_t bits = __c11_atomic_load((_Atomic uintptr_t *)&isa.bits, __ATOMIC_RELAXED);if (bits.nonpointer) {uintptr_t rc = bits.extra_rc;if (bits.has_sidetable_rc) {rc += sidetable_getExtraRC_nolock();}sidetable_unlock();return rc;}sidetable_unlock();return sidetable_retainCount();}
- 没有
+1的处理,直接获取extra_rc。如果使用散列表,再加上散列表中的引用计数
这里的变化,源于alloc的底层修改。当对象alloc时,调用initIsa函数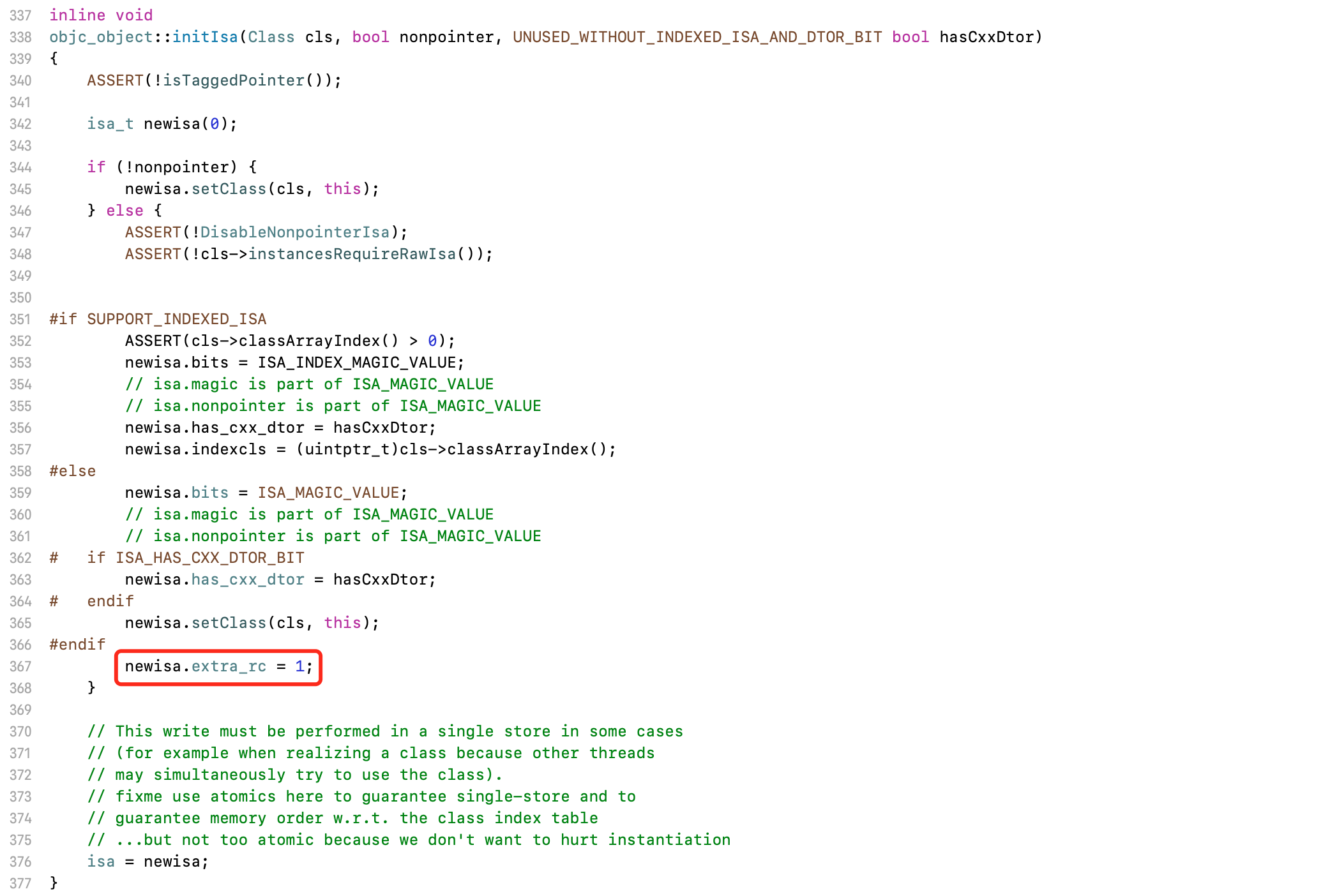
- 在
isa初始化时,引用计数已经设置为1
5.2 验证weakObjc的引用计数
将对象赋值给使用__weak修饰的变量,打印它的引用计数
- (void)viewDidLoad {[super viewDidLoad];NSObject *objc = [[NSObject alloc] init];__weak typeof(objc) weakObjc = objc;NSLog(@"objc:%ld,%@",CFGetRetainCount((__bridge CFTypeRef)objc), objc);NSLog(@"weakObjc:%ld,%@",CFGetRetainCount((__bridge CFTypeRef)weakObjc), weakObjc);}-------------------------//输出以下内容:objc:1,<NSObject: 0x28132c7f0>weakObjc:2,<NSObject: 0x28132c7f0>
- 对象被弱引用变量持有,并不会对自身的引用计数
+1,所以objc仍然输出为1 - 但问题是,为什么
weakObjc的引用计数输出为2?
