什么是阻塞队列? 当阻塞队列是空的时候,从队列中获取元素的操作将会被阻塞。 当阻塞队列是满的时候,往队列里添加元素的操作将会被阻塞。
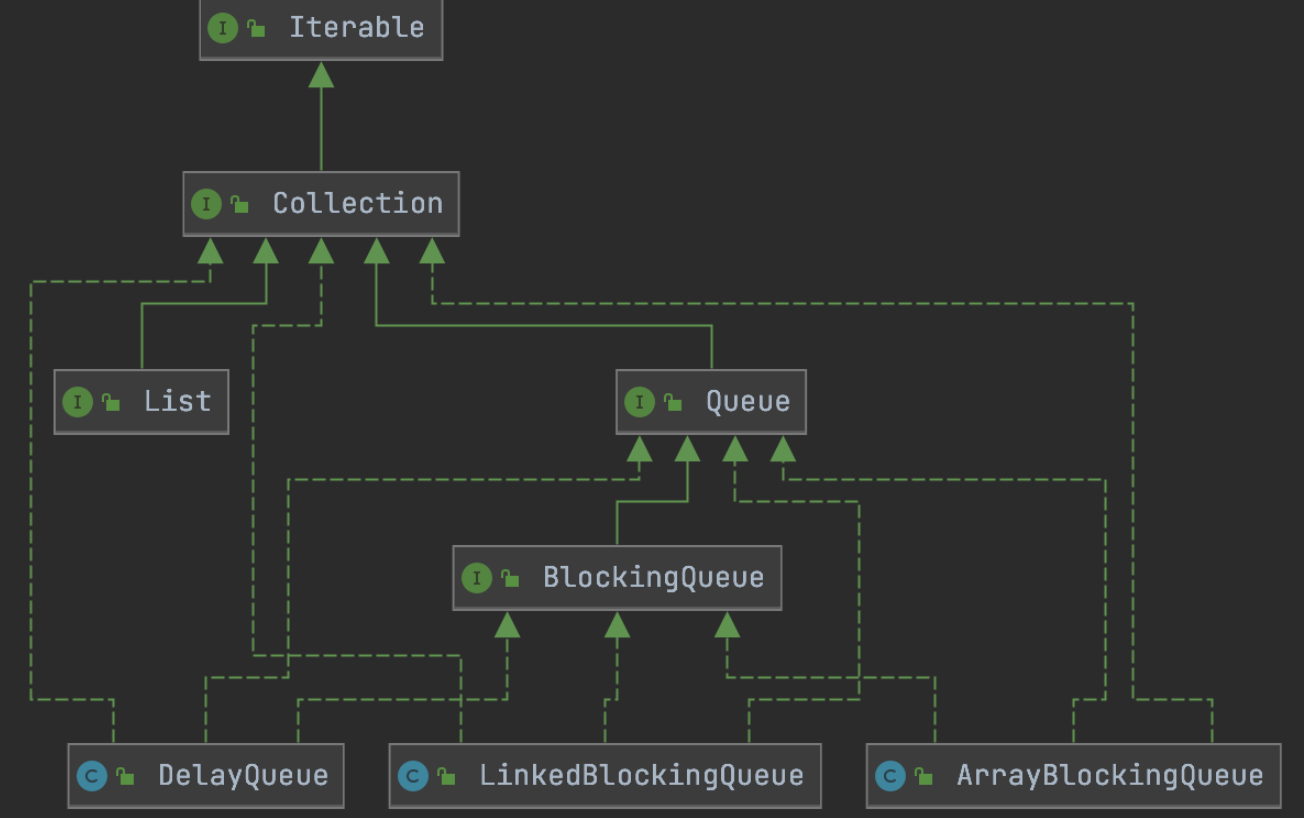
在多线程领域,所谓阻塞,在某些情况下会被挂起线程(即阻塞),一旦条件满足,被挂起的线程又会自动被唤醒。
为什么需要blockingqueue?
