执行main方法
启动的时候执行,虚拟机参数添加: -XX:+HeapDumpBeforeFullGC -XX:HeapDumpPath=d:\student.hprof
/*** 有一个学生浏览网页的记录程序,它将记录 每个学生访问过的网站地址。* 它由三个部分组成:Student、WebPage和StudentTrace三个类* 启动的时候执行,虚拟机参数添加: -XX:+HeapDumpBeforeFullGC -XX:HeapDumpPath=d:\student.hprof*/public class StudentTrace {static List<WebPage> webpages = new ArrayList<WebPage>();public static void createWebPages() {for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {WebPage wp = new WebPage();wp.setUrl("http://www." + Integer.toString(i) + ".com");wp.setContent(Integer.toString(i));webpages.add(wp);}}public static void main(String[] args) {createWebPages();//创建了100个网页//创建3个学生对象Student st3 = new Student(3, "Tom");Student st5 = new Student(5, "Jerry");Student st7 = new Student(7, "Lily");for (int i = 0; i < webpages.size(); i++) {if (i % st3.getId() == 0)st3.visit(webpages.get(i));if (i % st5.getId() == 0)st5.visit(webpages.get(i));if (i % st7.getId() == 0)st7.visit(webpages.get(i));}//清理掉webpages.clear();//触发gc垃圾回收System.gc();}}class Student {private int id;private String name;private List<WebPage> history = new ArrayList<>();public Student(int