栈和队列的介绍
栈和队列是两种重要的线性结构,从数据结构角度看,栈和队列也是线性表,其特殊性在与栈和队列的基本操作是线性表操作的子集,它们是受限制的线性表,因此可称为限定性数据结构,但从数据类型角度看,它们是和线性表大不相同的两类重要的抽象数据类型。
队列和栈都可以使用顺序线性表和链线性表的方式实现
栈
是限定仅在表尾进行插入或删除操作的线性表。因此,对栈来说,表尾端有其特殊的含义,称为“栈顶”,相应的表头端称为“栈底”。不含元素的空表叫做“空栈”,栈又叫做先进后出的线性表。
- InitStack(&S); // 初始化栈
- DestroyStack(&S); // 销毁栈
- ClearStack(&S); // 清空栈
- StackEmpty(&S); // 检测是不是空栈,若为空返回TRUE,不为空返回FALSE
- StackLength(&S); // 返回栈的长度
- StackGetTop(&S, &e); // 返回栈顶元素
- StackPush(&S, &e); // 向栈顶插入元素
- StackPop(&S, &e); // 删除栈顶元素,并通过e返回
- StackTraverse(&S, visit()); // 栈中所有元素依次调用visit()。一旦visit()失败,则操作失败
和线性表一样,栈也有两种存储表示方式(顺序栈,先给个默认长度,然后在给一个递增长度,递增类型的)
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#define TRUE 1#define FALSE 0#define ERROR 0#define OK 1#define OVERFLOW -2#define STACK_INIT_SIZE 100#define STACKINCREMENT 10typedef int ElemType;typedef int Status;typedef struct {ElemType *base; // 栈底ElemType *top; // 栈顶int stacksize;}SqStack;Status InitStack(SqStack *S) {S -> base = (ElemType *)malloc(STACK_INIT_SIZE * sizeof(ElemType));if (!S-> base) {exit(OVERFLOW);}S -> top = S -> base;S -> stacksize = STACK_INIT_SIZE;return OK;}Status StackGetTop(SqStack *S, ElemType *e) {if (S -> top == S -> base) {return ERROR;}*e = *(S -> top -1);return OK;}Status StackPush(SqStack *S, ElemType e) {if (S -> top - S -> base >= S -> stacksize) {S -> base = (ElemType *)realloc(S -> base,(S -> stacksize + STACKINCREMENT) * sizeof(ElemType));if (!S -> base) {exit(OVERFLOW);}S -> top = S -> base + S -> stacksize;S -> stacksize += STACKINCREMENT;}*S -> top++ = e;return OK;}Status StackPop(SqStack *S, ElemType *e) {if (S -> top == S -> base ) {return ERROR;}*e = *--S -> top;return OK;}Status StackEmpty(SqStack *S) {Status z = S -> top == S -> base ? TRUE : FALSE;return z;}int main() {SqStack S;InitStack(&S);// ElemType e = 2;// ElemType v;// StackPush(&S, e);// StackPop(&S, &v);// StackGetTop(&S, &v);// printf("d=%d\n", v);int n;ElemType e;scanf("%d", &n);while (n) {StackPush(&S, n % 8);n /= 8;}while(!StackEmpty(&S)) {StackPop(&S, &e);printf("%d", e);}printf("\n");return 0;}
栈的应用实例
数制转换
(1348)十进制 = (2504) 八进制
1348 % 8 = 4
1348 / 8 = 168; 168 % 8 = 0;
168 / 8 = 21; 21 % 8 = 5;
21 / 8 = 2; 2 % 8 = 2;
int main() {SqStack S;InitStack(&S);int n;ElemType e;scanf("%d", &n);while (n) {StackPush(&S, n % 8);n /= 8;}while(!StackEmpty(&S)) {StackPop(&S, &e);printf("%d", e);}printf("\n");return 0;}
行编辑程序
