1. 类扩展 VS 分类
1.1 类扩展(Extension)
- 特殊的分类,也称作匿名分类
- 可以给类添加成员属性,但是为私有变量
- 可以给类添加方法,也是私有方法
1.2 分类(Category)
- 专门用来给类添加新的方法
- 不能给类添加成员属性,添加后无法读取(可通过
Runtime给分类添加属性) - 分类中使用
@property定义变量,只会生成变量的getter/setter方法的声明,不能生成方法的实现和下划线开头的成员变量
2. 类扩展的分析
2.1 cpp文件探索
在main函数中,写入LGPerson的类扩展
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {@autoreleasepool {NSLog(@"Hello, World!");}return 0;}@interface LGPerson : NSObject@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *lgName;- (void)say666;@end@interface LGPerson ()@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *ext_name;- (void)ext_sayNB;@end@implementation LGPerson- (void)say666{NSLog(@"%@ - %s",self , __func__);}- (void)ext_sayNB{NSLog(@"%@ - %s",self , __func__);}@end
- 类扩展的书写位置:声明之后,实现之前
生成cpp文件
clang -rewrite-objc main.m -o main.cpp
对于类扩展中声明的属性,同样会生成下划线开头的成员变量
extern "C" unsigned long OBJC_IVAR_$_LGPerson$_lgName;extern "C" unsigned long OBJC_IVAR_$_LGPerson$_ext_name;struct LGPerson_IMPL {struct NSObject_IMPL NSObject_IVARS;NSString *_lgName;NSString *_ext_name;};
生成属性的getter/setter方法
static NSString * _I_LGPerson_lgName(LGPerson * self, SEL _cmd) { return (*(NSString **)((char *)self + OBJC_IVAR_$_LGPerson$_lgName)); }extern "C" __declspec(dllimport) void objc_setProperty (id, SEL, long, id, bool, bool);static void _I_LGPerson_setLgName_(LGPerson * self, SEL _cmd, NSString *lgName) { objc_setProperty (self, _cmd, __OFFSETOFIVAR__(struct LGPerson, _lgName), (id)lgName, 0, 1); }static NSString * _I_LGPerson_ext_name(LGPerson * self, SEL _cmd) { return (*(NSString **)((char *)self + OBJC_IVAR_$_LGPerson$_ext_name)); }static void _I_LGPerson_setExt_name_(LGPerson * self, SEL _cmd, NSString *ext_name) { objc_setProperty (self, _cmd, __OFFSETOFIVAR__(struct LGPerson, _ext_name), (id)ext_name, 0, 1); }
找到LGPerson的成员变量列表
extern "C" unsigned long int OBJC_IVAR_$_LGPerson$_lgName __attribute__ ((used, section ("__DATA,__objc_ivar"))) = __OFFSETOFIVAR__(struct LGPerson, _lgName);extern "C" unsigned long int OBJC_IVAR_$_LGPerson$_ext_name __attribute__ ((used, section ("__DATA,__objc_ivar"))) = __OFFSETOFIVAR__(struct LGPerson, _ext_name);static struct /*_ivar_list_t*/ {unsigned int entsize; // sizeof(struct _prop_t)unsigned int count;struct _ivar_t ivar_list[2];} _OBJC_$_INSTANCE_VARIABLES_LGPerson __attribute__ ((used, section ("__DATA,__objc_const"))) = {sizeof(_ivar_t),2,{{(unsigned long int *)&OBJC_IVAR_$_LGPerson$_lgName, "_lgName", "@\"NSString\"", 3, 8},{(unsigned long int *)&OBJC_IVAR_$_LGPerson$_ext_name, "_ext_name", "@\"NSString\"", 3, 8}}};
找到LGPerson的方法列表
