5、playbook
> playbook是由一个或多个"play"组成的列表> play的主要功能在于将预定义的一组主机,装扮成事先通过ansible中的task定义好的角色。Task实际是调用ansible的一个module,将多个play组织在一个playbook中,即可以让它们联合起来,按事先编排的机制执行预定义的动作> Playbook采用YAML语言编写
5.1、playbook图解
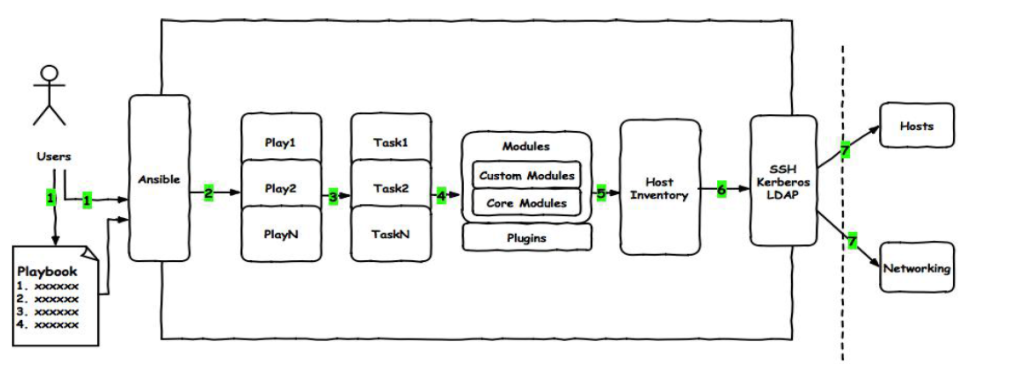
用户通过ansible命令直接调用yml语言写好的playbook,playbook由多条play组成每条play都有一个任务(task)相对应的操作,然后调用模块modules,应用在主机清单上,通过ssh远程连接从而控制远程主机或者网络设备
5.2、YAML介绍
YAML是一个可读性高的用来表达资料序列的格式。YAML参考了其他多种语言,包括:XML、C语言、Python、Perl以及电子邮件格式RFC2822等。Clark Evans在2001年在首次发表了这种语言,另外Ingy döt Net与Oren Ben-Kiki也是这语言的共同设计者YAML Ain't Markup Language,即YAML不是XML。不过,在开发的这种语言时,YAML的意思其实是:"Yet Another Markup Language"(仍是一种标记语言)特性YAML的可读性好YAML和脚本语言的交互性好YAML使用实现语言的数据类型YAML有一个一致的信息模型YAML易于实现YAML可以基于流来处理YAML表达能力强,扩展性好更多的内容及规范参见:http://www.yaml.org
5.2.1、YAML语法简介
> 在单一档案中,可用连续三个连字号(——)区分多个档案。另外,还有选择性的连续三个点号( ... )用来表示档案结尾> 次行开始正常写Playbook的内容,一般建议写明该Playbook的功能> 使用#号注释代码> 缩进必须是统一的,不能空格和tab混用> 缩进的级别也必须是一致的,同样的缩进代表同样的级别,程序判别配置的级别是通过缩进结合换行来实现的> YAML文件内容是区别大小写的,k/v的值均需大小写敏感> 多个k/v可同行写也可换行写,同行使用:分隔> v可是个字符串,也可是另一个列表[]> 一个完整的代码块功能需最少元素需包括 name 和 task> 一个name只能包括一个task> YAML文件扩展名通常为yml或yaml
List:列表,其所有元素均使用“-”打头列表代表同一类型的元素示例:# A list of tasty fruits- Apple- Orange- Strawberry- MangoDictionary:字典,通常由多个key与value构成 键值对示例:---# An employee recordname: Example Developerjob: Developerskill: Elite也可以将key:value放置于{}中进行表示,用,分隔多个key:value示例:---# An employee record{name: Example Developer, job: Developer, skill: Elite} 有空格
5.2.2、YAML语法
YAML的语法和其他高阶语言类似,并且可以简单表达清单、散列表、标量等数据结构。其结构(Structure)通过空格来展示,序列(Sequence)里的项用"-"来代表,Map里的键值对用":"分隔示例name: John Smithage: 41gender: Malespouse:name: Jane Smithage: 37gender: Femalechildren:- name: Jimmy Smithage: 17gender: Male- name: Jenny Smithage 13gender: Female
5.2.3、三种常见的数据交换格式
5.3、playbook核心元素
Hosts 执行的远程主机列表(应用在哪些主机上)Tasks 任务集Variables 内置变量或自定义变量在playbook中调用Templates模板 可替换模板文件中的变量并实现一些简单逻辑的文件Handlers和notify结合使用,由特定条件触发的操作,满足条件方才执行,否则不执行tags标签 指定某条任务执行,用于选择运行playbook中的部分代码。ansible具有幂等性,因此会自动跳过没有变化的部分,即便如此,有些代码为测试其确实没有发生变化的时间依然会非常地长。此时,如果确信其没有变化,就可以通过tags跳过此些代码片断ansible-playbook -t tagsname useradd.yml
5.4、playbook基础组件
Hosts:> playbook中的每一个play的目的都是为了让特定主机以某个指定的用户身份执行任务。hosts用于指定要执行指定任务的主机,须事先定义在主机清单中> 可以是如下形式:one.example.comone.example.com:two.example.com192.168.1.50192.168.1.*> Websrvs:dbsrvs 或者,两个组的并集> Websrvs:&dbsrvs 与,两个组的交集> webservers:!phoenix 在websrvs组,但不在dbsrvs组示例: - hosts: websrvs:dbsrvsremote_user:可用于Host和task中。也可以通过指定其通过sudo的方式在远程主机上执行任务,其可用于play全局或某任务;此外,甚至可以在sudo时使用sudo_user指定sudo时切换的用户- hosts: websrvsremote_user: root (可省略,默认为root) 以root身份连接tasks: 指定任务- name: test connectionping:remote_user: magedusudo: yes 默认sudo为rootsudo_user:wang sudo为wangtask列表和action任务列表task:由多个动作,多个任务组合起来的,每个任务都调用的模块,一个模块一个模块执行1> play的主体部分是task list,task list中的各任务按次序逐个在hosts中指定的所有主机上执行,即在所有主机上完成第一个任务后,再开始第二个任务2> task的目的是使用指定的参数执行模块,而在模块参数中可以使用变量。模块执行是幂等的,这意味着多次执行是安全的,因为其结果均一致3> 每个task都应该有其name,用于playbook的执行结果输出,建议其内容能清晰地描述任务执行步骤。如果未提供name,则action的结果将用于输出
