相比一维数据的自己跟自己过不去,二维数据,就是自己跟其他数据过不去。
这里我们先介绍的是,二个数据间的差异。
差异检验
两组比较
- 正态分布数据, t 检验

默认下使用的是Welch Two Sample t-test,不需要满足方差齐性:
> t.test(a2,a3, var.equal=T)Two Sample t-testdata: a2 and a3t = 3.746, df = 198, p-value = 0.0002356alternative hypothesis: true difference in means is not equal to 095 percent confidence interval:1.592921 5.134473sample estimates:mean of x mean of y34.64285 31.27916
可以修改。
还可以通过指定信息,获得可能出现二型错误(假阴性)的可能:
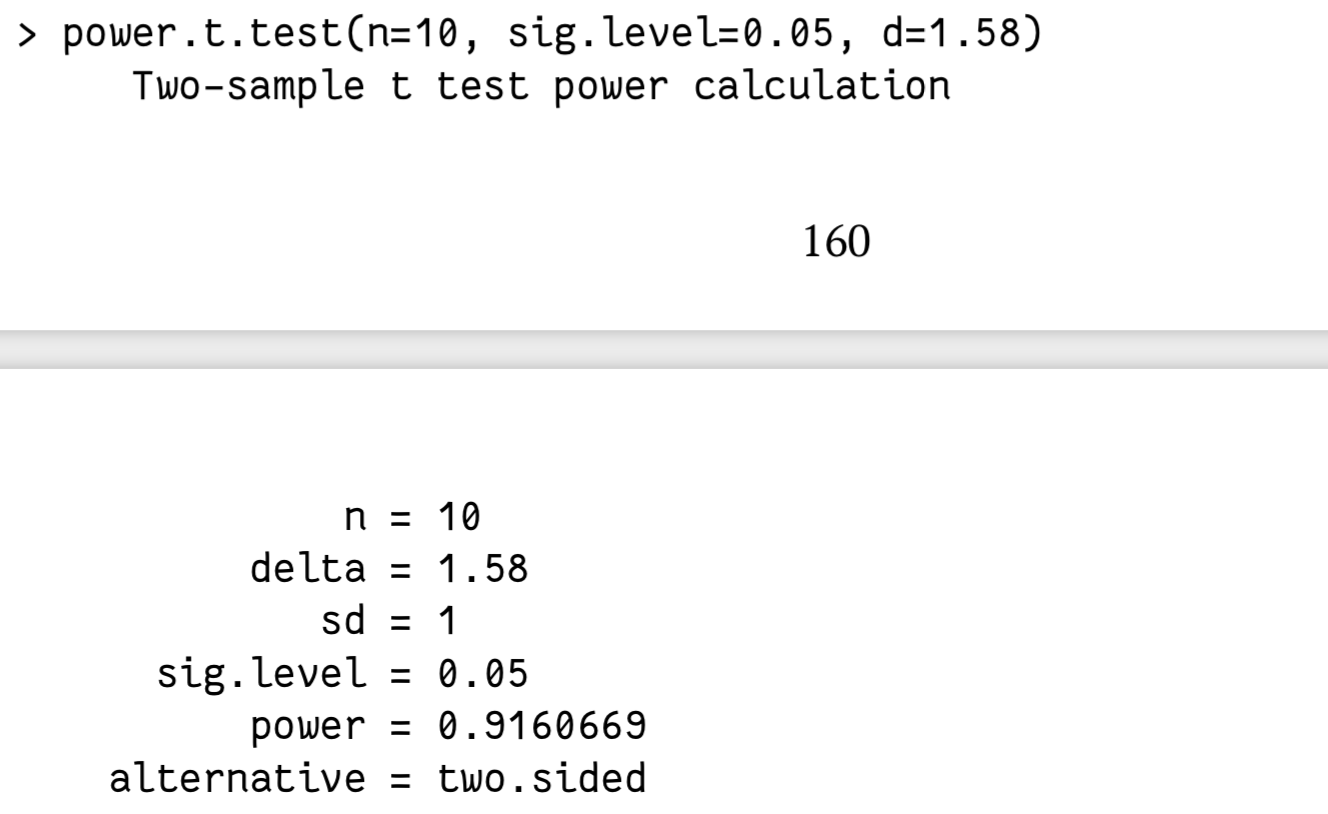
多组比较
单纯的通过多组在两两比较来实现多组比较,有以下坏处:
- 容易增大错误发生的可能性
- 繁琐且麻烦
参数检验、方差齐性
- anova(ANalysis Of VAriance)
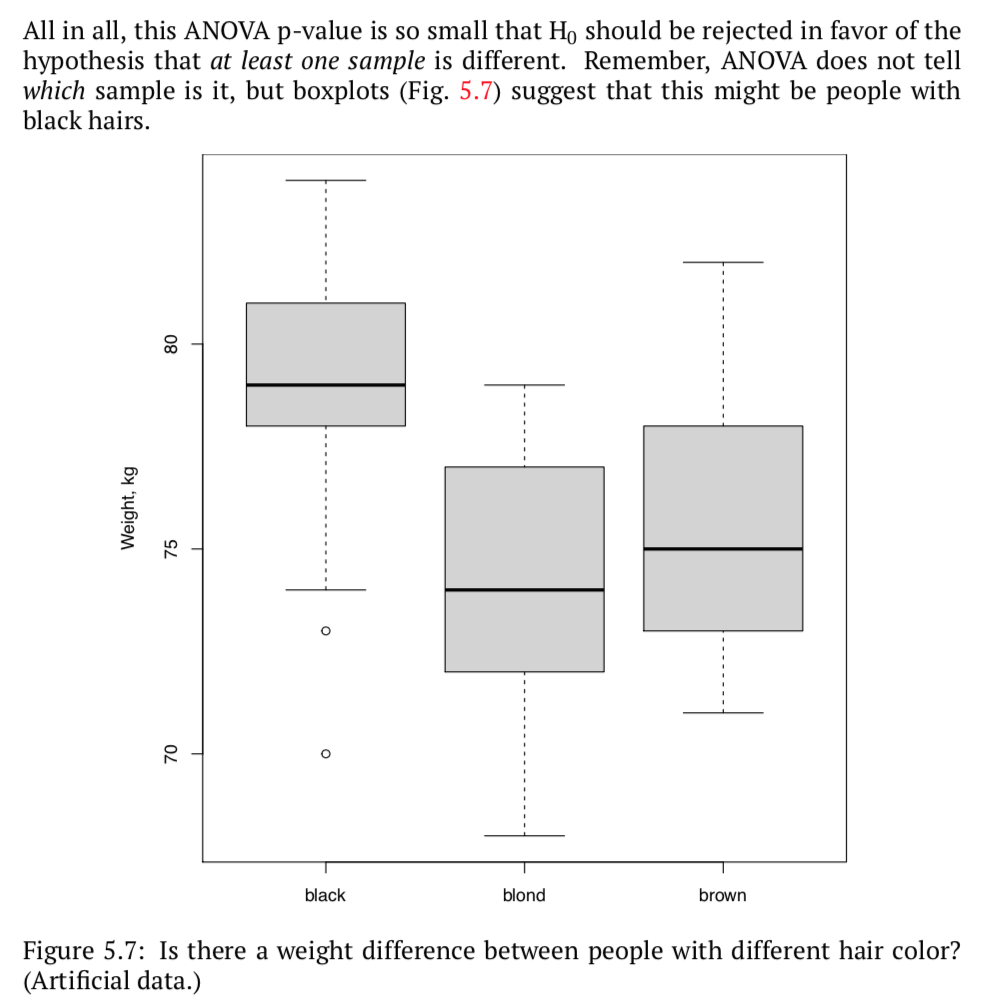
我们并不能直接通过anova 获得组别的差异信息:

但可以通过anova 得到结果后,再通过其他检测进一步验证(比如箱线图)。
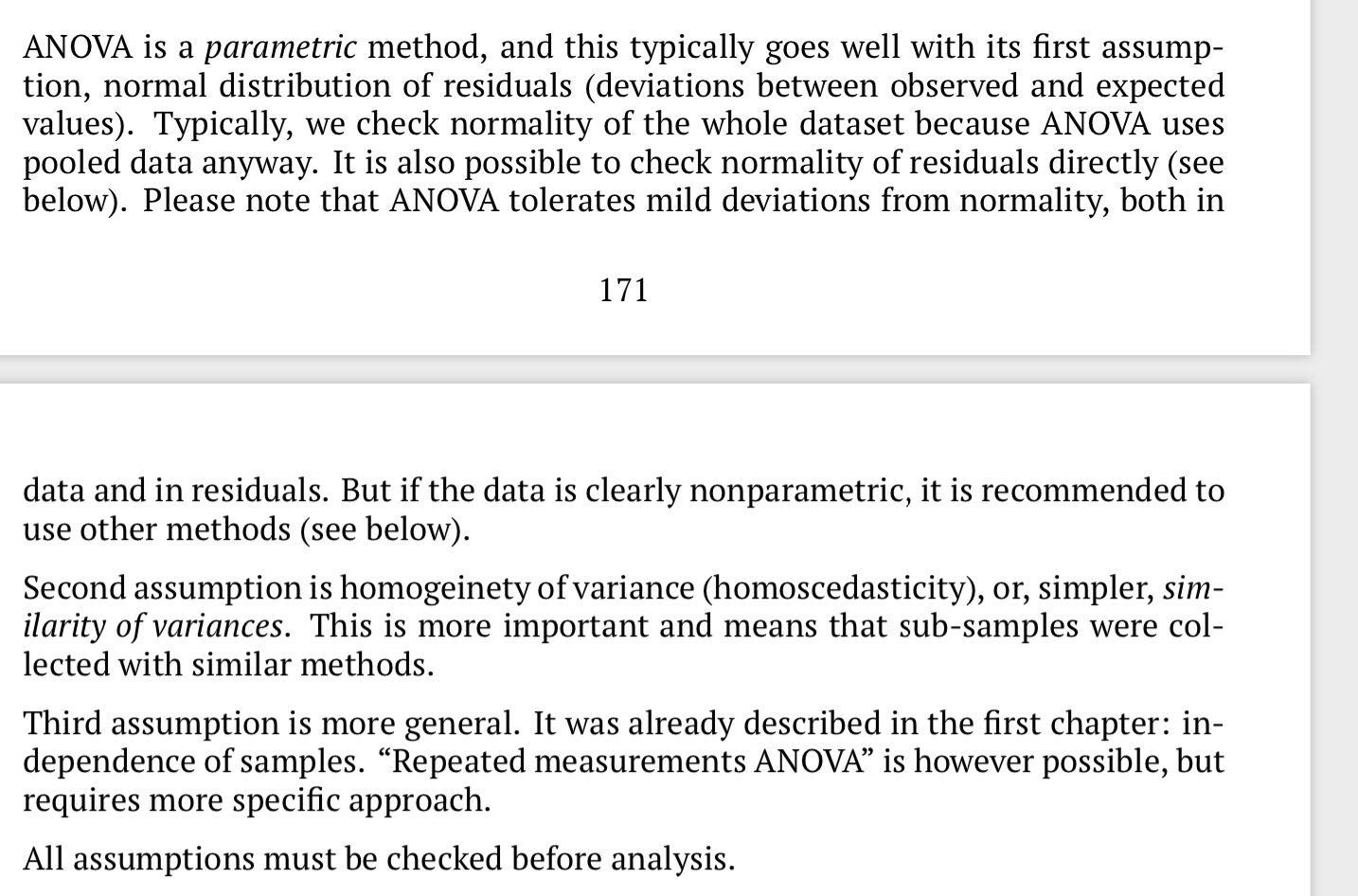
三个前提:
下面几个方法可以验证anova 中显著差异的分组:
- 配对t 检验
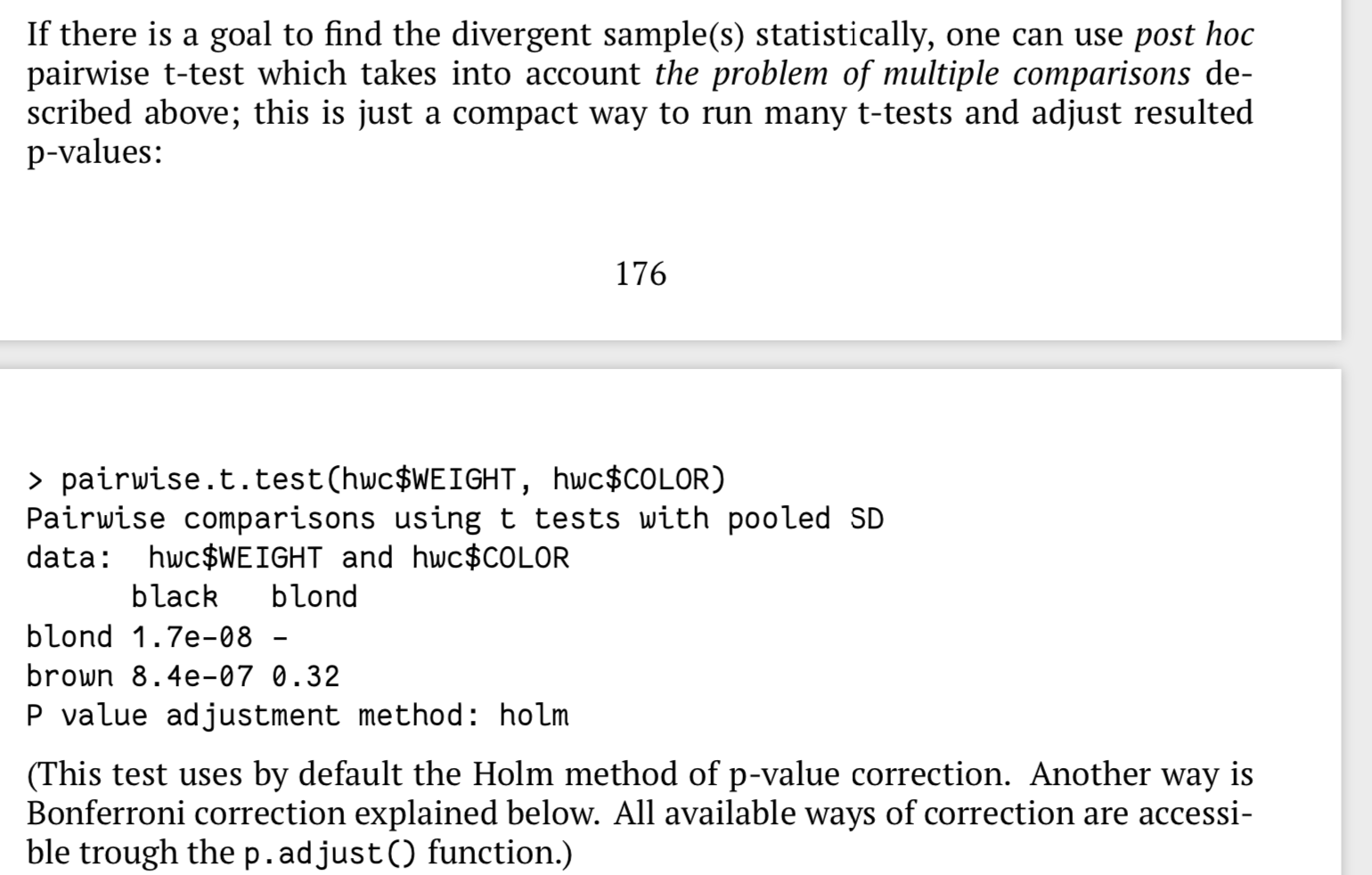
- tukey HSD test