static struct /*_method_list_t*/ {unsigned int entsize; // sizeof(struct _objc_method)unsigned int method_count;struct _objc_method method_list[10];} _OBJC_$_INSTANCE_METHODS_LGPerson __attribute__ ((used, section ("__DATA,__objc_const"))) = {sizeof(_objc_method),10,{{(struct objc_selector *)"say666", "v16@0:8", (void *)_I_LGPerson_say666},{(struct objc_selector *)"ext_sayNB", "v16@0:8", (void *)_I_LGPerson_ext_sayNB},{(struct objc_selector *)"lgName", "@16@0:8", (void *)_I_LGPerson_lgName},{(struct objc_selector *)"setLgName:", "v24@0:8@16", (void *)_I_LGPerson_setLgName_},{(struct objc_selector *)"ext_name", "@16@0:8", (void *)_I_LGPerson_ext_name},{(struct objc_selector *)"setExt_name:", "v24@0:8@16", (void *)_I_LGPerson_setExt_name_},{(struct objc_selector *)"lgName", "@16@0:8", (void *)_I_LGPerson_lgName},{(struct objc_selector *)"setLgName:", "v24@0:8@16", (void *)_I_LGPerson_setLgName_},{(struct objc_selector *)"ext_name", "@16@0:8", (void *)_I_LGPerson_ext_name},{(struct objc_selector *)"setExt_name:", "v24@0:8@16", (void *)_I_LGPerson_setExt_name_}}};
类扩展和分类的明显区别,不会生成额外的结构体存储类扩展的信息、类扩展中的属性和方法,和LGPerson主类的属性和方法融为一体
2.2 objc源码探索
在项目中,创建LGPerson+Ext.h类扩展
#import "LGPerson.h"@interface LGPerson ()@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *ext_name;- (void)ext_say666;@end
在LGPerson中,实现ext_say666方法
#import "LGPerson.h"#import "LGPerson+Ext.h"@implementation LGPerson+ (void)load{NSLog(@"%@ - %s",self , __func__);}- (void)say1{NSLog(@"%@ : %s",self,__func__);}- (void)ext_say666{NSLog(@"%@ : %s",self,__func__);}@end
主类执行流程没有任何变化,在realizeClassWithoutSwift函数中,读取ro方法列表中,同时也包含类扩展中声明的方法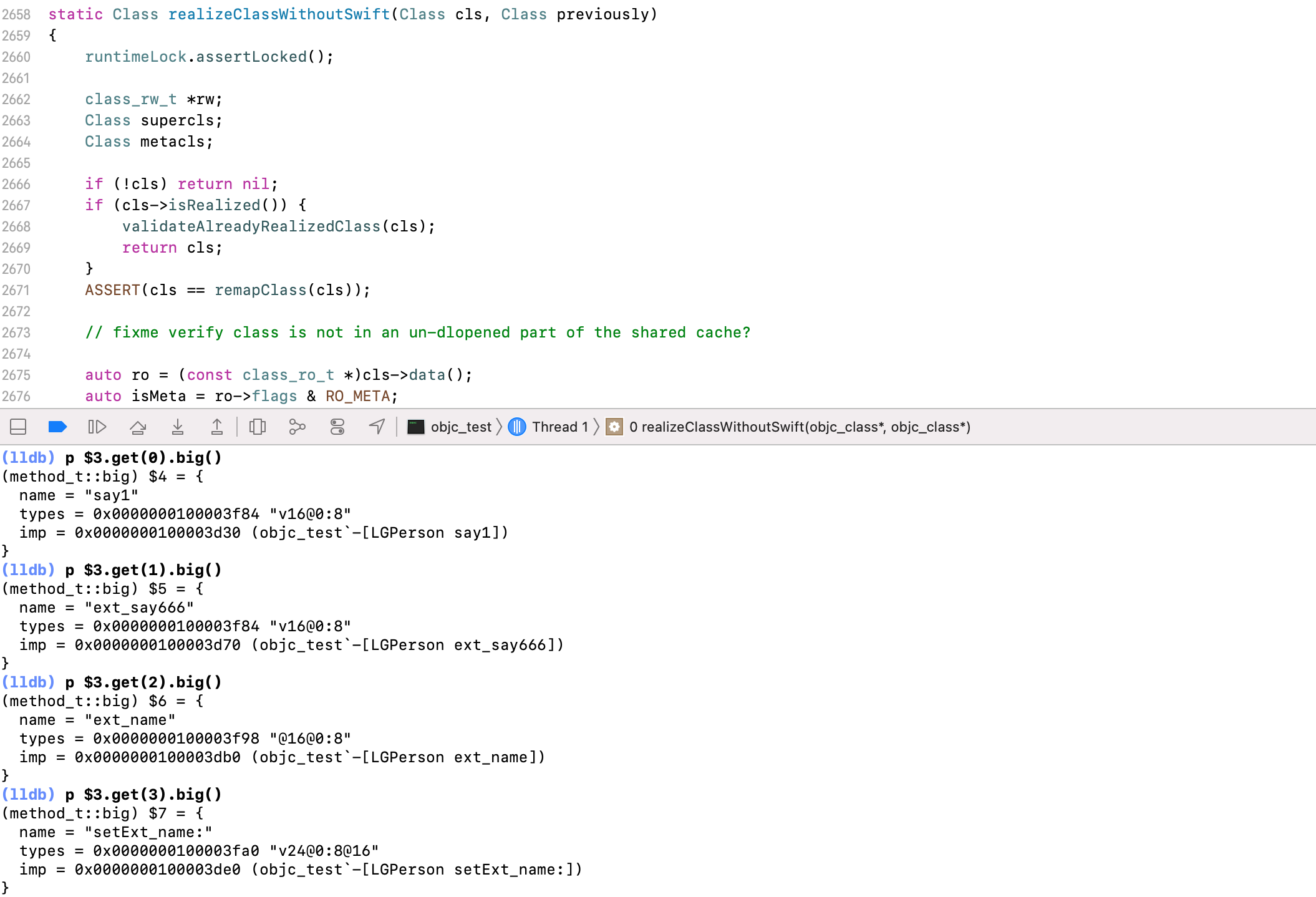
所以类扩展并不会影响主类的加载流程,在编译时,类扩展中的属性和方法和主类融为一体
创建的类扩展只有·h文件,所以只做声明,实现需要依赖于当前的主类
3. 关联对象
分类中,不能直接使用属性的getter/setter方法,只能使用关联对象的方式实现成员变量的效果
关联对象的两个核心方法,值的存储和读取
值的存储
voidobjc_setAssociatedObject(id object, const void *key, id value, objc_AssociationPolicy policy)
object:被关联者key:标识符value:值policy:关联策略
值的读取
void objc_removeAssociatedObjects(id object)
object:被关联者key:标识符
关联策略
typedef OBJC_ENUM(uintptr_t, objc_AssociationPolicy) {OBJC_ASSOCIATION_ASSIGN = 0, /**< Specifies a weak reference to the associated object. */OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC = 1, /**< Specifies a strong reference to the associated object.* The association is not made atomically. */OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY_NONATOMIC = 3, /**< Specifies that the associated object is copied.* The association is not made atomically. */OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN = 01401, /**< Specifies a strong reference to the associated object.* The association is made atomically. */OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY = 01403 /**< Specifies that the associated object is copied.* The association is made atomically. */};
nonatomic、atomic、assign、retain、copy等修饰
3.1 objc_setAssociatedObject & objc_getAssociatedObject
voidobjc_setAssociatedObject(id object, const void *key, id value, objc_AssociationPolicy policy){_object_set_associative_reference(object, key, value, policy);}idobjc_getAssociatedObject(id object, const void *key){return _object_get_associative_reference(object, key);}
objc_setAssociatedObject和objc_getAssociatedObject函数为中间层层代码,目的是对业务层进行隔离。因为底层API根据不同版本会发生变化,但中间层代码是保持不变的,所以开发者不用担心因底层API变化导致程序的修改