id, String name) {super();this.id = id;this.name = name;}public int getId() {return id;}public void setId(int id) {this.id = id;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public List<WebPage> getHistory() {return history;}public void setHistory(List<WebPage> history) {this.history = history;}public void visit(WebPage wp) {if (wp != null) {history.add(wp);}}}class WebPage {private String url;private String content;public String getUrl() {return url;}public void setUrl(String url) {this.url = url;}public String getContent() {return content;}public void setContent(String content) {this.content = content;}}
导入hprof文件开始分析
查看线程概述
打开hprof文件后点击下面图片的图标来查看线程概述
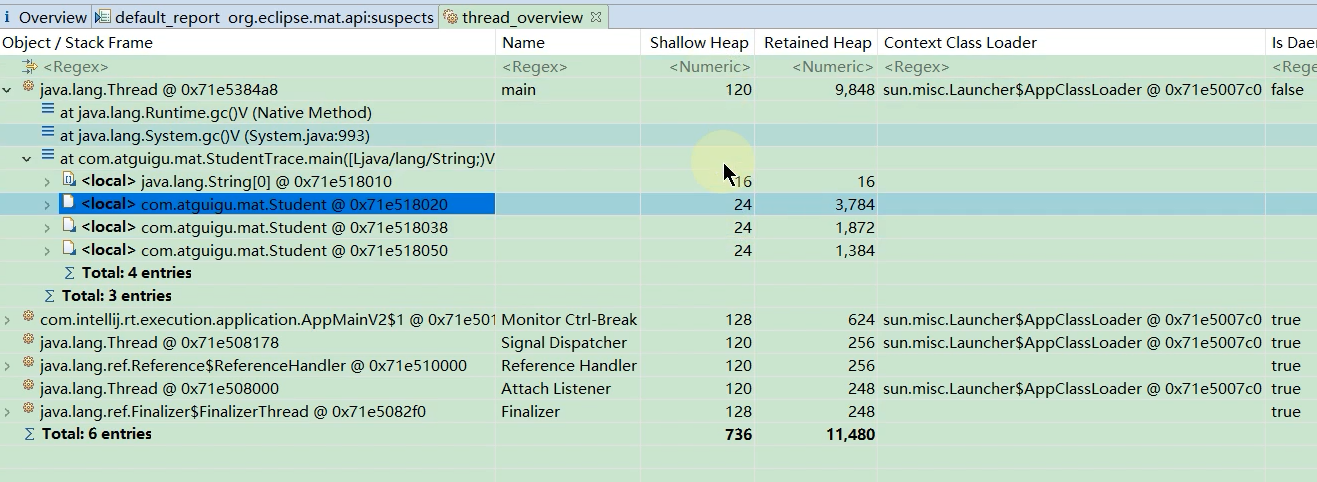
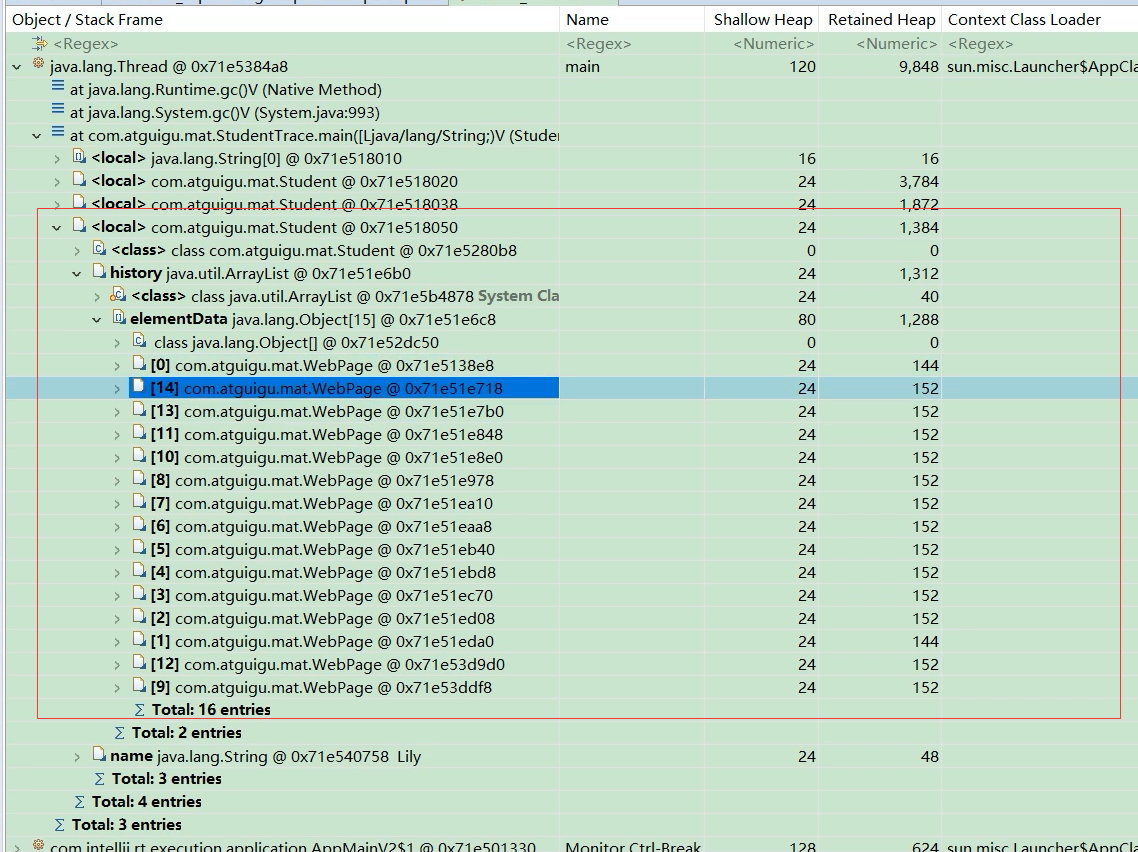
能看到main方法方法里面3个Student对象,三个student的shallow heap(浅堆)大小都是24, 但是三个对象的retained heap (深堆)都是不一样的.
第一个student对象如果被回收的话,就会回收3784个字节
第二个student对象如果被回收的话,就会回收1872个字节
第三个student对象如果被回收的话,就会回收1384个字节
为什么从第一个student对象到第三个student对象 深堆会越来越少呢???, 因为示例代码往三个student对象里面设置值
因为不同的分支条件不一样,进入第一个分支的多进入第二个分支的稍微少点,进入第三个分支的更少,所以第一个student对象深堆就大, 第二个student对象就稍微少点,第三个student对象就更少了.
