一:包装类的分类
- 针对八种基本数据类型相应的引用类型—包装类
- 有了类的特点,就可以调用类中的方法 | 基本数据类型 | 包装类 | | —- | —- | | boolean | Boolean | | byte | Character | | byte | Byte | | short | Short | | int | Integer | | long | Long | | float | Float | | double | Double |
二:包装类和基本数据类型的转换
- jdk5前的手动装箱和拆箱方式,
- 装箱 : 基本类型->包装类型
- 拆箱 : 包装类型-> 基本类型
- jdk5以后 ( 含jdk5 ) 的自动装箱和拆箱方式
- 自动装箱底层调用的是 valueOf 方法,比如 Integer.valueof ( )
:::info
valueOf() 方法用于返回给定参数的原生 Number 对象值,参数可以是原生数据类型, String等。__该方法是静态方法。该方法可以接收两个参数一个是字符串,一个是基数。
:::
该方法有三种格式: static Integer valueOf(int i) static Integer valueOf(String s) static Integer valueOf(String s, int radix)
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {//手动装箱:int -> Integerint n1 = 11;Integer integer = new Integer(n1);Integer integer1 = Integer.valueOf(n1);//手动拆箱:Integer -> intint i = integer.intValue();}}
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {//自动装箱:int -> Integerint Num = 10;Integer integer =Num; //底层使用的是 Integer.valueOf(n2)//自动拆箱:Integer -> intint Sum = Num; //底层仍然使用的是 intValue()方法}}
三:包装类测试题(面试题)
1:
2:经典的面试题
四:包装类型和String类型相互转换
public class Test1 {public static void main(String[] args) {//包装类(Integer) -> StringInteger n = 100;//方式一;String str = n +"";//方式二:String str2 = n.toString();String str3 = Integer.toString(n);//方式三:String str4 = String.valueOf(n);//String -> 包装类(Integer)String name ="123";int s = Integer.parseInt(name);int ss = new Integer(s);}}
五:Integer 类和Character 类的常用方法
public class WrapperMethod {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(Integer.MIN_VALUE); //返回最小值 System.out.println(Integer.MAX_VALUE);//返回最大值System.out.println(Character.isDigit('a'));//判断是不是数字System.out.println(Character.isLetter('a'));//判断是不是字母System.out.println(Character.isUpperCase('a'));//判断是不是大写System.out.println(Character.isLowerCase('a'));//判断是不是小写System.out.println(Character.isWhitespace('a'));//判断是不是空格System.out.println(Character.toUpperCase('a'));//转成大写System.out.println(Character.toLowerCase('A'));//转成小写}}
六:Intege 类面试题总结
1:
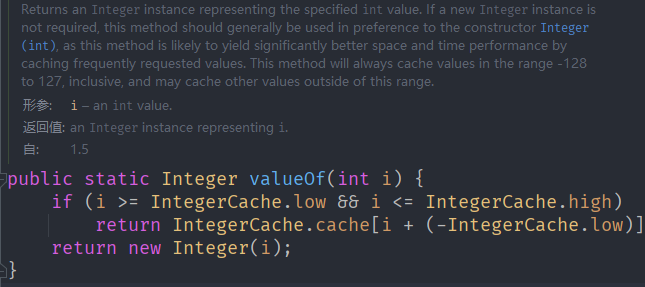
public static void main(String[] args) {Integer i = new Integer(1);Integer j = new Integer(1);System.out.println(i == j);//False//1. 如果 i 在 IntegerCache.low(-128)~IntegerCache.high(127),// 就直接从数组返回//2. 如果不在 -128~127,就直接 new Integer(i)Integer m = 1; //底层 Integer.valueOf(1); -> 阅读源码Integer n = 1;//底层 Integer.valueOf(1);System.out.println(m == n); //TInteger x = 128;//底层 Integer.valueOf(1);Integer y = 128;//底层 Integer.valueOf(1);System.out.println(x == y);//False}}
:::info
需要看源码,如果数在 -128~127 中, 直接return
因为catche数组中预先设置了 -128~127 ,所有在这个范围直接return
如果不在 ,创建一个Ingeter对象
:::
2:
 :::info
主要有基本数据类型,判断是值是否相同
:::
:::info
主要有基本数据类型,判断是值是否相同
:::

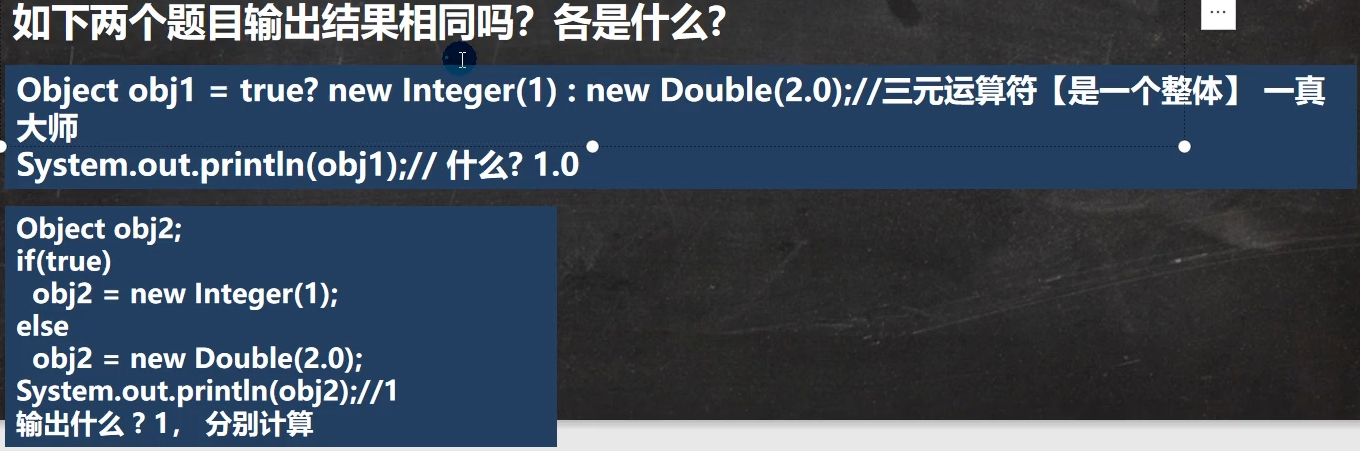 :::info
三元运算符是一个整体
:::
:::info
三元运算符是一个整体
:::

