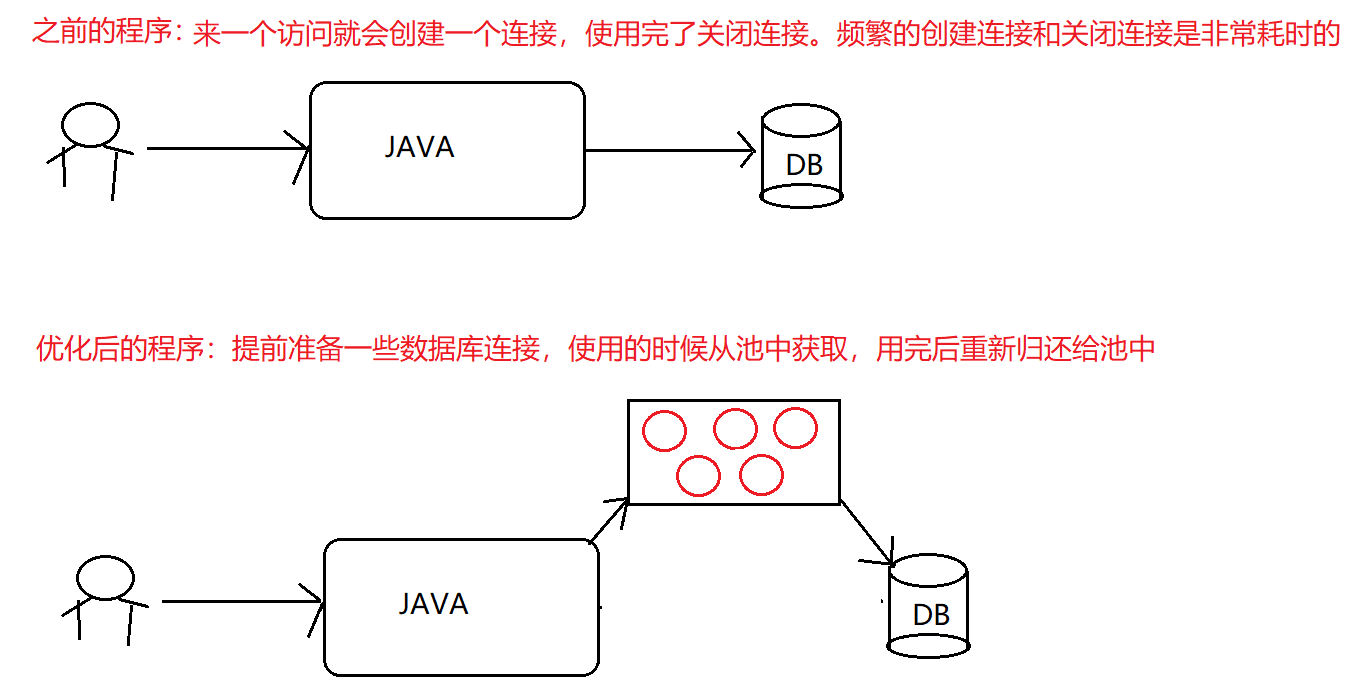
1. 数据库连接池
1.1 数据库连接池概念
- 数据库连接背景
- 数据库连接是一种关键的、有限的、昂贵的资源,这一点在多用户的网页应用程序中体现得尤为突出。对数据库连接的管理能显著影响到整个应用程序的伸缩性和健壮性,影响到程序的性能指标。数据库连接池正是针对这个问题提出来的。
- 数据库连接池
- 数据库连接池负责分配、管理和释放数据库连接,它允许应用程序重复使用一个现有的数据库连接,而不是再重新建立一个。这项技术能明显提高对数据库操作的性能。
- 数据库连接池原理
1.2 自定义连接池
1.2.1 DataSource接口概述
- java.sql.DataSource接口:数据源(也称为:数据库连接池)。java官方提供的数据库连接池规范(接口)
- 如果想完成数据库连接池技术,就必须实现DataSource接口
核心功能:获取数据库连接对象:Connection getConnection();
1.2.2 自定义数据库连接池

项目目录如下:开始就是导入jar包;复制基础篇的配置文件和JDBCUtils工具类;然后创建数据库连接池,其实现DataSource接口,实现方法,方法很多,但重要的只有getConnection;方法体中就是上面的几步,很简单,方法只有两个,重写的只有getConnection,至于这里的集合,用的是线程安全的,为了让ArrayList线程安全,使用了Collections工具类。
/*自定义连接池类*/public class MyDataSource implements DataSource{// 1. 定义集合容器,用于保存多个数据库连接对象private static List<Connection> pool = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<Connection>());//2. 静态代码块,生成10个数据库连接保存到集合中static {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {Connection con = JDBCUtils.getConnection();pool.add(con);}}//4. 返回连接池的大小public int getSize() {return pool.size();}// 3. 从池中返回一个数据库连接@Overridepublic Connection getConnection() {if(pool.size() > 0) {//从池中获取数据库连接return pool.remove(0);}else {throw new RuntimeException("连接数量已用尽");}}@Overridepublic Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {return null;}@Overridepublic <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException {return null;}@Overridepublic boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException {return false;}@Overridepublic PrintWriter getLogWriter() throws SQLException {return null;}@Overridepublic void setLogWriter(PrintWriter out) throws SQLException {}@Overridepublic void setLoginTimeout(int seconds) throws SQLException {}@Overridepublic int getLoginTimeout() throws SQLException {return 0;}@Overridepublic Logger getParentLogger() throws SQLFeatureNotSupportedException {return null;}}
1.3 自定义连接池测试
public class MyDataSourceTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{//创建数据库连接池对象MyDataSource dataSource = new MyDataSource();System.out.println("使用之前连接池数量:" + dataSource.getSize());//获取数据库连接对象Connection con = dataSource.getConnection();System.out.println(con.getClass());// JDBC4Connection//查询学生表全部信息String sql = "SELECT * FROM student";PreparedStatement pst = con.prepareStatement(sql);ResultSet rs = pst.executeQuery();while(rs.next()) {System.out.println(rs.getInt("sid") + "\t" + rs.getString("name") + "\t" + rs.getInt("age") + "\t" + rs.getDate("birthday"));}//释放资源rs.close();pst.close();//目前的连接对象close方法,是直接关闭连接,而不是将连接归还池中con.close();System.out.println("使用之后连接池数量:" + dataSource.getSize());}}
1.4 归还连接(4种方式)
对于上面的数据库连接,是关闭的,而非归还到容器,这显然不是我们想要的。
继承方式(其实不行)
继承方式是我们最容易想到的,我们继承这个类,重写方法就可以完成归还。其中连接类是JDBC4Connection。
- 继承方式归还数据库连接的思想。
- 通过打印连接对象,发现DriverManager获取的链接实现类是JDBC4Connection(上面的System.out.println(con.getClass());// JDBC4Connection)
- 那我们就可以自定义一个类,继承JDBC4Connection这个类,重写close()方法,完成连接对象的归还
- 继承方式归还数据库连接的实现步骤:

继承这个类时IDEA提示:必须创建和父类匹配的构造方法!!!这是为什么呢?还是很有意思的,这些Java小知识。
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35324400/article/details/103633880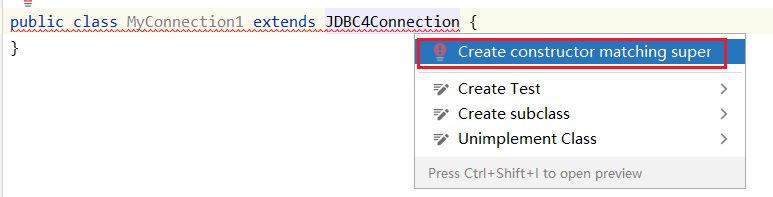
/*自定义Connection类*/public class MyConnection1 extends JDBC4Connection {//声明连接对象和连接池集合对象private Connection con;private List<Connection> pool;//通过构造方法给成员变量赋值public MyConnection1(String hostToConnectTo, int portToConnectTo, Properties info, String databaseToConnectTo, String url,Connection con,List<Connection> pool) throws SQLException {super(hostToConnectTo, portToConnectTo, info, databaseToConnectTo, url);this.con = con;this.pool = pool;}//重写close()方法,将连接归还给池中@Overridepublic void close() throws SQLException {pool.add(con);}}
- 3.但是这种方式行不通,通过查看JDBC工具类获取连接的方法我们发现:我们虽然自定义了一个子类,完成了归还连接的操作。但是DriverManager获取的还是JDBC4Connection这个对象,并不是我们的子类对象。而我们又不能整体去修改驱动包中类的功能! ```java //将之前的连接对象换成自定义的子类对象 private static MyConnection1 con;