5.3 weak的底层探索
在weak修饰的变量处设置断点,运行项目,查看汇编代码: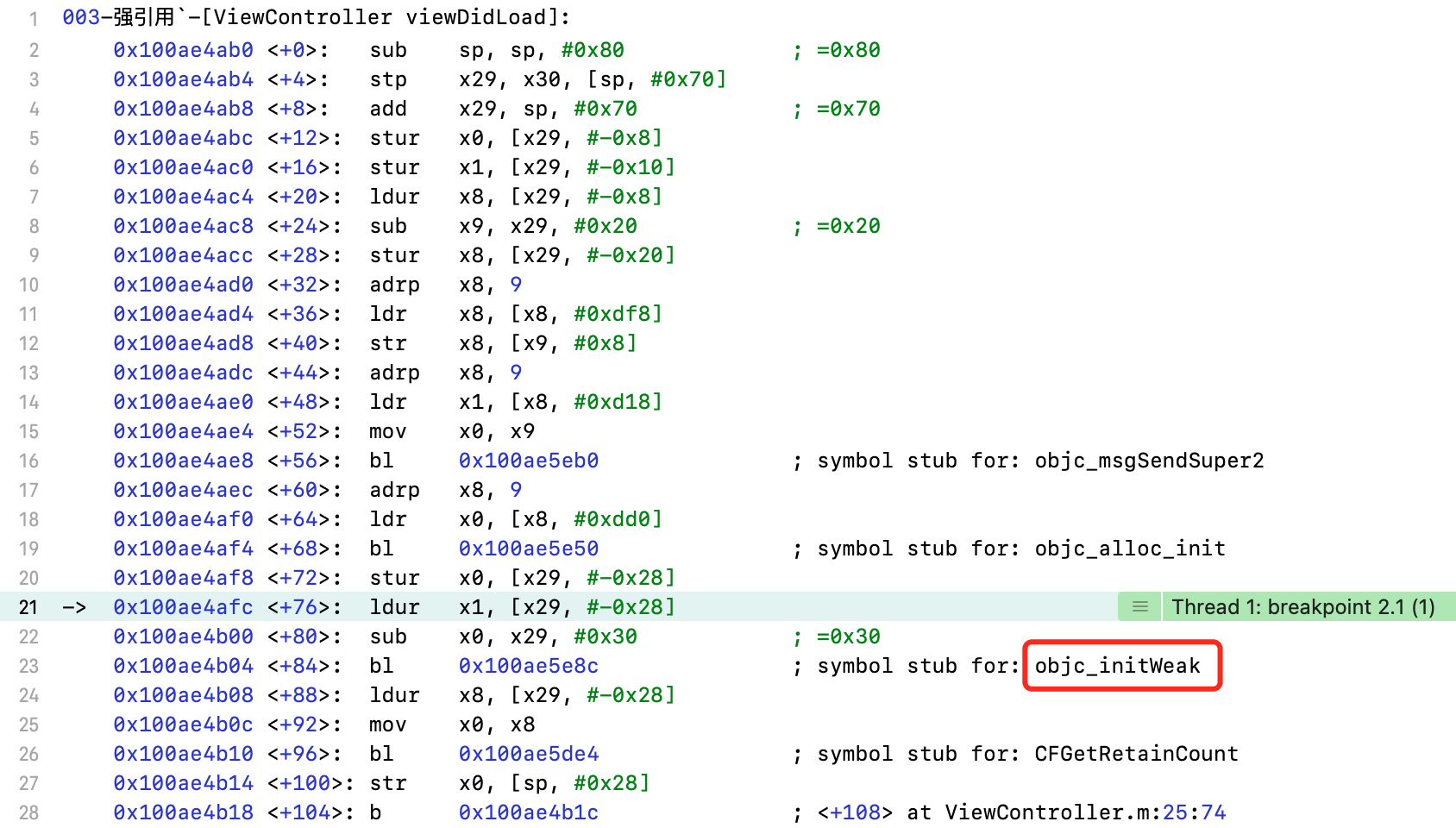
调用objc_initWeak函数,来自libobjc框架
在objc4-818.2源码中,进入objc_initWeak函数
idobjc_initWeak(id *location, id newObj){if (!newObj) {*location = nil;return nil;}return storeWeak<DontHaveOld, DoHaveNew, DoCrashIfDeallocating>(location, (objc_object*)newObj);}
storeWeak是一个模板类,内部逻辑具有高度可封装,通过传入的参数不同,执行不同的逻辑分支
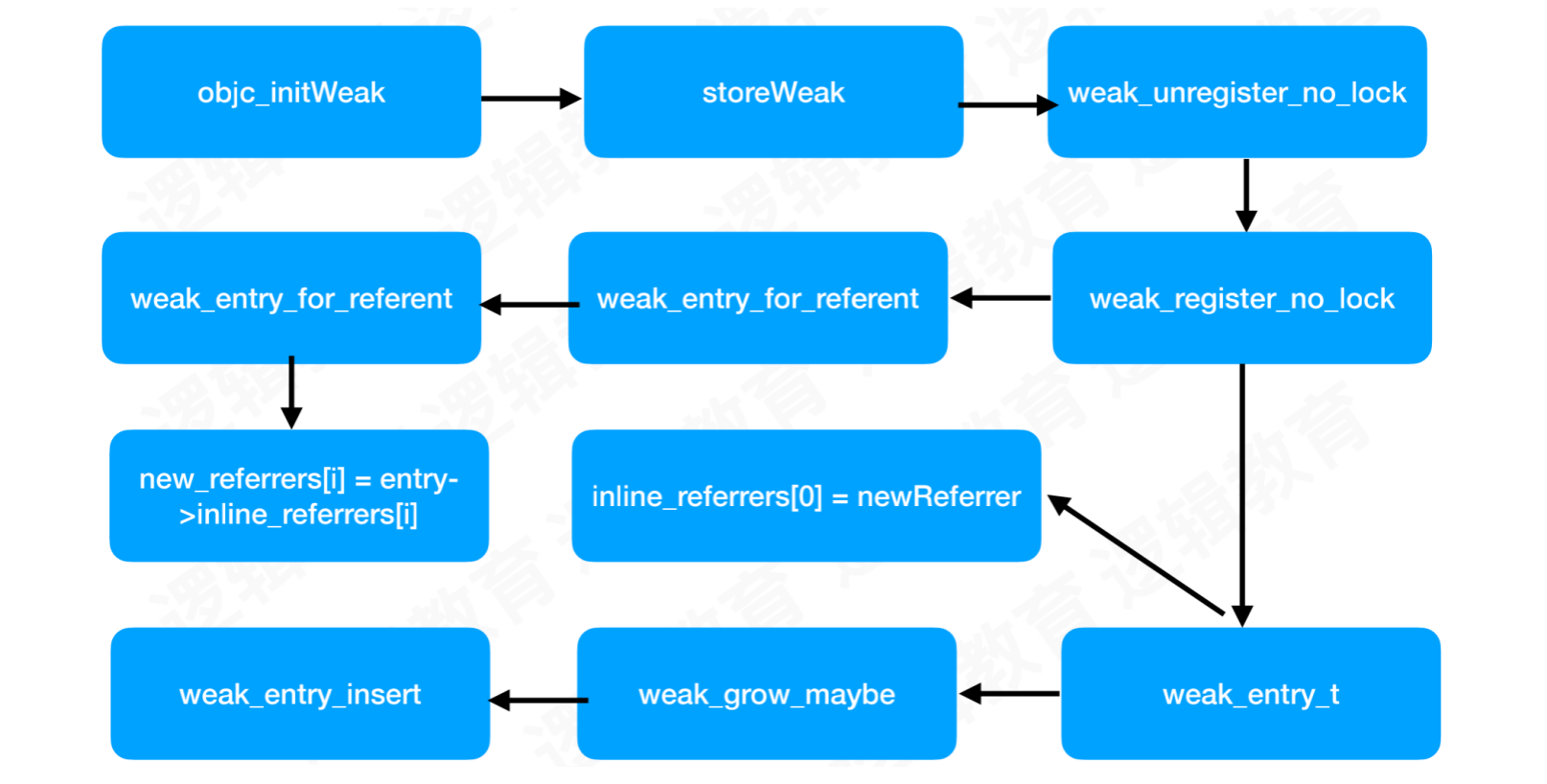
5.2.1 storeWeak
进入storeWeak函数
template <HaveOld haveOld, HaveNew haveNew,enum CrashIfDeallocating crashIfDeallocating>static idstoreWeak(id *location, objc_object *newObj){ASSERT(haveOld || haveNew);if (!haveNew) ASSERT(newObj == nil);//location:弱引用对象指针//newObj:原始对象Class previouslyInitializedClass = nil;id oldObj;SideTable *oldTable;SideTable *newTable;// Acquire locks for old and new values.// Order by lock address to prevent lock ordering problems.// Retry if the old value changes underneath us.retry://判断haveOldif (haveOld) {oldObj = *location;oldTable = &SideTables()[oldObj];} else {//在objc_initWeak中调用时,传入的DontHaveOld,不存在//将oldTable设置为niloldTable = nil;}//判断haveNewif (haveNew) {//在objc_initWeak中调用时,传入的DoHaveNew,存在//找到原始对象所在的SideTablenewTable = &SideTables()[newObj];} else {newTable = nil;}SideTable::lockTwo<haveOld, haveNew>(oldTable, newTable);if (haveOld && *location != oldObj) {SideTable::unlockTwo<haveOld, haveNew>(oldTable, newTable);goto retry;}// Prevent a deadlock between the weak reference machinery// and the +initialize machinery by ensuring that no// weakly-referenced object has an un-+initialized isa.//防止弱引用机制之间的死锁//确保Class的初始化//为弱引用对象未初始化isaif (haveNew && newObj) {Class cls = newObj->getIsa();if (cls != previouslyInitializedClass &&!((objc_class *)cls)->isInitialized()){SideTable::unlockTwo<haveOld, haveNew>(oldTable, newTable);class_initialize(cls, (id)newObj);// If this class is finished with +initialize then we're good.