好处是我们不需要关心什么时候需要阻塞线程,什么时候需要唤醒线程,因为这一切blockingqueue都给包办了。
在concurrent包发布以前,在多线程环境下,我们每个程序员都必须去自己控制这些细节,尤其还要兼顾效率和线程安全,而这会给我们的程序带来不小的复杂度。
blockingqueue核心方法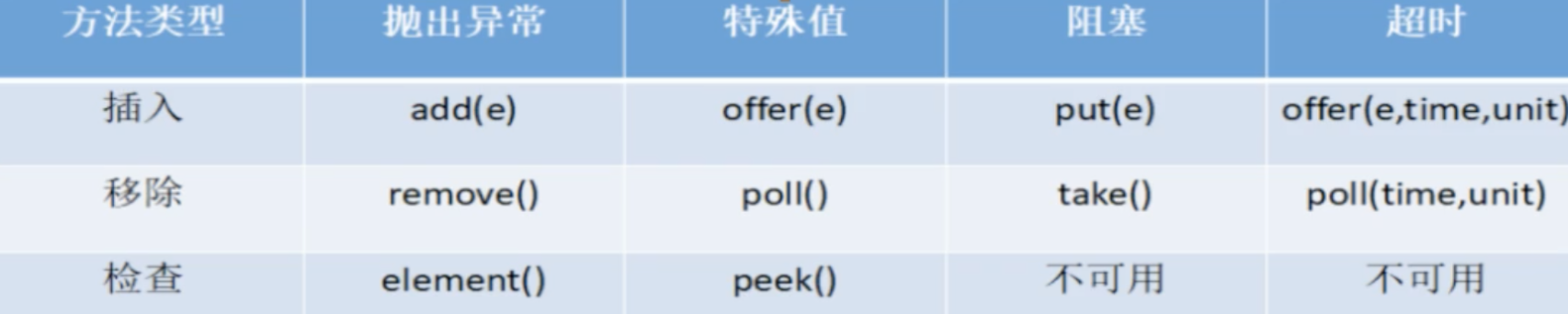
add:超过队列长度会报错,成功会返回true
Element() 返回队首元素
remove:移除 元素,没有元素可以移除则报错
offset:插入成功true,失败false,不报错
poll:取不到就返回null
peek,取出队首元素,不报错
put:只管插入没有返回值,当队列容量满时,则会等待(阻塞)
take:取出元素并返回,当无元素可取时,则会等待
Offer(e,time,unit):插入后遇到队列已满,则会等待两秒,2秒之后还是队列满的状态,则返回false
blockingQueue.offer("a", 2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
一、队列分类
ArrayBlockingQueue:由数组结构组成的有界阻塞队列
LinkedBlockingQueue:由链表结构组成的有界(但大小默认值为Integer.MAX_VALUE)阻塞队列
SynchronousQueue:不存储元素的阻塞队列,也即单个元素的队列。即只存储单个元素。
。。。。。。。
ArrayBlockingQueue
public class BlockingQueueDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {BlockingQueue<Object> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("a"));System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("b"));System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("c"));System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("x"));}}
输出,第四个会报错,队列已满
truetruetrueException in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalStateException: Queue fullat java.util.AbstractQueue.add(AbstractQueue.java:98)at java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue.add(ArrayBlockingQueue.java:312)at com.supkingx.base.j_collection.Queue.BlockingQueueDemo.main(BlockingQueueDemo.java:20)
LinkedBlockingQueue
https://blog.csdn.net/Evankaka/article/details/51706109
从LinkedBlockingQueue的源码中,我们可以看出他和ArrayBlockingQueue主要有以下两点区别: 1、ArrayBlockingQueue数据是放在一个数组中。LinkedBlockingQueue是放在一个Node节点中,构成一个链接。 2、ArrayBlockingQueue取元素和放元素都是同一个锁,而LinkedBlockingQueue有两个锁,一个放入锁,一个取得锁。分别对应放入元素和取得元素时的操作。这是由链表的结构所确定的。但是删除一个元素时,要同时获得放入锁和取得锁。
SynchronousQueue
SynchronousQueue 这个队列实现了 BlockingQueue接口。该队列的特点 1.容量为0,无论何时 size方法总是返回0
- put操作阻塞, 直到另外一个线程取走队列的元素。 3.take操作阻塞,直到另外的线程put某个元素到队列中。
- 任何线程只能取得其他线程put进去的元素,而不会取到自己put进去的元素
产生一个元素,消费一个元素。依次进行
public class BlockingQueueDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {// BlockingQueue<Object> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(1);// SynchronousQueue 只存储单个元素,直到被消费,否则就会一直阻塞,等待被消费BlockingQueue<Object> blockingQueue = new SynchronousQueue<>();new Thread(()->{try {blockingQueue.put("1");// 只有当SynchronousQueue里的元素被使用了,才会走到下一步,否则会一直阻塞,等待被使用System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t put 1");blockingQueue.put("2");System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t put 2");blockingQueue.put("3");System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t put 3");} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}},"AAA").start();new Thread(()->{try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+blockingQueue.take());TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+blockingQueue.take());TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+blockingQueue.take());} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}},"BBB").start();}}
