链式调用
var sched = {wakeup: function () {console.log('wakeup');return this;},morning: function () {console.log('morning');return this;},afternoon: function () {console.log('afternoon');return this;},night: function(){console.log('night');return this;}}sched.wakeup().morning().afternoon().night();
this是sched对象,返回sched对象,在对象中this就指代对象本身
数组语法调用对象属性
var myLang = {NO1: 'HTMl',NO2: 'CSS',NO3: 'JS',myStudyingLang:function(num){//console.log(myLang["NO" + num]);//与this一样console.log(this["NO"+num]);}}myLang.myStudyingLang(1); // HTMlmyLang.myStudyingLang(2); //CSSmyLang.myStudyingLang(3); // JSvar obj = {name:'123'}console.log(obj.name) // 123console.log(obj['name']) // 123// js引擎内部 obj.name -> obj[name]
对象属性的遍历
键值对 key键名:value键值
for in既可以遍历对象,也可以遍历数组
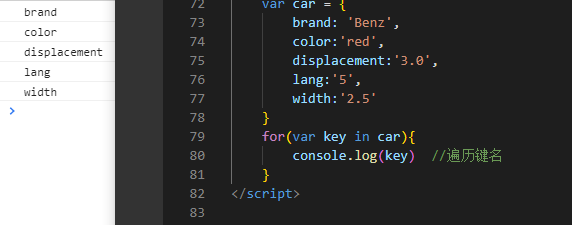
//for in 遍历对象var car = {brand: 'Benz',color:'red',displacement:'3.0',lang:'5',width:'2.5'}for(var key in car){//遍历键名,key是键名console.log(key)//遍历键值//1.错误写法console.log(car.key) // 5个undefined// console.log(car.key) => console.log(car['key']) 找不到名字为key的属性 name的属性//因为先转换成car['key'],不是转换成car[key]//2.正确写法console.log(car[key]); //Benz red 3.0 5 2.5}//for in 遍历数组var arr = [1,2,3,4,5];for(var i in arr){console.log(i); // 0 1 2 3 4// 数组是特殊的对象不写键名默认0 1 2 3 嘛? 已验证是的 p15/* i也可以看作键名,因为数组也可以看作对象,键名从0-4 *///for in同样可以遍历数组console.log(arr[i]); // 1 2 3 4 5}
hasOwnProperty
实例对象.hasOwnProperty(key)返回true
hasOwnProperty() 方法会返回一个布尔值,指示对象自身属性中是否具有指定的属性(也就是,是否有指定的键),不包括原型链。
hasOwnProperty对象自身不包括原型链上是否有目标属性、键名
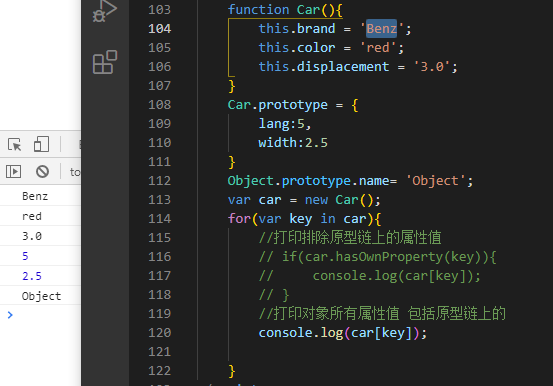
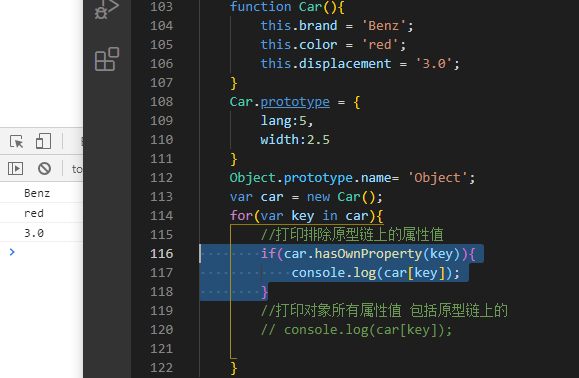
