一、原型
ptototype:构造函数的原型。
proto:实例化对象的一个属性,指向构造函数的原型ptototype。
实例化对象的proto属性指向构造函数的原型ptototype
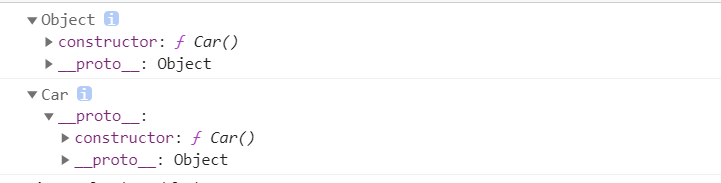
function Car() {}var car = new Car();console.log(Car.prototype);console.log(car);
function Car() {this.a=1;}Car.prototype.name='benz'var car = new Car();car.color='red';console.log(Car.prototype);console.log(car);
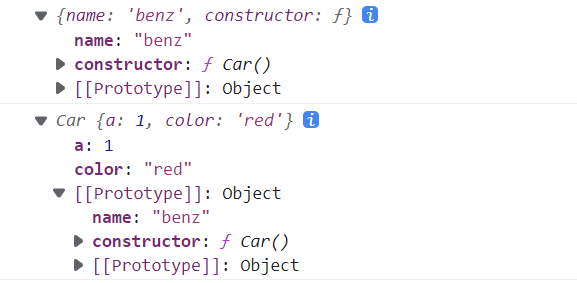
function Car() {this.a=1;}Car.prototype.name='benz'var car = new Car();car.color='red';console.log(Car.prototype);console.log(car);console.log(car.__proto__===Object)//falseconsole.log(car.__proto__===Car.prototype)//trueconsole.log(car.__proto__.__proto__===Object.__proto__)//falseconsole.log(car.__proto__.__proto__===Object.prototype)//trueconsole.log(car.__proto__.__proto__===Car.prototype.__proto__)//trueconsole.log(car.__proto__.__proto__.__proto__)//nullconsole.log(Object.prototype.prototype)//undefinedconsole.log(Object.prototype.__proto__)//nullconsole.log(car.prototype)//undefined
实例对象car->Car.prototype->Object.prototype 得实例对象先指向原型,实例对象是第一个,它自身的原型是第二个
实例对象没有prototype属性,只有proto属性
原型中也有原型prototype,但不能.prototype,需要.proto
原型链指向构造函数的原型,不指向构造函数,叫原型链肯定与原型有关,都指向原型
二、原型链
从上往下继承,
实例化对象通过 proto 属性向上查找属性和方法的链条就叫做原型链。
原型链的顶端是 Object.prototype。
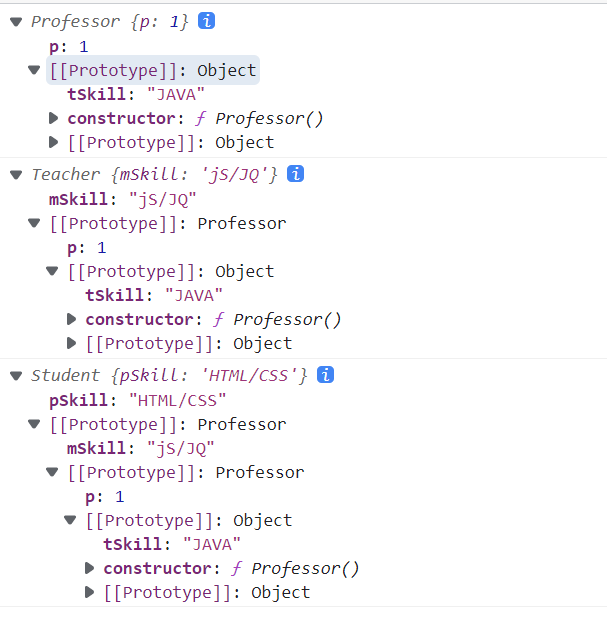