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#define TRUE 1#define FALSE 0#define ERROR 0#define OK 1#define OVERFLOW -2#define STACK_INIT_SIZE 100#define STACKINCREMENT 10typedef char ElemType;typedef char Status;typedef struct {ElemType *base; // 栈底ElemType *top; // 栈顶int stacksize;}SqStack;Status InitStack(SqStack *S) {S -> base = (ElemType *)malloc(STACK_INIT_SIZE * sizeof(ElemType));if (!S-> base) {exit(OVERFLOW);}S -> top = S -> base;S -> stacksize = STACK_INIT_SIZE;return OK;}Status StackGetTop(SqStack *S, ElemType *e) {if (S -> top == S -> base) {return ERROR;}*e = *(S -> top -1);return OK;}Status StackPush(SqStack *S, ElemType e) {if (S -> top - S -> base >= S -> stacksize) {S -> base = (ElemType *)realloc(S -> base,(S -> stacksize + STACKINCREMENT) * sizeof(ElemType));if (!S -> base) {exit(OVERFLOW);}S -> top = S -> base + S -> stacksize;S -> stacksize += STACKINCREMENT;}*S -> top++ = e;return OK;}Status StackPop(SqStack *S, ElemType *e) {if (S -> top == S -> base ) {return ERROR;}*e = *--S -> top;return OK;}Status ClearStack(SqStack *S) {S -> top = S -> base;return OK;}Status StackEmpty(SqStack *S) {Status z = S -> top == S -> base ? TRUE : FALSE;return z;}void LineEdit(SqStack *S) {printf("请输入字符:\n");InitStack(S);char ch;scanf("%c", &ch);while ((int)ch != 27) {switch(ch) {case '#':StackPop(S, &ch);break;case '@': // 期待删除 \n?.*@.*\n 之间的内容ClearStack(S);break;default: StackPush(S, ch);}scanf("%c", &ch);if (ch == '\n') {StackPush(S, ch);scanf("%c", &ch);}}}int main() {SqStack S;LineEdit(&S);char e;while(!StackEmpty(&S)) {StackPop(&S, &e);printf("%c", e);}printf("\n");return 0;}
括号匹配的检测
{[][]{}}
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#define TRUE 1#define FALSE 0#define ERROR 0#define NO 0#define OK 1#define OVERFLOW -2#define STACK_INIT_SIZE 100#define STACKINCREMENT 10typedef char ElemType;typedef char Status;typedef struct {ElemType *base; // 栈底ElemType *top; // 栈顶int stacksize;}SqStack;Status InitStack(SqStack *S) {S -> base = (ElemType *)malloc(STACK_INIT_SIZE * sizeof(ElemType));if (!S-> base) {exit(OVERFLOW);}S -> top = S -> base;S -> stacksize = STACK_INIT_SIZE;return OK;}Status StackGetTop(SqStack *S, ElemType *e) {if (S -> top == S -> base) {return ERROR;}*e = *(S -> top -1);return OK;}Status StackPush(SqStack *S, ElemType e) {if (S -> top - S -> base >= S -> stacksize) {S -> base = (ElemType *)realloc(S -> base,(S -> stacksize + STACKINCREMENT) * sizeof(ElemType));if (!S -> base) {exit(OVERFLOW);}S -> top = S -> base + S -> stacksize;S -> stacksize += STACKINCREMENT;}*S -> top++ = e;return OK;}Status StackPop(SqStack *S, ElemType *e) {if (S -> top == S -> base) {return ERROR;}*e = *--S -> top;return OK;}Status ClearStack(SqStack *S) {S -> top = S -> base;return OK;}Status StackEmpty(SqStack *S) {Status z = S -> top == S -> base ? TRUE : FALSE;return z;}Status Match(char a,char b){if (a + 1 == b || a + 2 == b) {return OK;}return NO;}Status BracketsMatching(char *str) {SqStack S;InitStack(&S);int i;char ch;for (i = 0; str[i] != '\0'; i++) {switch (str[i]) {case '{':case '(':case '[':StackPush(&S, str[i]);break;case '}':case ')':case ']':if (StackEmpty(&S)){return NO;}StackGetTop(&S, &ch);if (Match(ch, str[i])) {StackPop(&S, &ch);} else {return NO;}break;default:break;}}if (!StackEmpty(&S)) {return NO;}return OK;}int main() {Status StackEmpty(SqStack *S);Status StackPush(SqStack *S, ElemType e);Status StackPop(SqStack *S, ElemType *e);char str[50];printf("请输入你要收入的字符串:");scanf("%s", str);int h = BracketsMatching(str);if(h == 0)printf("括号不匹配\n");elseprintf("括号匹配\n");return 0;}
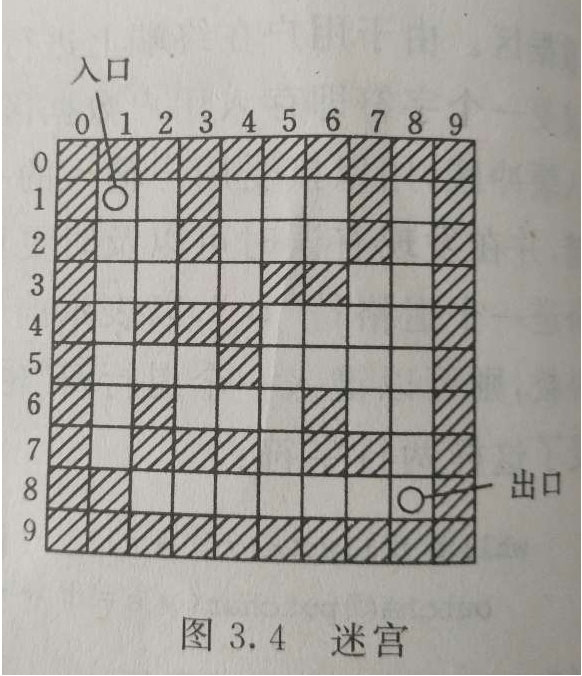
迷宫求解
求迷宫从入口到出口的所有路径是一个经典的程序设计问题。由于计算机解迷宫时,通常用的是“穷举求解”的方法,即从入口出发,顺某一个方向向前探索,若能走通,则继续向前,否则按原路退回,换一个方向继续探索,直至所有可能的路线都探索到了为止。为了保证在任何位置上都能按原路退回,显然需要用一个后进先出的结构来保存从入口到当前位置的路径。因此求解迷宫通路的算法中应用“栈”也就是自然而然的事情了。
首先,在计算机中可以用如图所示的方块图表示迷宫。图中空白处可以通行,阴影处表示是墙壁。所求路径必须是简单路径,即在求得路径上不能重复出现同一通道块。
假设“当前位置”指的是“在搜索过程中某一时刻所在图中某个方块的位置”,则求迷宫中一条路径的算法的基本思想是:
若当前位置“可通”,则纳入“当前路径”,并继续朝下一个位置探索,即切换“下一位置”为当前位置,如此反复直至到达出口;若当前位置“不可通”,则顺应“来向”退回到前一块通道,然后朝则除“来向”之外的其他地方探索;若该通道块的四周四个方块均不可通,则应顺从“当前路径”上删除该通道块。所谓“下一位置”指的是当前位置的四周4个方向(上,下,左,右)上相邻的方块。
假设栈S纪录当前路径,则栈顶中存放的是“当前路径上最后一个通道块”。由此“纳入路径”的操作即为“当前位置入栈“,“从当前路径上最后一个通道块”的操作即为“出栈”。
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#define TRUE 1#define FALSE 0#define ERROR 0#define NO 0#define OK 1#define OVERFLOW -2#define STACK_INIT_SIZE 100#define STACKINCREMENT 10typedef struct{int x;int y;}PosType;typedef struct{int ord; // 通道块在路径上的“序号”PosType seat; // 通道块在迷宫中的坐标位置int di; // 通道块走向下一通道块的方向 1上, 2右,3下,4左}MazeElemType;typedef struct {int rowsLength; // 行长度int columnLength; // 列长度int *mazeArr; // 地图数组}MazeType;typedef MazeElemType ElemType;typedef int Status;#define StatusPrintf "%d\n"typedef struct {ElemType *base; // 栈底ElemType *top; // 栈顶int stacksize;}SqStack;Status InitStack(SqStack *S) {S -> base = (ElemType *)malloc(STACK_INIT_SIZE * sizeof(ElemType));if (!S-> base) {exit(OVERFLOW);}S -> top = S -> base;S -> stacksize = STACK_INIT_SIZE;return OK;}Status StackGetTop(SqStack *S, ElemType *e) {if (S -> top == S -> base) {return ERROR;}*e = *(S -> top -1);return OK;}Status StackPush(SqStack *S, ElemType e) {if (S -> top - S -> base >= S -> stacksize) {S -> base = (ElemType *)realloc(S -> base,(S -> stacksize + STACKINCREMENT) * sizeof(ElemType));if (!S -> base) {exit(OVERFLOW);}S -> top = S -> base + S -> stacksize;S -> stacksize += STACKINCREMENT;}*S -> top++ = e;return OK;}Status StackPop(SqStack *S, ElemType *e) {if (S -> top == S -> base) {return ERROR;}*e = *--S -> top;return OK;}Status ClearStack(SqStack *S) {S -> top = S -> base;return OK;}Status StackEmpty(SqStack *S) {Status z = S -> top == S -> base ? TRUE : FALSE;return z;}PosType NextPos(PosType curpos, int di) {switch(di) {case 1:curpos.x -= 1;break;case 2:curpos.y += 1;break;case 3:curpos.x += 1;break;case 4:curpos.y -= 1;break;default:break;}int i = 0;int num = 0;for (; i < 1000000; i += 1) {num = i;}return curpos;}Status Pass(MazeType *maze, PosType curpos) { // 是否可通行块if (curpos.x > maze -> rowsLength|| curpos.y > maze -> columnLength|| curpos.x < 0|| curpos.y < 0) {return FALSE;}int *p = maze -> mazeArr;int q = *(p + curpos.x * 10 + curpos.y);Status z = q > 0 ? TRUE : FALSE;return z;}Status MarkPrint(MazeType *maze, PosType curpos) { // 标记地图不能行走int *p = maze -> mazeArr;*(p + curpos.x * 10 + curpos.y) = 0;return OK;}Status TheWayThrough(SqStack *S, PosType temp) { // 判断是否存在链表中SqStack Temp;InitStack(&Temp);Status z = FALSE;MazeElemType e;while(!StackEmpty(S)) {StackPop(S, &e);StackPush(&Temp, e);if (e.seat.x == temp.x && e.seat.y == temp.y) {z = TRUE;}}while(!StackEmpty(&Temp)) {StackPop(&Temp, &e);StackPush(S, e);}return z;}/*如果下个位置存在与链表中,跳过此次*/Status CurposNext(MazeType *maze, SqStack *S, PosType *curpos, MazeElemType *e) {while (TheWayThrough(S, *curpos)) {if (e -> di == 4) {MarkPrint(maze, *curpos);StackPop(S, e);printf("F pop:%d:%d di=%d\n", e -> seat.x, e -> seat.y, e -> di);} else {StackPop(S, e);e -> di += 1;StackPush(S, *e);printf("E :%d:%d di=%d\n", e -> seat.x, e -> seat.y, e -> di);*curpos = NextPos(e -> seat, e -> di);}}return OK;}Status MazePath(MazeType *maze, PosType start, PosType end) {SqStack S;InitStack(&S);PosType curpos = start; // 设置起始位置 8,8int curstep = 1; // 第一步MazeElemType e;int i;do {i++;Status z = Pass(maze, curpos); // 是否可通行块if (z) { // 