3.2 _object_set_associative_reference
void_object_set_associative_reference(id object, const void *key, id value, uintptr_t policy){// This code used to work when nil was passed for object and key. Some code// probably relies on that to not crash. Check and handle it explicitly.// rdar://problem/44094390if (!object && !value) return;if (object->getIsa()->forbidsAssociatedObjects())_objc_fatal("objc_setAssociatedObject called on instance (%p) of class %s which does not allow associated objects", object, object_getClassName(object));//将不同类型的object,保存成统一结构DisguisedPtr<objc_object> disguised{(objc_object *)object};//将关联策略和值,以面向对象的方式进行存储ObjcAssociation association{policy, value};// retain the new value (if any) outside the lock.//根据不同的关联策略进行处理association.acquireValue();bool isFirstAssociation = false;{//调用构造函数,加锁。函数作用域结束AssociationsManager释放,调用析构函数,解锁AssociationsManager manager;//获取唯⼀的全局静态哈希Map//验证方式:get函数中调用_mapStorage.get(),而_mapStorage为static修饰AssociationsHashMap &associations(manager.get());if (value) {//被关联者和ObjectAssociationMap进行关联auto refs_result = associations.try_emplace(disguised, ObjectAssociationMap{});if (refs_result.second) {/* it's the first association we make *///首次关联,打标记isFirstAssociation = true;}/* establish or replace the association *///建立或替换关联auto &refs = refs_result.first->second;auto result = refs.try_emplace(key, std::move(association));if (!result.second) {//如果存在旧值,替换为新值association.swap(result.first->second);}} else {//value不存在,移除关联//通过关联对象寻址Iteratorauto refs_it = associations.find(disguised);if (refs_it != associations.end()) {//获取ObjectAssociationMapauto &refs = refs_it->second;//通过key寻址Iteratorauto it = refs.find(key);if (it != refs.end()) {//替换ObjcAssociation,新值替换旧值association.swap(it->second);//移除旧值refs.erase(it);if (refs.size() == 0) {//如果关联对象关联的Iterator为空,直接移除associations.erase(refs_it);}}}}}// Call setHasAssociatedObjects outside the lock, since this// will call the object's _noteAssociatedObjects method if it// has one, and this may trigger +initialize which might do// arbitrary stuff, including setting more associated objects.//在nonpointerIsa中标记if (isFirstAssociation)object->setHasAssociatedObjects();// release the old value (outside of the lock).//释放旧值association.releaseHeldValue();}
【步骤一】
将不同类型的
object,保存成统一的DisguisedPtr<objc_object>结构将关联策略和值,以面向对象的方式进行存储
ObjcAssociation类中根据不同的关联策略进行处理
【步骤二】
调用构造函数,加锁。函数作用域结束
AssociationsManager释放,调用析构函数,解锁AssociationsHashMap为单例,在内存中只有一份
【步骤三】
如果
value存在,进行关联调用
AssociationsHashMap的try_emplace函数,将object和ObjectAssociationMap关联返回结果
refs_result,如果是首次关联,打标记在
refs_result中找到object关联的Bucket调用
Bucket的try_emplace函数,将key关联ObjcAssociation类如果存在旧值,替换为新值
如果传入的
value不存在,移除关联通过关联对象寻址
Iterator获取
ObjectAssociationMap替换
ObjcAssociation,新值替换旧值移除旧值
如果关联对象关联的
Iterator为空,直接移除
【步骤四】
在
nonpointerIsa中标记,当对象销毁时,关联对象也要跟随销毁释放旧值
3.2.1 AssociationsHashMap单例