// If this class is still running +initialize on this thread// (i.e. +initialize called storeWeak on an instance of itself)// then we may proceed but it will appear initializing and// not yet initialized to the check above.// Instead set previouslyInitializedClass to recognize it on retry.//赋值previouslyInitializedClass,防止重复初始化previouslyInitializedClass = cls;goto retry;}}// Clean up old value, if any.if (haveOld) {//存在旧值,将其移除weak_unregister_no_lock(&oldTable->weak_table, oldObj, location);}// Assign new value, if any.if (haveNew) {//调用weak_register_no_lock函数,传入当前对象所在散列表中的weak_table,并传入原始对象和弱引用对象指针newObj = (objc_object *)weak_register_no_lock(&newTable->weak_table, (id)newObj, location,crashIfDeallocating ? CrashIfDeallocating : ReturnNilIfDeallocating);// weak_register_no_lock returns nil if weak store should be rejected// Set is-weakly-referenced bit in refcount table.if (!newObj->isTaggedPointerOrNil()) {newObj->setWeaklyReferenced_nolock();}// Do not set *location anywhere else. That would introduce a race.//将原始对象赋值给弱引用对象*location = (id)newObj;}else {// No new value. The storage is not changed.}SideTable::unlockTwo<haveOld, haveNew>(oldTable, newTable);// This must be called without the locks held, as it can invoke// arbitrary code. In particular, even if _setWeaklyReferenced// is not implemented, resolveInstanceMethod: may be, and may// call back into the weak reference machinery.callSetWeaklyReferenced((id)newObj);return (id)newObj;}
将弱引用对象指针
location和原始对象newObj函数判断
haveOld,在objc_initWeak中调用时,传入的DontHaveOld,不存在- 将
oldTable设置为nil
- 将
判断
haveNew,在objc_initWeak中调用时,传入的DoHaveNew,存在- 找到原始对象所在的
SideTable
- 找到原始对象所在的
判断
haveNew和原始对象,防止弱引用机制之间的死锁,确保Class的初始化,为弱引用对象未初始化isa判断
haveOld,存在旧值,将其移除判断
haveNew存在调用
weak_register_no_lock函数,传入当前对象所在散列表中的weak_table,并传入原始对象和弱引用对象指针将原始对象赋值给弱引用对象