student实例对象->Student.prototype->Teacher.prototype->Professor.prototype->Object.prototype
不是student实例对象->实例对象teacher对象->professor对象->Professor.prototype->Object.prototype
Teacher.prototype与之前的Car.prototype有区别,因为把Teacher.prototype的指向改变了,变成了实例对象,Teacher.prototype.proto不会是Object.prototype了,而是实例对象对应构造函数的prototype
// Professor原型上添加属性Professor.prototype.tSkill = "JAVA";function Professor() {this.p=1;}// 实例化一个Professor对象var professor = new Professor();console.log(professor)// Teacher构造函数原型指向professor对象Teacher.prototype = professor;function Teacher() {this.mSkill = "jS/JQ";}// 实例化一个Teacher对象var teacher = new Teacher();console.log(teacher)// Student构造函数原型指向teacher对象Student.prototype = teacher;console.log(teacher)function Student() {this.pSkill = "HTML/CSS";}// 实例化一个Student对象var student = new Student();console.log(student)console.log(Teacher.prototype===professor)//true 因为之前把Teacher.prototype指向professor
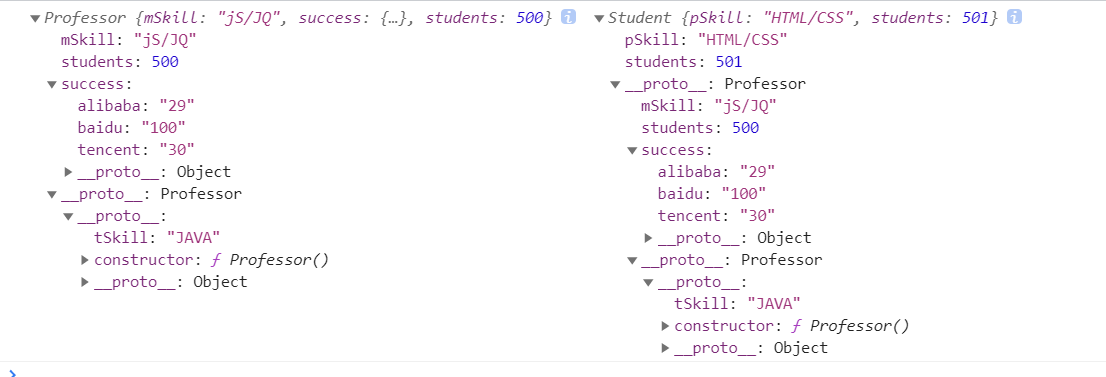
// Professor原型上添加属性Professor.prototype.tSkill = 'JAVA';function Professor() {}// 实例化一个Professor对象var professor = new Professor();// Teacher构造函数原型指向professor对象Teacher.prototype = professor;function Teacher() {this.mSkill = 'jS/JQ';this.success = {alibaba: '28',tencent: '30'}this.students = 500;}// 实例化一个Teacher对象var teacher = new Teacher();// Student构造函数原型指向teacher对象Student.prototype = teacher;function Student() {this.pSkill = 'HTML/CSS';}// 实例化一个Student对象var student = new Student();/*** 1. student对象没有success属性,沿着原型链向上查找* 2. student.success = student.