class AssociationsManager {using Storage = ExplicitInitDenseMap<DisguisedPtr<objc_object>, ObjectAssociationMap>;static Storage _mapStorage;public:AssociationsManager() { AssociationsManagerLock.lock(); }~AssociationsManager() { AssociationsManagerLock.unlock(); }AssociationsHashMap &get() {return _mapStorage.get();}static void init() {_mapStorage.init();}};
AssociationsManager的get函数,调用_mapStorage的get函数_mapStorage:使用static修饰,全局静态对象AssociationsManager():构造函数,加锁~AssociationsManager():析构函数,解锁- 加锁、解锁操作,保证对象的安全性,防止冲突
验证AssociationsManager和AssociationsHashMap的单例模式,将AssociationsManager中的构造函数和析构函数注释,避免锁递归报错
void test(){AssociationsManager manager1;AssociationsHashMap &associations1(manager1.get());printf("AssociationsManager1:%p\n", &manager1);printf("AssociationsHashMap1:%p\n", &associations1);AssociationsManager manager2;AssociationsHashMap &associations2(manager2.get());printf("AssociationsManager2:%p\n", &manager2);printf("AssociationsHashMap2:%p\n", &associations2);AssociationsManager manager3;AssociationsHashMap &associations3(manager3.get());printf("AssociationsManager3:%p\n", &manager3);printf("AssociationsHashMap3:%p\n", &associations3);}-------------------------AssociationsManager1:0x7ffeefbff258AssociationsHashMap1:0x100370188AssociationsManager2:0x7ffeefbff248AssociationsHashMap2:0x100370188AssociationsManager3:0x7ffeefbff238AssociationsHashMap3:0x100370188
AssociationsManager不是单例对象,每次创建的内存地址都不一样AssociationsHashMap为单例对象,内存地址一致
3.2.2 AssociationsManager的初始化
AssociationsManager的init函数使用static修饰,表示类对象函数,找到它的初始化时机
_objc_associations_init函数
void_objc_associations_init(){AssociationsManager::init();}
arr_init函数
void arr_init(void){AutoreleasePoolPage::init();SideTablesMap.init();_objc_associations_init();}
map_images_nolock函数
voidmap_images_nolock(unsigned mhCount, const char * const mhPaths[],const struct mach_header * const mhdrs[]){...if (firstTime) {sel_init(selrefCount);arr_init();...}...}
AssociationsManager初始化流程:map_images→map_images_nolock→arr_init→_objc_associations_init
也就是在此时,系统创建了AssociationsHashMap关联对象表。和它一起被创建的全局系统表,还有AutoreleasePoolPage自动释放池,以及SideTablesMap散列表
SideTablesMap散列表中包含两张子表,分别是RefcountMap引用计数表,还有weak_table_t弱引用表
3.2.3 AssociationsHashMap结构
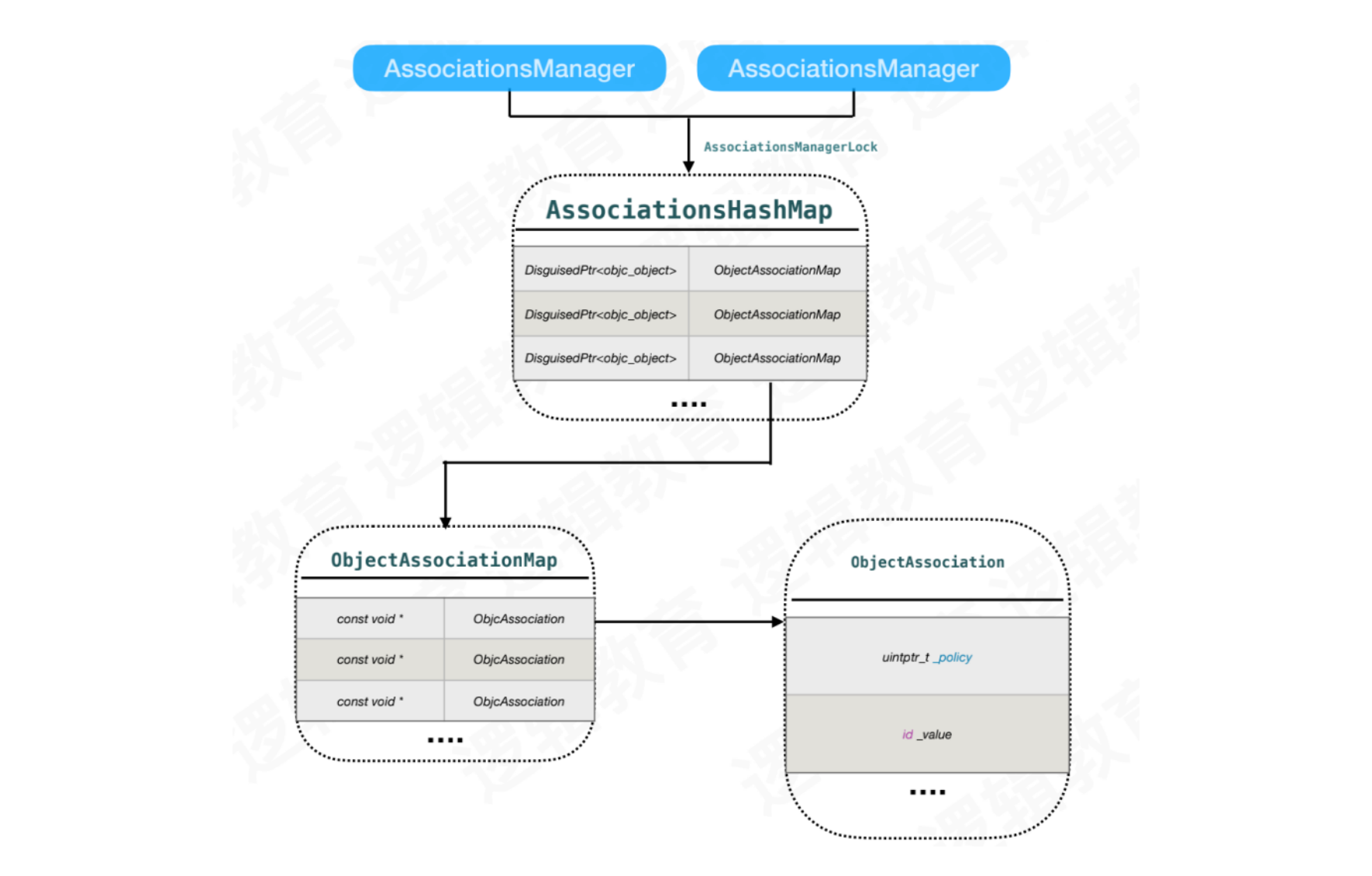
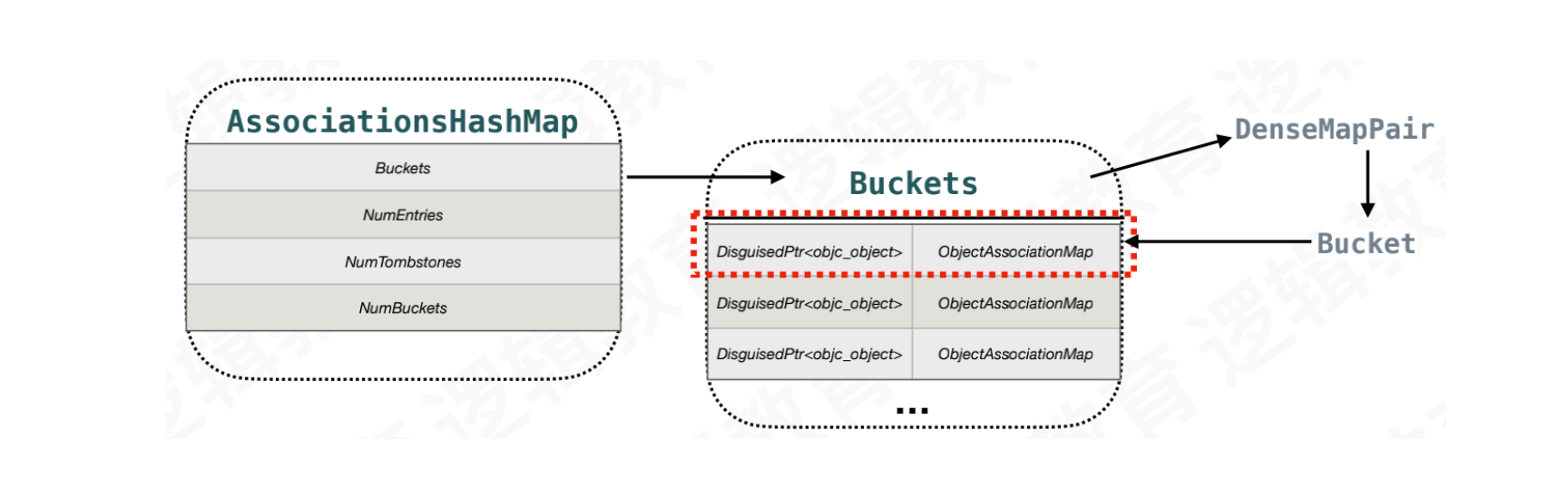
AssociationsHashMap为双层HashMap结构
typedef DenseMap<DisguisedPtr<objc_object>, ObjectAssociationMap> AssociationsHashMap;
DisguisedPtr<objc_object>为被关联者,它所对应的值还是一张HashMap
ObjectAssociationMap为HashMap结构
typedef DenseMap<const void *, ObjcAssociation> ObjectAssociationMap;
const void *为标识号,它所对应的值为ObjcAssociation类
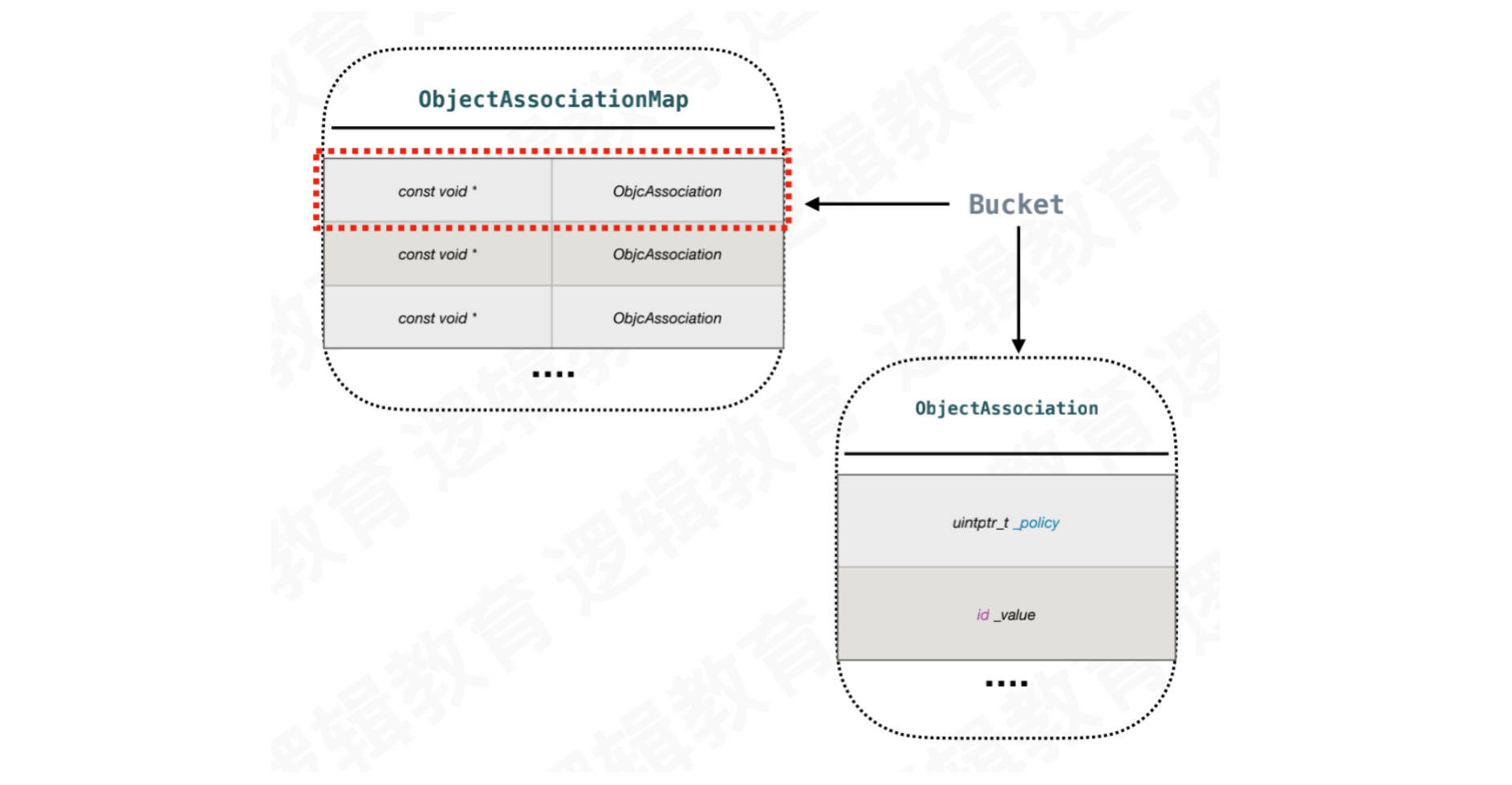
ObjcAssociation为class结构
class ObjcAssociation {uintptr_t _policy;id _value;...}
_policy:关联策略_value:值
3.2.4 try_emplace函数