将原始对象返回,流程结束
5.2.2 weak_register_no_lock
进入weak_register_no_lock函数
idweak_register_no_lock(weak_table_t *weak_table, id referent_id,id *referrer_id, WeakRegisterDeallocatingOptions deallocatingOptions){//referent_id:原始对象//referrer_id:弱引用对象的指针objc_object *referent = (objc_object *)referent_id;objc_object **referrer = (objc_object **)referrer_id;if (referent->isTaggedPointerOrNil()) return referent_id;// ensure that the referenced object is viable//确保引用的对象是可用的if (deallocatingOptions == ReturnNilIfDeallocating ||deallocatingOptions == CrashIfDeallocating) {bool deallocating;if (!referent->ISA()->hasCustomRR()) {deallocating = referent->rootIsDeallocating();}else {// Use lookUpImpOrForward so we can avoid the assert in// class_getInstanceMethod, since we intentionally make this// callout with the lock held.auto allowsWeakReference = (BOOL(*)(objc_object *, SEL))lookUpImpOrForwardTryCache((id)referent, @selector(allowsWeakReference),referent->getIsa());if ((IMP)allowsWeakReference == _objc_msgForward) {return nil;}deallocating =! (*allowsWeakReference)(referent, @selector(allowsWeakReference));}if (deallocating) {if (deallocatingOptions == CrashIfDeallocating) {_objc_fatal("Cannot form weak reference to instance (%p) of ""class %s. It is possible that this object was ""over-released, or is in the process of deallocation.",(void*)referent, object_getClassName((id)referent));} else {return nil;}}}// now remember it and where it is being storedweak_entry_t *entry;//判断在表中是否能找到对象的存储if ((entry = weak_entry_for_referent(weak_table, referent))) {//已存在,将弱引用对象追加到表中append_referrer(entry, referrer);}else {//不存在,创建weak_entry_t,将原始对象和弱引用对象关联weak_entry_t new_entry(referent, referrer);//重新开辟一张表weak_grow_maybe(weak_table);//将new_entry插入到表中weak_entry_insert(weak_table, &new_entry);}// Do not set *referrer. objc_storeWeak() requires that the// value not change.return referent_id;}