- post hoc test

参数、方差非齐性

非参数方法
- kruskal.test

验证方法也有所不同,使用非参数的配对秩和检验:

dunn.test:

方差齐性检验
- F 检验

> var.test(a$a1, a$a2)F test to compare two variancesdata: a$a1 and a$a2F = 0.21446, num df = 19, denom df = 19, p-value = 0.00153alternative hypothesis: true ratio of variances is not equal to 195 percent confidence interval:0.08488522 0.54181849sample estimates:ratio of variances0.2144583
- sign test
- 多组比较bartlett.test:
> bartlett.test(bb~aa, data=a1)Bartlett test of homogeneity of variancesdata: bb by aaBartlett's K-squared = 0.11603, df = 2, p-value = 0.9436
- 非参数方法Fligner-Killeen test:

效应估计
分别对应参数模型与非参数模型:
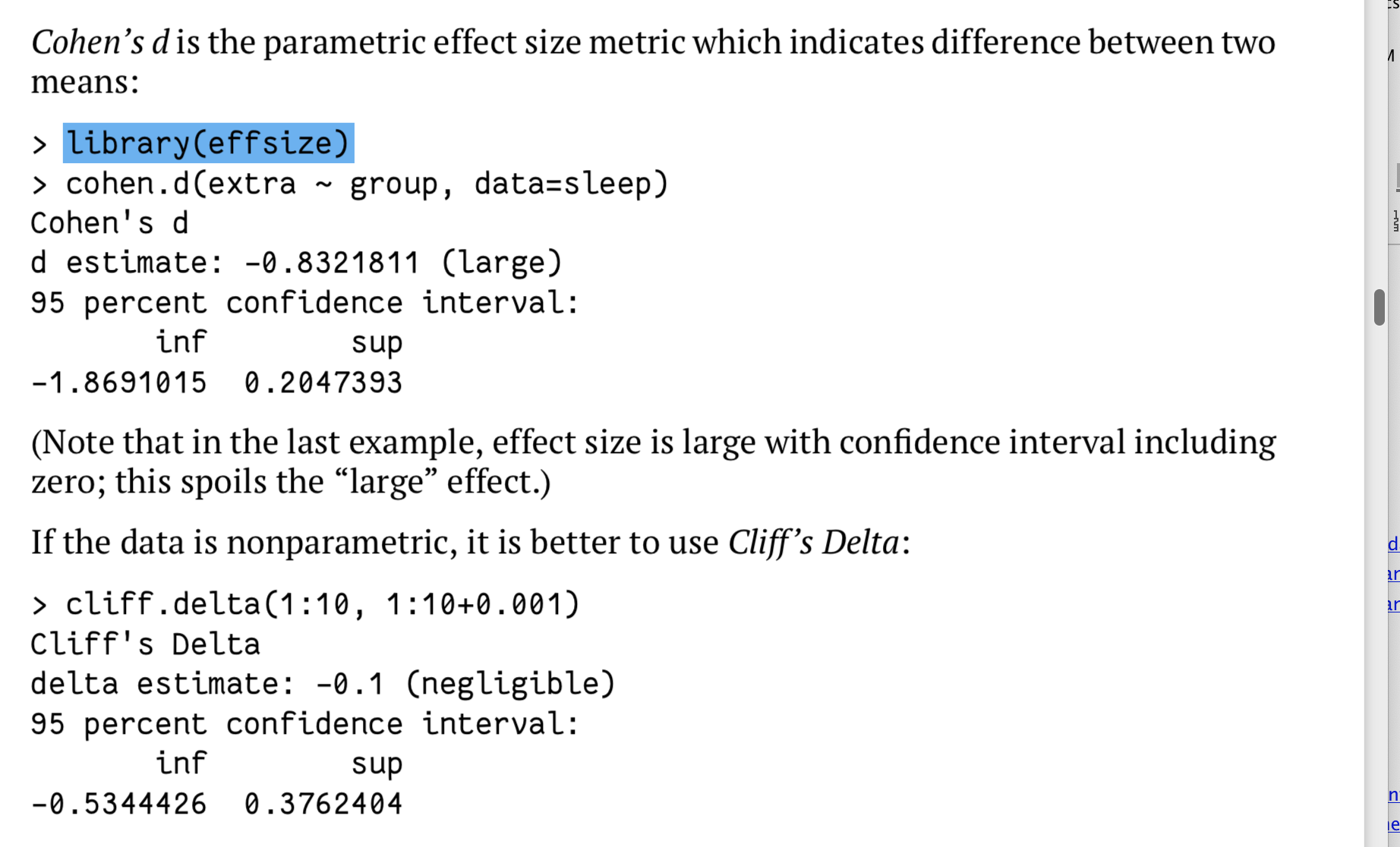
此外,还有计算差异系数的(有点类似变异系数的计算):

此外,还有anova 的估计方法:

总结

步骤:
- 数据结构和类型是否规范、是否有缺失值、是否有非法数据
- 箱线图绘图
- 正态性检验、方差齐性检验
- 差异检验
- 效应检验
- 具体配对检验(post hoc test)