//4.获取数据库连接的方法 public static Connection getConnection() { try { //等效于:MyConnection1 con = new JDBC4Connection(); 语法错误!父类指向子类 con = DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
return con;
}
<a name="wiuHv"></a>### 装饰设计模式> 这个好好学学,很不容易有设计模式的案例> 这个对于理解装饰设计模式很有用> 所谓装饰,无非是装饰一个类的功能,想更换或者增强功能> 比如I接口有A的实现类,原本肯定是在哪里用这个A实现类> 但是呢?我现在觉得A实现类的某个方法不满足我们的需求,但是其它方法满足> 怎么办???> 搞一个B类,实现I接口,然后用构造方法将A的实例传过来,对其进行包装。> 对于不需要的方法,换一下,其它方法,就用A对象的方法。> 然后调用A对象的地方呢?包装成B对象返回即可。> 缺点??> 可能有大量的方法需要在自定义类中进行重写1.装饰设计模式归还数据库连接的思想。- 我们可以自定义一个类,实现Connection接口。这样就具备了和JDBC4Connection相同的行为了(即相同方法)- 重写close()方法,完成连接的归还。其余的功能还调用mysql驱动包实现类原有的方法即可。2.装饰设计模式归还数据库连接的实现步骤<br />1.自定义一个类,实现Connection接口<br />2.定义Connection连接对象和连接池容器<br />3.通过有参构造完成对成员变量的赋值<br />4.重写close()方法,将连接对象添加到池中<br />5.剩余方法,只需要调用mysql驱动包的连接对象完成即可<br />6.在自定义连接池中,将获取的连接对象通过自定义连接对象进行包装。```java/*自定义Connection类。通过装饰设计模式,实现和mysql驱动包中的Connection实现类相同的功能!实现步骤:1.定义一个类,实现Connection接口2.定义Connection连接对象和连接池容器对象的变量3.提供有参构造方法,接收连接对象和连接池对象,对变量赋值4.在close()方法中,完成连接的归还5.剩余方法,只需要调用mysql驱动包的连接对象完成即可*/public class MyConnection2 implements Connection {//2.定义Connection连接对象和连接池容器对象的变量private Connection con;private List<Connection> pool;//3.提供有参构造方法,接收连接对象和连接池对象,对变量赋值public MyConnection2(Connection con,List<Connection> pool) {this.con = con;this.pool = pool;}//4.在close()方法中,完成连接的归还@Overridepublic void close() throws SQLException {pool.add(con);}// 5.剩余方法,只需要调用mysql驱动包的连接对象完成即可@Overridepublic Statement createStatement() throws SQLException {return con.createStatement();}@Overridepublic PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql) throws SQLException {return con.prepareStatement(sql);}@Overridepublic CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql) throws SQLException {return con.prepareCall(sql);}@Overridepublic String nativeSQL(String sql) throws SQLException {return con.nativeSQL(sql);}@Overridepublic void setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit) throws SQLException {con.setAutoCommit(autoCommit);}@Overridepublic boolean getAutoCommit() throws SQLException {return con.getAutoCommit();}@Overridepublic void commit() throws SQLException {con.commit();}@Overridepublic void rollback() throws SQLException {con.rollback();}@Overridepublic boolean isClosed() throws SQLException {return con.isClosed();}@Overridepublic DatabaseMetaData getMetaData() throws SQLException {return con.getMetaData();}@Overridepublic void setReadOnly(boolean readOnly) throws SQLException {con.setReadOnly(readOnly);}@Overridepublic boolean isReadOnly() throws SQLException {return con.isReadOnly();}@Overridepublic void setCatalog(String catalog) throws SQLException {con.setCatalog(catalog);}@Overridepublic String getCatalog() throws SQLException {return con.getCatalog();}@Overridepublic void setTransactionIsolation(int level) throws SQLException {con.setTransactionIsolation(level);}@Overridepublic int getTransactionIsolation() throws SQLException {return con.getTransactionIsolation();}@Overridepublic SQLWarning getWarnings() throws SQLException {return con.getWarnings();}@Overridepublic void clearWarnings() throws SQLException {con.clearWarnings();}@Overridepublic Statement createStatement(int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {return con.createStatement(resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency);}@Overridepublic PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {return con.prepareStatement(sql,resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency);}@Overridepublic CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {return con.prepareCall(sql,resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency);}@Overridepublic Map<String, Class<?