图通常由顶点和弧线组成。 有时,它们也称为节点(而不是顶点)和边(而不是弧)。 为了本教程的缘故,我将使用节点和边作为参考。

图通常看起来像这样:
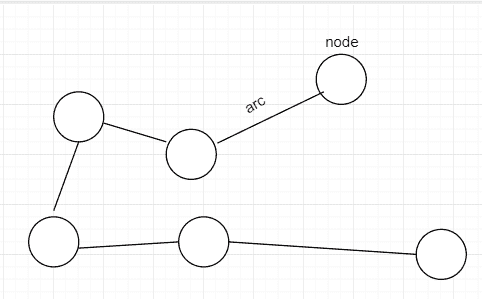
图可视化
在许多情况下,节点和边被分配了值。 一个非常有用的图的著名示例是,当节点代表城市并且边沿代表这两个节点(或与此有关的城市)之间的距离时。 这样的例子可以在下面看到:

从上图判断,很容易理解它代表什么,也很容易阅读。 芝加哥到纽约的距离是 791.5 英里,纽约和华盛顿特区的距离是 227.1 英里。
这只是一个简单的示例,说明如何使用图很有用,但是还有更多示例。
图的其他有用示例可能是表示家谱,facebook 联系人,甚至是旅行路线。
无向图
当图无向时,这意味着可以在两个方向上遍历边。
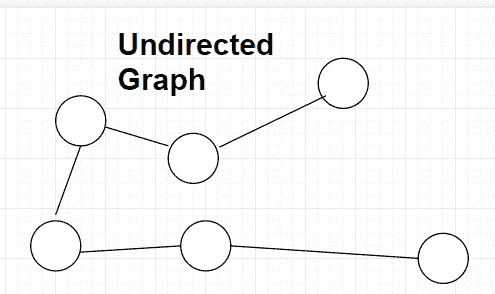
无向图
有向图
定向图时,这意味着只能沿其“指向”的方向遍历这些边。
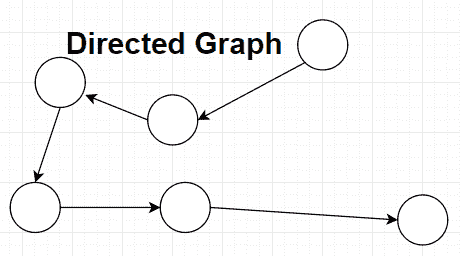
有向图
Java 中的图实现
Node.java
import java.util.*;public class Node {private int id;private List<Edge> neighbours = new ArrayList<Edge>();public int getNodeId() {return this.id;}public void addNeighbour(Edge e) {if(this.neighbours.contains(e)) {System.out.println("This edge has already been used for this node.");} else {System.out.println("Successfully added " + e);this.neighbours.add(e);}}public void getNeighbours() {System.out.println("List of all edges that node " + this.id +" has: ");System.out.println("=================================");for (int i = 0; i < this.neighbours.size(); i++ ){System.out.println("ID of Edge: " + neighbours.get(i).getId() + "\nID of the first node: " + neighbours.get(i).getIdOfStartNode() +"\nID of the second node: " + neighbours.get(i).getIdOfEndNode());System.out.println();}System.out.println(neighbours);}public Node(int id) {this.id = id;}}
Node.java有 3 个方法和 1 个构造函数。
getNodeId()仅返回每个节点的 ID。
addNeighbour(Edge e)通过边创建连接,该边作为参数传递到另一个节点。 这是通过将指定的边添加到Node类的边列表中来完成的。 注意,存在一个if条件,用于检查此节点的当前边中是否已经存在指定的边e。
getNeighbours()仅用于显示目的。 查看输出,以查看此方法显示信息的精确程度。
构造函数将id作为参数。
Edge.java
public class Edge {private Node start;private Node end;private double weight;private int id;public int getId() {return this.id;}public Node getStart() {return this.start;}public int getIdOfStartNode() {return this.start.getNodeId();}public Node getEnd() {return this.end;}public int getIdOfEndNode() {return this.end.getNodeId();}public double getWeight() {return this.weight;}public Edge(Node s, Node e, double w, int id) {this.start = s;this.end = e;this.weight = w;this.id = id;}}
Edge.java有 6 个方法和 1 个构造函数。
getId()仅返回当前边的 ID。
getStart()返回边从其开始的Node对象。
getIdOfStartNode()返回边从其开始的Node对象的 ID。
getEnd()返回边“停止”在的Node对象。
getIdOfEndNode()返回边“停止”在的Node对象的 ID。
getWeight()获取当前Node对象的权重。
Edge构造函数采用 4 个参数,并使用它们初始化构造函数。
Graph.java
