热替换
热替换(Hot Module Replacement) 指的是修改代码后无需刷新页面即可生效。经常跟 Hot Module Reload 搞混。一个成熟的框架是必须要具备热替换能力的。Vite 的热替换实现与业界知名的一些模块如 webpack-dev-server 的实现类似。本质都是通过 websocket 建立服务端与浏览器的通信。如果对 WebSocket 不了解的可能需要先去学习下相关知识点。这里我们将分别分析修改几种不同类型的文件如 .vue, .js, .css 文件的热替换机制在 Vite 是具体如何实现的。同时也会分析 Vite 提供的热替换相关的 API,如: import.meta.hot
监听文件变化
首先服务端向浏览器发送消息肯定是在文件有变动才发送。在 webpack 的生态中,大多数 middleware/plugin 都是通过监听 webpack 提供的一些钩子函数,如下方代码摘自 webpack-dev-server 源码:
const addHooks = (compiler) => {const { compile, invalid, done } = compiler.hooksdone.tap('webpack-dev-server', (stats) => {// 通过开启webpack --watch选项,在webpack每次编译完新的文件时,触发这个钩子,向sockjs发送新的message,内容为新的静态资源的hash// 在_sendStats方法末尾会根据当前编译情况发送error/warning/ok三种类型的message给clientthis._sendStats(this.sockets, this.getStats(stats))})}
Node.js 本身提供了官方的 API 例如 fs.watch fs.watchFile 来监听文件的变化,Vite 则使用了这些 API 更上层的封装模块 chokidar 来进行文件系统的变动监听。
// src/node/server/index.ts// 监听整个项目根目录。忽略 node_modules 和 .git 文件夹const watcher = chokidar.watch(root, {ignored: [/\bnode_modules\b/, /\b\.git\b/]}) as HMRWatcher
css 热替换
有两种情况都可以修改样式,一种是修改外部 css 源文件。例如 import './index.css', 或者直接改 Vue 组件的 style 标签。这两种修改方式的热更新策略也不一样。
watcher.on('change', (filePath) => {if (isCSSRequest(filePath)) {const publicPath = resolver.fileToRequest(filePath)if (srcImportMap.has(filePath)) {// handle HMR for <style src="xxx.css">// it cannot be handled as simple css import because it may be scopedconst styleImport = srcImportMap.get(filePath)vueCache.del(filePath)vueStyleUpdate(styleImport)return}}})
查看注释我们可以知道当我们使用 <style src="xxx.css"> 这种方式来引入外部 css 文件,且文件变动时,需要执行 vueStyleUpdate 。我们不能简单的把它当作一个外部的 css 文件来处理。因为它可能是 scoped 局部作用域的。
if (filePath.includes('.module')) {moduleCssUpdate(filePath, resolver)}const boundaries = getCssImportBoundaries(filePath)if (boundaries.size) {for (let boundary of boundaries) {if (boundary.includes('.module')) {moduleCssUpdate(boundary, resolver)} else if (boundary.includes('.vue')) {vueCache.del(cleanUrl(boundary))vueStyleUpdate(resolver.fileToRequest(boundary))} else {normalCssUpdate(resolver.fileToRequest(boundary))}}return}// no boundariesnormalCssUpdate(publicPath)
css 导入关系链
以以下代码为例

const boundaries = getCssImportBoundaries(filePath)
这一行代码就是获取当前文件在 css 层级被导入关系链。包括独立的 css 文件以及 vue 组件的 style 标签 举个例子
// src/index.module.css.big {width: 200px}// src/index.css@import './index.module.css';
这时候 index.module.css 就是 index.css 的依赖(dependencies), Vite 会生成两个 Map 对象分别存储导入者,和被导入者的依赖关系