function Car() {var a=1;//不会被for in遍历,不会打印this.brand = 'Benz';this.color = 'red';this.displacement = '3.0';}Car.prototype = {lang: 5,width: 2.5}Object.prototype.name = 'Object';var car = new Car();for (var key in car) {console.log(key, car[key])}console.log('------')//会遍历prototype原型上的属性,不只是构造函数本身的属性for (var key in car) {//打印自身的(非继承)属性,继承的打印不出来,返回trueif (car.hasOwnProperty(key)) {console.log(key, car[key]); // Benz red 3.0}//in的作用 :打印对象所有属性值 包括原型链上的// console.log(car[key]);}

function Car(){this.brand = 'Benz';this.color = 'red';this.displacement = '3.0';}Car.prototype = {lang:5,width:2.5}Object.prototype.name= 'Object';var car = new Car();for(var key in car){//打印自身的(非继承)属性,继承的打印不出来,返回trueif(car.hasOwnProperty(key)){console.log(car[key]); // Benz red 3.0}//in的作用 :打印对象所有属性值 包括原型链上的// console.log(car[key]);}
instanceof
实例对象 instanceof xx构造函数 ,实例对象的原型链中有没有xx,包含xx吗,有true
原型链上的也算
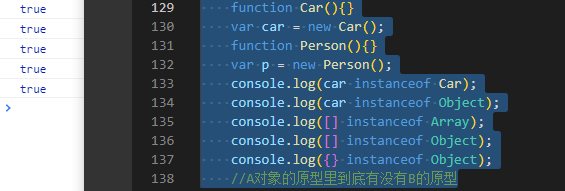
function Car(){}var car = new Car();function Person(){}var p = new Person();console.log(car instanceof Car);console.log(car instanceof Object);console.log([] instanceof Array);console.log([] instanceof Object);console.log({} instanceof Object);//A对象的原型里到底有没有B的原型
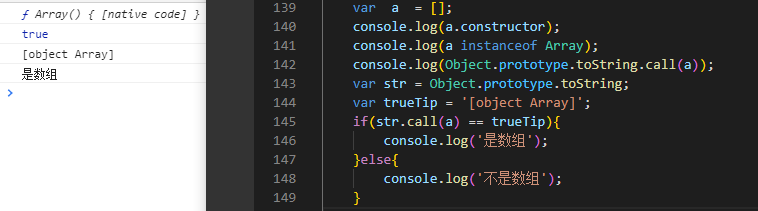
判断数组(对象)的方法
var a = [];console.log(a.constructor);console.log(a instanceof Array);console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(a)); //也可以判断对象 比instanceof好//最推荐方法 Object.prototype.toString.call();var str = Object.prototype.toString;var trueTip = '[object Array]';if(str.call(a) == trueTip){console.log('是数组');}else{console.log('不是数组');}
This
全局this指向window
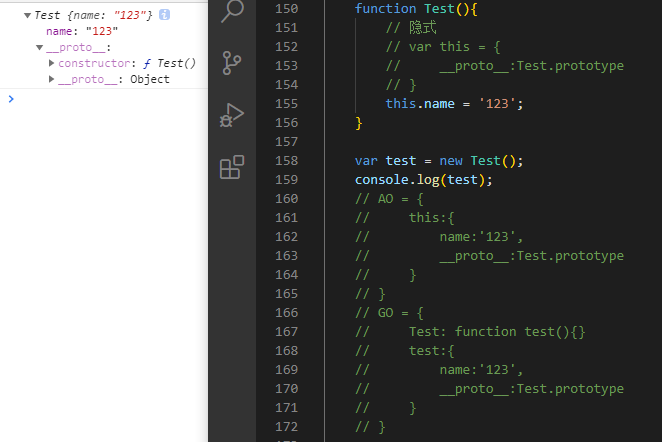