template <typename... Ts>std::pair<iterator, bool> try_emplace(const KeyT &Key, Ts &&... Args) {BucketT *TheBucket;//查看Bucket在map中是否存在,存在将Bucket返回if (LookupBucketFor(Key, TheBucket))return std::make_pair(makeIterator(TheBucket, getBucketsEnd(), true),false); // Already in map.// Otherwise, insert the new element.//不存在,插入Bucket并返回TheBucket = InsertIntoBucket(TheBucket, Key, std::forward<Ts>(Args)...);return std::make_pair(makeIterator(TheBucket, getBucketsEnd(), true),true);}
- 通过
std::make_pair生成相应的键值对 LookupBucketFor函数,查看Bucket在map中是否存在,存在将Bucket返回- 不存在,调用
InsertIntoBucket函数,插入Bucket并返回
3.2.5 LookupBucketFor函数
- 两个函数的区别在于
Bucket参数的const修饰 - 作用:为
value查找适当的Bucket,并将其返回
LookupBucketFor函数一,Bucket使用const修饰
template<typename LookupKeyT>bool LookupBucketFor(const LookupKeyT &Val,const BucketT *&FoundBucket) const {const BucketT *BucketsPtr = getBuckets();const unsigned NumBuckets = getNumBuckets();if (NumBuckets == 0) {FoundBucket = nullptr;return false;}// FoundTombstone - Keep track of whether we find a tombstone while probing.const BucketT *FoundTombstone = nullptr;const KeyT EmptyKey = getEmptyKey();const KeyT TombstoneKey = getTombstoneKey();assert(!KeyInfoT::isEqual(Val, EmptyKey) &&!KeyInfoT::isEqual(Val, TombstoneKey) &&"Empty/Tombstone value shouldn't be inserted into map!");//哈希函数,计算下标unsigned BucketNo = getHashValue(Val) & (NumBuckets-1);unsigned ProbeAmt = 1;while (true) {//内存平移,获取Bucketconst BucketT *ThisBucket = BucketsPtr + BucketNo;// Found Val's bucket? If so, return it.//找到Bucket,直接返回if (LLVM_LIKELY(KeyInfoT::isEqual(Val, ThisBucket->getFirst()))) {FoundBucket = ThisBucket;return true;}// If we found an empty bucket, the key doesn't exist in the set.// Insert it and return the default value.//Bucket为空,返回默认值if (LLVM_LIKELY(KeyInfoT::isEqual(ThisBucket->getFirst(), EmptyKey))) {// If we've already seen a tombstone while probing, fill it in instead// of the empty bucket we eventually probed to.FoundBucket = FoundTombstone ? FoundTombstone : ThisBucket;return false;}// If this is a tombstone, remember it. If Val ends up not in the map, we// prefer to return it than something that would require more probing.// Ditto for zero values.//哈希冲突,再次哈希if (KeyInfoT::isEqual(ThisBucket->getFirst(), TombstoneKey) &&!FoundTombstone)FoundTombstone = ThisBucket; // Remember the first tombstone found.if (ValueInfoT::isPurgeable(ThisBucket->getSecond()) && !FoundTombstone)FoundTombstone = ThisBucket;// Otherwise, it's a hash collision or a tombstone, continue quadratic// probing.if (ProbeAmt > NumBuckets) {FatalCorruptHashTables(BucketsPtr, NumBuckets);}BucketNo += ProbeAmt++;BucketNo &= (NumBuckets-1);}}
- 哈希函数,计算下标
- 内存平移,获取
Bucket - 找到
Bucket,直接返回 Bucket为空,返回默认值- 哈希冲突,再次哈希
LookupBucketFor函数二,Bucket未使用const修饰
template <typename LookupKeyT>bool LookupBucketFor(const LookupKeyT &Val, BucketT *&FoundBucket) {//创建空Bucketconst BucketT *ConstFoundBucket;//调用LookupBucketFor函数一bool Result = const_cast<const DenseMapBase *>(this)->LookupBucketFor(Val, ConstFoundBucket);//将ConstFoundBucket赋值FoundBucketFoundBucket = const_cast<BucketT *>(ConstFoundBucket);//返回结果,是否查找到Bucketreturn Result;}
- 创建空
Bucket - 调用