__proto__.success* 3. student.students.baidu = '100'* 4. student.success.alibaba = '29'success是引用值,可以增加、修改成功,在Teacher的原型上直接修改,可以修改,但不推荐修改原型上的值*/student.success.baidu = '100';student.success.alibaba = '29';/*** 1. student对象没有students属性,沿着原型链向上查找* 2. student.students = student.__proto__.student* 3. student.students++students是原始值,不直接修改,会在student新建students属性,并把teacher的students属性赋值因为不能修改原型上的值,所以会在studuent上新建students属性先赋值原型上studnets的值,再加一*/student.students++;console.log(teacher, student);
访问对象的属性和方法时,优先访问自身的属性和方法,没有再按照原型链查找。
function Car() {this.brand = 'Benz';}Car.prototype = {brand: 'Mazda',intro: function () {console.log('我是' + this.brand + '车');}}var car = new Car();car.intro(); // '我是Benz车'//this指向实例对象car,car最上面有 this.brand = 'Benz';Car.prototype.intro()//'我是Mazda车' this指向Car.prototype//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------function Person() {this.smoke = function () {this.weight--;}}Person.prototype = {weight: 130}var person = new Person();person.smoke();//undefined 函数没写return返回undefined new函数返回thisconsole.log(person);

三、对象继承
3.1 创建对象的方法
1.字面量
2.Object构造函数