tasks:任务列表两种格式:(1) action: module arguments(2) module: arguments 建议使用 模块: 参数注意:shell和command模块后面跟命令,而非key=value某任务的状态在运行后为changed时,可通过"notify"通知给相应的handlers任务可以通过"tags"打标签,可在ansible-playbook命令上使用-t指定进行调用示例:tasks:- name: disable selinux 描述command: /sbin/setenforce 0 模块名: 模块对应的参数
如果命令或脚本的退出码不为零,可以使用如下方式替代tasks:- name: run this command and ignore the resultshell: /usr/bin/somecommand || /bin/true转错为正 如果命令失败则执行 true或者使用ignore_errors来忽略错误信息tasks:- name: run this command and ignore the resultshell: /usr/bin/somecommandignore_errors: True 忽略错误
5.5、playbook命令
运行playbook的方式ansible-playbook <filename.yml> ... [options]常见选项--check -C 只检测可能会发生的改变,但不真正执行操作(只检查语法,如果执行过程中出现问题,-C无法检测出来)(执行playbook生成的文件不存在,后面的程序如果依赖这些文件,也会导致检测失败)--list-hosts 列出运行任务的主机--list-tags 列出tag (列出标签)--list-tasks 列出task (列出任务)--limit 主机列表 只针对主机列表中的主机执行-v -vv -vvv 显示过程示例ansible-playbook hello.yml --check 只检测ansible-playbook hello.yml --list-hosts 显示运行任务的主机ansible-playbook hello.yml --limit websrvs 限制主机
5.6、Playbook VS ShellScripts
安装httpd
SHELL脚本#!/bin/bash# 安装Apacheyum install --quiet -y httpd# 复制配置文件cp /tmp/httpd.conf /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.confcp/tmp/vhosts.conf /etc/httpd/conf.d/# 启动Apache,并设置开机启动service httpd startchkconfig httpd on
Playbook定义---- hosts: allremote_user: roottasks:- name: "安装Apache"yum: name=httpd yum模块:安装httpd- name: "复制配置文件"copy: src=/tmp/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/ copy模块: 拷贝文件- name: "复制配置文件"copy: src=/tmp/vhosts.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf.d/- name: "启动Apache,并设置开机启动"service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes service模块: 启动服务
5.7、Playbook 示例
5.7.1、创建用户
示例:sysuser.yml---- hosts: allremote_user: roottasks:- name: create mysql useruser: name=mysql system=yes uid=36- name: create a groupgroup: name=httpd system=yes
5.7.2、安装httpd服务
示例:httpd.yml- hosts: websrvsremote_user: roottasks:- name: Install httpdyum: name=httpd state=present- name: Install configure filecopy: src=files/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/- name: start serviceservice: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
5.7.3、 安装nginx服务
示例 nginx.yml- hosts: allremote_user: roottasks:- name: add group nginxuser: name=nginx state=present- name: add user nginxuser: name=nginx state=present group=nginx- name: Install Nginxyum: name=nginx state=present- name: Start Nginxservice: name=nginx state=started enabled=yes
5.8、handlers和notify
5.8.1、handlers和notify结合使用触发条件