1、如果是使用 ArrayBlockingQueue 则结果如下
AAA put 1BBB 1AAA put 2BBB 2AAA put 3BBB 3
2、如果是使用 SynchronousQueue 则结果如下
输出结果:BBB 1AAA put 1BBB 2AAA put 2BBB 3AAA put 3
注意观察结果:
blockingQueue.put(“1”);之后,会去BBB现场take()到该元素,然后回到AAA线程继续执行。
即先put,再take,一次一个元素,依次执行。
二、使用场景
1、消费者/生产者
定义资源类
public class MyResource {// 利用volatile修饰,提高可见性private volatile boolean FLAG = true; // 默认开启,进行生产+消费private AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger();BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = null;public MyResource(BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue) {this.blockingQueue = blockingQueue;System.out.println(blockingQueue.getClass().getName());}public void myProd() throws InterruptedException {String data = null;boolean retValue;while (FLAG) {// 获取数据塞入队列data = atomicInteger.incrementAndGet() + "";// 向队列添加数据,队列满了则等待2秒retValue = blockingQueue.offer(data, 2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);if (retValue) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t 插入队列" + data + "成功");} else {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t 插入队列" + data + "失败");}// 降低生产频率,给消费以时间TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500);}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t大老板叫停了,表示FLAG=false,生产动作结束");}public void myConsumer() throws InterruptedException {String result = null;while (FLAG) {// 2s取不到,就不取了result = blockingQueue.poll(2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);if (null == result || result.equalsIgnoreCase("")) {FLAG = false;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t 超过2s没取到");System.out.println();System.out.println();return;}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t 消费队列" + result + "成功");}}public void stop() {this.FLAG = false;}}
public class ProdConsumer {public static void main(String[] args) {// 定义队列容量大小为10,超过10则插入失败MyResource myResource = new MyResource(new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(10));new Thread(()->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"生产线程启动");try {myResource.myProd();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}},"prod").start();new Thread(()->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"消费线程启动");try {myResource.myConsumer();System.out.println();System.out.println();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}},"consumer").start();try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println();System.out.println();System.out.println();System.out.println("5秒钟时间到,大老板main线程叫停,活动结束");myResource.stop();}}
产出结果
java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueueprod生产线程启动consumer消费线程启动prod 插入队列1成功consumer 消费队列1成功prod 插入队列2成功consumer 消费队列2成功prod 插入队列3成功consumer 消费队列3成功prod 插入队列4成功consumer 消费队列4成功prod 插入队列5成功consumer 消费队列5成功5秒钟时间到,大老板main线程叫停,活动结束prod 大老板叫停了,表示FLAG=false,生产动作结束consumer 超过2s没取到

