1、文档
- ModbusTCP协议 介绍
- Modbus功能码
- 模拟工具下载链接: 密码:6v8r
- Java实现ModbusTCP通信
- modbus tcp 通讯modbus-master-tcp Java使用说明
- modbus4j官网(java实现)
2、相关问题
2.1、报文解析
- 描述:
使用wireshark 抓包分析
- 解决方案:
问题的解决方案
请求:00 C4 00 00 00 06 03 03 00 00 00 04事务处理标识 协议标识:tcp 后面的数据长度 设备地址 功能码 起始地址 寄存器数量4个响应00 C4 00 00 00 0B 03 03 08 45 0F 4B AE 00 02 00 03事务处理标识 协议标识:tcp 后面的数据长度 设备地址 功能码 报文长度 寄存器0的值 寄存器1的值 寄存器2的值 寄存器3的值
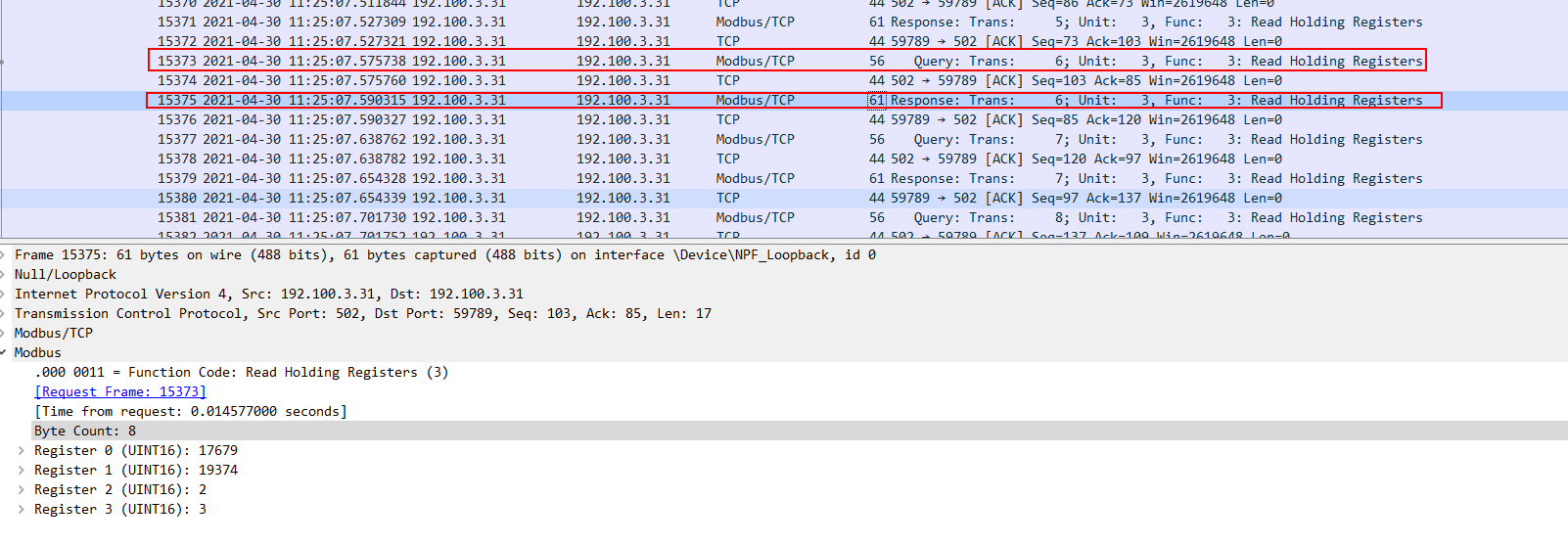
请求到相应的时间差15ms
2.2、字节数组转为浮点类型
1、data为四个字节的字节数组,类型:Float AB CD AB低位字节 CD高位字节
big-endian:大端,将高序字节存储在起始地址(高位编址)
将最低的字节移到最高位,所以索引0左移24位,1左移16位 依次类推
Float.intBitsToFloat((data[offset] & 255) << 24 |(data[offset + 1] & 255) << 16 |(data[offset + 2] & 255) << 8 |data[offset + 3] & 255);
2、bytes为四个字节的字节数组,类型:Float CD AB AB低位字节 CD高位字节
little-endian by swap:小端交换,将低序字节存储在起始地址(低位编址)
Float.intBitsToFloat(((bytes[0] & 0xff) << 8) |(bytes[1] & 0xff) |((bytes[2] & 0xff) << 24) |((bytes[3] & 0xff) << 16));
3、bytes为四个字节的字节数组,类型:Float BA DC AB低位字节 CD高位字节
big-endian by swap:大端交换,将高序字节存储在起始地址(高位编址)
public static float toFloatBigEndianBySwap(byte[] bytes) {return Float.intBitsToFloat(((bytes[0] & 0xff) << 16) |((bytes[1] & 0xff) << 24) |(bytes[2] & 0xff) |((bytes[3] & 0xff) << 8));}
4、bytes为四个字节的字节数组,类型:Float DC BA AB低位字节 CD高位字节
little-endian :小端,将低序字节存储在起始地址(低位编址)
public static float toFloatLittleEndian(byte[] bytes) {return Float.intBitsToFloat((bytes[0] & 0xff) |(bytes[1] & 0xff) << 8 |(bytes[2] & 0xff) << 16 |(bytes[3] & 0xff) << 24);}