function Test(){// 隐式// var this = {// __proto__:Test.prototype// }this.name = '123';}var test = new Test();// AO = {// this:{// name:'123',// __proto__:Test.prototype// }// }// GO = {// Test: function test(){}// test:{// name:'123',// __proto__:Test.prototype// }// }
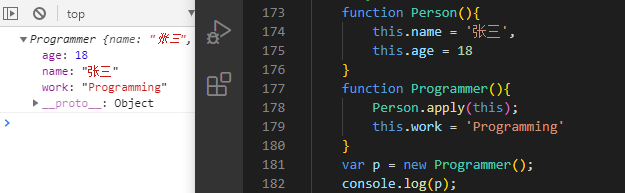
function Person(){this.name = '张三',this.age = 18}function Programmer(){Person.apply(this);this.work = 'Programming'}var p = new Programmer();console.log(p);//传参写法function Person(name,age){this.name = name;this.age = age;}function Programmer(name,age){Person.apply(this,[name,age]);this.work = 'Programming'}var p = new Programmer('张三',18);console.log(p);
总结: this指向
call/apply
//全局this ->window
//预编译函数this -> window
//apply/call改变this指向
//构造函数的this指向实例化对象
callee/caller
1.callee
**callee** 是 arguments 对象的一个属性。它可以用于引用该函数的函数体内当前正在执行的函数。这在函数的名称是未知时很有用,例如在没有名称的函数表达式 (也称为“匿名函数”)内。
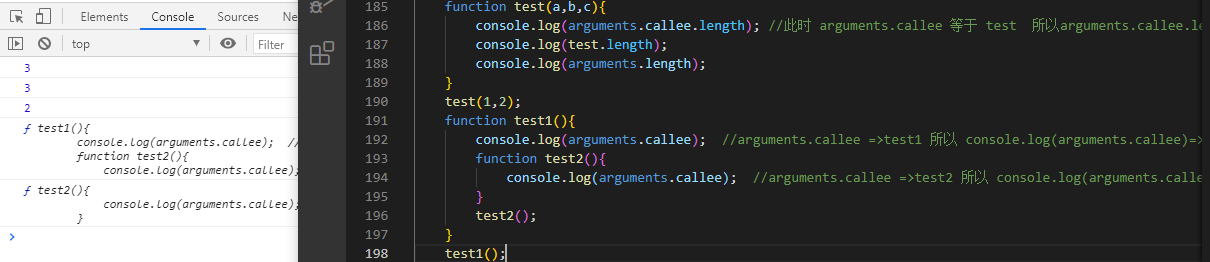
function test(a,b,c){console.log(arguments.callee.length); //此时 arguments.callee 等于 test 所以arguments.callee.length=>test.lengthconsole.log(test.length);console.log(arguments.length);}test(1,2);function test1(){console.log(arguments.callee); //arguments.callee =>test1 所以 console.log(arguments.callee)=>console.log(test1),就是函数本身,打印这个函数function test2(){console.log(arguments.callee); //arguments.callee =>test2 所以 console.log(arguments.callee)=>console.log(test2)}test2();}test1();//demo递归求累加值 一般写法function sum(n){if(n<=1){return 1;}return n + sum(n-1);}console.log(sum(10)); //50callee写法,因为函数名称没有了,用 arguments callee找回函数=func()执行函数var sum = (function(n){if(n<=1){return 1;}return n + arguments.callee(n-1); // arguments.callee => 等于此立即执行函数本身,相当于函数名,这是递归})(10);console.log(sum); //50
2.caller
该特性是非标准的,请尽量不要在生产环境中使用它!