var obj1 = {}console.log(obj1);var obj2 = new Object(); // 一般不用console.log(obj2);function Obj() {}var obj3 = new Obj();console.log(obj3.__proto__ === Obj.prototype)//true
create
3、Object.create(proto) 指定对象的原型,当参数为 null 时可以创建出没有原型的对象。
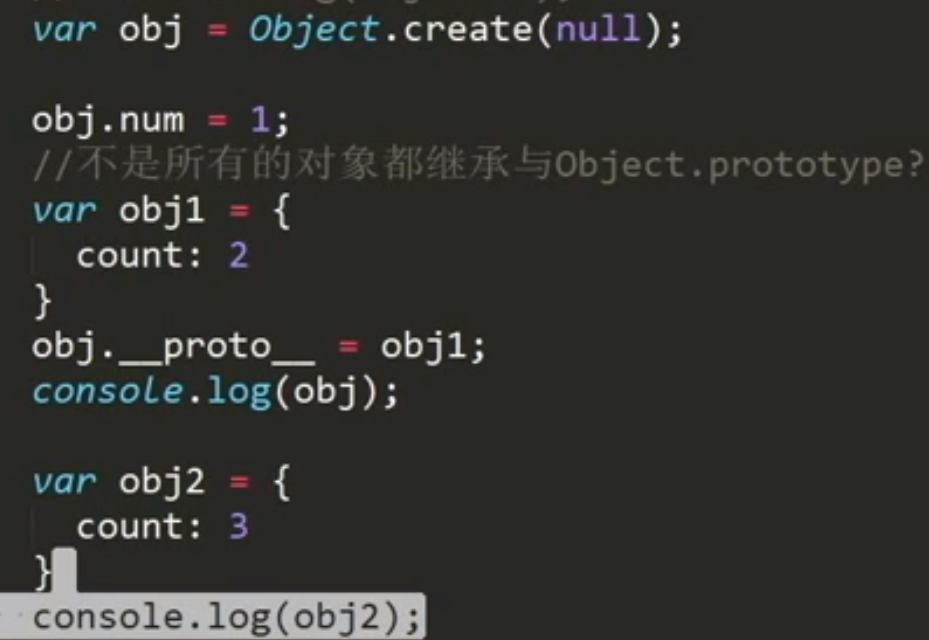
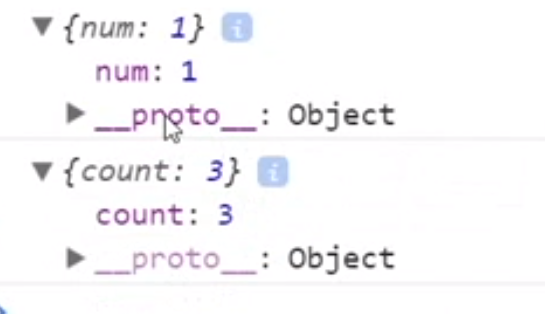
// 创建obj1空对象// 不是所有的对象都继承于Object.prototypevar obj1 = Object.create(null);console.log(obj1);obj1.num = 1;var obj2 = Object.create(obj1);console.log(obj2);console.log(obj2.num);var obj = Object.create(null);obj.num = 1;var obj1 = {count: 2}obj.__proto__ = obj1;// 给空对象添加__proto__属性无效console.log(obj.count); // undefined
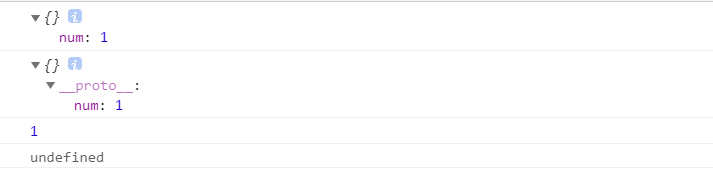
create放的是原型
函数 参数是什么类型 什么意思
返回值是什么类型 什么意思
obj1与obj2相等 一样
function Obj() {}Obj.prototype.num = 1;var obj1 = Object.create(Obj.prototype);// 实例化obj2// 调用构造函数Obj原型上的属性和方法// 指定实例对象的原型var obj2 = new Obj();console.log(obj1);console.log(obj2);
create作用:自定义实例对象的原型,object.create(xx)相当于构造函数.原型=xx 再用构造函数new一个实例对象,就相当基础的写法
var test={num=2}function Obj(){}obj.prototype.num=1;var obj1=Object.create(test);// 实例化obj2// 调用构造函数Obj原型上的属性和方法// 指定实例对象的原型var obj2=new Obj();console.log(obj1)console.log(obj2)
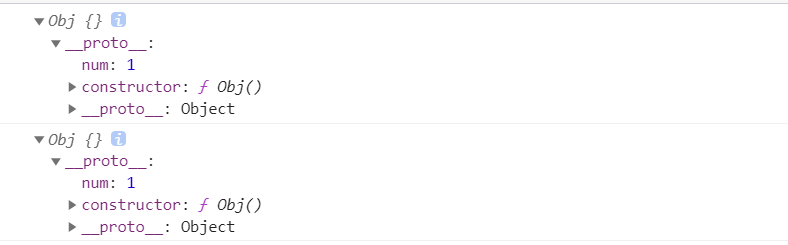
相当于新建构造函数obj1的实列对象obj2,相当于new构造函数
新建null对象,打印空 没有原型链
new新建实例对象包含create操作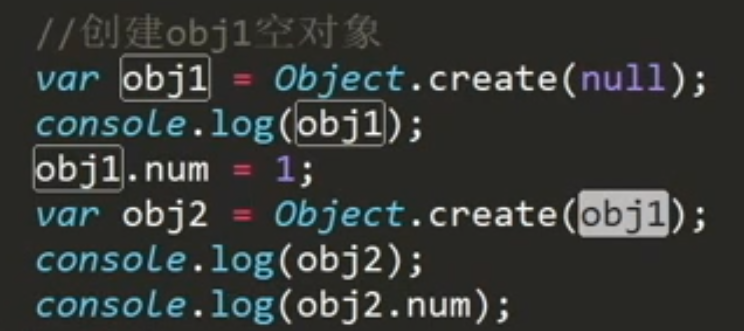
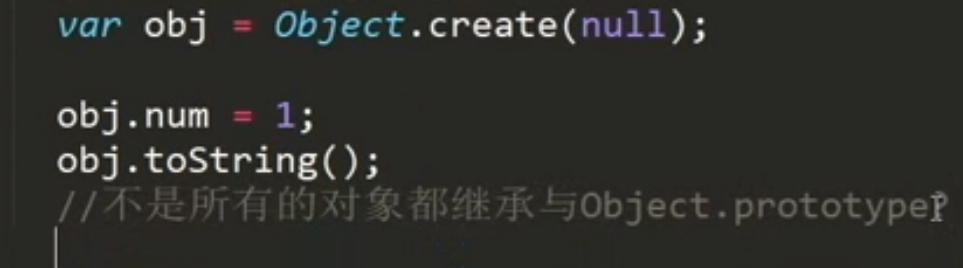