>> getTypeMap() throws SQLException {return con.getTypeMap();}@Overridepublic void setTypeMap(Map<String, Class<?>> map) throws SQLException {con.setTypeMap(map);}@Overridepublic void setHoldability(int holdability) throws SQLException {con.setHoldability(holdability);}@Overridepublic int getHoldability() throws SQLException {return con.getHoldability();}@Overridepublic Savepoint setSavepoint() throws SQLException {return con.setSavepoint();}@Overridepublic Savepoint setSavepoint(String name) throws SQLException {return con.setSavepoint(name);}@Overridepublic void rollback(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException {con.rollback(savepoint);}@Overridepublic void releaseSavepoint(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException {con.releaseSavepoint(savepoint);}@Overridepublic Statement createStatement(int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException {return con.createStatement(resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency,resultSetHoldability);}@Overridepublic PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException {return con.prepareStatement(sql,resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency,resultSetHoldability);}@Overridepublic CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException {return con.prepareCall(sql,resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency,resultSetHoldability);}@Overridepublic PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int autoGeneratedKeys) throws SQLException {return con.prepareStatement(sql,autoGeneratedKeys);}@Overridepublic PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int[] columnIndexes) throws SQLException {return con.prepareStatement(sql,columnIndexes);}@Overridepublic PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, String[] columnNames) throws SQLException {return con.prepareStatement(sql,columnNames);}@Overridepublic Clob createClob() throws SQLException {return con.createClob();}@Overridepublic Blob createBlob() throws SQLException {return con.createBlob();}@Overridepublic NClob createNClob() throws SQLException {return con.createNClob();}@Overridepublic SQLXML createSQLXML() throws SQLException {return con.createSQLXML();}@Overridepublic boolean isValid(int timeout) throws SQLException {return con.isValid(timeout);}@Overridepublic void setClientInfo(String name, String value) throws SQLClientInfoException {con.setClientInfo(name,value);}@Overridepublic void setClientInfo(Properties properties) throws SQLClientInfoException {con.setClientInfo(properties);}@Overridepublic String getClientInfo(String name) throws SQLException {return con.getClientInfo(name);}@Overridepublic Properties getClientInfo() throws SQLException {return con.getClientInfo();}@Overridepublic Array createArrayOf(String typeName, Object[] elements) throws SQLException {return con.createArrayOf(typeName,elements);}@Overridepublic Struct createStruct(String typeName, Object[] attributes) throws SQLException {return con.createStruct(typeName,attributes);}@Overridepublic void setSchema(String schema) throws SQLException {con.setSchema(schema);}@Overridepublic String getSchema() throws SQLException {return con.getSchema();}@Overridepublic void abort(Executor executor) throws SQLException {con.abort(executor);}@Overridepublic void setNetworkTimeout(Executor executor, int milliseconds) throws SQLException {con.setNetworkTimeout(executor,milliseconds);}@Overridepublic int getNetworkTimeout() throws SQLException {return con.getNetworkTimeout();}@Overridepublic <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException {return con.unwrap(iface);}@Overridepublic boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException {return con.isWrapperFor(iface);}}
- 自定义连接池类
这里只是更改了这里!!!