返回调用指定函数的函数.,返回谁调用了它,只有执行才能打印,得放函数里,放全局没有用
该属性的常用形式arguments.callee.caller替代了被废弃的 arguments.caller.
https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Function/caller
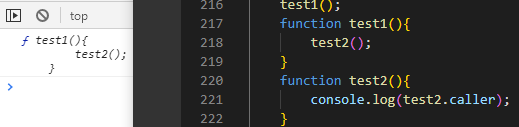
test1();function test1(){test2();}function test2(){console.log(test2.caller); // test2.caller => 是谁调用的?是test1函数,打印test1函数}
习题
1.
function foo(){bar.apply(null,arguments);// 等价于=>bar(arguments); 没有this指向问题}function bar(){console.log(arguments); // 1,2,3,4,5}foo(1,2,3,4,5);// bar() -> bar.call(arguments)->bar(arguments)// 关键 bar.call(null) => bar()
foo的argument传入bar函数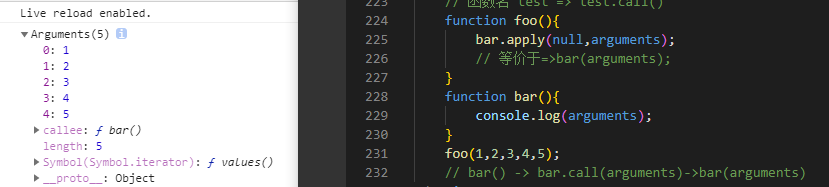
引JS 方法名.call()
2. JS的typeof可能返回的值有哪些?
object(null)/boolean/number/string/undefined/function
3.
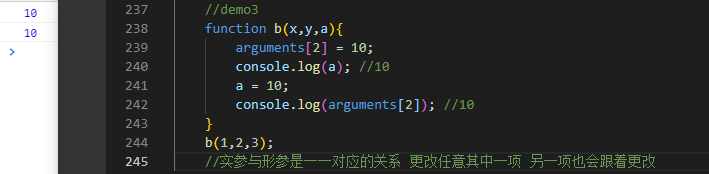
function b(x,y,a){arguments[2] = 10;console.log(a); //10a = 10;console.log(arguments[2]); //10}b(1,2,3);//实参与形参是--对应的关系 更改任意其中一项 另一项也会跟着更改
4.
var f = (function f(){return '1';},function g(){return 2;});console.log(f)//func g(){...} g函数console.log(f())//2console.log(typeof(f)); //function(string类型的) =>//等价于 f(f(),g()) 但g()函数未执行,没有运行结果var f = (function f(){return '1';},function g(){return 2;})();console.log(typeof(f)); //number(string类型的) =>//等价于 f(f(),g())() =>typeof(2)
5.isNaN原理
console.log(undefined==null); //true// undefined 不大于小于等于0 null 也不大于小于等于0 所以 trueconsole.log(undefined===null); //false// 长得不一样 所以falseconsole.log(isNaN('100')); //false 会隐式的先 Number('100') => 100 100!=NaN 所以等于false// function isNaN(num){// var res = Number(num) + '';// if(res == 'NaN'){// return true;// }else{// return false;// }// }console.log(parseInt('1a'))==1; //true//parseInt('1a') 等于 1
6.
// 1.空对象是否等于空对象 不相等// {}=={} //false// 2.为什么不相等 以为引用型数据对比的是内存地址// 3.如何让他们相等// var obj = {}// obj1 = obj// obj == obj //true
7.
var a = '1';function test(){var a = '2';this.a = '3';console.log(a);//如果是this.a,new出来就是3}test(); //2new test(); //2 因为this.a=3 —> this{a=3} var a='2'; a=3在this对象中console.log(a); //3 全局this ->window// GO{// a: undefined -> 1 -> 3// }
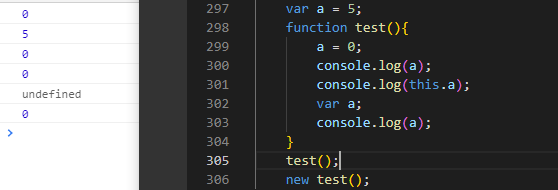
8.
var a = 5;function test(){a = 0;console.log(a);console.log(this.a);var a;console.log(a);}test();new test(); // 此时 var this = {} 没有a这个属性 所以等于空