如何启动FutureTask线程
public Future<Object> create(String startTime) {FutureTask<Object> futureTask = new FutureTask(() -> {// todo:处理相关异步任务return object;});// 使用线程池等方式调用futureTaskExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();executor.submit(futureTask);// Thread thread = new Thread(futureTask);// thread.start();return futureTask;}
public<T> Object invokeServiceMethod(Class<T> clazz, String methodName, int seconds, Object... params) {Class<?>[] paramTypes = new Class<?>[params.length];for (int i=0; i < params.length; i++){paramTypes[i] = params[i].getClass();}FutureTask<Object> future = new FutureTask<Object>(new Callable<Object>(){@Overridepublic Object call() throws Exception {Method method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod(methodName, paramTypes);method.setAccessible(true);T bean = SpringBeanUtils.getBean(clazz);return method.invoke(bean, params);}});ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();executor.execute(future);try {// 设定获取值的阻塞等待时间Object result = future.get(seconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS);return result;} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException | TimeoutException e) {LogUtil.error("数据访问异常");LogUtil.error(e.getMessage(), e);return Boolean.FALSE;} finally{future.cancel(true);executor.shutdown();}}
针对FutureTask的创建过程分析问题
问题一: FutureTask 的构造函数,如何通过new来创建自带返回值的FutureTask对象
(1)FutureTask的构造函数源码
