一、机器学习的一些概念
基本概念
- 特征:一组数据的多个属性
- 标签:人为指定特征
- 监督学习:就像分类(离散化的标签),回归(连续性的标签)、【“有标准答案”】
- 无监督学习:就像聚类【“无标准答案”】
- 数据:是机器学习的命脉
基本框架图
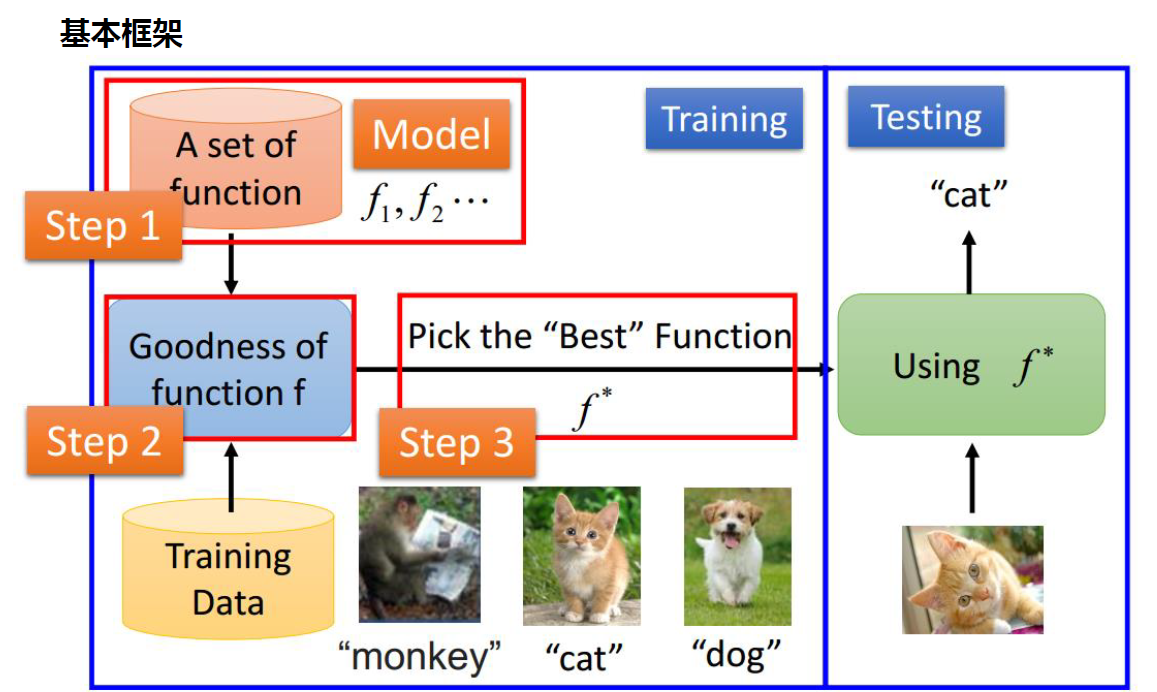
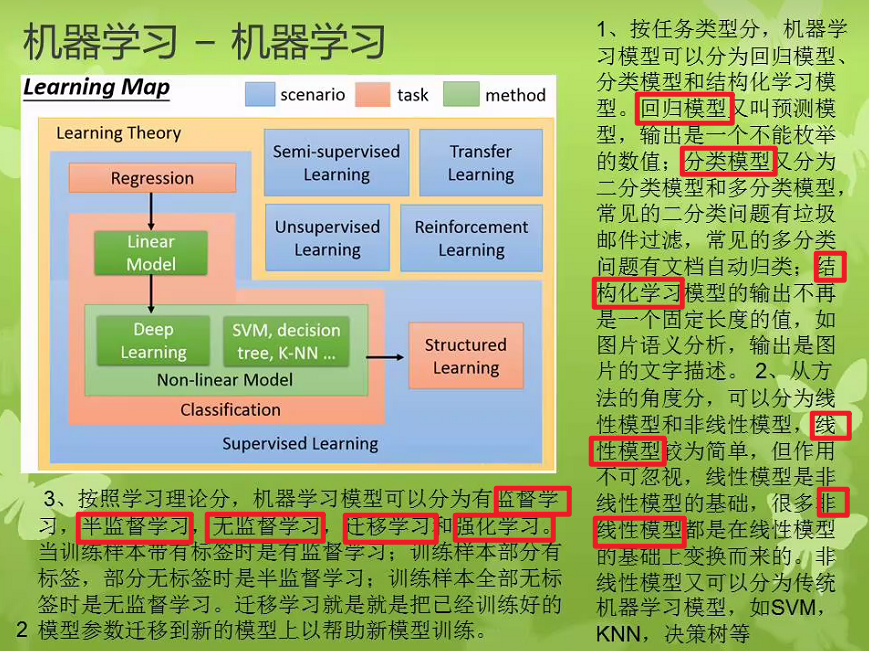
二、机器学习的一些阶段/步骤
sklearn相关提及
官网scikit-learn
- 包含聚类、分类、回归等算法
eg:随机森林、k-means、SVM等 - 包含模型筛选、降维、预处理等算法
- 要特别注意安装该包使用要注意的细节,具体参考上一篇博客
sklearn处理机器学习的一般化sop
- 准备数据集
- 数据分析:(利用np.reshape()成二维(n_samples,n_features))
- 划分数据集:train_test_split()
- 特征工程:特征的提取、特征的归一化nomalization
- 选择模型
- 在训练集上训练模型,并调整参数
- 经验选定参数
- 交叉验证确定最优的参数cross validation
- 在测试集上测试模型
- predict预测、score真实值预测值评分、etc
- 保存模型
主成分分析:将特征降维
- 统计学相关知识:方差(衡量在一个维度的偏差)、协方差(衡量一个维度是否对另一个维度有影响cov(x,y))
- 线代相关知识:特征值、特征向量、协方差向量
- PCA
相关代码html页面
三、通过scikit-learn认识机器学习
加载示例数据集
from sklearn import datasetsiris = datasets.load_iris()#用sklearn自身配带的数据digits = datasets.load_digits()# C:\Users\wztli\Anaconda3\pkgs\scikit-learn-0.21.3-py37h6288b17_0\Lib\site-packages\sklearn\datasets\data# 数据集在电脑中的位置
# 查看数据集# irisprint(iris.data[:5])print(iris.data.shape)print(iris.target_names)print(iris.target)
[[5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2] [4.9 3. 1.4 0.2] [4.7 3.2 1.3 0.2] [4.6 3.1 1.5 0.2] [5. 3.6 1.4 0.2]](150, 4)['setosa' 'versicolor' 'virginica'][0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2]
# digitsprint(digits.data)print(digits.data.shape)print(digits.target_names)print(digits.target)
[[ 0. 0. 5. ... 0. 0. 0.] [ 0. 0. 0. ... 10. 0. 0.] [ 0. 0. 0. ... 16. 9. 0.] ... [ 0. 0. 1. ... 6. 0. 0.] [ 0. 0. 2. ... 12. 0. 0.] [ 0. 0. 10. ... 12. 1. 0.]](1797, 64)[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9][0 1 2 ... 8 9 8]
在训练集上训练模型
# 手动划分训练集、测试集 n_test = 100 # 测试样本个数train_X = digits.data[:-n_test, :]train_y = digits.target[:-n_test]test_X = digits.data[-n_test:, :]y_true = digits.target[-n_test:]
# 选择SVM模型from sklearn import svmsvm_model = svm.SVC(gamma=0.001, C=100.)# svm_model = svm.SVC(gamma=100., C=1.)# 训练模型svm_model.fit(train_X, train_y)#训练要放入两个参数:样本的特征数据,样本的标签
SVC(C=100.0, cache_size=200, class_weight=None, coef0=0.0, decision_function_shape='ovr', degree=3, gamma=0.001, kernel='rbf', max_iter=-1, probability=False, random_state=None, shrinking=True, tol=0.001, verbose=False)