public class MyDataSource implements DataSource{//定义集合容器,用于保存多个数据库连接对象private static List<Connection> pool = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<Connection>());//静态代码块,生成10个数据库连接保存到集合中static {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {Connection con = JDBCUtils.getConnection();pool.add(con);}}//返回连接池的大小public int getSize() {return pool.size();}//从池中返回一个数据库连接@Overridepublic Connection getConnection() {if(pool.size() > 0) {//从池中获取数据库连接Connection con = pool.remove(0);//通过自定义连接对象进行包装MyConnection2 mycon = new MyConnection2(con,pool);//返回包装后的连接对象return mycon;}else {throw new RuntimeException("连接数量已用尽");}}}
3.装饰设计模式归还数据库连接存在的问题。
- 实现Connection接口之后,有大量的方法需要在自定义类中进行重写。
适配器设计模式
这个可以解决上面的缺点!! 这个适配器类只是一个中间类,对于其它方法,全部还是用JDBC4Connection类的方法。 首先还是I接口,A实现类,但是我们不想要A中的一个方法,其它方法满足。A对象在一处被使用。 这个中间类自然要实现Connection接口,然后通过构造方法传入A对象,所有方法都用A对象的,除了不想要的(这个我们也不重写),因此该中间类需要是抽象方法。 下面就是定义一个类,其实是和A同等级别的,实现这个中间类,重写不想要的方法即可。至于构造传参什么就不需要说的 至于使用,和上面的一样,就是在连接池中对原有的连接对象进行包装即可。 适配器模式问题??? 虽然自定义连接类很简单,但是适配器是我们写的,还是很麻烦!! 甚至有点换汤不换药。当然如果你有好几个close方法,那么用适配器模式的话,想要保留的方法在这里只需要写一次即可。
1.适配器设计模式归还数据库连接的思想
- 我们可以提供一个适配器类,实现Connection接口,将所有方法进行实现(除了close方法)
- 自定义连接类只需要继承这个适配器类,重写需要改进的close()方法即可
2.适配器设计模式归还数据库连接的实现步骤。
1.定义一个适配器,实现Connectio接口。
2.定义Connection连接对象的成员变量。
3.通过有参构造方法完成对成员变量的赋值。
4.重写所有方法(除了close),调用mysql驱动包的链接对象完成即可。
5.定义一个连接池,继承适配器类。
6.定义Connection链接对象和连接池对象的成员变量,并通过有参构造进行赋值。
7.重写close()方法,完成归还连接。
8.在自定义连接池中,将获取的链接对象通过自定义连接对象进行包装。
/*适配器抽象类。实现Connection接口。实现所有的方法,调用mysql驱动包中Connection连接对象的方法*/public abstract class MyAdapter implements Connection {// 定义数据库连接对象的变量private Connection con;// 通过构造方法赋值public MyAdapter(Connection con) {this.con = con;}// 所有的方法,均调用mysql的连接对象实现@Overridepublic Statement createStatement() throws SQLException {return con.createStatement();}@Overridepublic PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql) throws SQLException {return con.prepareStatement(sql);}@Overridepublic CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql) throws SQLException {return con.prepareCall(sql);}@Overridepublic String nativeSQL(String sql) throws SQLException {return con.nativeSQL(sql);}@Overridepublic void setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit) throws SQLException {con.setAutoCommit(autoCommit);}@Overridepublic boolean getAutoCommit() throws SQLException {return con.getAutoCommit();}@Overridepublic void commit() throws SQLException {con.commit();}@Overridepublic void rollback() throws SQLException {con.rollback();}@Overridepublic boolean isClosed() throws SQLException {return con.isClosed();}@Overridepublic DatabaseMetaData getMetaData() throws SQLException {return con.getMetaData();}@Overridepublic void setReadOnly(boolean readOnly) throws SQLException {con.setReadOnly(readOnly);}@Overridepublic boolean isReadOnly() throws SQLException {return con.isReadOnly();}@Overridepublic void setCatalog(String catalog) throws SQLException {con.setCatalog(catalog);}@Overridepublic String getCatalog() throws SQLException {return con.getCatalog();}@Overridepublic void setTransactionIsolation(int level) throws SQLException {con.setTransactionIsolation(level);}@Overridepublic int getTransactionIsolation() throws SQLException {return con.getTransactionIsolation();}@Overridepublic SQLWarning getWarnings() throws SQLException {return con.getWarnings();}@Overridepublic void clearWarnings() throws SQLException {con.clearWarnings();}@Overridepublic Statement createStatement(int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {return con.createStatement(resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency);}@Overridepublic PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {return con.prepareStatement(sql,resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency);}@Overridepublic CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {return con.prepareCall(sql,resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency);}@Overridepublic Map<String, Class<?>> getTypeMap() throws SQLException {return con.getTypeMap();}@Overridepublic void setTypeMap(Map<String, Class<?>> map) throws SQLException {con.setTypeMap(map);}@Overridepublic void setHoldability(int holdability) throws SQLException {con.setHoldability(holdability);}@Overridepublic int getHoldability() throws SQLException {return con.getHoldability();}@Overridepublic Savepoint setSavepoint() throws SQLException {return con.setSavepoint();}@Overridepublic Savepoint setSavepoint(String name) throws SQLException {return con.setSavepoint(name);}@Overridepublic void rollback(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException {con.rollback(savepoint);}@Overridepublic void releaseSavepoint(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException {con.releaseSavepoint(savepoint);}@Overridepublic Statement createStatement(int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException {return con.createStatement(resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency,resultSetHoldability);}@Overridepublic PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException {return con.prepareStatement(sql,resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency,resultSetHoldability);}@Overridepublic CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException {return con.prepareCall(sql,resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency,resultSetHoldability);}@Overridepublic PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int autoGeneratedKeys) throws SQLException {return con.prepareStatement(sql,autoGeneratedKeys);}@Overridepublic PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int[] columnIndexes) throws SQLException {return con.prepareStatement(sql,columnIndexes);}@Overridepublic PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, String[] columnNames) throws SQLException {return con.prepareStatement(sql,columnNames);}@Overridepublic Clob createClob() throws SQLException {return con.createClob();}@Overridepublic Blob createBlob() throws SQLException {return con.createBlob();}@Overridepublic NClob createNClob() throws SQLException {return con.createNClob();}@Overridepublic SQLXML createSQLXML() throws SQLException {return con.createSQLXML();}@Overridepublic boolean isValid(int timeout) throws SQLException {return con.isValid(timeout);}@Overridepublic void setClientInfo(String name, String value) throws SQLClientInfoException {con.setClientInfo(name,value);}@Overridepublic void setClientInfo(Properties properties) throws SQLClientInfoException {con.setClientInfo(properties);}@Overridepublic String getClientInfo(String name) throws SQLException {return con.getClientInfo(name);}@Overridepublic Properties getClientInfo() throws SQLException {return con.getClientInfo();}@Overridepublic Array createArrayOf(String typeName, Object[] elements) throws SQLException {return con.createArrayOf(typeName,elements);}@Overridepublic Struct createStruct(String typeName, Object[] attributes) throws SQLException {return con.createStruct(typeName,attributes);}@Overridepublic void setSchema(String schema) throws SQLException {con.setSchema(schema);}@Overridepublic String getSchema() throws SQLException {return con.getSchema();}@Overridepublic void abort(Executor executor) throws SQLException {con.abort(executor);}@Overridepublic void setNetworkTimeout(Executor executor, int milliseconds) throws SQLException {con.setNetworkTimeout(executor,milliseconds);}@Overridepublic int getNetworkTimeout() throws SQLException {return con.getNetworkTimeout();}@Overridepublic <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException {return con.unwrap(iface);}@Overridepublic boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException {return con.isWrapperFor(iface);}}
自定义连接类
/*自定义Connection连接类。通过适配器设计模式。完成close()方法的重写1.定义一个类,继承适配器父类2.定义Connection连接对象和连接池容器对象的变量3.提供有参构造方法,接收连接对象和连接池对象,对变量赋值4.在close()方法中,完成连接的归还*/public class MyConnection3 extends MyAdapter {//2.定义Connection连接对象和连接池容器对象的变量private Connection con;private List<Connection> pool;//3.提供有参构造方法,接收连接对象和连接池对象,对变量赋值public MyConnection3(Connection con,List<Connection> pool) {super(con); // 将接收的数据库连接对象给适配器父类传递this.con = con;this.pool = pool;}//4.在close()方法中,完成连接的归还@Overridepublic void close() throws SQLException {pool.add(con);}}
自定义连接池类
使用时,也只是包装
public class MyDataSource implements DataSource{//定义集合容器,用于保存多个数据库连接对象private static List<Connection> pool = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<Connection>());//静态代码块,生成10个数据库连接保存到集合中static {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {Connection con = JDBCUtils.getConnection();pool.add(con);}}//返回连接池的大小public int getSize() {return pool.size();}//从池中返回一个数据库连接@Overridepublic Connection getConnection() {if(pool.size() > 0) {//从池中获取数据库连接Connection con = pool.remove(0);//通过自定义连接对象进行包装//MyConnection2 mycon = new MyConnection2(con,pool);MyConnection3 mycon = new MyConnection3(con,pool);//返回包装后的连接对象return mycon;}else {throw new RuntimeException("连接数量已用尽");}}}
3.适配器设计模式归还数据库连接存在的问题。
自定义连接类虽然很简洁了,但适配器类还是我们自己编写的,也比较的麻烦
动态代理
动态代理学习
印子: ```java // 这个是一个类 public class Student { public void eat(String name) {
System.out.println("学生吃" + name);
}
public void study() {
System.out.println("在家自学");
} }
// 这里是使用这个类 public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Student stu = new Student(); stu.eat(“米饭”); stu.study(); } }
但是我们现在有一个很不合理的要求!!!```java/** 要求:在不改变Study类中任何代码的前提下,通过study方法输出一句话:来黑马学习* */
动态代理介绍:
- 动态代理:在不改变目标对象方法的情况下对方法进行增强
- 组成
被代理对象:真实的对象
代理对象:内存中的一个对象
- 要求
代理对象必须和被代理对象实现相同的接口
- 实现
Proxy.newProxyInstance()
首先要有接口
public interface StudentInterface {void eat(String name);void study();}public class Student implements StudentInterface {public void eat(String name) {System.out.println("学生吃" + name);}public void study() {System.out.println("在家自学");}}
然后直接在使用处代理该对象