深堆数量是怎么算出来的
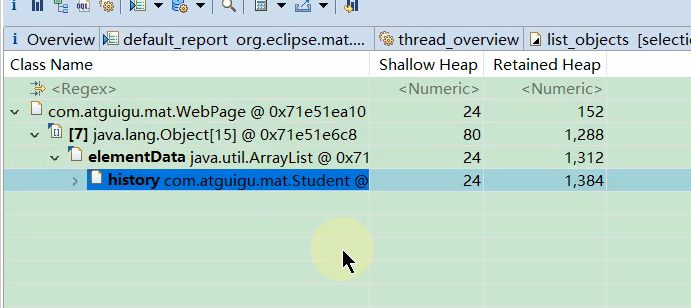
以最下面的student对象为例子,history深堆大小是1288 ,打开history这个ArrayList之后,发现ArrayList内部的elementData数组有一堆元素,再打开elementData数组之后,就能看到elementData这个数组里面有一堆WebPage对象了
elementData数组的浅堆是80个字节,而elementData数组中的所有WebPage对象的深堆之和是1208个字节,所以加在一起就是elementData数组的深堆之和,也就是1288个字节.
如果elementData数组要是被回收的话,只能回收掉1288个字节,原因是有一些WebPage还被别的student所引用,
15个WebPage对象,每个对应152字节, 15*152=2280字节,即2280位elementData的实际大小,但是为什么elementData的深堆是1288呢?
因为能被7整除且能被3整除,以及能被5整除的数值有: 0 21 35 42 63 84 70 ,总共七个数, 这七个数儿对应的WebPage不只是被这个student独享,还被其它的student对象引用了,这些是不能计算深堆里面的, 7*152就是1064个字节 ,
2280-1064 =1216 , 是1216这个数字,但是1216和显示的1288还是不一样,为什么这样呢?还差72个字节,这72个字节是什么呢? 因为elementData这个Object的数组引用也要占据一些空间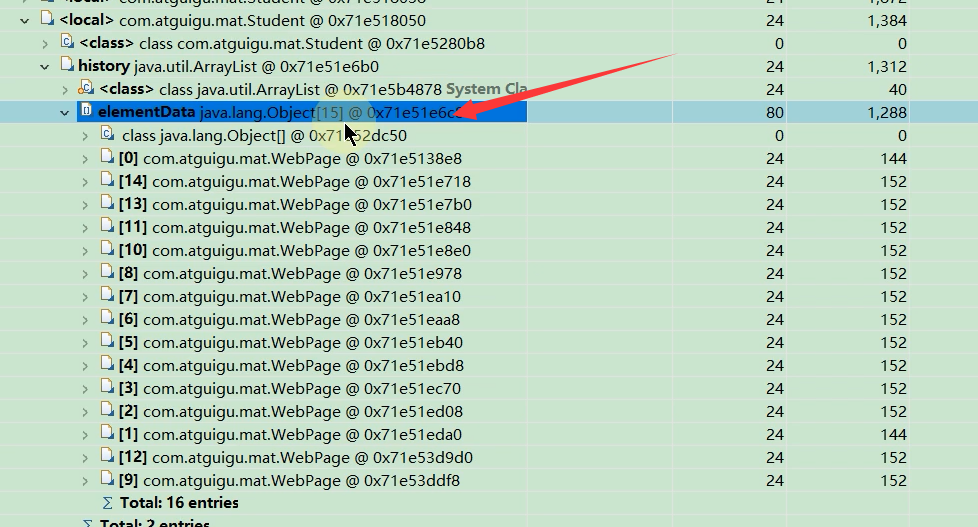
虽然elementData存了15个元素,但是不代表elementData数组长度就是15. 数组默认长度是10,如果装不下了就扩容成1.5倍,就变成了15了 ,数组长度15就能被第三个student对象装得下.
15个elementData的元素,每个元素占用4个字节, 15*4 = 60字节.
60+8个对象头的字节数+数组自己长度计数(4个字节) = 72字节
所以这就匹配上了:
因为第三个student对象在触发gc的时候只能有8个对象被回收掉, 每个占用152个字节,8个就是1216.