当前位置是可通行块e.ord = curstep;e.seat = curpos;e.di = 1; // 通过di留下足迹StackPush(&S, e);printf("A push:%d:%d di=%d\n", e.seat.x, e.seat.y, e.di);if (curpos.x == end.x&& curpos.y == end.y) {printf("i=%d\n", i);return OK;}curpos = NextPos(curpos, 1); // 下一个位置CurposNext(maze, &S, &curpos, &e);curstep++;} else { // 当前位置为不可通行块if (!StackEmpty(&S)) {StackPop(&S, &e);printf("B pop:%d:%d di=%d\n", e.seat.x, e.seat.y, e.di);while(e.di == 4 && !StackEmpty(&S)) {// 标记地图不可通行MarkPrint(maze, curpos);StackPop(&S, &e);printf("D MarkPrint pop:%d:%d di=%d\n", e.seat.x, e.seat.y, e.di);curpos = e.seat;}if (e.di < 4) {e.di += 1;StackPush(&S, e);printf("C push:%d:%d di=%d\n", e.seat.x, e.seat.y, e.di);curpos = NextPos(e.seat, e.di);CurposNext(maze, &S, &curpos, &e);}}}} while (!StackEmpty(&S));printf("i=%d\n", i);return FALSE;}int main() {Status StackEmpty(SqStack *S);Status StackPush(SqStack *S, ElemType e);Status StackPop(SqStack *S, ElemType *e);Status MarkPrint(MazeType *maze, PosType curpos);PosType NextPos(PosType curpos, int di);Status Pass(MazeType *maze, PosType curpos);Status MazePath(MazeType *maze, PosType start, PosType end);Status TheWayThrough(SqStack *S, PosType temp);Status CurposNext(MazeType *maze, SqStack *S, PosType *curpos, MazeElemType *e);int Maze[10][10] = { // 迷宫 2为出口,3为入口,1为可通行块,0为不可通行块{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },{ 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0 },{ 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0 },{ 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0 },{ 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0 },{ 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0 },{ 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0 },{ 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0 },{ 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 3, 0 },{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },};int *p = &Maze[0][0];MazeType maze = { 10, 10, p };PosType start = { 8, 8 };PosType end = { 1, 1 };int i = MazePath(&maze, start, end);if (i == 0) {printf("没有找到出口\n");} else {printf("找到出口了\n");}return 0;}
表达式求值