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {Student stu = new Student();/** 要求:在不改变Study类中任何代码的前提下,通过study方法输出一句话:来黑马学习* */StudentInterface si = (StudentInterface) Proxy.newProxyInstance(stu.getClass().getClassLoader(), new Class[]{StudentInterface.class}, new InvocationHandler() {/** 执行Student类中所有的方法都会经过invoke方法* 对method方法进行判断* 如果是study,则对其增强* 如果不是,还调用写生对象原有的功能即可* */@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {if (method.getName().equals("study")) {System.out.println("来黑马学习");return null;} else {return method.invoke(stu, args);}}});si.eat("米饭");si.study();}}
动态代理实现连接归还
动态代理非常简单,直接在使用处修改即可。
public class MyDataSource implements DataSource{//定义集合容器,用于保存多个数据库连接对象private static List<Connection> pool = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<Connection>());//静态代码块,生成10个数据库连接保存到集合中static {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {Connection con = JDBCUtils.getConnection();pool.add(con);}}//返回连接池的大小public int getSize() {return pool.size();}//动态代理方式@Overridepublic Connection getConnection() {if(pool.size() > 0) {//从池中获取数据库连接Connection con = pool.remove(0);Connection proxyCon = (Connection)Proxy.newProxyInstance(con.getClass().getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Connection.class}, new InvocationHandler() {/*执行Connection实现类所有方法都会经过invoke如果是close方法,则将连接还回池中如果不是,直接执行实现类的原有方法*/@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {if(method.getName().equals("close")) {pool.add(con);return null;}else {return method.invoke(con,args);}}});return proxyCon;}else {throw new RuntimeException("连接数量已用尽");}}//从池中返回一个数据库连接/*@Overridepublic Connection getConnection() {if(pool.size() > 0) {//从池中获取数据库连接Connection con = pool.remove(0);//通过自定义连接对象进行包装//MyConnection2 mycon = new MyConnection2(con,pool);MyConnection3 mycon = new MyConnection3(con,pool);//返回包装后的连接对象return mycon;}else {throw new RuntimeException("连接数量已用尽");}}*/}
1.5 开源连接池的使用
C3P0
1.C3P0数据库连接池的使用步骤。
1.导入ja包(需要两个)
2.导入配置文件到src目录下(最好是这个目录,因为是C3P0默认目录,会到这里查找配置文件)
3.创建C3P0连接池对象
4.获取数据库连接进行使用
注意:C3P0的配置文件会自动加载,但是必须叫c3p0-config.xml或c3p0-config.properties。
配置文件
<c3p0-config><!-- 使用默认的配置读取连接池对象 --><default-config><!-- 连接参数 --><property name="driverClass">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property><property name="jdbcUrl">jdbc:mysql://192.168.59.129:3306/db14</property><property name="user">root</property><property name="password">root</property><!-- 连接池参数 --><!-- 初始化的连接数量--><property name="initialPoolSize">5</property><!-- 最大连接数量--><property name="maxPoolSize">10</property><!-- 超时时间,当你用完10个,想要用第十一个的时候,会等待三秒钟,超过时间,就会告诉你,用完了--><property name="checkoutTimeout">3000</property></default-config><!-- 这个是指定一个名称,如果你不指定,则C3P0创建连接池用上面的默认配置--><!-- 如果指定了名称,则用这里的配置--><named-config name="otherc3p0"><!-- 连接参数 --><property name="driverClass">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property><property name="jdbcUrl">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db15</property><property name="user">root</property><property name="password">root</property><!-- 连接池参数 --><property name="initialPoolSize">5</property><property name="maxPoolSize">8</property><property name="checkoutTimeout">1000</property></named-config></c3p0-config>
直接使用
/*使用C3P0连接池1.导入jar包2.导入配置文件到src目录下3.创建c3p0连接池对象4.获取数据库连接进行使用*/public class C3P0Demo1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{//创建c3p0连接池对象 用空参构造,则是用的默认配置DataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();//获取数据库连接进行使用Connection con = dataSource.getConnection();//查询全部学生信息String sql = "SELECT * FROM student";PreparedStatement pst = con.prepareStatement(sql);ResultSet rs = pst.executeQuery();while(rs.next()) {System.out.println(rs.getInt("sid") + "\t" + rs.getString("name") + "\t" + rs.getInt("age") + "\t" + rs.getDate("birthday"));}//释放资源rs.close();pst.close();con.close(); // 将连接对象归还池中}}
配置演示,能拿到10个连接。如果要拿11个,3s钟后报错。close方法是归还
public class C3P0Demo2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{//创建c3p0连接池对象DataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();//获取数据库连接进行使用for(int i = 1; i <= 11; i++) {Connection con = dataSource.getConnection();System.out.println(i + ":" + con);if(i == 5) {con.close();}}}}
Druid
Druid使用
Druid
基本使用
/*Druid连接池1.导入jar包(1个jar包)2.编写配置文件,放在src目录下3.通过Properties集合加载配置文件(这个不会自动加载配置文件,需要自己读取)4.通过Druid连接池工厂类获取数据库连接池对象5.获取数据库连接,进行使用注意:Druid不会自动加载配置文件,需要我们手动加载,但是文件的名称可以自定义。*/public class DruidDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{//通过Properties集合加载配置文件InputStream is = DruidDemo1.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("druid.properties");Properties prop = new Properties();prop.load(is);//通过Druid连接池工厂类获取数据库连接池对象DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(prop);//获取数据库连接,进行使用Connection con = dataSource.getConnection();//查询全部学生信息String sql = "SELECT * FROM student";PreparedStatement pst = con.prepareStatement(sql);ResultSet rs = pst.executeQuery();while(rs.next()) {System.out.println(rs.getInt("sid") + "\t" + rs.getString("name") + "\t" + rs.getInt("age") + "\t" + rs.getDate("birthday"));}//释放资源rs.close();pst.close();con.close(); // 将连接对象归还池中}}
自定义数据库连接池工具类
```java / 数据库连接池工具类 / public class DataSourceUtils { //1.私有构造方法 private DataSourceUtils(){}
//2.定义DataSource数据源变量 private static DataSource dataSource;
//3.提供静态代码块,完成配置文件的加载和获取连接池对象 static { try{