Handlers 实际上就是一个触发器是task列表,这些task与前述的task并没有本质上的不同,用于当关注的资源发生变化时,才会采取一定的操作Notify此action可用于在每个play的最后被触发,这样可避免多次有改变发生时每次都执行指定的操作,仅在所有的变化发生完成后一次性地执行指定操作。在notify中列出的操作称为handler,也即notify中调用handler中定义的操作
5.8.2、Playbook中handlers使用
- hosts: websrvsremote_user: roottasks:- name: Install httpdyum: name=httpd state=present- name: Install configure filecopy: src=files/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/notify: restart httpd- name: ensure apache is runningservice: name=httpd state=started enabled=yeshandlers:- name: restart httpdservice: name=httpd state=restarted
- hosts: webnodesvars:http_port: 80max_clients: 256remote_user: roottasks:- name: ensure apache is at the latest versionyum: name=httpd state=latest- name: ensure apache is runningservice: name=httpd state=started- name: Install configure filecopy: src=files/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/notify: restart httpdhandlers:- name: restart httpdservice: name=httpd state=restarted
- hosts: websrvsremote_user: roottasks:- name: add group nginxtags: useruser: name=nginx state=present- name: add user nginxuser: name=nginx state=present group=nginx- name: Install Nginxyum: name=nginx state=present- name: configcopy: src=/root/config.txt dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.confnotify:- Restart Nginx- Check Nginx Processhandlers:- name: Restart Nginxservice: name=nginx state=restarted enabled=yes- name: Check Nginx processshell: killall -0 nginx > /tmp/nginx.log
5.9、Playbook中tags使用
tage: 添加标签可以指定某一个任务添加一个标签,添加标签以后,想执行某个动作可以做出挑选来执行多个动作可以使用同一个标签示例:httpd.yml- hosts: websrvsremote_user: roottasks:- name: Install httpdyum: name=httpd state=presenttage: install- name: Install configure filecopy: src=files/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/tags: conf- name: start httpd servicetags: serviceservice: name=httpd state=started enabled=yesansible-playbook –t install,conf httpd.yml 指定执行install,conf 两个标签
5.9.1、示例
//heartbeat.yaml- hosts: hbhostsremote_user: roottasks:- name: ensure heartbeat latest versionyum: name=heartbeat state=present- name: authkeys configure filecopy: src=/root/hb_conf/authkeys dest=/etc/ha.d/authkeys- name: authkeys mode 600file: path=/etc/ha.d/authkeys mode=600notify:- restart heartbeat- name: ha.cf configure filecopy: src=/root/hb_conf/ha.cf dest=/etc/ha.d/ha.cfnotify:- restart heartbeathandlers:- name: restart heartbeatservice: name=heartbeat state=restarted
- hosts: testsrvremote_user: roottags: inshttpd 针对整个playbook添加tagetasks:- name: Install httpdyum: name=httpd state=present- name: Install configure filecopy: src=files/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/tags: rshttpdnotify: restart httpdhandlers:- name: restart httpdservice: name=httpd status=restartedansible-playbook –t rshttpd httpd2.yml