1216再加上elementData元素的字节+对象头的字节数+数组自己长度计数 就是 1288个字节
查看某个对象是否被别的对象引用
通过这个功能可以查看某个对象是否能被GC清理掉,是否存在内存泄露问题
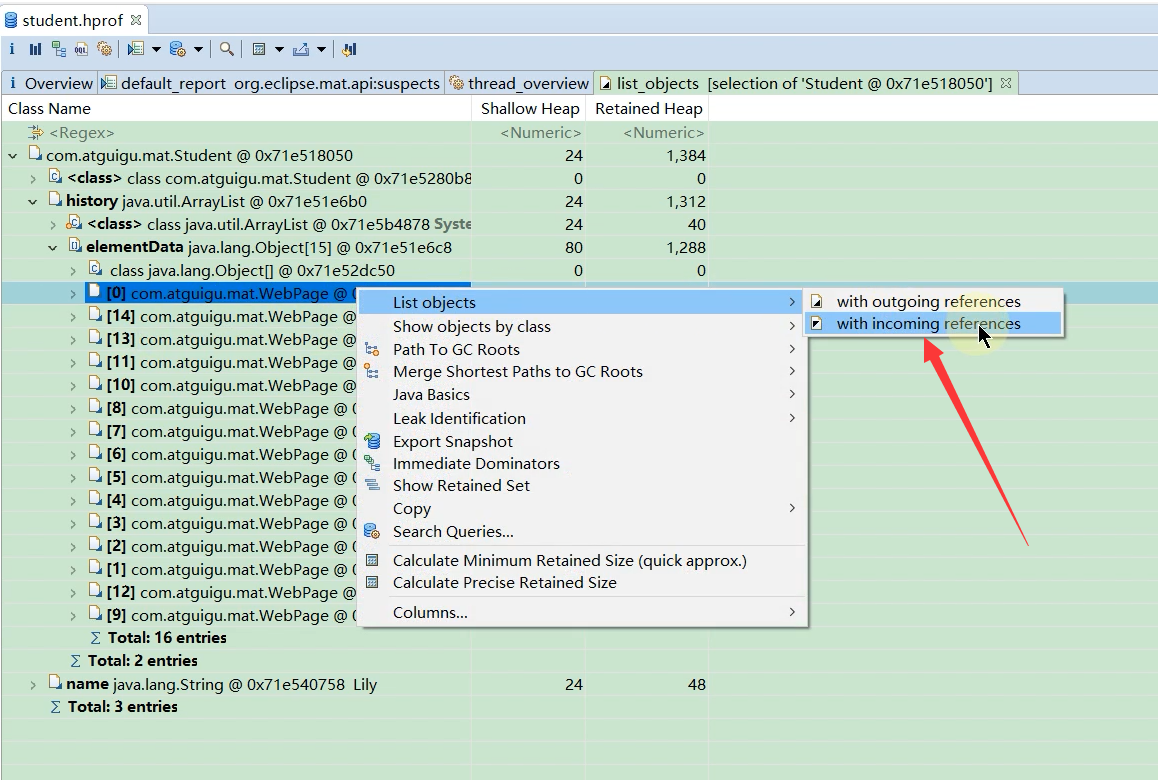
