1 reco.proto
syntax = "proto3";// 使用message定义数据类型, 类似于 struct// 必须指定参数的序号message UserRequest {string user_id=1;int32 channel_id=2;int32 article_num=3;int64 time_stamp=4;}message Track {string click=1;string collect=2;string share=3;string read=4;}message Article {int64 article_id=1;Track track=2;}message ArticleResponse {string exposure=1;int64 time_stamp=2;// repeated表示Article可能会出现多次repeated Article recommends=3;}// 使用service定义一个服务, 相当于类service UserRecommend {// 使用rpc定义被调用的方法rpc user_recommend(UserRequest) returns(ArticleResponse) {}}
2 根据proto文件生成py文件
(1) 安装protobuf编译器和grpc库
pip install grpcio-tools
(2) 编译生成代码
python -m grpc_tools.protoc -I . —python_out=. —grpc_python_out=. reco.proto python -m grpc_tools.protoc -I . —python_out=. —grpc_python_out=. restartDocker.proto
- -I表示搜索proto文件中被导入文件的目录
- —python_out表示保存生成Python文件的目录,生成的文件中包含接口定义中的数据类型
- —grpc_python_out表示保存生成Python文件的目录,生成的文件中包含接口定义中的服务类型
运行后会生成两个新文件
- reco_pb2.py 保存接口定义文件中的数据类型(给python调用)
- reco_pb2_grpc.py 保存接口定义文件中的RPC方法(给grpc调用)
3 server.py
```python import time from concurrent.futures.thread import ThreadPoolExecutor
import grpc
import reco_pb2 import reco_pb2_grpc
class UserRecommandServicer(reco_pb2_grpc.UserRecommendServicer): ‘’’通过子类继承重写的方式’’’ def user_recommend(self, request, context): user_id = request.user_id channel_id = request.channel_id article_num = request.article_num time_stamp = request.time_stamp
resp = reco_pb2.ArticleResponse()resp.exposure = 'exposure param'resp.time_stamp = round(time.time() * 1000) # 以毫秒为单位_recommands = []for i in range(article_num):article = reco_pb2.Article()article.article_id = i + 1article.track.click = 'click param'article.track.collect = 'collect param'article.track.share = 'share param'article.track.read = 'read param'_recommands.append(article)resp.recommends.extend(_recommands)return resp
if name == ‘main‘:
# 创建一个rpc服务器server = grpc.server(ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=10))# 将自己实现的被调用方法与服务器绑定reco_pb2_grpc.add_UserRecommendServicer_to_server(UserRecommandServicer(), server)# 绑定IP地址和端口server.add_insecure_port('127.0.0.1:8888')# 开启服务器运行, 注意start()方法是非阻塞server.start()server.wait_for_termination()
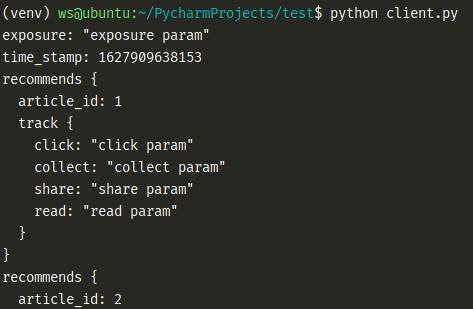
> nohup python3 -u server.py > out.log 2>&1 &- nohup: 不挂断地运行命令,忽略所有挂断信号(SIGNUP信号)- -u: python的输出是有缓冲的,即使在py脚本中每次遍历都有打印输出,但是因为缓冲的作用,我们不能在nohup.out日志中立即看到打印的输出。加上-u参数,使得python不使用缓冲。- > out.log: > 表示覆盖式重定向。正常输出是把内容输出到显示器上,重定向是把内容输出到文件中。 command > out.log,将输出重定向到xxx文件中。- 2 > &1: 2是标准错误输出,1是标准输出,这里的&表示引用的意思,对标准输出的引用, 将标准错误输出也重定向到标准输出指向的文件中。- 最后的&: 表示后台运行。<a name="qUrME"></a># 4 client.py```pythonimport timeimport grpcimport reco_pb2_grpcimport reco_pb2def feed_articles():with grpc.insecure_channel('127.0.0.1:8888') as channel:# 创建调用的辅助工具对象 stubstub = reco_pb2_grpc.UserRecommendStub(channel)# 创建请求对象, 并设置请求参数user_request = reco_pb2.UserRequest()user_request.user_id = '1'user_request.channel_id = 1user_request.article_num = 10user_request.time_stamp = round(time.time())# 通过stub进行rpc调用ret = stub.user_recommend(user_request)return retif __name__ == '__main__':ret = feed_articles()print(ret)
python server.py python client.py