一、概述
- 反射被视为动态语言的关键,反射机制允许程序在执行期间借助于Reflection API取得任何类的内部信息,并能直接操作任意对象的内部属性及方法。
- 加载完类后,方法区(MetaSpace)会有这个类的字节码文件,在堆内存中就会产生一个CLass类型的对象,这个对象就包含了类的结构信息。我们可以通过这个对象看到类的结构。这个对象就像一面镜子,透过这个镜子看到类的结构(通过CLass看方法区中的字节码),所以,我们形象的称之为:反射。
二、反射简单示例
public class Person {private int age;private String name;public Person(int age, String name) {this.age = age;this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public void show(){System.out.println("秀一下");}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Person{" +"age=" + age +", name='" + name + '\'' +'}';}}
public class Demo01 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {Class<Person> personClass = Person.class;Constructor<Person> constructor = personClass.getConstructor(int.class,String.class);// 创建了这个对象Person king = constructor.newInstance( 12,"king");System.out.println(king);// 获取class中的这个字段Field age = personClass.getDeclaredField("age");// 无视privateage.setAccessible(true);// 给king对象中的age字段设置参数age.set(king,100);System.out.println(king);age.setAccessible(false);// 获取class中的show方法Method show = personClass.getDeclaredMethod("show");// 执行king对象中的show方法show.invoke(king);}}
疑问:
1、通过直接new的方式或反射的方式都可以直接调用公共的结构,开发中到底用哪个?
建议直接用new的方式
2、什么时候用到反射
编译的时候不确定用哪个对象,反射特征:动态性,例如动态代理
3、反射机制与面向对象中的封装性是不是矛盾的?如果看待两个技术?
不矛盾。反射解决的问题是怎么调用,封装解决的问题是:哪些方法建议使用,哪些方法不建议使用
三、理解Class类并获取Class实例(掌握)
1、类的加载过程
程序经过javac命令后,会生成一个或多个字节码文件(.class),接着我们使用java命令来对某个字节码文件进行解释运行,相当于将某个字节码文件加载到内存中。此过程称之为加载。加载到内存中的类,我们称之为运行时类,此运行时类,就作为Class的一个实例。
换句话说,Class的实例就对应着加载到内存中的一个运行时类。
2、获取Class实例
- 方式一:调用运行时类的属性:class
Class<Person> personClass = Person.class;
- 方式二:通过运行时类的对象,调用getClass()
Person person = new Person();Class aClass = person.getClass();
- 方式三:调用Class的静态方法,forName(String classPath)
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.supkingx.base.h_reflect.Person");
- 方式四:使用类的加载器
ClassLoader classLoader = Demo01.class.getClassLoader();Class aClass1 = classLoader.loadClass("com.supkingx.base.h_reflect.Person");
四、类的加载与ClassLoader的理解(了解)

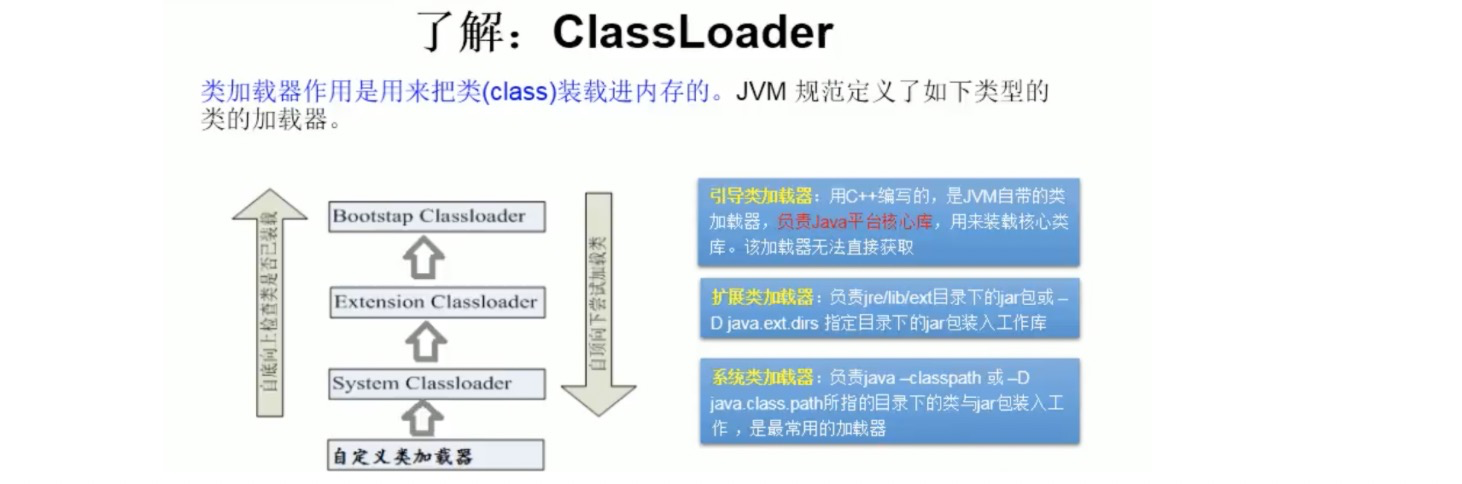
// 方式四:使用类的加载器ClassLoader classLoader = Demo01.class.getClassLoader();Class aClass1 = classLoader.loadClass("com.supkingx.base.h_reflect.Person");
public class Test01 {public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {// 获取系统类加载器ClassLoader classLoader = Test01.class.getClassLoader();Class aClass1 = classLoader.loadClass("com.supkingx.base.h_reflect.Person");System.out.println(aClass1);System.out.println(classLoader);// 通过系统类加载器的getParent(),获取扩展类加载器System.out.println(classLoader.getParent());// 通过扩展类加载器的getParent(),获取引导类加载器// 引导类加载器主要负责java的核心类库,无法加载自定义类System.out.println(classLoader.getParent().getParent());}}