错误 不继承object原型,没有tostring方法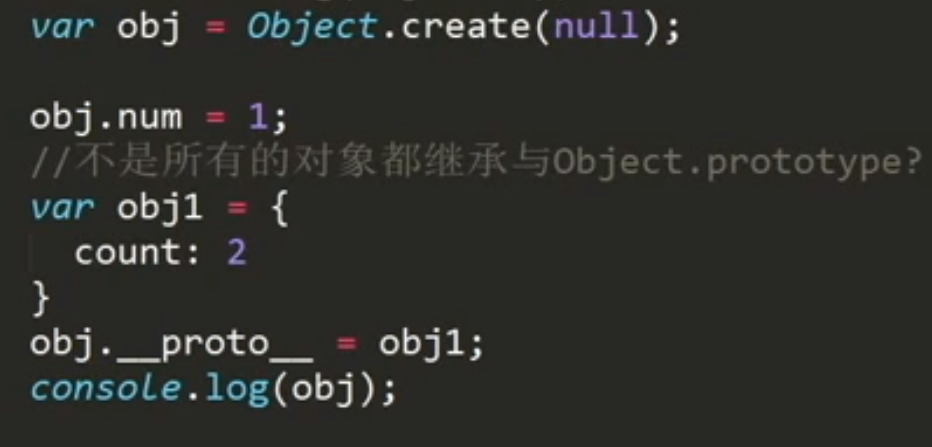
系统内置是浅色的,自定义是深色的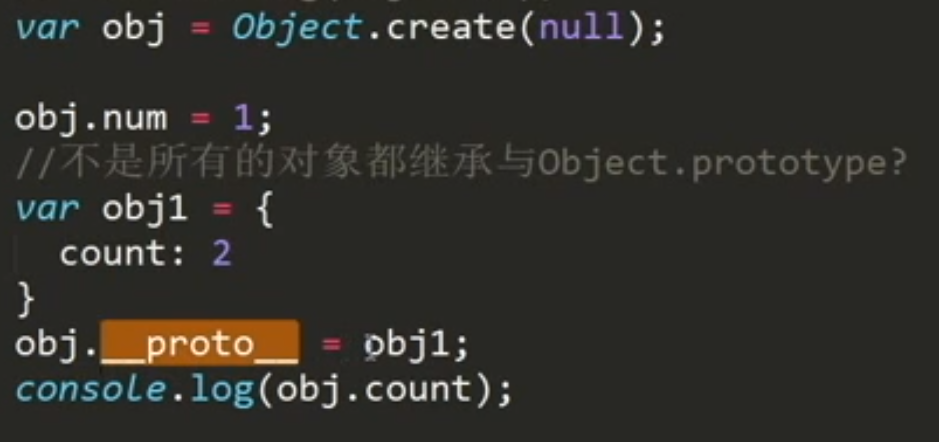
undefined自己指定proto没用,得是系统指定才有用
系统内置你可以更改它,但不能自造它
四、toString方法
4.1 undefined、null没有属性和方法。
不能.toString,没有包装类,没有原型
var num = 1;// 原始值没有属性和方法num.toString();// new Number(1) -> toString();var num2 = new Number(num);console.log(num2.toString());
4.2 document.write()会调用打印对象的toString方法。
隐式转换
var num = 1;var obj = {};var obj2 = Object.create(null);document.write(num);document.write(obj);document.write(obj2); // TypeError: Cannot convert object to primitive valueobj2.toString = function () {return 'sss'}document.write(obj2); // 'sss'
4.3 通过Object.prototype.toString方法判断对象类型。
var toString = Object.prototype.toString;console.log(toString.call(1)); // [object Number]console.log(toString.call('a')); // [object String]console.log(toString.call(true)); // [object Boolean]console.log(toString.call([])); // [object Array]console.log(toString.call({})); // [object Object]
五、call、apply改变this指向
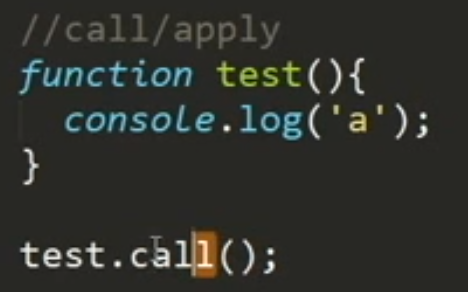
function test(){console.log('a')}test()test.call()test.call(window)
全是a,不光结果一样,效果意思也一样默认的this是window,this是返回的对象
其实test()默认在test之后加上.call,其实test()相当于test.call()
function test(){this.n=1;console.log('a')}test()// test.call()// test.call(window)console.log(n)//1 弄到window中
