我们使用两个栈,就能对四则运算表达式进行求值:一个栈存数据,一个栈存运算符。
顶部求值
首先考虑一个最简单的例子,即表达式3 + 4。将数字压入 number stack,将运算符压入 operator stack。然后弹出两个数字和运算符,用运算符结合两个数字,并将结果压入栈中。
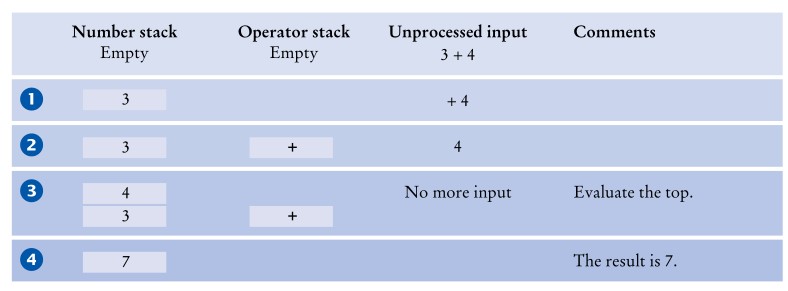
此操作是该算法的基础:顶部求值。
优先级
在代数运算中,每个运算符都有优先级。在四则运算下,我们先* /,后+ -。
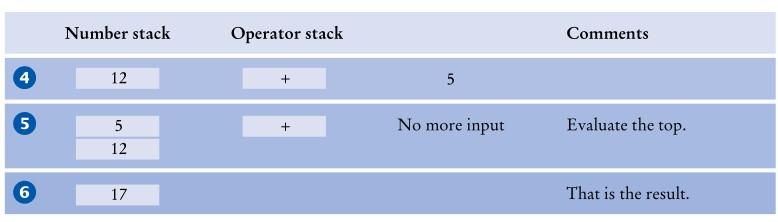
考虑表达式3 * 4 + 5,如下是它的处理步骤:

因为*比+优先级高,故对其顶部求值:
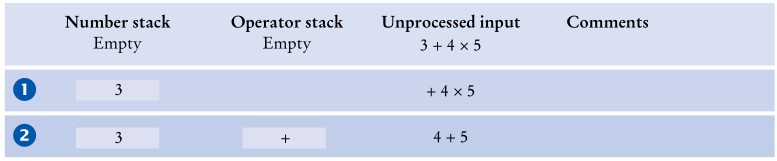
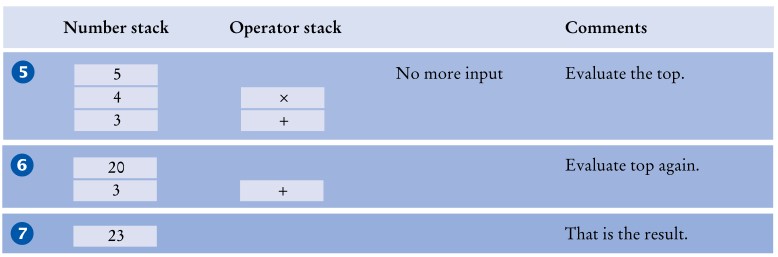
对于表达式3 + 4 * 5我们的操作过程如下:

括号
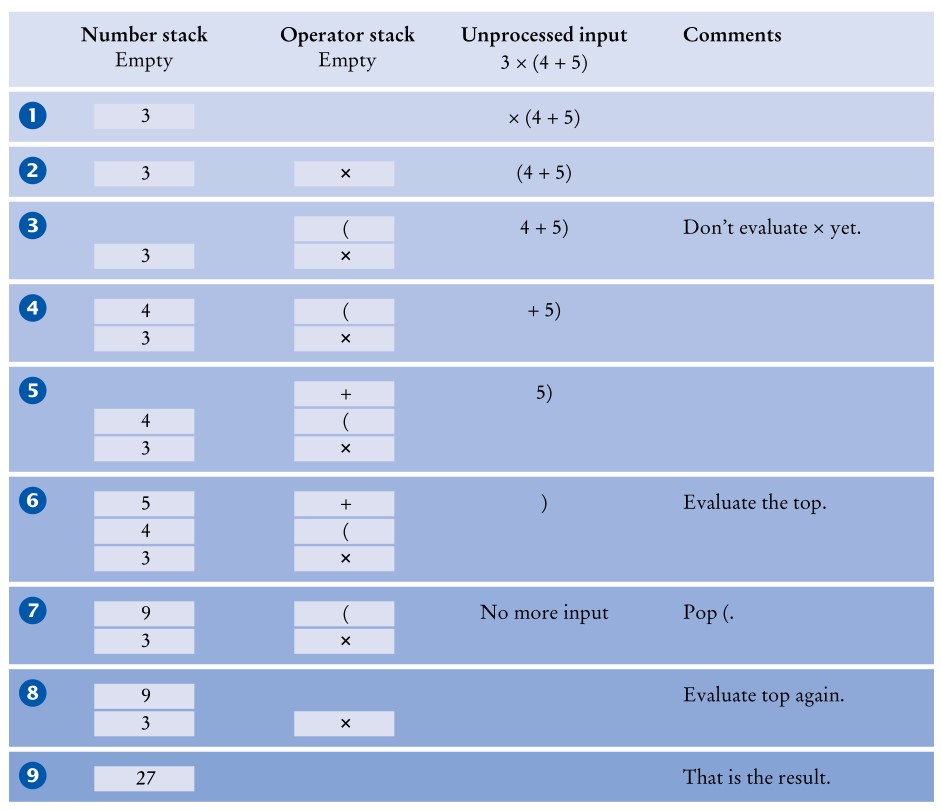
现在我们的表达式加入了括号:3 * (4 + 5)。首先一个左括号(被压入 operator stack,接着运算符+也被压入。当遇到右括号)时,我们就可以顶部求值了。整个过程如下:
算法描述
if you read a number:Push it on the number stack;else if you read a '(':Push it on the operator stack;else if you read an operator 'op':while precedence( top of operator stack ) >= precedence(op):Evaluate the top;Push 'op' on the operator stack;else if you read a ')':while the top of the stack if not a '(':Evaluate the top;Pop the '(';else if there is no more input:while the operator stack is not empty:Evaluate the top;
Cpp 代码实现
#include <iostream>#include <sstream>#include <stack>#include <string>#include <vector>static void eval_top(std::stack<double> &num_stack,std::stack<char> &op_stack) {double arg2 = num_stack.top();num_stack.pop();double arg1 = num_stack.top();num_stack.pop();char op = op_stack.top();op_stack.pop();switch (op) {case '+':num_stack.push(arg1 + arg2);return;case '-':num_stack.push(arg1 - arg2);return;case '*':num_stack.push(arg1 * arg2);return;case '/':if (arg2 == 0) {std::fprintf(stderr, "divisior can not be zero!\n");std::exit(1);}num_stack.push(arg1 / arg2);return;}std::fprintf(stderr, "Unknown character ...