// cssImporterMap 被导入关系链Map(1) {'/Users/yuuang/Desktop/github/vite_test/src/index.module.css' => Set(1) { '/Users/yuuang/Desktop/github/vite_test/src/index.css' }}// cssImporteeMap 导入关系链Map(3) {'/Users/yuuang/Desktop/github/vite_test/src/App.vue?type=style&index=0' => Set(0) {},'/Users/yuuang/Desktop/github/vite_test/src/index.module.css' => Set(0) {},'/Users/yuuang/Desktop/github/vite_test/src/index.css' => Set(1) {'/Users/yuuang/Desktop/github/vite_test/src/index.module.css'}}
举个例子。当我们修改 src/index.module.css 时,那么依赖这个文件的文件都需要根据以下策略进行对应的更新。
即修改 src/index.module.css 时, src/index.css 也需要更新
我们可以看到 css 的更新策略分为三种
1、normalCssUpdate: 普通的外部 css 文件更新 例如 import './index.css'
2、moduleCssUpdate: 当 import 的 css 文件包含 .module 关键字时文件变动时, 或者 被导入关系链上含有 .module 文件。
3、vueStyleUpdate: 当通过 <style src="xxx.css"> 这种方式导入的文件变动时,或者被导入关系链上含有 .vue 文件
接下来让我们分别分析三种更新策略的具体行为
normalCssUpdate
普通的外部 css 文件更新例如 import './index.css'
function normalCssUpdate(publicPath: string) {// bust process cacheprocessedCSS.delete(publicPath)watcher.send({type: 'style-update',path: publicPath,changeSrcPath: publicPath,timestamp: Date.now()})}
通过 WebSocket 向浏览器发送了类型为 style-update 的消息并且附带修改的文件地址 src/index.css
case 'style-update':// check if this is referenced in html via <link>const el = document.querySelector(`link[href*='${path}']`)if (el) {el.setAttribute('href',`${path}${path.includes('?') ? '&' : '?'}t=${timestamp}`)break}// imported CSSconst importQuery = path.includes('?') ? '&import' : '?import'await import(`${path}${importQuery}&t=${timestamp}`)console.log(`[vite] ${path} updated.`)break
浏览器接收到该消息后做的事情也非常简单,根据传入的 path 在后面拼接上类型为 import 的 query 参数。并且附上时间参数 t 防止被缓存。接着使用 import 关键字让浏览器发起一个最新的 css 文件的请求
/src/index.css?import&t=1598530856590
moduleCssUpdate
针对使用了 css-modules 的文件的更新
首先要对 css-modules 有个基本的了解。如果没有开启 css-modules, 当我们使用 import style from './index.css'时,并不能得到具体的对象。在 Vite 中针对这种普通 css 文件将会导出 css 字符串。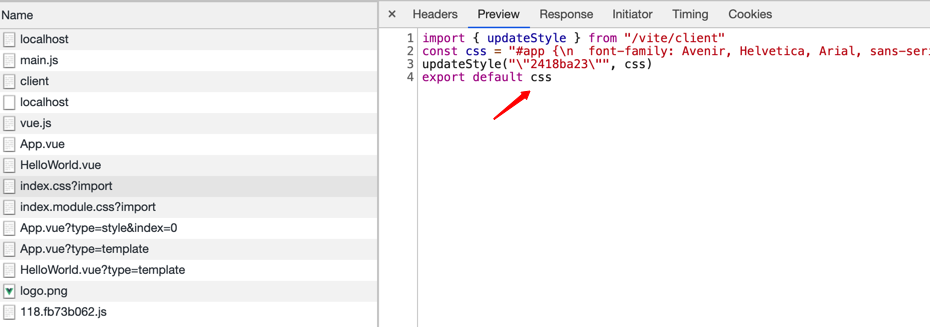 当我们开启 css-modules 后,通过
当我们开启 css-modules 后,通过 import style from './index.module.css' 可以得到具体的 css 类名关系映射对象

function moduleCssUpdate(filePath: string, resolver: InternalResolver) {// bust process cacheprocessedCSS.delete(resolver.fileToRequest(filePath))watcher.handleJSReload(filePath)}
因为启动了 css-modules 实质是导出一个对象。我们可以把这个文件当作 js 文件来看待。所以更新策略与我们后面讲到的 js 文件的热更新策略是一样的,接着让我们看看 handleJSReload 究竟干了什么
const handleJSReload = (watcher.handleJSReload = (filePath: string,timestamp: number = Date.now()) => {const publicPath = resolver.fileToRequest(filePath)const importers = importerMap.get(publicPath)})
首先获取被导入关系链,找到依赖 index.module.css 的文件,这里的 importers 是 App.vue
const dirtyFiles = new Set<string>()dirtyFiles.add(publicPath)const hasDeadEnd = walkImportChain(publicPath,importers || new Set(),hmrBoundaries,dirtyFiles)