LookupBucketFor函数一 - 将
ConstFoundBucket赋值FoundBucket - 返回结果,是否查找到
Bucket
3.2.6 InsertIntoBucket函数
template <typename KeyArg, typename... ValueArgs>BucketT *InsertIntoBucket(BucketT *TheBucket, KeyArg &&Key,ValueArgs &&... Values) {TheBucket = InsertIntoBucketImpl(Key, Key, TheBucket);TheBucket->getFirst() = std::forward<KeyArg>(Key);::new (&TheBucket->getSecond()) ValueT(std::forward<ValueArgs>(Values)...);return TheBucket;}
- 调用
InsertIntoBucketImpl函数
InsertIntoBucketImpl函数
template <typename LookupKeyT>BucketT *InsertIntoBucketImpl(const KeyT &Key, const LookupKeyT &Lookup,BucketT *TheBucket) {// If the load of the hash table is more than 3/4, or if fewer than 1/8 of// the buckets are empty (meaning that many are filled with tombstones),// grow the table.//// The later case is tricky. For example, if we had one empty bucket with// tons of tombstones, failing lookups (e.g. for insertion) would have to// probe almost the entire table until it found the empty bucket. If the// table completely filled with tombstones, no lookup would ever succeed,// causing infinite loops in lookup.unsigned NewNumEntries = getNumEntries() + 1;unsigned NumBuckets = getNumBuckets();if (LLVM_UNLIKELY(NewNumEntries * 4 >= NumBuckets * 3)) {this->grow(NumBuckets * 2);LookupBucketFor(Lookup, TheBucket);NumBuckets = getNumBuckets();} else if (LLVM_UNLIKELY(NumBuckets-(NewNumEntries+getNumTombstones()) <=NumBuckets/8)) {this->grow(NumBuckets);LookupBucketFor(Lookup, TheBucket);}ASSERT(TheBucket);// Only update the state after we've grown our bucket space appropriately// so that when growing buckets we have self-consistent entry count.// If we are writing over a tombstone or zero value, remember this.if (KeyInfoT::isEqual(TheBucket->getFirst(), getEmptyKey())) {// Replacing an empty bucket.incrementNumEntries();} else if (KeyInfoT::isEqual(TheBucket->getFirst(), getTombstoneKey())) {// Replacing a tombstone.incrementNumEntries();decrementNumTombstones();} else {// we should be purging a zero. No accounting changes.ASSERT(ValueInfoT::isPurgeable(TheBucket->getSecond()));TheBucket->getSecond().~ValueT();}return TheBucket;}
- 如果哈希表的负载大于
3/4,两倍扩容
3.3 _object_get_associative_reference
id_object_get_associative_reference(id object, const void *key){ObjcAssociation association{};{//调用构造函数,加锁。函数作用域结束AssociationsManager释放,调用析构函数,解锁AssociationsManager manager;//获取唯⼀的全局静态哈希MapAssociationsHashMap &associations(manager.get());//通过关联对象寻址IteratorAssociationsHashMap::iterator i = associations.find((objc_object *)object);if (i != associations.end()) {//获取ObjectAssociationMapObjectAssociationMap &refs = i->second;//通过key寻址IteratorObjectAssociationMap::iterator j = refs.find(key);if (j != refs.end()) {//获取ObjcAssociationassociation = j->second;//保留返回值association.retainReturnedValue();}}}//生成自动返回值return association.autoreleaseReturnedValue();}
【第一步】
调用构造函数,加锁。函数作用域结束
AssociationsManager释放,调用析构函数,解锁AssociationsHashMap为单例,在内存中只有一份