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#define TRUE 1#define FALSE 0#define OK 1#define ERROR 0#define INFEASIBLE -1#define OVERFLOW -2#define STACK_INIT_SIZE 100 //存储空间初始分配量#define STACKINCREMENT 10 //存储空间分配增量typedef char SElemType;typedef char OperandType; //表达式求值的运算类型typedef int Status;typedef struct{SElemType *base;SElemType *top;int stacksize;}SqStack;//构造一个空栈Status InitStack(SqStack *S){S->base = (SElemType *)malloc(STACK_INIT_SIZE * sizeof(SElemType));if(!S->base){printf("内存分配失败!\n");exit(OVERFLOW);}S->top = S->base;S->stacksize = STACKINCREMENT;return OK;}//若栈不为空,则用e返回S的栈顶元素,并返回OK;否则返回ERRORStatus GetTop(SqStack *S, SElemType *e){if(S->top == S->base)return ERROR;*e = *(S->top - 1);return OK;}//插入元素e为新的栈顶元素Status Push(SqStack *S, SElemType e){if(S->top - S->base >= STACK_INIT_SIZE) //栈满, 追加存储空间{S->base = (SElemType *)realloc(S->base, (S->stacksize + STACKINCREMENT) * sizeof(SElemType));if(!S->base){printf("内存分配失败!\n");exit(OVERFLOW);}S->top = S->base + S->stacksize;S->stacksize += STACKINCREMENT;}*S->top++ = e;return OK;}//若栈不为空,则删除S的栈顶元素,用e返回其值,并返回Ok;否则返回ERRORStatus Pop(SqStack *S, SElemType *e){if(S->top == S->base)return ERROR;*e = *--S->top;return OK;}//销毁栈S,使其不复存在Status StackDestroy(SqStack *S){free(S->base);S->base = NULL;S->top = NULL;S->stacksize = 0;return OK;}//清空栈S,保留栈底指针void ClearStack(SqStack *S){S->top = S->base;}//根据教科书表3.1,判断两符号的优先关系char Precede(char t1, char t2){int i,j;char pre[][7]={//运算符之间的优先级制作成一张表格{'>','>','<','<','<','>','>'},{'>','>','<','<','<','>','>'},{'>','>','>','>','<','>','>'},{'>','>','>','>','<','>','>'},{'<','<','<','<','<','=','0'},{'>','>','>','>','0','>','>'},{'<','<','<','<','<','0','='}};switch(t1){case '+': i=0; break;case '-': i=1; break;case '*': i=2; break;case '/': i=3; break;case '(': i=4; break;case ')': i=5; break;case '=': i=6; break;}switch(t2){case '+': j=0; break;case '-': j=1; break;case '*': j=2; break;case '/': j=3; break;case '(': j=4; break;case ')': j=5; break;case '=': j=6; break;}return pre[i][j];}//判断c是否为运算符Status In(OperandType c){switch(c){case '+':case '-':case '*':case '/':case '(':case ')':case '=':return TRUE;default:return FALSE;}}//二元运算(a theta b)OperandType Operate(OperandType a, OperandType theta, OperandType b){OperandType c;switch(theta){case '+':c = a + b;break;case '-':c = a - b;break;case '*':c = a * b;break;case '/':c = a / b;break;}return c;}//算术表达式求值的算符优先算法,设OPTR和OPND分别为运算符栈和运算数栈,OP为运算符集合OperandType EvaluateExpression(){SqStack OPTR, OPND;OperandType a, b, d, x, theta;char c; //存放有键盘输入的字符串char z[6]; //存放整数字符串int i;InitStack(&OPTR); //初始化运算符栈Push(&OPTR, '='); //=是表达式结束符InitStack(&OPND); //初始化运算数栈c = getchar();GetTop(&OPTR, &x);while(c != '=' || x != '='){if(In(c)) //是7种运算符之一{printf("%c\n", Precede(x, c));switch(Precede(x, c)){case '<': //当前已经压栈一个运算符(x)比后一个运算符(c)低时,就将c压栈Push(&OPTR, c);c = getchar();break;case '=':Pop(&OPTR, &x); //脱括号并接收下一字符c = getchar();break;case '>':Pop(&OPTR, &theta); //退栈并将运算结果压入OPND中Pop(&OPND, &b);Pop(&OPND, &a);Push(&OPND, Operate(a, theta, b));break;}}else if(c >= '0' && c <= '9') //c是操作数{i = 0;do{z[i] = c;i++;c = getchar();}while(c >= '0' && c <= '9');z[i] = 0;d = atoi(z); //将字符数组转为整型存于dprintf("%d\n", d);Push(&OPND, d);}else //c为非法字符{printf("ERROR3\n");exit(1);}GetTop(&OPTR, &x);}GetTop(&OPND, &x);StackDestroy(&OPTR);StackDestroy(&OPND);return x;}int main(){printf("请输入算术表达式,负数要用(0-正数:\n");printf("%d\n", EvaluateExpression());return 0;}
栈和递归 hanoi塔
#include <stdio.h>int c = 0;void move(char a,int m,char b);void hanoi(int n,char x,char y,char z);int main(){int n = 4;char x = 'x';char y = 'y';char z = 'z';hanoi(n,x,y,z);}void hanoi(int n,char x,char y,char z)//将塔座x上按直径由小到大且自上而下编号为1至n的n个圆盘按规则搬到//塔座z上,y可用辅助塔座。{if(n==1)move(x,1,z);else{hanoi(n-1,x,z,y);move(x,n,z);hanoi(n-1,y,x,z);}}void move(char a,int m,char b){printf("第%d步:将第%d个圆盘从%c移到%c\n",++c,m,a,b);}
队列
- 和栈相反队列是一种先进先出的线性表,也是利用线性表的实现
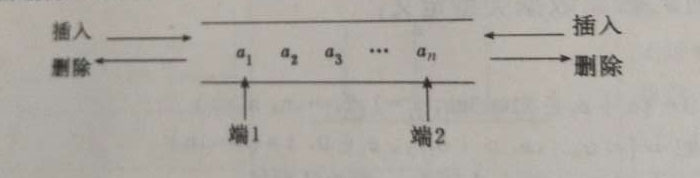
- 有一种队列叫做,双端队列,两头都可以删除和插入,分为端点1,端点2
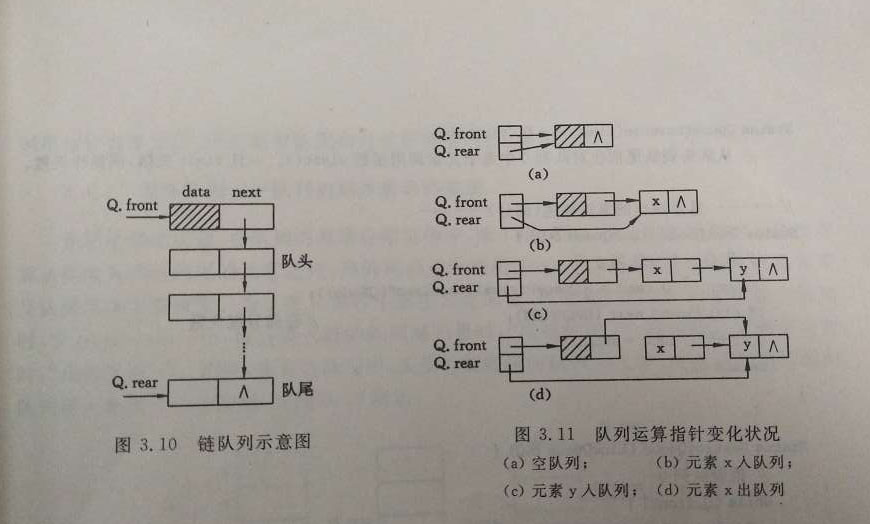
链队列
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#define TRUE 1#define FALSE 0#define ERROR 0#define NO 0#define OK 1#define OVERFLOW -2#define STACK_INIT_SIZE 100#define STACKINCREMENT 10typedef int QElemType;typedef int Status;typedef struct QNode{QElemType data;struct QNode *next;}QNode, *QueuePtr;typedef struct {QueuePtr front; // 对头指针QueuePtr rear; // 队尾指针}LinkQueue;Status InitQueue(LinkQueue *Q) {Q -> front = Q -> rear = (QueuePtr)malloc(sizeof(QNode));if (!Q-> front) {exit(OVERFLOW);}Q -> front = NULL;return OK;}Status EnQueue(LinkQueue *Q, QElemType e) {QueuePtr p = (QueuePtr)malloc(sizeof(QNode));if (!p) {exit(OVERFLOW);}p -> data = e;p -> next = NULL;Q -> rear -> next = p;Q -> rear = p;return OK;}Status DeQueue(LinkQueue *Q, QElemType *e) {if (Q -> front == Q -> rear) {return ERROR;}QueuePtr p = Q -> front -> next;*e = p -> data;Q -> front -> next = p -> next;if (Q -> rear == p) {Q -> rear = Q -> front;}free(p);return OK;}int main () {return 0;}
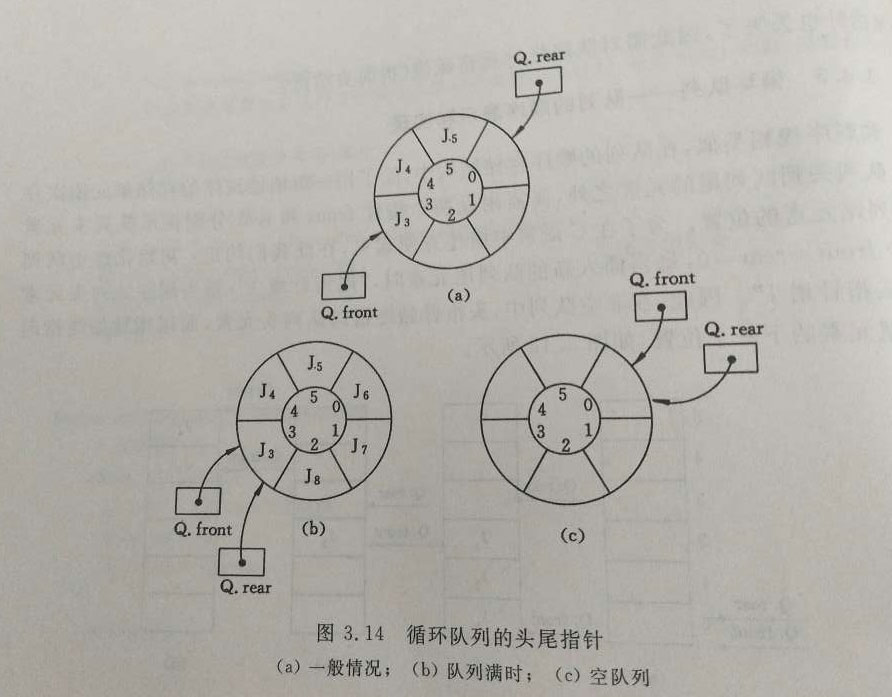
循环队列—队列的顺序表示
- 假设当前队列分配的最大空间为6,填满,然后出队列4个,还剩2个位置时,不能在继续向队尾插入新元素,否则会因数组越界而导致程序代码被破坏。然而此时又不宜如顺序栈哪样,进行存储在分配扩大数组空间,因为队列的实际可用空间未被占满,一个巧妙的办法是将顺序队列臆造为一个环形的空间。