/*** Creates a {@code FutureTask} that will, upon running, execute the* given {@code Callable}.** @param callable the callable task* @throws NullPointerException if the callable is null*/public FutureTask(Callable<V> callable) {if (callable == null)throw new NullPointerException();this.callable = callable;this.state = NEW; // ensure visibility of callable}/*** Creates a {@code FutureTask} that will, upon running, execute the* given {@code Runnable}, and arrange that {@code get} will return the* given result on successful completion.** @param runnable the runnable task* @param result the result to return on successful completion. If* you don't need a particular result, consider using* constructions of the form:* {@code Future<?> f = new FutureTask<Void>(runnable, null)}* @throws NullPointerException if the runnable is null*/public FutureTask(Runnable runnable, V result) {this.callable = Executors.callable(runnable, result);this.state = NEW; // ensure visibility of callable}
FutureTask的构造函数传递的参数类型是Callable,Callable与Runnable相似,但是Callable可以抛出异常。
同时,Callable中的call()方法相比Runnable中的run()方法, 前者有返回值,后者没有。
(2) Callable接口和Runnable区别
Callable与Runnable相似,但是Callable可以抛出异常。
Callable中的call()方法有返回值,Runnable中的run()方法没有返回值。
@FunctionalInterfacepublic interface Callable<V> {V call() throws Exception;}
(3) Runnable接口
@FunctionalInterfacepublic interface Runnable {public abstract void run();}
(4) FutureTask如何使用callable