// 读取配置文件public class Test02 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {Properties properties = new Properties();// 读取配置方式一// FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("/Users/superking/Documents/project/examination/src/main/resources/jdbc.properties");// 方式二:InputStream resourceAsStream = Test02.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");properties.load(resourceAsStream);String user = (String) properties.get("user");String password = (String) properties.get("password");System.out.println("user:" + user + "," + "password:" + password);}}
五、创建运行时类的对象(掌握)
public class Demo02 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {Class<Person> personClass = Person.class;// 调用此方法创建运行时类的对象(内部调用运行实时类的空参构造器)// 想要用此方法创建,必须提供public权限的空参构造器// 在javabean中要求提供一个public的空参构造器,原因:// 便于反射创建运行时类的对象// 便于子类继承此运行时类,默认调用super()时,保证父类有次构造器Person person = personClass.newInstance();System.out.println(person);}}
以下创建运行时类的方式用的比较少
Class<Person> personClass = Person.class;Constructor<Person> constructor = personClass.getConstructor(int.class,String.class);// 创建了这个对象Person king = constructor.newInstance( 12,"king");
六、调用运行时类的指定结构(掌握)
public class FieldTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {Class<Person> personClass = Person.class;Person person = personClass.newInstance();Field nameField = personClass.getDeclaredField("name");nameField.setAccessible(true);nameField.set(person,"king");System.out.println(person);String name = (String)nameField.get(person);System.out.println(name);}}
public class MethodTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException {Class<Person> personClass = Person.class;Person person = personClass.newInstance();final Method show = personClass.getDeclaredMethod("show");show.invoke(person);// 第二个参数是返回类型final Method display = personClass.getDeclaredMethod("display", String.class);System.out.println(display.invoke(person, "哈哈哈"));}}
public class ConstructorTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException {Class<Person> personClass = Person.class;Constructor<Person> declaredConstructor = personClass.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true);final Person person = declaredConstructor.newInstance("king");System.out.println(person);}}
七、反射应用:动态代理
见 代理 章节
https://www.yuque.com/wangchao-volk4/fdw9ek/pc33e3#Tzo7H
八、总结
- 关注上面几个需要掌握的内容。
- 加了declared就是获取本类的所有方法,包含私有,如果要多给私有Field设置参数,需要Field.setAccessible(true)。
- 没有加declared就是获取包含父类的所有公开方法。