我们将当前文件 src/index/module.css 加入脏文件的集合当中,因为当前文件需要修改。接着我们通过 walkImportChain 顾名思义,遍历导入链。做一些信息收集操作。并且判断需不需要页面的全量更新即页面刷新。这里的 importers 导入链只包含直接使用 import 关键字的文件。比如在 App.vue 中 import style from './index.module.css' 或者 main.js 中 import style from './index.module.css'。如果是在另一个 css 文件通过 @import './index.module.css' 的方式导入则不会被计入导入链
// 在这个例子里我们称 App.vue 为导入模块 称 index.module.css 为被导入模块function walkImportChain(importee: string,importers: Set<string>,hmrBoundaries: Set<string>,dirtyFiles: Set<string>,currentChain: string[] = []): boolean {if (hmrDeclineSet.has(importee)) {// 如果模块明确通过 import.meta.hot.decline 拒绝热更新,则直接页面刷新返回 truereturn true}if (isHmrAccepted(importee, importee)) {// 如果模块通过 import.meta.hot.accept 接收自身的更新则直接返回 false 不需要刷新hmrBoundaries.add(importee)dirtyFiles.add(importee)return false}for (const importer of importers) {if (importer.endsWith('.vue') ||// 如果导入模块 通过 import.meta.hot.acceptDeps 接收了被导入模块的更新通知isHmrAccepted(importer, importee) ||// 如果导入模块通过 import.meta.hot.accept 接收自身的更新isHmrAccepted(importer, importer)) {// 如果导入模块是 vue 组件,则添加进 脏文件,代表此文件需要被更新if (importer.endsWith('.vue')) {dirtyFiles.add(importer)}hmrBoundaries.add(importer)currentChain.forEach((file) => dirtyFiles.add(file))} else {// 如果导入模块不是 vue 组件则走else分支// 这里的导入模块可以是 js 文件,比如我们在 main.js 里面 import style from './index.module.css'// 如果走到了这个else分支且没有更上层的导入模块。则认为该模块的导入链都是js文件且最上层的文件是main.js。这种情况需要整个页面刷新const parentImpoters = importerMap.get(importer)if (!parentImpoters) {return true} else if (!currentChain.includes(importer)) {// 如果有更上层的导入模块则继续递归判断上层模块一直往上找if (walkImportChain(importer,parentImpoters,hmrBoundaries,dirtyFiles,currentChain.concat(importer))) {return true}}}}return false}
结合上面的分析,其实我们只需要关注什么情况下会返回 true 的情况即可。因为这种情况需要整个页面 reload。大部分情况下我们都不会走到这个逻辑。即只有当你修改的文件的最顶层导入模块是 main.js 的时候才需要进行页面的 reload
if (hasDeadEnd) {send({type: 'full-reload',path: publicPath})console.log(chalk.green(`[vite] `) + `page reloaded.`)}
如果 hasDeadEnd 为 true 则进行整个页面的 reload
const boundaries = [...hmrBoundaries]const file =boundaries.length === 1 ? boundaries[0] : `${boundaries.length} files`console.log(chalk.green(`[vite:hmr] `) +`${file} hot updated due to change in ${relativeFile}.`)send({type: 'multi',updates: boundaries.map((boundary) => {return {type: boundary.endsWith('vue') ? 'vue-reload' : 'js-update',path: boundary,changeSrcPath: publicPath,timestamp}})})
接着是不需要全量更新的情况。处理方式也很简单。我们遍历导入链。根据链上的每个文件的类型,发送对应的更新消息给客户端。这里我们的导入链上只有 App.vue。
所以发送 vue-reload 的消息
case 'vue-reload':queueUpdate(import(`${path}?t=${timestamp}`).catch((err) => warnFailedFetch(err, path)).then((m) => () => {__VUE_HMR_RUNTIME__.reload(path, m.default)console.log(`[vite] ${path} reloaded.`)}))break
这里维护了一个队列,来保证组件的更新顺序是先进先出。

可以看到页面重新请求了一个新的 App.vue 文件。且由于这个新文件的代码中包含新的带有时间参数t的 index.module.css 请求。所以我们也同样发起请求获取了新的 index.module.css 文件。