// 成员变量callableprivate Callable<V> callable;public void run() {if (state != NEW ||!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset,null, Thread.currentThread()))return;try {Callable<V> c = callable;if (c != null && state == NEW) {V result;boolean ran;try {result = c.call();ran = true;} catch (Throwable ex) {result = null;ran = false;setException(ex);}if (ran)set(result);}} finally {// runner must be non-null until state is settled to// prevent concurrent calls to run()runner = null;// state must be re-read after nulling runner to prevent// leaked interruptsint s = state;if (s >= INTERRUPTING)handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s);}}
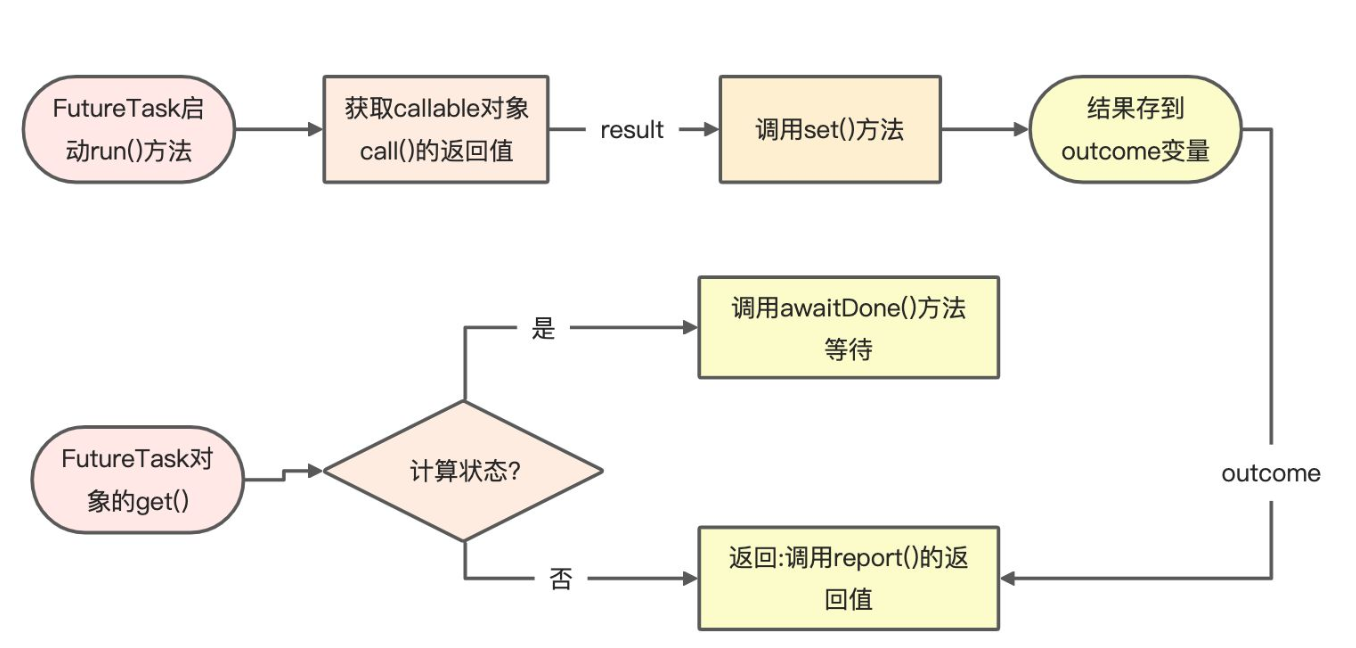
FutureTask启动run方法,会通过callable.call()获取到返回值result,然后将返回值result通过set()方法进行存储。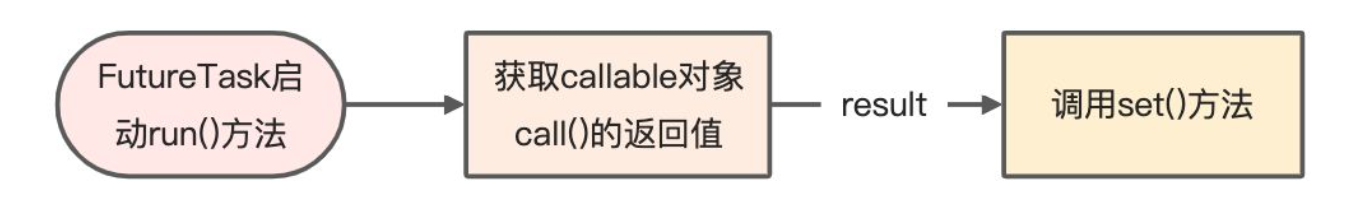
(5) set()方法和get()方法
set()方法中会把传入的callable的返回值,在线程安全的前提下,赋值给FutureTask的成员变量outcome。这个过程也代表了,启动Future会通过Callable来获取到一个结果,并将这个结果放到成员变量outcome,等待get()方法的获取。
protected void set(V v) {if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, COMPLETING)) {outcome = v;UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, NORMAL); // final statefinishCompletion();}}public V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {int s = state;if (s <= COMPLETING)s = awaitDone(false, 0L);return report(s);}
问题二:FutureTask类型的对象futureTask,为何可以传入到Thread对象构造方法中执行
FutureTask实现了RunnableFuture接口,RunnableFuture分别继承了Runnable接口和Future接口。
问题三:为何FutureTask可以当做Future类型的返回值
FutureTask实现了RunnableFuture接口,RunnableFuture分别继承了Runnable接口和Future接口。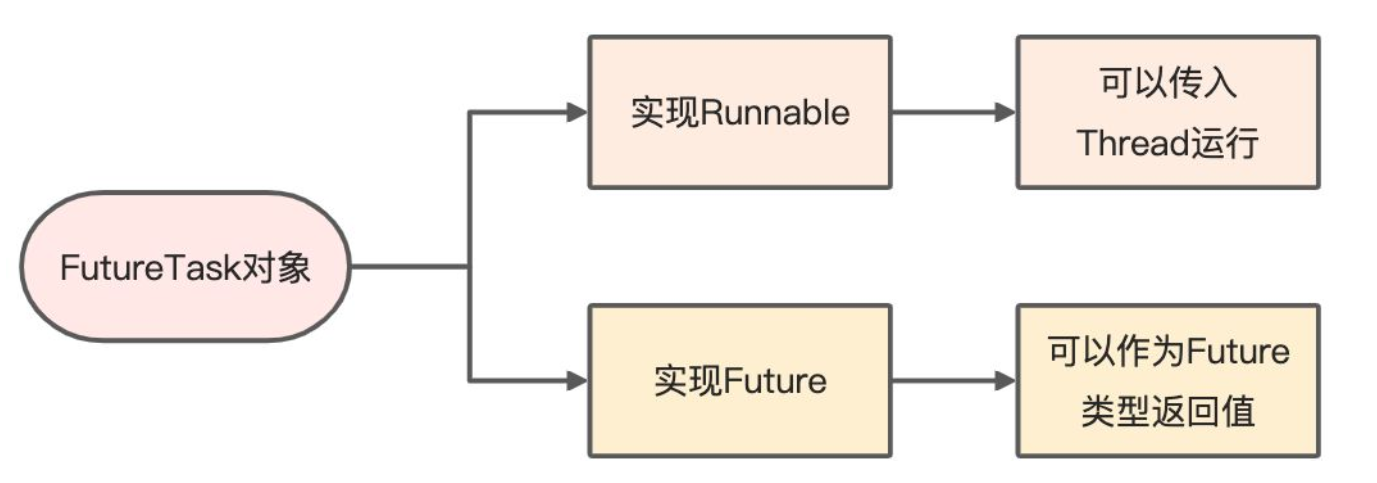
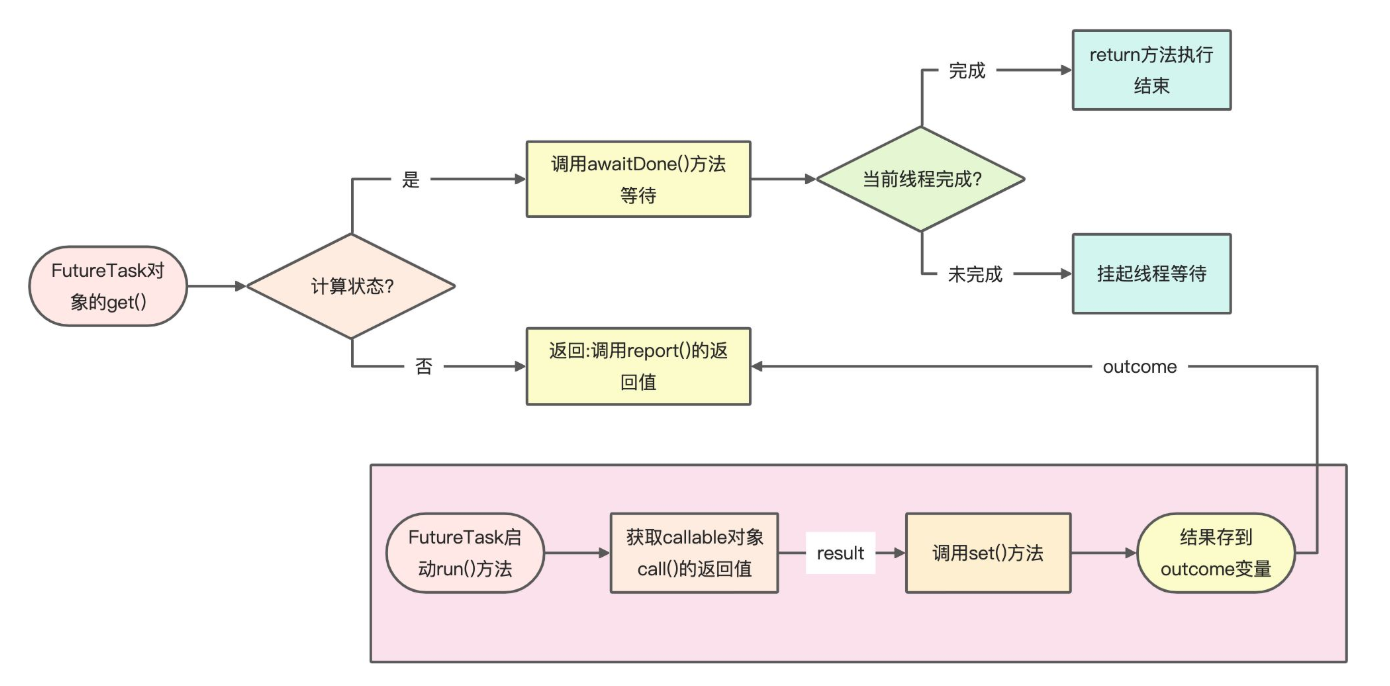
问题四:FutureTask对象执行get()方法时,是如何获取返回值的
调用get()方法时,如果state完成计算状态( s>COMPLETING ),会调用 report() 方法获取结果。