//加载配置文件InputStream is = DruidDemo1.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("druid.properties");Properties prop = new Properties();prop.load(is);//获取数据库连接池对象dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(prop);
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} }
//4.提供获取数据库连接的方法 public static Connection getConnection() { Connection con = null; try {
con = dataSource.getConnection();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} return con; }
//5.提供获取数据库连接池的方法(为什么要有提供连接池的方法,因为后面我们自定义框架需要连接池对象) public static DataSource getDataSource() { return dataSource; }
//6.提供释放资源的方法 public static void close(Connection con, Statement stat, ResultSet rs) { if(con != null) {
try {con.close();} catch (SQLException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
}
if(stat != null) {
try {stat.close();} catch (SQLException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
}
if(rs != null) {
try {rs.close();} catch (SQLException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
} }
// 后期增删改,没有rs对象,即结果集对象 public static void close(Connection con, Statement stat) { close(con,stat,null); }
}
测试工具类略!<a name="jIjYV"></a># 2. 自定义JDBC框架(JDBCTemplate)——这里视频没有看后面我们要学习JDBC框架了,其就是对JDBC的封装,我们提前先自己定义一个。<a name="VSzst"></a>## 2.1 分析前一天案例中的重复代码- dao层的重复代码- 定义必要的信息、获取数据库的连接、释放资源都是重复的代码!- 而我们最终的核心功能仅仅只是执行一条sql语句而已啊!- 所以我们可以抽取出一个JDBC模板类,来封装一些方法(update、query),专门帮我们执行增删改查的sql语句!- 将之前那些重复的操作,都抽取到模板类中的方法里。就能大大简化我们的使用步骤!<a name="w1nlS"></a>## 2.2 自定义JDBC框架<a name="S4aTL"></a>### 2.2.1数据库的源信息- DataBaseMetaData(了解):数据库的源信息- java.sql.DataBaseMetaData:封装了整个数据库的综合信息- 例如:- String getDatabaseProductName():获取数据库产品的名称- int getDatabaseProductVersion():获取数据库产品的版本号- ParameterMetaData:参数的源信息- java.sql.ParameterMetaData:封装的是预编译执行者对象中每个参数的类型和属性- 这个对象可以通过预编译执行者对象中的getParameterMetaData()方法来获取- 核心功能:- int getParameterCount():获取sql语句中参数的个数- ResultSetMetaData:结果集的源信息- java.sql.ResultSetMetaData:封装的是结果集对象中列的类型和属性- 这个对象可以通过结果集对象中的getMetaData()方法来获取- 核心功能:- int getColumnCount():获取列的总数- String getColumnName(int i):获取列名<a name="Dnaub"></a>### 2.2.2JDBCTemplate类增删改功能的编写```javapublic class JDBCTemplate {private DataSource dataSource;private Connection con;private PreparedStatement pst;private ResultSet rs;public JDBCTemplate(DataSource dataSource) {this.dataSource = dataSource;}//专用于执行增删改sql语句的方法public int update(String sql,Object...objs) {int result = 0;try{con = dataSource.getConnection();pst = con.prepareStatement(sql);//获取sql语句中的参数源信息ParameterMetaData pData = pst.getParameterMetaData();//获取sql语句中参数的个数int parameterCount = pData.getParameterCount();//判断参数个数是否一致if(parameterCount != objs.length) {throw new RuntimeException("参数个数不匹配");}//为sql语句中的?占位符赋值for (int i = 0; i < objs.length; i++) {pst.setObject(i+1,objs[i]);}//执行sql语句result = pst.executeUpdate();} catch(Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {//释放资源DataSourceUtils.close(con,pst);}//返回结果return result;}}
2.2.3JDBCTemplate类查询功能的编写
实体类
/*学生实体类*/public class Student {private Integer sid;private String name;private Integer age;private Date birthday;public Student() {}public Student(Integer sid, String name, Integer age, Date birthday) {this.sid = sid;this.name = name;this.age = age;this.birthday = birthday;}public Integer getSid() {return sid;}public void setSid(Integer sid) {this.sid = sid;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public Integer getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(Integer age) {this.age = age;}public Date getBirthday() {return birthday;}public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {this.birthday = birthday;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Student{" +"sid=" + sid +", name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +", birthday=" + birthday +'}';}}
ResultSetHandler接口
/*用于处理结果集的接口*/public interface ResultSetHandler<T> {//处理结果集的抽象方法。<T> T handler(ResultSet rs);}
BeanHandler实现类
/*实现类1:用于完成将查询出来的一条记录,封装到Student对象中*/public class BeanHandler<T> implements ResultSetHandler<T> {//1.声明对象类型变量private Class<T> beanClass;//2.有参构造对变量赋值public BeanHandler(Class<T> beanClass) {this.beanClass = beanClass;}/*将ResultSet结果集中的数据封装到beanClass类型对象中*/@Overridepublic T handler(ResultSet rs) {//3.声明对象T bean = null;try{//4.创建传递参数的对象bean = beanClass.newInstance();//5.判断是否有结果集if(rs.next()) {//6.得到所有的列名//6.1先得到结果集的源信息ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();//6.2还要得到有多少列int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();//6.3遍历列数for(int i = 1; i <= columnCount; i++) {//6.4得到每列的列名String columnName = rsmd.getColumnName(i);//6.5通过列名获取数据Object columnValue = rs.getObject(columnName);//6.6列名其实就是对象中成员变量的名称。于是就可以使用列名得到对象中属性的描述器(get和set方法)PropertyDescriptor pd = new PropertyDescriptor(columnName.toLowerCase(),beanClass);//6.7获取set方法Method writeMethod = pd.getWriteMethod();//6.8执行set方法,给成员变量赋值writeMethod.invoke(bean,columnValue);}}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}//7.将对象返回return bean;}}
BeanListHandler实现类
