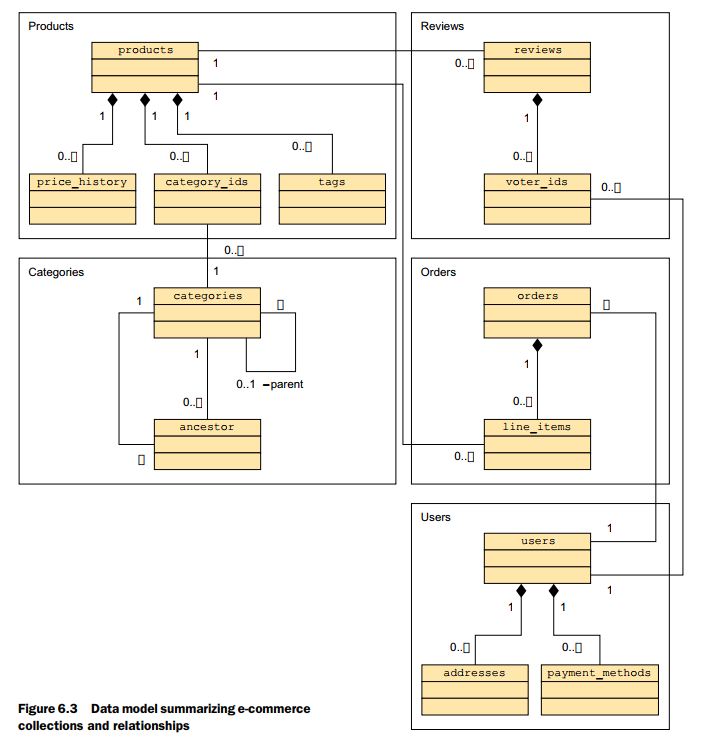
6.1 Aggregation framework overview
A call to the aggregation framework defines a pipeline , the aggregation pipeline, where the output from each step in the pipeline provides input to the next step. Each step executes a single operation on the input documents to transform the input and generate output documents.
$project: specify fields to be placed in the output document$match$limit$skip$unwind$group$sort$geoNear:Select documents near a geospatial location$out$redact: Control access to certain data
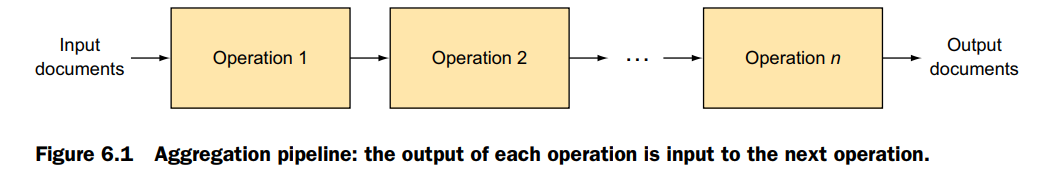
db.products.aggregate([ {$match: …}, {$group: …}, {$sort: …} ] )
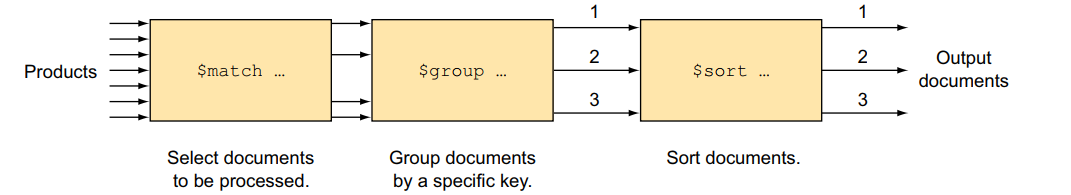
a detailed comparison of SQL commands to the aggregation framework operators
6.2 E-commerce aggregation example
6.2.1 Products, categories, and reviews
an example of counting the number of reviews for a given product using this query:
product = db.products.findOne({'slug': 'wheelbarrow-9092'})reviews_count = db.reviews.count({'product_id': product['_id']})
how to do this using the aggregation framework
db.reviews.aggregate([{$group : { _id:'$product_id', // Group the input documents by product_idcount:{$sum:1} }} // Count the number of reviews for each product]);

add one more operator to your pipline so that you select only the one product you want to get a count for:
product = db.products.findOne({'slug': 'wheelbarrow-9092'})ratingSummary = db.reviews.aggregate([{$match : { product_id: product['_id']} }, // Select only a single product{$group : { _id:'$product_id',count:{$sum:1} }}]).next(); // Return the first document in the results
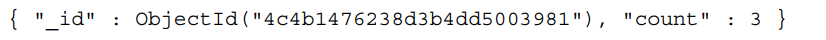
Calculating the average review
product = db.products.findOne({'slug': 'wheelbarrow-9092'})ratingSummary = db.reviews.aggregate([{$match : {'product_id': product['_id']}},{$group : { _id:'$product_id',average:{$avg:'$rating'}, // Calculate the average rating for a productcount: {$sum:1}}}]).next();
Counting reviews by rating
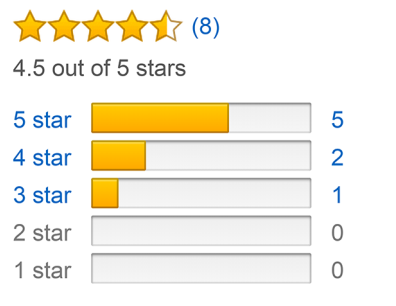
countsByRating = db.reviews.aggregate([{$match : {'product_id': product['_id']}}, // Select product{$group : { _id:'$rating', // Group by value of rating: '$rating'count:{$sum:1}}} // Count number of reviews for each rating]).toArray(); // Convert resulting cursor to an array
Joining collections
db.mainCategorySummary.remove({}); // Remove existing documents from mainCategorySummary collectiondb.products.aggregate([{$group : { _id:'$main_cat_id',count:{$sum:1}}}]).forEach(function(doc){var category = db.categories.findOne({_id:doc._id}); // Read category for a resultif (category !== null) { // You aren't guaranteed the category actually exists!doc.category_name = category.name;}else {doc.category_name = 'not found';}db.mainCategorySummary.insert(doc); // Insert cominned result into your summary collection})
$out and $project
With the $out operator, you can automatically save the output from a pipeline into a collection.
db.products.aggregate([{$group : { _id:'$main_cat_id',count:{$sum:1}}},{$out : 'mainCategorySummary'} // Save pipeline results to collection mainCategorySummary])
The $project operator allows you to filter which fields will be passed to the next stage of the pipeline.
Although $match allows you to limit how much data is passed to the next stage by limiting the number of documents passed, $project can be used to limit the size of each document passed to the next stage.
The following is an example of a $project operator that limits the output documents to just the list of category IDs used for each product:
db.products.aggregate([{$project : {category_ids:1}}]);
Faster joins with $unwind
db.products.aggregate([{$project : {category_ids:1}},{$unwind : '$category_ids'}, // Create an output document for every array entry in category_ids{$group : { _id:'$category_ids',count:{$sum:1}}},{$out : 'countsByCategory'}]);