import java.util.*;public class Graph {private List<Node> nodes = new ArrayList<Node>();private int numberOfNodes = 0;public boolean checkForAvailability() { // will be used in Main.javareturn this.numberOfNodes > 1;}public void createNode(Node node) {this.nodes.add(node);this.numberOfNodes++; // a node has been added}public int getNumberOfNodes() {return this.numberOfNodes;}}
Graph.java只有 3 个方法,没有构造函数。
checkForAvailability()检查是否有多个节点。 如果节点数不超过 1 个,则无法建立连接,因为节点本身不能具有优势。 它必须与另一个节点建立连接。
createNode(Node node)接受类型为Node的参数,并将该节点添加到节点List中。 添加节点后,当前图会将节点数增加 1。这样,我们就可以在某个时候将checkForAvailability()方法评估为true。
getNumberOfNodes()返回节点数。
Main.java
public class Main {public static void main(String args[]) {Graph graph = new Graph();Node node1 = new Node(1); // create a new node that contains id of 1Node node2 = new Node(2); // create a new node that contains id of 2Node node3 = new Node(3); // create a new node that contains id of 3graph.createNode(node1); // numberOfNodes should increment by 1graph.createNode(node2); // numberOfNodes should increment by 1graph.createNode(node3); // numberOfNodes should increment by 1Edge e12 = new Edge(node1, node2, 5, 1); // create an edge that connects node1 to node2 and contains weight of 5Edge e13 = new Edge(node1, node3, 10, 2); // create an edge that connects node1 to node3 and contains weight of 10if (graph.checkForAvailability()) {// two nodes can be connected via edgenode1.addNeighbour(e12); // connect 1 and 2 (nodes)node1.addNeighbour(e13);node1.getNeighbours();} else {System.out.println("There are less than 2 nodes. Add more to connect.");}}}
Main.java只有一个main方法。
在main方法中创建一个图。 之后,将创建 3 个Node实例。 然后,使用createNode(Node node)方法将这些Node实例添加到图中。 之后,将创建 2 个Edge实例。 第一个将节点 1 连接到节点 2。第二个将节点 1 连接到节点 3。
此后,存在一个if条件,该条件检查节点数是否大于 1,如果超过,则将Neighbour添加到node1。 (e12是连接node1和node2的边。)(e13是连接node1和node3的边)。
输出
Successfully added Edge@15db9742Successfully added Edge@6d06d69cList of all edges that node 1 has:=================================ID of Edge: 1ID of the first node: 1ID of the second node: 2ID of Edge: 2ID of the first node: 1ID of the second node: 3[Edge@15db9742, Edge@6d06d69c]
可视化以上输出:
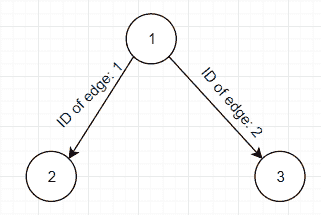
问题:是上述程序生成的无向还是有向图? 如果它生成未定义的图,您可以修改 API 来生成定向的图吗? 如果生成有向图,您是否可以修改 API 以生成无向?
答案:上面的图产生一个定向的图,因为顾名思义,弧线“指向”某个位置。 要使其成为无向,您只需删除圆弧的“箭头”,然后将其作为一条简单的线即可。 就像下面的图片代表无向图一样。