# 选择LR(逻辑回归)模型from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegressionlr_model = LogisticRegression()# 训练模型lr_model.fit(train_X, train_y)
C:\Users\wztli\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\sklearn\linear_model\logistic.py:432: FutureWarning: Default solver will be changed to 'lbfgs' in 0.22. Specify a solver to silence this warning. FutureWarning)C:\Users\wztli\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\sklearn\linear_model\logistic.py:469: FutureWarning: Default multi_class will be changed to 'auto' in 0.22. Specify the multi_class option to silence this warning. "this warning.", FutureWarning)LogisticRegression(C=1.0, class_weight=None, dual=False, fit_intercept=True, intercept_scaling=1, l1_ratio=None, max_iter=100, multi_class='warn', n_jobs=None, penalty='l2', random_state=None, solver='warn', tol=0.0001, verbose=0, warm_start=False)
在测试集上测试模型
y_pred_svm = svm_model.predict(test_X)y_pred_lr = lr_model.predict(test_X)
# 查看结果# 评价指标from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score#print '预测标签:', y_pred#print '真实标签:', y_trueprint('SVM结果:', accuracy_score(y_true, y_pred_svm))print('LR结果:', accuracy_score(y_true, y_pred_lr))
SVM结果: 0.98LR结果: 0.94
保存模型
import picklewith open('svm_model.pkl', 'wb') as f: pickle.dump(svm_model, f)
import numpy as np# 重新加载模型进行预测with open('svm_model.pkl', 'rb') as f: model = pickle.load(f)random_samples_index = np.random.randint(0, 1796, 5)random_samples = digits.data[random_samples_index, :]random_targets = digits.target[random_samples_index]random_predict = model.predict(random_samples)print(random_predict)print(random_targets)
[2 2 1 3 8][2 2 1 3 8]
四、scikit-learn入门
准备数据集
import numpy as npfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X = np.random.randint(0, 100, (10, 4))y = np.random.randint(0, 4, 10)y.sort()print('样本:')print(X)print('标签:', y)
样本:[[43 43 18 78] [74 24 42 37] [36 69 84 47] [70 62 77 30] [87 38 3 96] [68 67 24 7] [66 36 72 72] [12 94 87 72] [66 5 92 6] [41 59 60 91]]标签: [0 0 0 2 2 2 2 3 3 3]