/*实现类2:用于将结果集封装到集合中*/public class BeanListHandler<T> implements ResultSetHandler<T> {//1.声明对象变量private Class<T> beanClass;//2.有参构造为变量赋值public BeanListHandler(Class<T> beanClass) {this.beanClass = beanClass;}@Overridepublic List<T> handler(ResultSet rs) {//3.创建集合对象List<T> list = new ArrayList<>();try{//4.遍历结果集对象while(rs.next()) {//5.创建传递参数的对象T bean = beanClass.newInstance();//6.得到所有的列名//6.1先得到结果集的源信息ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();//6.2还要得到有多少列int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();//6.3遍历列数for(int i = 1; i <= columnCount; i++) {//6.4得到每列的列名String columnName = rsmd.getColumnName(i);//6.5通过列名获取数据Object columnValue = rs.getObject(columnName);//6.6列名其实就是对象中成员变量的名称。于是就可以使用列名得到对象中属性的描述器(get和set方法)PropertyDescriptor pd = new PropertyDescriptor(columnName.toLowerCase(),beanClass);//6.7获取set方法Method writeMethod = pd.getWriteMethod();//6.8执行set方法,给成员变量赋值writeMethod.invoke(bean,columnValue);}//7.将对象保存到集合中list.add(bean);}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}//8.返回结果return list;}}
ScalarHandler实现类
/*实现类3:用于返回一个聚合函数的查询结果*/public class ScalarHandler<T> implements ResultSetHandler<T> {@Overridepublic Long handler(ResultSet rs) {//1.声明一个变量Long value = null;try{//2.判断是否有结果if(rs.next()) {//3.获取结果集的源信息ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();//4.获取第一列的列名String columnName = rsmd.getColumnName(1);//5.根据列名获取值value = rs.getLong(columnName);}} catch(Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}//6.将结果返回return value;}}
JDBCTemplate类 ```java public class JDBCTemplate { private DataSource dataSource; private Connection con; private PreparedStatement pst; private ResultSet rs;
public JDBCTemplate(DataSource dataSource) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
/*
专用于执行聚合函数sql语句的方法
*/ public Long queryForScalar(String sql, ResultSetHandler
rsh, Object…objs) { Long result = null;try{con = dataSource.getConnection();pst = con.prepareStatement(sql);//获取sql语句中的参数源信息ParameterMetaData pData = pst.getParameterMetaData();int parameterCount = pData.getParameterCount();//判断参数个数是否一致if(parameterCount != objs.length) {throw new RuntimeException("参数个数不匹配");}//为sql语句中的?占位符赋值for (int i = 0; i < objs.length; i++) {pst.setObject(i+1,objs[i]);}//执行sql语句rs = pst.executeQuery();//通过ScalarHandler方式对结果进行处理result = rsh.handler(rs);} catch(Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {//释放资源DataSourceUtils.close(con,pst,rs);}//将结果返回return result;
}
/*
专用于查询所有记录sql语句的方法
*/ public
List queryForList(String sql, ResultSetHandler rsh, Object…objs) { List<T> list = new ArrayList<>();try{con = dataSource.getConnection();pst = con.prepareStatement(sql);//获取sql语句中的参数源信息ParameterMetaData pData = pst.getParameterMetaData();int parameterCount = pData.getParameterCount();//判断参数个数是否一致if(parameterCount != objs.length) {throw new RuntimeException("参数个数不匹配");}//为sql语句中的?占位符赋值for (int i = 0; i < objs.length; i++) {pst.setObject(i+1,objs[i]);}//执行sql语句rs = pst.executeQuery();//通过BeanListHandler方式对结果进行处理list = rsh.handler(rs);} catch(Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {//释放资源DataSourceUtils.close(con,pst,rs);}//将结果返回return list;
}
/*专用于执行查询一条记录sql语句的方法*/public <T> T queryForObject(String sql, ResultSetHandler<T> rsh, Object...objs) {T obj = null;try{con = dataSource.getConnection();pst = con.prepareStatement(sql);//获取sql语句中的参数源信息ParameterMetaData pData = pst.getParameterMetaData();int parameterCount = pData.getParameterCount();//判断参数个数是否一致if(parameterCount != objs.length) {throw new RuntimeException("参数个数不匹配");}//为sql语句中的?占位符赋值for (int i = 0; i < objs.length; i++) {pst.setObject(i+1,objs[i]);}//执行sql语句rs = pst.executeQuery();//通过BeanHandler方式对结果进行处理obj = rsh.handler(rs);} catch(Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {//释放资源DataSourceUtils.close(con,pst,rs);}//将结果返回return obj;}
}
<a name="ASERQ"></a>### 2.2.4 测试自定义JDBC框架的使用```javapublic class JDBCTemplateTest {//创建JDBCTemplate对象JDBCTemplate template = new JDBCTemplate(DataSourceUtils.getDataSource());@Testpublic void selectScalar() {//查询student表的记录条数String sql = "SELECT COUNT(*) FROM student";Long count = template.queryForScalar(sql, new ScalarHandler<Long>());System.out.println(count);}@Testpublic void selectAll() {//查询所有学生信息String sql = "SELECT * FROM student";List<Student> list = template.queryForList(sql, new BeanListHandler<Student>(Student.class));for(Student stu : list) {System.out.println(stu);}}@Testpublic void selectOne() {//查询张三这条记录String sql = "SELECT * FROM student WHERE sid=?";//通过BeanHandler将结果封装成一个Student对象Student stu = template.queryForObject(sql, new BeanHandler<Student>(Student.class), 1);System.out.println(stu);}@Testpublic void insert() {//新增周七记录String sql = "INSERT INTO student VALUES (?,?,?,?)";Object[] params = {5,"周七",27,"2007-07-07"};int result = template.update(sql, params);System.out.println(result);}@Testpublic void delete() {//删除周七这条记录String sql = "DELETE FROM student WHERE sid=?";int result = template.update(sql, 5);System.out.println(result);}@Testpublic void update() {//修改张三的年龄为33String sql = "UPDATE student SET age=? WHERE name=?";Object[] params = {33,"张三"};int result = template.update(sql,params);System.out.println(result);}}