BranchOperator 算子即分支算子,用于根据输入数据决策下游分支链路。 比如, 如果你有两个分支,你可以根据输入决定运行哪条路径。
有两种方式可以使用BranchOperator
通过一个分支映射来构建BranchOperator
将分支函数和任务名称的字典传递给BranchOperator构造函数
from dbgpt.core.awel import DAG, BranchOperator, MapOperatordef branch_even(x: int) -> bool:return x % 2 == 0def branch_odd(x: int) -> bool:return not branch_even(x)branch_mapping = {branch_even: "even_task",branch_odd: "odd_task"}with DAG("awel_branch_operator") as dag:task = BranchOperator(branches=branch_mapping)even_task = MapOperator(task_name="even_task",map_function=lambda x: print(f"{x} is even"))odd_task = MapOperator(task_name="odd_task",map_function=lambda x: print(f"{x} is odd"))
在上述例子中,<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">BranchOperator</font>算子有两个子任务,even_task和odd_task. BranchOperator 将根据输入数据来决定该运行哪个算子。因此我们将分支函数和任务名称的字典传递给BranchOperator函数来定义分支映射, 字典中的键值是分支函数,值是任务名称,当运行分支任务时,所有分支函数都会执行时,如果分支函数返回True,则任务将被执行,否则将被跳过。
实现一个自定义BranchOperator
通过重写branches方法,返回一个分支函数与任务名称映射的字典,即可实现自定义
from dbgpt.core.awel import DAG, BranchOperator, MapOperatordef branch_even(x: int) -> bool:return x % 2 == 0def branch_odd(x: int) -> bool:return not branch_even(x)class MyBranchOperator(BranchOperator[int]):def __init__(self, even_task_name: str, odd_task_name: str, **kwargs):self.even_task_name = even_task_nameself.odd_task_name = odd_task_namesuper().__init__(**kwargs)async def branches(self):return {branch_even: self.even_task_name,branch_odd: self.odd_task_name}with DAG("awel_branch_operator") as dag:task = MyBranchOperator(even_task_name="even_task", odd_task_name="odd_task")even_task = MapOperator(task_name="even_task",map_function=lambda x: print(f"{x} is even"))odd_task = MapOperator(task_name="odd_task",map_function=lambda x: print(f"{x} is odd")
样例
在awel_tutorial 目录下,创建一个文件名为branch_operator_even_or_odd.py 的文件,内容如下:
import asynciofrom dbgpt.core.awel import (DAG, BranchOperator, MapOperator, JoinOperator,InputOperator, SimpleCallDataInputSource,is_empty_data)def branch_even(x: int) -> bool:return x % 2 == 0def branch_odd(x: int) -> bool:return not branch_even(x)branch_mapping = {branch_even: "even_task",branch_odd: "odd_task"}def even_func(x: int) -> int:print(f"Branch even, {x} is even, multiply by 10")return x * 10def odd_func(x: int) -> int:print(f"Branch odd, {x} is odd, multiply by itself")return x * xdef combine_function(x: int, y: int) -> int:print(f"Received {x} and {y}")# Return the first non-empty datareturn x if not is_empty_data(x) else ywith DAG("awel_branch_operator") as dag:input_task = InputOperator(input_source=SimpleCallDataInputSource())task = BranchOperator(branches=branch_mapping)even_task = MapOperator(task_name="even_task", map_function=even_func)odd_task = MapOperator(task_name="odd_task", map_function=odd_func)join_task = JoinOperator(combine_function=combine_function)input_task >> task >> even_task >> join_taskinput_task >> task >> odd_task >> join_taskprint("First call, input is 5")assert asyncio.run(join_task.call(call_data=5)) == 25print("=" * 80)print("Second call, input is 6")assert asyncio.run(join_task.call(call_data=6)) == 60
运行上述代码,查看程序输出
poetry run python awel_tutorial/branch_operator_even_or_odd.pyFirst call, input is 5Branch odd, 5 is odd, multiple by itselfReceived EmptyData(SKIP_DATA) by 25================================================================================Second call, input is 6Branch even, 6 is even, multiply by 10Received 60 by EmptyData(SKIP_DATA)
DAG图如下所示
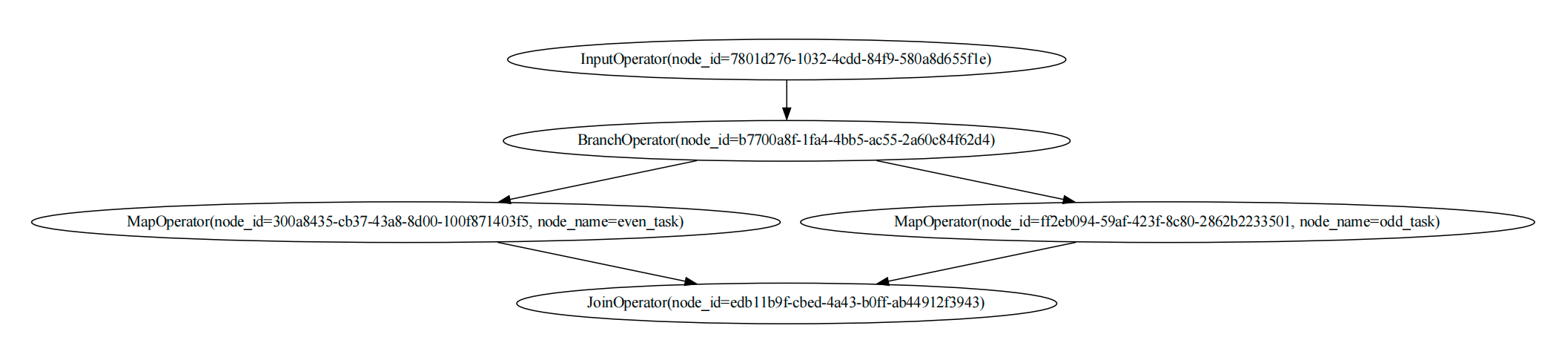
在上述案例中,BranchOperator 算子有两个子任务,even_task 和 odd_task, 它将根据输入数据决定运行哪个分支。
同时我们也是用JoinOperator 算子来组合两个子任务,如果一个路径被跳过,JoinOperator算子将接收到一个 EmptyData(SKIP_DATA)作为输入数据,我们可以通过dbgpt.core.awel.is_empty_data方法来检测是否时一个空数据。