# 分割训练集、测试集# random_state确保每次随机分割得到相同的结果X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=1/3., random_state=7) print('训练集:')print(X_train)print(y_train)print('测试集:')print(X_test)print(y_test)
训练集:[[63 56 7 42] [40 47 17 23] [41 31 26 8] [79 30 22 88] [54 85 48 54] [89 73 77 41]][0 1 1 0 1 1]测试集:[[ 3 0 42 86] [42 96 83 38] [33 45 8 37] [ 1 44 75 7]][1 1 0 0]
# 特征归一化from sklearn import preprocessingx1 = np.random.randint(0, 1000, 5).reshape(5,1)x2 = np.random.randint(0, 10, 5).reshape(5, 1)x3 = np.random.randint(0, 100000, 5).reshape(5, 1)X = np.concatenate([x1, x2, x3], axis=1)print(X)
[[ 353 4 27241] [ 999 4 34684] [ 911 4 78606] [ 310 6 44593] [ 817 9 6356]]
print(preprocessing.scale(X))
[[-1.12443958 -0.71443451 -0.46550183] [ 1.11060033 -0.71443451 -0.15209341] [ 0.80613669 -0.71443451 1.69736578] [-1.27321159 0.30618622 0.26515287] [ 0.48091416 1.83711731 -1.34492342]]
# 生成分类数据进行验证scale的必要性from sklearn.datasets import make_classificationimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt%matplotlib inlineX, y = make_classification(n_samples=300, n_features=2, n_redundant=0, n_informative=2, random_state=25, n_clusters_per_class=1, scale=100)plt.scatter(X[:,0], X[:,1], c=y)plt.show()
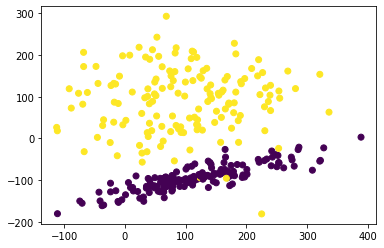
from sklearn import svm# 注释掉以下这句表示不进行特征归一化 X = preprocessing.scale(X)X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=1/3., random_state=7) svm_classifier = svm.SVC()svm_classifier.fit(X_train, y_train)svm_classifier.score(X_test, y_test)
C:\Users\wztli\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\sklearn\svm\base.py:193: FutureWarning: The default value of gamma will change from 'auto' to 'scale' in version 0.22 to account better for unscaled features. Set gamma explicitly to 'auto' or 'scale' to avoid this warning. "avoid this warning.", FutureWarning)0.25
训练模型
# 回归模型from sklearn import datasetsboston_data = datasets.load_boston()X = boston_data.datay = boston_data.targetprint('样本:')print(X[:5, :])print('标签:')print(y[:5])
样本:[[6.3200e-03 1.8000e+01 2.3100e+00 0.0000e+00 5.3800e-01 6.5750e+00 6.5200e+01 4.0900e+00 1.0000e+00 2.9600e+02 1.5300e+01 3.9690e+02 4.9800e+00] [2.7310e-02 0.0000e+00 7.0700e+00 0.0000e+00 4.6900e-01 6.4210e+00 7.8900e+01 4.9671e+00 2.0000e+00 2.4200e+02 1.7800e+01 3.9690e+02 9.1400e+00] [2.7290e-02 