传入原始对象
referent_id和弱引用对象的指针referrer_id一系列判断,确保引用的对象是可用的
判断在表中是否能找到对象的存储
已存在,将弱引用对象追加到表中
不存在
创建
weak_entry_t,将原始对象和弱引用对象关联重新开辟一张表
将
new_entry插入到表中
将原始对象返回,流程结束
5.2.3 append_referrer
进入append_referrer函数
static void append_referrer(weak_entry_t *entry, objc_object **new_referrer){if (! entry->out_of_line()) {// Try to insert inline.//传入原始对象所属的weak_entry_t结构体指针和弱引用对象指针//找到weak_entry_t下的inline_referrers,一个对象可能被赋值给多个弱引用对象//循环找到空位,如果存在空位直接赋值for (size_t i = 0; i < WEAK_INLINE_COUNT; i++) {if (entry->inline_referrers[i] == nil) {entry->inline_referrers[i] = new_referrer;return;}}// Couldn't insert inline. Allocate out of line.//没有空位,重新创建new_referrersweak_referrer_t *new_referrers = (weak_referrer_t *)calloc(WEAK_INLINE_COUNT, sizeof(weak_referrer_t));// This constructed table is invalid, but grow_refs_and_insert// will fix it and rehash it.//将现有entry下的inline_referrers中的元素,循环导入到新创建的new_referrers中for (size_t i = 0; i < WEAK_INLINE_COUNT; i++) {new_referrers[i] = entry->inline_referrers[i];}//相关成员变量的覆盖entry->referrers = new_referrers;entry->num_refs = WEAK_INLINE_COUNT;entry->out_of_line_ness = REFERRERS_OUT_OF_LINE;entry->mask = WEAK_INLINE_COUNT-1;entry->max_hash_displacement = 0;}ASSERT(entry->out_of_line());//扩容相关操作if (entry->num_refs >= TABLE_SIZE(entry) * 3/4) {return grow_refs_and_insert(entry, new_referrer);}size_t begin = w_hash_pointer(new_referrer) & (entry->mask);size_t index = begin;size_t hash_displacement = 0;while (entry->referrers[index] != nil) {hash_displacement++;index = (index+1) & entry->mask;if (index == begin) bad_weak_table(entry);}if (hash_displacement > entry->max_hash_displacement) {entry->max_hash_displacement = hash_displacement;}weak_referrer_t &ref = entry->referrers[index];ref = new_referrer;entry->num_refs++;}
传入原始对象所属的
weak_entry_t结构体指针和弱引用对象指针找到