vueStyleUpdate
修改 vue 组件 style 标签样式
function vueStyleUpdate(styleImport: string) {const publicPath = cleanUrl(styleImport)const index = qs.parse(styleImport.split('?', 2)[1]).indexconst path = `${publicPath}?type=style&index=${index}`console.log(chalk.green(`[vite:hmr] `) + `${publicPath} updated. (style)`)watcher.send({type: 'style-update',path,changeSrcPath: path,timestamp: Date.now()})}
处理方式也非常简单。找到修改的具体组件发起新的请求且请求类型为 style
 可以看的新的请求只包含我们修改的新样式
可以看的新的请求只包含我们修改的新样式
js 热替换
js 文件的热更新其实在上面分析 css-modules 时已经顺带提到了。会被 handleJSReload 这个方法处理。处理结果也是两种
- 导入链最上层是 main.js 这种情况页面 reload
- 不需要全量更新,根据导入链发起新文件的请求
vue 组件热替换
vue 组件的热替换分为以下几种情况
vue-rerender只发起请求类型为 template 的请求。无需请求整个完整的新组件vue-reload发起新组件的完整请求style-updatestyle 标签更新style-removestyle 标签移除
接下来我们来分析每种情况的更新时机
更新类型
发起新组件的完整请求
//src/node/server/serverPluginVue.tswatcher.on('change', (file) => {if (file.endsWith('.vue')) {handleVueReload(file)}})
vue 文件修改时触发 handleVueReload 方法
const descriptor = await parseSFC(root, filePath, content)
首先用官方提供的库来将单文件组件编译成 descriptor。这里我们摘出比较重要的信息省略 sourcemap信息。
{filename: '/Users/yuuang/Desktop/github/vite_test/src/App.vue',source: '<template>\n' +' <img alt="Vue logo" src="./assets/logo.png" :class="style.big"/>\n' +' <div class="small">\n' +' small1\n' +' </div>\n' +' <HelloWorld msg="Hello Vue 3.0 + Vite" />\n' +'</template>\n' +'\n' +'<script>\n' +"import HelloWorld from './components/HelloWorld.vue'\n" +"import style from './index.module.css'\n" +'\n' +'export default {\n' +" name: 'App',\n" +' components: {\n' +' HelloWorld\n' +' },\n' +' data() {\n' +' return {\n' +' style: style\n' +' }\n' +' },\n' +' mounted () {\n' +" console.log('mounted')\n" +' }\n' +'}\n' +'</script>\n' +'\n' +'<style>\n' +'.small {\n' +' width:21px\n' +'}\n' +'</style>\n' +'\n',template: {type: 'template',content: '\n' +' <img alt="Vue logo" src="./assets/logo.png" :class="style.big"/>\n' +' <div class="small">\n' +' small1\n' +' </div>\n' +' <HelloWorld msg="Hello Vue 3.0 + Vite" />\n',loc: {source: '\n' +' <img alt="Vue logo" src="./assets/logo.png" :class="style.big"/>\n' +' <div class="small">\n' +' small1\n' +' </div>\n' +' <HelloWorld msg="Hello Vue 3.0 + Vite" />\n',start: [Object],end: [Object]},attrs: {},map: xxx},script: {type: 'script',content: '\n' +"import HelloWorld from './components/HelloWorld.vue'\n" +"import style from './index.module.css'\n" +'\n' +'export default {\n' +" name: 'App',\n" +' components: {\n' +' HelloWorld\n' +' },\n' +' data() {\n' +' return {\n' +' style: style\n' +' }\n' +' },\n' +' mounted () {\n' +" console.log('mounted')\n" +' }\n' +'}\n',loc: {source: '\n' +"import