function Car(brand,color){this.brand=brand;this.color = color;}var newCar={}Car.call(newCar,'Benz','red')console.log(newCar)

相当于把this对象变成newCar对象
function Car(brand,color){newCar.brand=brand;newCar.color = color;}var newCar={}// Car.call(newCar,'Benz','red')Car('Benz','red')console.log(newCar)
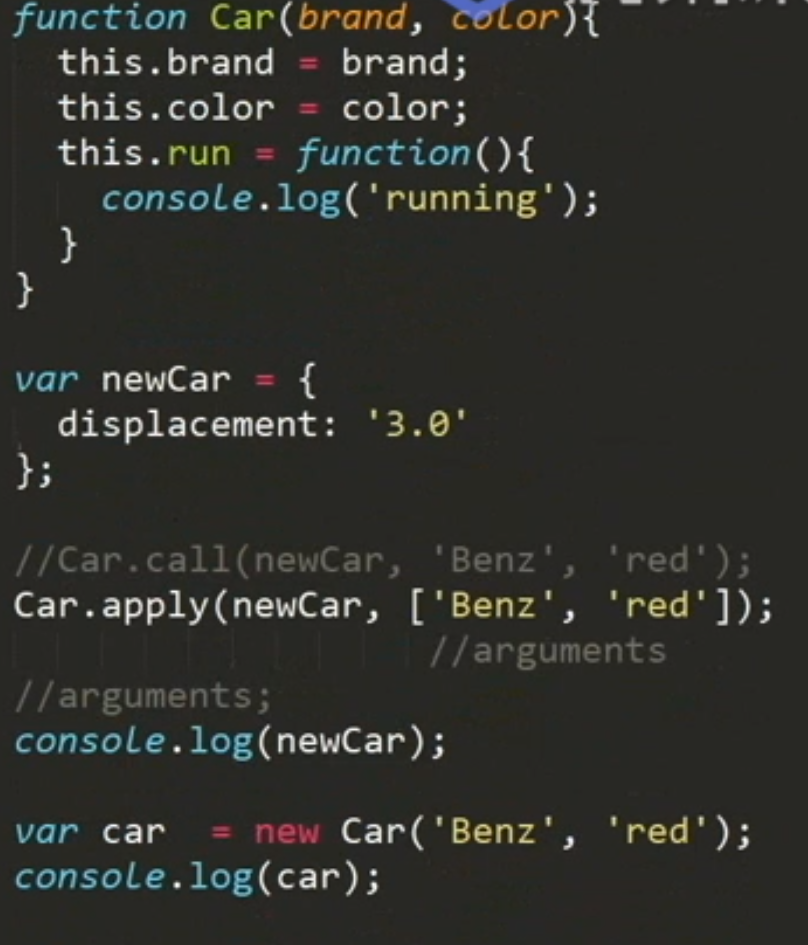
function Car(brand, color) {this.brand = brand;this.color = color;this.run = function () {console.log('running');}}var newCar = {displacement: '3.0'};// Car.call(newCar, 'Benz', 'red');Car.apply(newCar, ['Benz', 'red']);console.log(newCar);var car = new Car('Benz', 'red');console.log(car);
使用call、apply借用其它对象的属性和方法。
function Compute() {this.plus = function (a, b) {console.log(a + b);}this.minus = function (a, b) {console.log(a - b);}}function FullCompute() {// Compute.call(this); //与apply一样Compute.apply(this);this.mul = function (a, b) {console.log(a * b);}this.div = function (a, b) {console.log(a / b);}}var compute = new FullCompute();/*上面的this指的是FullCompute的实例对象,首先运行实例对象compute.plus、compute.minus之后运行实例对象compute.mul、compute.div,本来是this.mul等,但这里this就是实例对象Compute.apply(this)等函数运行、实例化时运行,但也可以看作,把Compute的this的内容,添加到FullCompute中*/compute.plus(1, 2);compute.minus(1, 2);compute.mul(1, 2);compute.div(1, 2);
六、作业
年龄为多少岁,姓名为xx买了一辆排量为XX的什么颜色的什么牌子的车 call apply。
