1.1 从迭代到流的操作
流与集合的差异:
- 流并不存储其元素
- 流的操作不会修改其数据源
- 流的操作是尽可能惰性执行的 ```java package streams;
import java.io.IOException; import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets; import java.nio.file.Files; import java.nio.file.Paths; import java.util.List;
/**
Created by ql on 2022/5/30 */ public class CountLongWords { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
var contents = new String(Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D:\\IdeaProjects\\java-study\\gutenberg\\alice30.txt")), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);List<String> words = List.of(contents.split("\\PL+"));long count = 0;for (String w : words) {if (w.length() > 12)count++;}System.out.println(count);count = words.stream().filter(w -> w.length() > 12).count();System.out.println(count);count = words.parallelStream().filter(w -> w.length() > 12).count();System.out.println(count);
} }
运行结果:<br />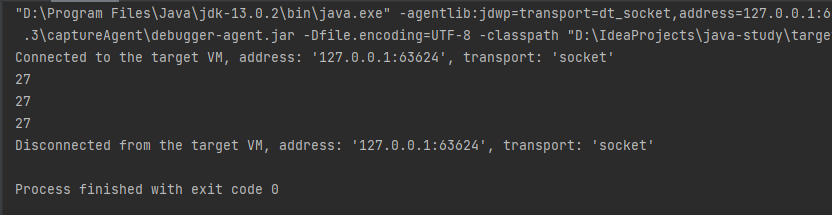```java//产生一个流,其中包含当前流中满足p的所有元素Stream<T> filter(Predicate<? super T> predicate);//产生当前流中元素的数量。这是一个终止操作long count();
//产生当前集合中所有元素的顺序流或并行流default Stream<E> stream()default Stream<E> parallelStream()
1.2 流的创建
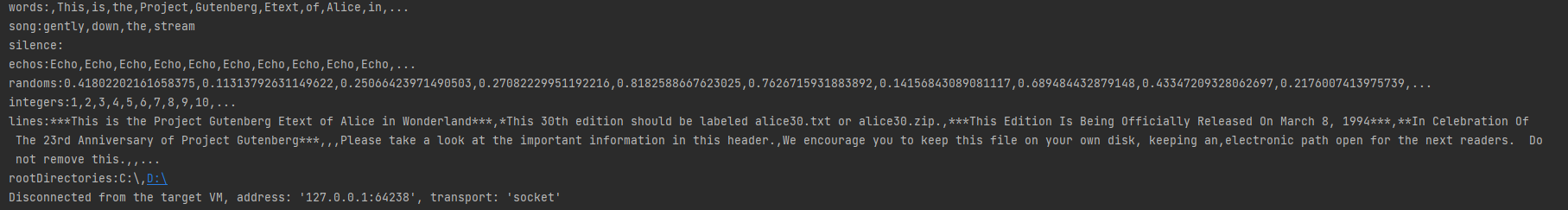
package streams;import java.io.IOException;import java.math.BigInteger;import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;import java.nio.file.FileSystems;import java.nio.file.Files;import java.nio.file.Path;import java.nio.file.Paths;import java.util.List;import java.util.stream.Collectors;import java.util.stream.Stream;import java.util.stream.StreamSupport;/*** Created by ql on 2022/5/30*/public class CreatingStreams {public static <T> void show(String title, Stream<T> stream){final int SIZE = 10;List<T> firstElements = stream.limit(SIZE + 1).collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.print(title + ":");for (int i = 0; i < firstElements.size(); i++) {if (i > 0)System.out.print(",");if (i < SIZE)System.out.print(firstElements.get(i));elseSystem.out.print("...");}System.out.println();}public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {Path path = Paths.get("D:\\IdeaProjects\\java-study\\gutenberg\\alice30.txt");String contents = new String(Files.readAllBytes(path), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);Stream<String> words = Stream.of(contents.split("\\PL+"));show("words", words);// 产生一个元素为给定值的流Stream<String> song = Stream.of("gently", "down", "the", "stream");show("song", song);//产生一个不包含任何元素的流Stream<String> silence = Stream.empty();show("silence", silence);//产生一个无限流,它的值是通过反复调用函数而构建的Stream<String> echos = Stream.generate(() -> "Echo");show("echos", echos);Stream<Double> randoms = Stream.generate(Math::random);show("randoms", randoms);//public static<T> Stream<T> iterate(final T seed, final UnaryOperator<T> f)// 产生一个无限流,它的元素包含seed,在seed上调用f产生的值、在前一个元素上调用f产生的值Stream<BigInteger> integers = Stream.iterate(BigInteger.ONE, n -> n.add(BigInteger.ONE));show("integers", integers);// 产生一个流,元素是指定文件中的行,并指定字符集try (Stream<String> lines = Files.lines(path, StandardCharsets.UTF_8)){show("lines", lines);}Iterable<Path> iterable = FileSystems.getDefault().getRootDirectories();Stream<Path> rootDirectories = StreamSupport.stream(iterable.spliterator(), false);show("rootDirectories", rootDirectories);}}