HelloWorld from './components/HelloWorld.vue'\n" +"import style from './index.module.css'\n" +'\n' +'export default {\n' +" name: 'App',\n" +' components: {\n' +' HelloWorld\n' +' },\n' +' data() {\n' +' return {\n' +' style: style\n' +' }\n' +' },\n' +' mounted () {\n' +" console.log('mounted')\n" +' }\n' +'}\n',start: [Object],end: [Object]},attrs: {},map: xxx},scriptSetup: null,styles: [{type: 'style',content: '\n.small {\n width:21px\n}\n',loc: [Object],attrs: {},map: [Object]}],customBlocks: []}
拿到 parse 之后的组件 descriptor 后 我们继续往下看
const prevDescriptor = cacheEntry && cacheEntry.descriptorif (!prevDescriptor) {// the file has never been accessed yetdebugHmr(`no existing descriptor found for ${filePath}`)return}
从缓存中读取之前的组件缓存。如果没有则说明该组件还没有被渲染。什么都不用做。这里解释一下什么情况下会走到这里。当我们启动本地服务,但是并没有真正访问过该服务时。此时所有的文件缓存除了预优化的部分 都是 undefined, 这时候我们直接修改组件会走到此 if 分支。
if (!isEqualBlock(descriptor.script, prevDescriptor.script) ||!isEqualBlock(descriptor.scriptSetup, prevDescriptor.scriptSetup)) {return sendReload()}function isEqualBlock(a: SFCBlock | null, b: SFCBlock | null) {// 首先比较两个对象的src属性,如果一样直接返回true// 接着遍历两个对象的 attrs 进行比较if (!a && !b) return trueif (!a || !b) return falseif (a.src && b.src && a.src === b.src) return trueif (a.content !== b.content) return falseconst keysA = Object.keys(a.attrs)const keysB = Object.keys(b.attrs)if (keysA.length !== keysB.length) {return false}return keysA.every((key) => a.attrs[key] === b.attrs[key])}
第一种需要重新 vue-reload 的情况,当我们同一个组件前后两次渲染时的 script 或者 scriptSetup 不一致时,需要重新 load 整个组件。setup 是 Vue3 中新提出的特性。如果前后组件的 script* 相等,则继续往下判断。
if (!isEqualBlock(descriptor.template, prevDescriptor.template)) {needRerender = true}
接下来判断如果前后的 template 不一致,则发送 vue-rerender 消息。只需要发起 type 为 template 的请求即可。
接下来是进行 style 的分析
// css modules update causes a reload because the $style object is changed// and it may be used in JS. It also needs to trigger a vue-style-update// event so the client busts the sw cache.if (prevStyles.some((s) => s.module != null) ||nextStyles.some((s) => s.module != null)) {return sendReload()}
如果应用了 css-modules 的 css 文件内容更新了则需要 vue-reload。 通过注释我们也可以看出原因。因为 css-modules 导出了一个对象,并且该对象在 js 文件中可能被使用了。同时它也需要触发 vue-style-update 类型的消息去清楚之前的 service worker 的缓存的文件。
 可以看到当我们修改 index.module.css 文件时,发送了两个消息分别是 vue-reload以及 style-update
可以看到当我们修改 index.module.css 文件时,发送了两个消息分别是 vue-reload以及 style-update
// force reload if CSS vars injection changedif (prevStyles.some((s, i) => {const next = nextStyles[i]if (s.attrs.vars && (!next || next.attrs.vars !== s.attrs.vars)) {return true}})) {return sendReload()}
如果 inject 注入的 css 变量改变, 触发 vue-reload