【第二步】
通过关联对象寻址
Iterator获取
ObjectAssociationMap
【第三步】
通过
key寻址Iterator获取
ObjcAssociation保留返回值
【第四步】
- 生成自动返回值
3.4 关联对象的销毁
关联对象的销毁,依赖于被关联对象的生命周期。当被关联对象被销毁时,它的关联对象会自动销毁
对象销毁流程:
C++函数释放 :objc_cxxDestruct- 关联对象销毁:
_object_remove_assocations - 弱引用销毁:
weak_clear_no_lock - 清空引用计数:
table.refcnts.erase - 销毁对象:
free
3.4.1 dealloc
- (void)dealloc {_objc_rootDealloc(self);}
3.4.2 _objc_rootDealloc
void_objc_rootDealloc(id obj){ASSERT(obj);obj->rootDealloc();}
3.4.3 rootDealloc
inline voidobjc_object::rootDealloc(){if (isTaggedPointer()) return; // fixme necessary?if (fastpath(isa.nonpointer &&!isa.weakly_referenced &&!isa.has_assoc &&#if ISA_HAS_CXX_DTOR_BIT!isa.has_cxx_dtor &&#else!isa.getClass(false)->hasCxxDtor() &&#endif!isa.has_sidetable_rc)){assert(!sidetable_present());free(this);}else {object_dispose((id)this);}}
- 判断
C++析构函数的调用、关联对象的销毁、弱引用的销毁、引用计数是否清空,全部符合条件,调用free函数销毁对象 - 否则,调用
object_dispose函数,继续销毁流程
3.4.4 object_dispose
idobject_dispose(id obj){if (!obj) return nil;objc_destructInstance(obj);free(obj);return nil;}
3.4.5 objc_destructInstance
void *objc_destructInstance(id obj){if (obj) {// Read all of the flags at once for performance.bool cxx = obj->hasCxxDtor();bool assoc = obj->hasAssociatedObjects();// This order is important.if (cxx) object_cxxDestruct(obj);if (assoc) _object_remove_assocations(obj, /*deallocating*/true);obj->clearDeallocating();}return obj;}
object_cxxDestruct:调用C++的析构函数_object_remove_assocations:关联对象销毁clearDeallocating,弱引用销毁、清空引用计数
3.4.6 _object_remove_assocations
void_object_remove_assocations(id object, bool deallocating){ObjectAssociationMap refs{};{//调用构造函数,加锁。函数作用域结束AssociationsManager释放,调用析构函数,解锁AssociationsManager manager;//获取唯⼀的全局静态哈希MapAssociationsHashMap &associations(manager.get());//通过关联对象寻址IteratorAssociationsHashMap::iterator i = associations.find((objc_object *)object);if (i != associations.end()) {//替换refs.swap(i->second);// If we are not deallocating, then SYSTEM_OBJECT associations are preserved.bool didReInsert = false;if (!deallocating) {for (auto &ref: refs) {if (ref.second.policy() & OBJC_ASSOCIATION_SYSTEM_OBJECT) {i->second.insert(ref);didReInsert = true;}}}//移除Iteratorif (!didReInsert)associations.erase(i);}}// Associations to be released after the normal ones.SmallVector<ObjcAssociation *, 4> laterRefs;// release everything (outside of the lock).for (auto &i: refs) {if (i.second.policy() & OBJC_ASSOCIATION_SYSTEM_OBJECT) {// If we are not deallocating, then RELEASE_LATER associations don't get released.if (deallocating)laterRefs.append(&i.second);} else {i.second.releaseHeldValue();}}//循环销毁for (auto *later: laterRefs) {later->releaseHeldValue();}}
关联对象销毁流程:dealloc→_objc_rootDealloc→rootDealloc→object_dispose→objc_destructInstance→_object_remove_assocations
3.4.7 clearDeallocating
