对象拷贝
它们两种工具本质上就是对象拷贝工具,而对象拷贝又分为深拷贝和浅拷贝,下面进行详细解释。
浅拷贝和深拷贝
在Java中,除了 基本数据类型之外,还存在 类的实例对象这个引用数据类型,而一般使用 “=”号做赋值操作的时候,对于基本数据类型,实际上是拷贝的它的值,但是对于对象而言,其实赋值的只是这个对象的引用,将原对象的引用传递过去,他们实际还是指向的同一个对象。
而浅拷贝和深拷贝就是在这个基础上做的区分,如果在拷贝这个对象的时候,只对基本数据类型进行了拷贝,而对引用数据类型只是进行引用的传递,而没有真实的创建一个新的对象,则认为是浅拷贝。反之,在对引用数据类型进行拷贝的时候,创建了一个新的对象,并且复制其内的成员变量,则认为是深拷贝。
简单来说:
- 浅拷贝:对基本数据类型进行值传递,对引用数据类型进行引用传递般的拷贝,此为浅拷贝
- 深拷贝:对基本数据类型进行值传递,对引用数据类型,创建一个新的对象,并复制其内容,此为深拷贝。
BeanUtils
Apache 的 BeanUtils
BeanUtils的例子
从上面的例子可以看出,对象拷贝非常简单,BeanUtils最常用的方法就是:public class PersonSource {private Integer id;private String username;private String password;private Integer age;// getters/setters omiited}public class PersonDest {private Integer id;private String username;private Integer age;// getters/setters omiited}public class TestApacheBeanUtils {public static void main(String[] args) throws InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {//下面只是用于单独测试PersonSource personSource = new PersonSource(1, "pjmike", "12345", 21);PersonDest personDest = new PersonDest();BeanUtils.copyProperties(personDest,personSource);System.out.println("persondest: "+personDest);}}persondest: PersonDest{id=1, username='pjmike', age=21}
默认情况下,使用//将源对象中的值拷贝到目标对象public static void copyProperties(Object dest, Object orig) throws IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {BeanUtilsBean.getInstance().copyProperties(dest, orig);}
org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanUtils对复杂对象的复制是引用,这是一种浅拷贝
但是由于 Apache下的BeanUtils对象拷贝性能太差,不建议使用,而且在阿里巴巴Java开发规约插件上也明确指出:Ali-Check | 避免用Apache Beanutils进行属性的copy。
commons-beantutils 对于对象拷贝加了很多的检验,包括类型的转换,甚至还会检验对象所属的类的可访问性,可谓相当复杂,这也造就了它的差劲的性能,具体实现代码如下:
public void copyProperties(final Object dest, final Object orig)throws IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {// Validate existence of the specified beansif (dest == null) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("No destination bean specified");}if (orig == null) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("No origin bean specified");}if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug("BeanUtils.copyProperties(" + dest + ", " +orig + ")");}// Copy the properties, converting as necessaryif (orig instanceof DynaBean) {final DynaProperty[] origDescriptors =((DynaBean) orig).getDynaClass().getDynaProperties();for (DynaProperty origDescriptor : origDescriptors) {final String name = origDescriptor.getName();// Need to check isReadable() for WrapDynaBean// (see Jira issue# BEANUTILS-61)if (getPropertyUtils().isReadable(orig, name) &&getPropertyUtils().isWriteable(dest, name)) {final Object value = ((DynaBean) orig).get(name);copyProperty(dest, name, value);}}} else if (orig instanceof Map) {@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")final// Map properties are always of type <String, Object>Map<String, Object> propMap = (Map<String, Object>) orig;for (final Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : propMap.entrySet()) {final String name = entry.getKey();if (getPropertyUtils().isWriteable(dest, name)) {copyProperty(dest, name, entry.getValue());}}} else /* if (orig is a standard JavaBean) */ {final PropertyDescriptor[] origDescriptors =getPropertyUtils().getPropertyDescriptors(orig);for (PropertyDescriptor origDescriptor : origDescriptors) {final String name = origDescriptor.getName();if ("class".equals(name)) {continue; // No point in trying to set an object's class}if (getPropertyUtils().isReadable(orig, name) &&getPropertyUtils().isWriteable(dest, name)) {try {final Object value =getPropertyUtils().getSimpleProperty(orig, name);copyProperty(dest, name, value);} catch (final NoSuchMethodException e) {// Should not happen}}}}}
Spring的 BeanUtils
使用Spring的BeanUtils进行对象拷贝:
public class TestSpringBeanUtils {public static void main(String[] args) throws InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {//下面只是用于单独测试PersonSource personSource = new PersonSource(1, "pjmike", "12345", 21);PersonDest personDest = new PersonDest();BeanUtils.copyProperties(personSource,personDest);System.out.println("persondest: "+personDest);}}
Spring下的BeanUtils也是使用 copyProperties方法进行拷贝,只不过它的实现方式非常简单,就是对两个对象中相同名字的属性进行简单的get/set,仅检查属性的可访问性。
去源码里面:
- 版本:spring-benas-4.3.8.RELEASE
方法:
org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils#copyProperties(java.lang.Object, java.lang.Object, java.lang.Class<?>, java.lang.String...)private static void copyProperties(Object source, Object target, @Nullable Class<?> editable, @Nullable String... ignoreProperties) throws BeansException {Assert.notNull(source, "Source must not be null");Assert.notNull(target, "Target must not be null");Class<?> actualEditable = target.getClass();if (editable != null) {if (!editable.isInstance(target)) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Target class [" + target.getClass().getName() + "] not assignable to Editable class [" + editable.getName() + "]");}actualEditable = editable;}PropertyDescriptor[] targetPds = getPropertyDescriptors(actualEditable);List<String> ignoreList = ignoreProperties != null ? Arrays.asList(ignoreProperties) : null;PropertyDescriptor[] var7 = targetPds;int var8 = targetPds.length;for(int var9 = 0; var9 < var8; ++var9) {PropertyDescriptor targetPd = var7[var9];Method writeMethod = targetPd.getWriteMethod();if (writeMethod != null && (ignoreList == null || !ignoreList.contains(targetPd.getName()))) {PropertyDescriptor sourcePd = getPropertyDescriptor(source.getClass(), targetPd.getName());if (sourcePd != null) {Method readMethod = sourcePd.getReadMethod();if (readMethod != null && ClassUtils.isAssignable(writeMethod.getParameterTypes()[0], readMethod.getReturnType())) {try {if (!Modifier.isPublic(readMethod.getDeclaringClass().getModifiers())) {readMethod.setAccessible(true);}Object value = readMethod.invoke(source);if (!Modifier.isPublic(writeMethod.getDeclaringClass().getModifiers())) {writeMethod.setAccessible(true);}writeMethod.invoke(target, value);} catch (Throwable var15) {throw new FatalBeanException("Could not copy property '" + targetPd.getName() + "' from source to target", var15);}}}}}}
这个方法的源码其实很短,只有 44 行,我给大家把关键的地方写上注释,截图如下:
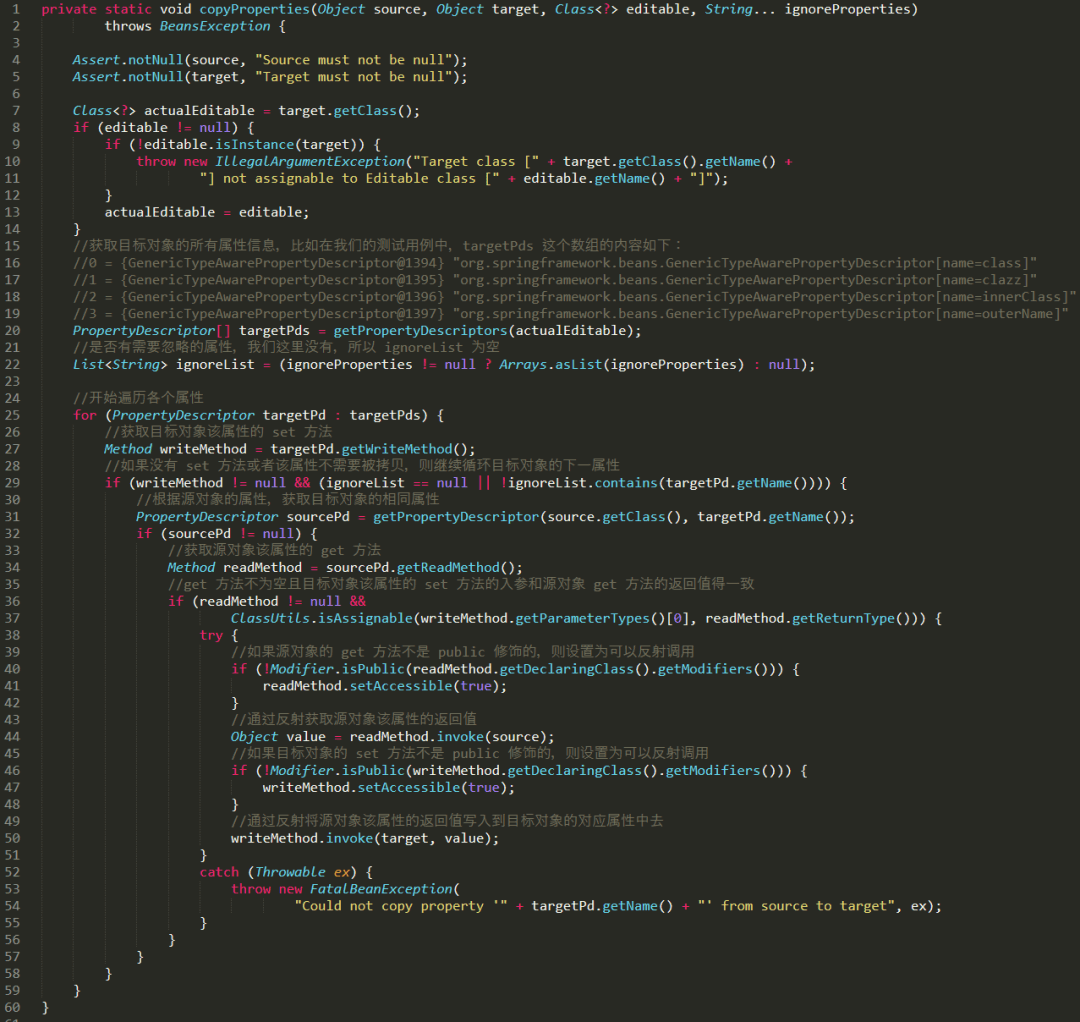
可以看到,成员变量赋值是基于目标对象的成员列表,并且会跳过ignore的以及在源对象中不存在,所以这个方法是安全的,不会因为两个对象之间的结构差异导致错误,但是必须保证同名的两个成员变量类型相同
所以从上面的源码解读中我可以得到这样的几条结论:
- 对于要复制的属性,目标对象必须要有对应的 set 方法(上图的第 27 行),源对象必须要有对应的 get 方法(上图的第 34 行)。
- 对于要复制的属性,目标对象和源对象的属性名称得一模一样。(上图的第 34 行)。
目标对象对应的 set 方法的入参和源对象对应的 get 方法的返回类型必须得一致(上图的第 37 行)。
Spring 的 BeanUtils 的
CopyProperties方法拷贝内部类的时候有问题内部类其实就是 Java 的一颗语法糖而已。
比如常用的自动拆箱、自动装箱、高级 for 循环、泛型等等,包括 JDK 10 那个不三不四的局部变量类型推断功能,就是那个 var,也是语法糖而已。
那么内部类这颗语法糖长什么样子呢?
现在先记住这个几个 class 类。
通过代码来验证一下内部类拷贝时的问题:
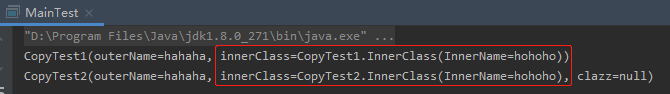
两个对象 CopyTest1 和 CopyTest2,对象的结构和里面的属性看起来是一模一样的:@ToString@Datapublic class CopyTest1 {public String outerName;public CopyTest1.InnerClass innerClass;public List<CopyTest1.InnerClass> clazz;@ToString@Datapublic static class InnerClass {public String InnerName;}}
@ToString@Datapublic class CopyTest2 {public String outerName;public CopyTest2.InnerClass innerClass;public List<CopyTest2.InnerClass> clazz;@ToString@Datapublic static class InnerClass {public String InnerName;}}
public class MainTest {public static void main(String[] args) {CopyTest1 test1 = new CopyTest1();test1.outerName = "hahaha";CopyTest1.InnerClass innerClass = new CopyTest1.InnerClass();innerClass.InnerName = "hohoho";test1.innerClass = innerClass;System.out.println(test1.toString());CopyTest2 test2 = new CopyTest2();BeanUtils.copyProperties(test1, test2);System.out.println(test2.toString());}}
来验证一下。
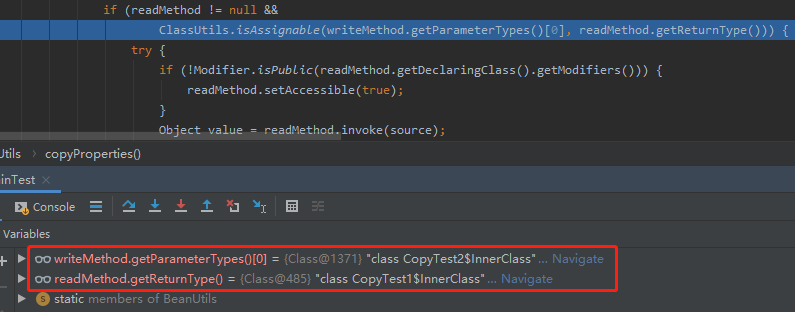
源对象set方法的入参是CopyTest2$InnerClass,而目标对象get方法的返参是CopyTest1$InnerClass。
不满足前面总结出来的第三点,所以不会拷贝成功。
解决方案是单独设置一下内部类,单独 copy。
如果内部类的 bean 属性较多或者递归的 bean 属性很多,那可以自己封装一个方法,用于递归拷贝,这里只有一层,所以直接额外 copy 一次。public class MainTest {public static void main(String[] args) {CopyTest1 test1 = new CopyTest1();test1.outerName = "hahaha";CopyTest1.InnerClass innerClass = new CopyTest1.InnerClass();innerClass.InnerName = "hohoho";test1.innerClass = innerClass;System.out.println(test1.toString());CopyTest2 test2 = new CopyTest2();test2.innerClass = new CopyTest2.InnerClass();BeanUtils.copyProperties(test1, test2);BeanUtils.copyProperties(test1.innerClass, test2.innerClass);System.out.println(test2.toString());}}
小结
以上简要的分析两种BeanUtils,因为Apache下的BeanUtils性能较差,不建议使用,可以使用 Spring的BeanUtils,或者使用其他拷贝框架,比如 cglib BeanCopier,基于javassist的Orika等,这些也是非常优秀的类库,值得去尝试。