weak_entry_t下的inline_referrers,一个对象可能被赋值给多个弱引用对象循环找到空位,如果存在空位直接赋值
没有空位,重新创建
new_referrers将现有
entry下的inline_referrers中的元素,循环导入到新创建的new_referrers中相关成员变量的覆盖
扩容相关操作
5.4 weakObjc引用计数为2的原因
查看汇编代码:
- 弱引用对象在使用时,会调用
objc_loadWeakRetained函数 - 汇编代码中的两次调用,第一次在执行
CFGetRetainCount函数之前,第二次在执行NSLog方法之前
在objc4-818.2源码中,进入objc_loadWeakRetained函数
idobjc_loadWeakRetained(id *location){id obj;id result;Class cls;SideTable *table;retry:// fixme std::atomic this load//对弱引用对象指针取值obj = *location;if (obj->isTaggedPointerOrNil()) return obj;table = &SideTables()[obj];table->lock();if (*location != obj) {table->unlock();goto retry;}//赋值给result临时变量result = obj;cls = obj->ISA();if (! cls->hasCustomRR()) {// Fast case. We know +initialize is complete because// default-RR can never be set before then.ASSERT(cls->isInitialized());//调用retain函数,对引用计数+1if (! obj->rootTryRetain()) {result = nil;}}else {// Slow case. We must check for +initialize and call it outside// the lock if necessary in order to avoid deadlocks.// Use lookUpImpOrForward so we can avoid the assert in// class_getInstanceMethod, since we intentionally make this// callout with the lock held.if (cls->isInitialized() || _thisThreadIsInitializingClass(cls)) {BOOL (*tryRetain)(id, SEL) = (BOOL(*)(id, SEL))lookUpImpOrForwardTryCache(obj, @selector(retainWeakReference), cls);if ((IMP)tryRetain == _objc_msgForward) {result = nil;}else if (! (*tryRetain)(obj, @selector(retainWeakReference))) {result = nil;}}else {table->unlock();class_initialize(cls, obj);goto retry;}}table->unlock();return result;}
- 传入弱引用对象指针
- 对弱引用对象指针取值,赋值给
obj,相当于原始对象 - 将
obj赋值给result,此时引用计数不变 - 核心代码:
if (! obj->rootTryRetain()),调用obj调用retain函数,引用计数+1
使用弱引用对象,触发objc_loadWeakRetained函数,为对象进行一次retain操作
这样做的目的,避免弱引用对象在使用过程中,由于原始对象被释放,导致所有正在使用的弱引用对象全部取值异常,造成大面积的连锁反应
当objc_loadWeakRetained函数执行完毕,临时变量会释放,自动恢复对象的引用计数