// force reload if scoped status has changedif (prevStyles.some((s) => s.scoped) !== nextStyles.some((s) => s.scoped)) {return sendReload()}
如果 scoped 属性发生了变化,触发 vue-reload
// only need to update styles if not reloading, since reload forces// style updates as well.nextStyles.forEach((_, i) => {if (!prevStyles[i] || !isEqualBlock(prevStyles[i], nextStyles[i])) {didUpdateStyle = trueconst path = `${publicPath}?type=style&index=${i}`send({type: 'style-update',path,changeSrcPath: path,timestamp})}})
如果组件前后的 descriptor 的 styles 属性不相等且不涉及其他会触发 vue-reload 的条件,此时发送 style-update 消息。
// stale styles always need to be removedprevStyles.slice(nextStyles.length).forEach((_, i) => {didUpdateStyle = truesend({type: 'style-remove',path: publicPath,id: `${styleId}-${i + nextStyles.length}`})})
如果组件前后的 styles 属性长度不一致。通常是移除了整个 style 标签。此时需要发送 style-remove 消息
const prevCustoms = prevDescriptor.customBlocks || []const nextCustoms = descriptor.customBlocks || []// custom blocks update causes a reload// because the custom block contents is changed and it may be used in JS.if (nextCustoms.some((_, i) =>!prevCustoms[i] || !isEqualBlock(prevCustoms[i], nextCustoms[i]))) {return sendReload()}
如果自定义块发生了改变则需要 vue-reload。因为自定义块在 js 中可能被使用。
客户端接收消息
上面提到了各种情况我们向客户端浏览器发送的消息类型。下面我们看看浏览器接收到这些类型的消息后分别做了什么事情
vue-reload
比较简单。直接发起新的带有 t 参数的组件请求
case 'vue-reload':queueUpdate(import(`${path}?t=${timestamp}`).catch((err) => warnFailedFetch(err, path)).then((m) => () => {__VUE_HMR_RUNTIME__.reload(path, m.default)console.log(`[vite] ${path} reloaded.`)}))break
vue-rerender
如上面提到的,vue-rerender 只需要发起 type 为 template 的组件请求即可
case 'vue-rerender':const templatePath = `${path}?type=template`import(`${templatePath}&t=${timestamp}`).then((m) => {__VUE_HMR_RUNTIME__.rerender(path, m.render)console.log(`[vite] ${path} template updated.`)})break
style-remove
style-update 在 css 热替换时已经介绍了。这里介绍 style-remove,其实本质跟 style-update 差不多。
case 'style-remove':removeStyle(payload.id)breakfunction removeStyle(id: string) {let style = sheetsMap.get(id)if (style) {if (style instanceof CSSStyleSheet) {// @ts-ignoreconst index = document.adoptedStyleSheets.indexOf(style)// @ts-ignoredocument.adoptedStyleSheets = document.adoptedStyleSheets.filter((s: CSSStyleSheet) => s !== style)} else {document.head.removeChild(style)}sheetsMap.delete(id)}}
通过传入的文件对应的 hashid。在当前文档的 CSSStyleSheet 中移除该样式。
总结
综上我们可以总结出不同的消息的触发情况
vue-reload
- script 或者 sctiptSetup 改变
- css-modules 文件改变
- css vars 改变
- scoped 改变
- customBlocks 自定义块改变
vue-rerender
- template 改变且不涉及其他会触发 vue-reload 的条件
style-update
- 组件前后的 descriptor 的 styles 属性不相等且不涉及其他会触发 vue-reload 的条件,此时发送 style-update 消息
style-remove
- 移除了整个 style 标签。此时需要发送 style-remove 消息