inline voidobjc_object::clearDeallocating(){if (slowpath(!isa.nonpointer)) {// Slow path for raw pointer isa.sidetable_clearDeallocating();}else if (slowpath(isa.weakly_referenced || isa.has_sidetable_rc)) {// Slow path for non-pointer isa with weak refs and/or side table data.clearDeallocating_slow();}assert(!sidetable_present());}
3.4.8 clearDeallocating_slow
NEVER_INLINE voidobjc_object::clearDeallocating_slow(){ASSERT(isa.nonpointer && (isa.weakly_referenced || isa.has_sidetable_rc));SideTable& table = SideTables()[this];table.lock();if (isa.weakly_referenced) {weak_clear_no_lock(&table.weak_table, (id)this);}if (isa.has_sidetable_rc) {table.refcnts.erase(this);}table.unlock();}
weak_clear_no_lock:弱引用销毁table.refcnts.erase:清空引用计数
总结
类扩展 VS 分类:
- 类扩展(
Extension)- 特殊的分类,也称作匿名分类
- 可以给类添加成员属性,但是为私有变量
- 可以给类添加方法,也是私有方法
- 分类(
Category)- 专门用来给类添加新的方法
- 不能给类添加成员属性,添加后无法读取(可通过
Runtime给分类添加属性) - 分类中使用
@property定义变量,只会生成变量的getter/setter方法的声明,不能生成方法的实现和下划线开头的成员变量
类扩展的分析:
- 所以类扩展并不会影响主类的加载流程,在编译时,类扩展中的属性和方法和主类融为一体
- 创建的类扩展只有
·h文件,所以只做声明,实现需要依赖于当前的主类
关联对象:
- 分类中,不能直接使用属性的
getter/setter方法,只能使用关联对象的方式实现成员变量的效果 objc_setAssociatedObjectobject:被关联者key:标识符value:值policy:关联策略
objc_removeAssociatedObjectsobject:被关联者key:标识符
- 关联策略:
nonatomic、atomic、assign、retain、copy等修饰
objc_setAssociatedObject & objc_getAssociatedObject:
- 函数为中间层层代码,目的是对业务层进行隔离。因为底层
API根据不同版本会发生变化,但中间层代码是保持不变的,所以开发者不用担心因底层API变化导致程序的修改
_object_set_associative_reference:
【步骤一】
- 将不同类型的
object,保存成统一的DisguisedPtr<objc_object>结构 - 将关联策略和值,以面向对象的方式进行存储
ObjcAssociation类中 - 根据不同的关联策略进行处理
【步骤二】
- 调用构造函数,加锁。函数作用域结束
AssociationsManager释放,调用析构函数,解锁 AssociationsHashMap为单例,在内存中只有一份
【步骤三】
- 如果
value存在,进行关联- 调用
AssociationsHashMap的try_emplace函数,将object和ObjectAssociationMap关联 - 返回结果
refs_result,如果是首次关联,打标记 - 在
refs_result中找到object关联的Bucket - 调用
Bucket的try_emplace函数,将key关联ObjcAssociation类 - 如果存在旧值,替换为新值
- 调用
- 如果传入的
value不存在,移除关联- 通过关联对象寻址
Iterator - 获取
ObjectAssociationMap - 替换
ObjcAssociation,新值替换旧值 - 移除旧值
- 如果关联对象关联的
Iterator为空,直接移除
- 通过关联对象寻址
【步骤四】
- 在
nonpointerIsa中标记,当对象销毁时,关联对象也要跟随销毁 - 释放旧值
_object_get_associative_reference:
【第一步】
- 调用构造函数,加锁。函数作用域结束
AssociationsManager释放,调用析构函数,解锁 AssociationsHashMap为单例,在内存中只有一份
【第二步】
- 通过关联对象寻址
Iterator - 获取
ObjectAssociationMap
【第三步】
- 通过
key寻址Iterator - 获取
ObjcAssociation - 保留返回值
【第四步】
- 生成自动返回值
关联对象的销毁:
- 关联对象的销毁,依赖于被关联对象的生命周期。当被关联对象被销毁时,它的关联对象会自动销毁
- 对象销毁流程:
C++函数释放 :objc_cxxDestruct- 关联对象销毁:
_object_remove_assocations - 弱引用销毁:
weak_clear_no_lock - 清空引用计数:
table.refcnts.erase - 销毁对象:
free
- 销毁流程:
dealloc→_objc_rootDealloc→rootDealloc→object_dispose→objc_destructInstance→_object_remove_assocations
AssociationsHashMap:
- 单例,使用
static修饰,全局静态对象 - 双层
HashMap结构
AssociationsManager:
- 可创建多份,并为唯一
AssociationsManager():构造函数,加锁~AssociationsManager():析构函数,解锁- 加锁、解锁操作,保证对象的安全性,防止冲突
AssociationsManager的初始化:
- 初始化流程:
map_images→map_images_nolock→arr_init→_objc_associations_init - 在
map_images时,系统创建AssociationsHashMap关联对象表。和它一起被创建的全局系统表,还有AutoreleasePoolPage自动释放池,以及SideTablesMap散列表 SideTablesMap散列表中包含两张子表,分别是RefcountMap引用计数表,还有weak_table_t弱引用表