\n");}static std::vector<std::string> split_string(std::string &input,char delimeter) {std::istringstream in(input); // turn string into input streamstd::string tmp;std::vector<std::string> symbol_list;while (std::getline(in, tmp, ' ')) {symbol_list.push_back(tmp);}return symbol_list;}double eval_expression(std::string &input) {if (input.empty()) {std::fprintf(stderr, "EMPTY INPUT!\n");return 0;}// Split symbols by white spacestd::vector<std::string> symbol_list = split_string(input, ' ');std::stack<double> number_stack;std::stack<char> operator_stack;for (auto i : symbol_list) {char ch = *(i.c_str());if (ch == '(') {operator_stack.push(ch);} else if (ch == '+' || ch == '-' || ch == '*' || ch == '/') {if (operator_stack.empty()) {operator_stack.push(ch);continue;}// while precedence(top of operator stack) >= precedence(ch)// We eval_topchar top_op = operator_stack.top();if (((ch == '+' || ch == '-') &&(top_op == '*' || top_op == '/')) ||((ch == '*' || ch == '/') &&(top_op == '*' || top_op == '/')) ||((ch == '+' || ch == '-') &&(top_op == '+' || top_op == '-'))) {eval_top(number_stack, operator_stack);}operator_stack.push(ch);} else if (ch == ')') {while (operator_stack.top() != '(') {eval_top(number_stack, operator_stack);}operator_stack.pop();} else {if (ch == ' ') {continue;}number_stack.push(std::stof(i));}}while (!operator_stack.empty()) {eval_top(number_stack, operator_stack);}return number_stack.top();}int main() {std::string input;input = "3 + 4"; // output: 7std::cout << eval_expression(input) << std::endl;input = "3 * 4 + 5"; // output: 17std::cout << eval_expression(input) << std::endl;input = "3 + 4 * 5"; // output: 23std::cout << eval_expression(input) << std::endl;input = "3 * ( 4 + 5 )"; // output: 27std::cout << eval_expression(input) << std::endl;input = "9 + ( 3 - 1 ) * 3 + 10 / 2"; // output: 20std::cout << eval_expression(input) << std::endl;input = "2 / 0"; // divisior can not be zero!std::cout << eval_expression(input) << std::endl;return 0;}