结果发现这个对象被三个对象引用了.
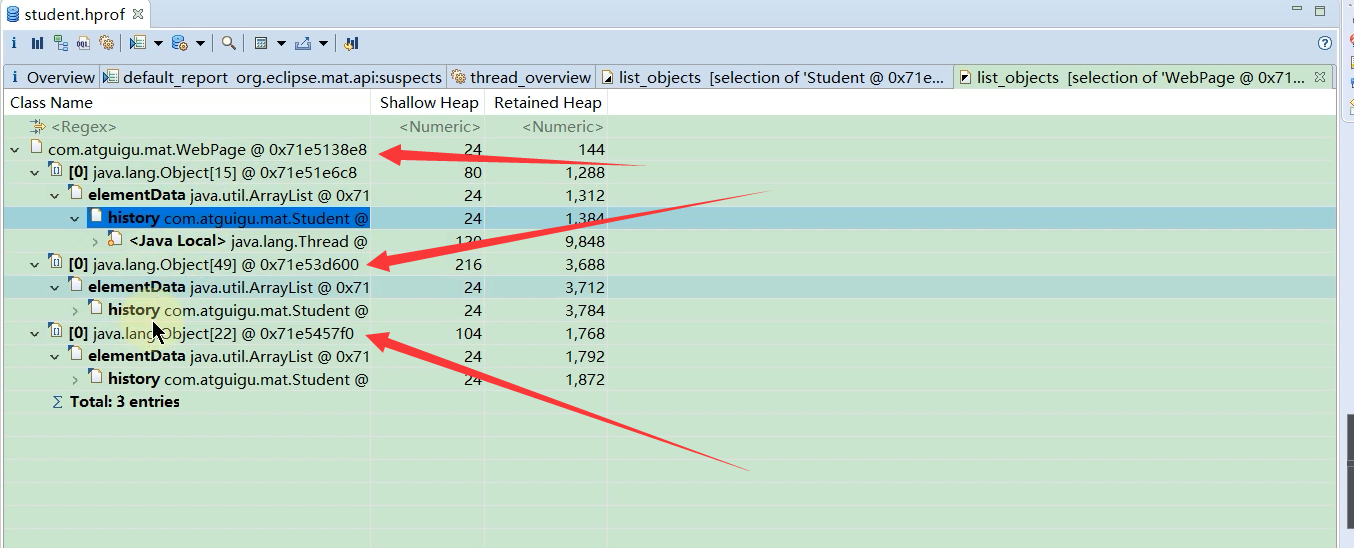
那么我们查看另外一个对象还有没有被其它对象引用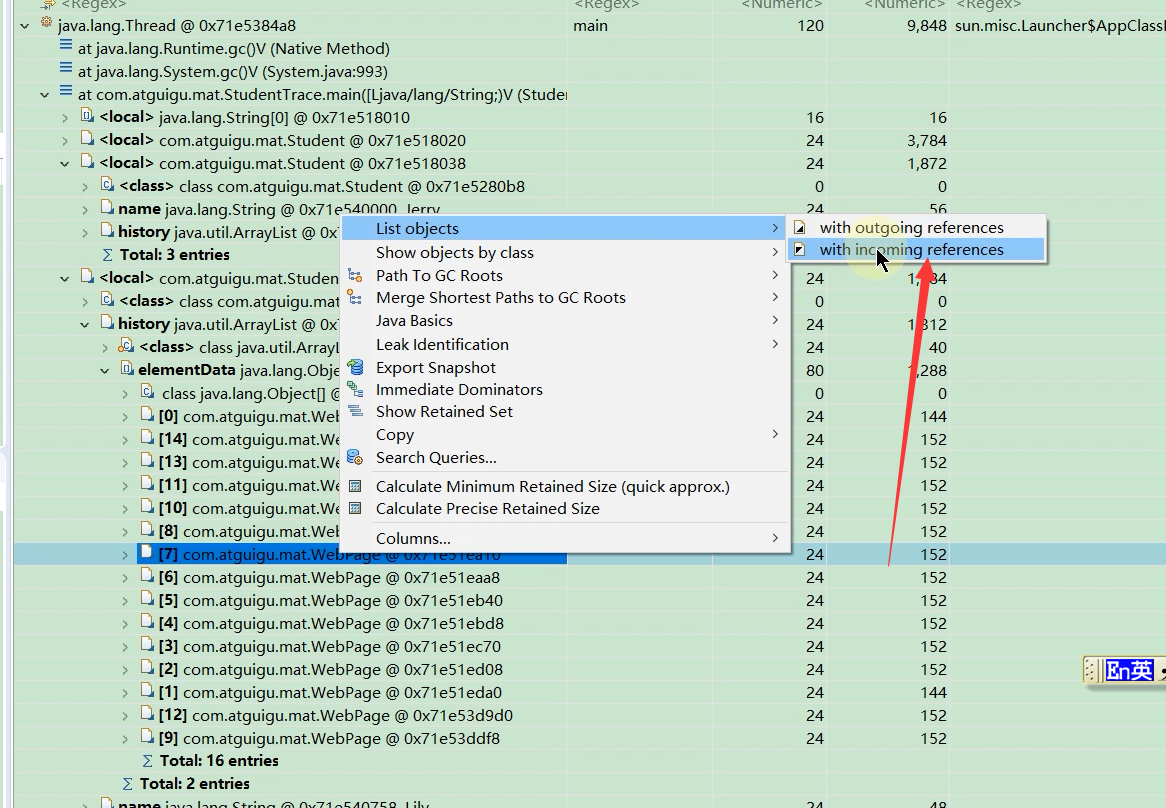
下图发现只有他自己引用了这个对象,那么当他自己被回收了之后,这个对象也会被回收