采用这种方式的好处,让原始对象和弱引用对象更加独立,对强弱引用对象进行分开管理
5.5 weak流程图
总结
内存布局:
当程序运行时,系统会开辟内核区、程序使用的内存五大区和保留区
内存五大区,主要分为栈区、堆区、全局区、常量区、代码区
内存管理方案:
MRC:对象通过引用计数判断是否销毁,需要手动调用对象的retain、release、autorelease等方法,维护对象引用计数ARC:ARC为自动引用计数管理,属于编译器的一种特性,在WWDC2011和iOS5时代被引入
Tagged Pointer:
专门用于存储小的对象,例如:
NSNumber、NSIndexPath、NSDate、NSString指针由
标志+值+类型组成,通过混淆编码成指针地址使用
Tagged Pointer类型的好处,节省内存空间,提升读取效率Tagged Pointer进入retain和release,什么都不处理直接返回。这意味着它不需要ARC进行管理,而是直接被系统自主回收释放Tagged Pointer的内存并不存储在堆中,而是在常量区中,所以不需要malloc和free。它的读取速度,相比存储在堆区的数据读取,效率上快了3倍左右。创建的效率相比堆区快了近100倍左右Tagged Pointer结构,在ARM64架构下:高地址第一位,标志位,表示该
isa为Tagged Pointer类型低地址最后三位,表示存储的类型,例如:
NSNumber、NSIndexPath、NSDate、NSString低地址
4~7位,记录扩展信息,例如:存储NSString记录字符串长度、存储NSNumber记录基本数据类型的枚举值其余
56位,用于存储值
SideTables:
retain操作,如果对象isa为NonpointerISA,当extra_rc存储已满,将extra_rc的一半存储到SideTables中release操作,如果extra_rc减空,从SideTables中读取出一半,存储到extra_rc中SideTable本质就是一张哈希表,底层使用StripedMap。根据不同系统架构,可创建8或64张。在iOS设置上,只能创建8张SideTable结构中,包含一把锁、一张引用计数表和一张弱引用表使用
SideTable存储引用计数,通过当前对象,找到所属的SideTable,找到在引用计数表的所属空间对
SideTable的存取,会牵扯加锁和解锁的耗时操作,为了线程安全。所以当多个对象同时操作SideTable时,为了保证效率,采用多张SideTable表分散压力当对象分散使用多张表时,当表中的对象全部释放后,该表也可以释放,这样可以及时回收内存
由于开表所消耗的内存过大,如果针对每个对象都开一张表,会造成很大程度的内存浪费
当
extra_rc存满后,只会分出一半存储到SideTable中- 因为对
SideTable的操作,需要经过加锁、解锁保证线程安全,相对耗时。如果extra_rc存满后全部导入SideTable中,在引用计数-1的时候,需要频繁对SideTable进行操作,效率太低
- 因为对
所属空间中并不是直接存储引用计数,而是使用位域存储很多信息。真正的
refcnt在位域中的第2位上存储,所以每次+1和-1的时候,需要进行1<<2的处理,目的就是不影响前面两位
WeakTable:
SideTable下的弱引用表,SideTable本身有多张表,通过对象可以找到所属的SideTableSideTable下存储weak_table_t,它是一个结构体,里面存储了weak_entry_t结构的另一张表weak_entry_t表中存储原始对象referent,以及一个weak_referrer_t结构的列表inline_referrersinline_referrers中存储了弱引用对象的指针,因为一个对象可能被赋值给多个弱引用对象,所以使用列表存储使用弱引用对象,触发
objc_loadWeakRetained函数,为对象进行一次retain操作这样做的目的,避免弱引用对象在使用过程中,由于原始对象被释放,导致所有正在使用的弱引用对象全部取值异常,造成大面积的连锁反应
当
objc_loadWeakRetained函数执行完毕,临时变量会释放,自动恢复对象的引用计数采用这种方式的好处,让原始对象和弱引用对象更加独立,对强弱引用对象进行分开管理