0.0000e+00 7.0700e+00 0.0000e+00 4.6900e-01 7.1850e+00 6.1100e+01 4.9671e+00 2.0000e+00 2.4200e+02 1.7800e+01 3.9283e+02 4.0300e+00] [3.2370e-02 0.0000e+00 2.1800e+00 0.0000e+00 4.5800e-01 6.9980e+00 4.5800e+01 6.0622e+00 3.0000e+00 2.2200e+02 1.8700e+01 3.9463e+02 2.9400e+00] [6.9050e-02 0.0000e+00 2.1800e+00 0.0000e+00 4.5800e-01 7.1470e+00 5.4200e+01 6.0622e+00 3.0000e+00 2.2200e+02 1.8700e+01 3.9690e+02 5.3300e+00]]标签:[24. 21.6 34.7 33.4 36.2]
# 选择线性回顾模型from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegressionlr_model = LinearRegression()
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split# 分割训练集、测试集X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=1/3., random_state=7)
# 训练模型lr_model.fit(X_train, y_train)
LinearRegression(copy_X=True, fit_intercept=True, n_jobs=None, normalize=False)
# 返回参数lr_model.get_params()
{'copy_X': True, 'fit_intercept': True, 'n_jobs': None, 'normalize': False}
lr_model.score(X_train, y_train)
0.7598132492351114
lr_model.score(X_test, y_test)
0.6693852753319398
交叉验证
from sklearn import datasetsfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, cross_val_scorefrom sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifierimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt%matplotlib inlineiris = datasets.load_iris()X = iris.datay = iris.targetX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=1/3., random_state=10) k_range = range(1, 31)cv_scores = []for n in k_range: knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n) scores = cross_val_score(knn, X_train, y_train, cv=10, scoring='accuracy') # 分类问题使用 #scores = cross_val_score(knn, X_train, y_train, cv=10, scoring='neg_mean_squared_error') # 回归问题使用 cv_scores.append(scores.mean())plt.plot(k_range, cv_scores)plt.xlabel('K')plt.ylabel('Accuracy')plt.show()
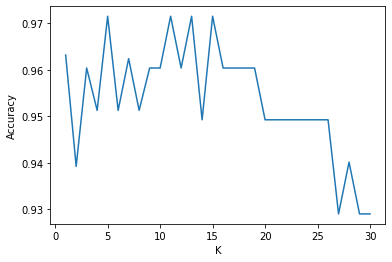
# 选择最优的Kbest_knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=5)best_knn.fit(X_train, y_train)print(best_knn.score(X_test, y_test))print(best_knn.predict(X_test))
0.96[1 2 0 1 0 1 2 1 0 1 1 2 1 0 0 2 1 0 0 0 2 2 2 0 1 0 1 1 1 2 1 1 2 2 2 0 2 2 2 2 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 2 2 2]
参考