report()方法变量x赋值了outcome,outcome是前面在set()方法中callable对象的返回值,最后report()返回x值。
public V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {int s = state;if (s <= COMPLETING)s = awaitDone(false, 0L);return report(s);}private V report(int s) throws ExecutionException {Object x = outcome;if (s == NORMAL)return (V)x;if (s >= CANCELLED)throw new CancellationException();throw new ExecutionException((Throwable)x);}
问题五:FutureTask对象执行get()方法时,为什么会阻塞
调用get()方法时,如果state还在计算状态(s <= COMPLETING),就会调用awaitDone()方法进行等待。
如果s=COMPLETING状态,就会调用Thread.yield()使线程进入就绪状态,等待CPU的调度。
如果s>COMPLETING状态,说明当前线程完成,可以通过 return 方式执行结束。
如果s<COMPLETING状态,会通过 LockSupport.park(this) 将线程进入阻塞等待状态。
public V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {int s = state;if (s <= COMPLETING)s = awaitDone(false, 0L);return report(s);}private int awaitDone(boolean timed, long nanos)throws InterruptedException {final long deadline = timed ? System.nanoTime() + nanos : 0L;WaitNode q = null;boolean queued = false;for (;;) {if (Thread.interrupted()) {removeWaiter(q);throw new InterruptedException();}int s = state;if (s > COMPLETING) {if (q != null)q.thread = null;return s;}else if (s == COMPLETING) // cannot time out yetThread.yield();else if (q == null)q = new WaitNode();else if (!queued)queued = UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset,q.next = waiters, q);else if (timed) {nanos = deadline - System.nanoTime();if (nanos <= 0L) {removeWaiter(q);return state;}LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanos);}elseLockSupport.park(this);}}