function Car(opt) {this.displacement = opt.displacement;this.color = opt.color;this.brand = opt.brand;}function Person(opt) {this.name = opt.name;this.age = opt.age;Car.call(this, {displacement: opt.displacement,color: opt.color,brand: opt.brand});console.log('姓名为' + this.name + '年龄为' + this.age + '买了一辆排量为' + this.displacement + '的' + this.color + '色的' + this.brand + '牌的车');}var person = new Person({name: '张三',age: '24',color: 'red',displacement: '100',brand: 'Benz'})
返回什么返回的是对象,构造函数返回的是对象this,也有返回值
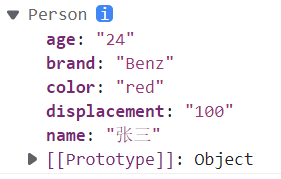
function Car(opt) {this.displacement = opt.displacement;this.color = opt.color;this.brand = opt.brand;}function Person(opt) {this.age = opt.age;this.name = opt.name;Car.call(this, opt)}var person = new Person({name: '张三',age: '24',color: 'red',displacement: '100',brand: 'Benz'})console.log(person)
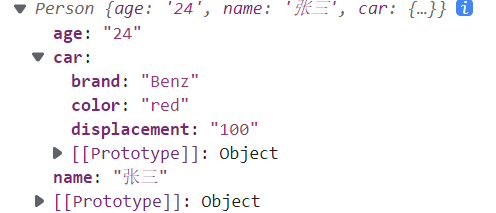
function Car(opt) {this.displacement = opt.displacement;this.color = opt.color;this.brand = opt.brand;}function Person(opt) {this.age = opt.age;this.name = opt.name;// this.car = {};Car.call(this.car={}, opt.car)//必须={}初始化}var person = new Person({name: '张三',age: '24',car:{color: 'red',displacement: '100',brand: 'Benz'}})console.log(person)
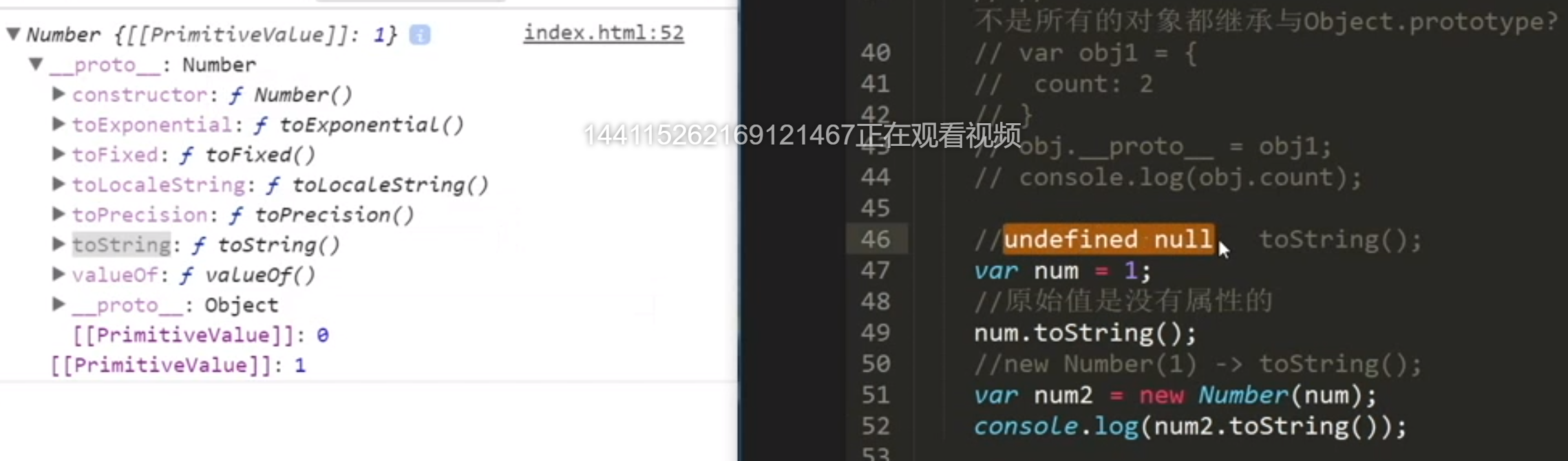 Number中重写了toString
Number中重写了toString


