
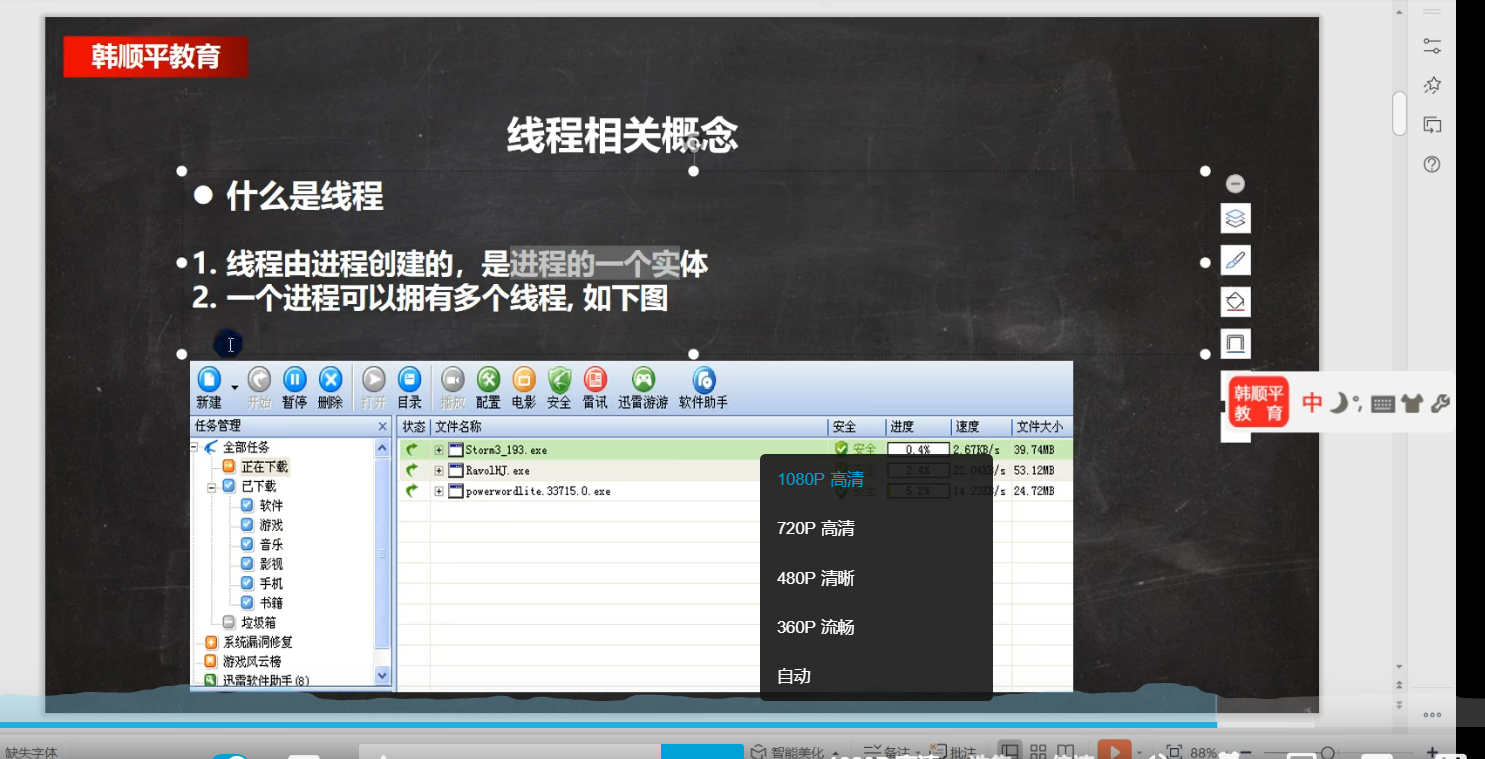

线程使用




class Hi implements Runnable { int times= 0; @Override public void run() { while (true){ try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("hi"+(++times)); if (times == 10){ break; } } } public static void main(String[] args) { Hi hi = new Hi(); //创建thread对象 Thread thread = new Thread(hi); thread.start(); }}
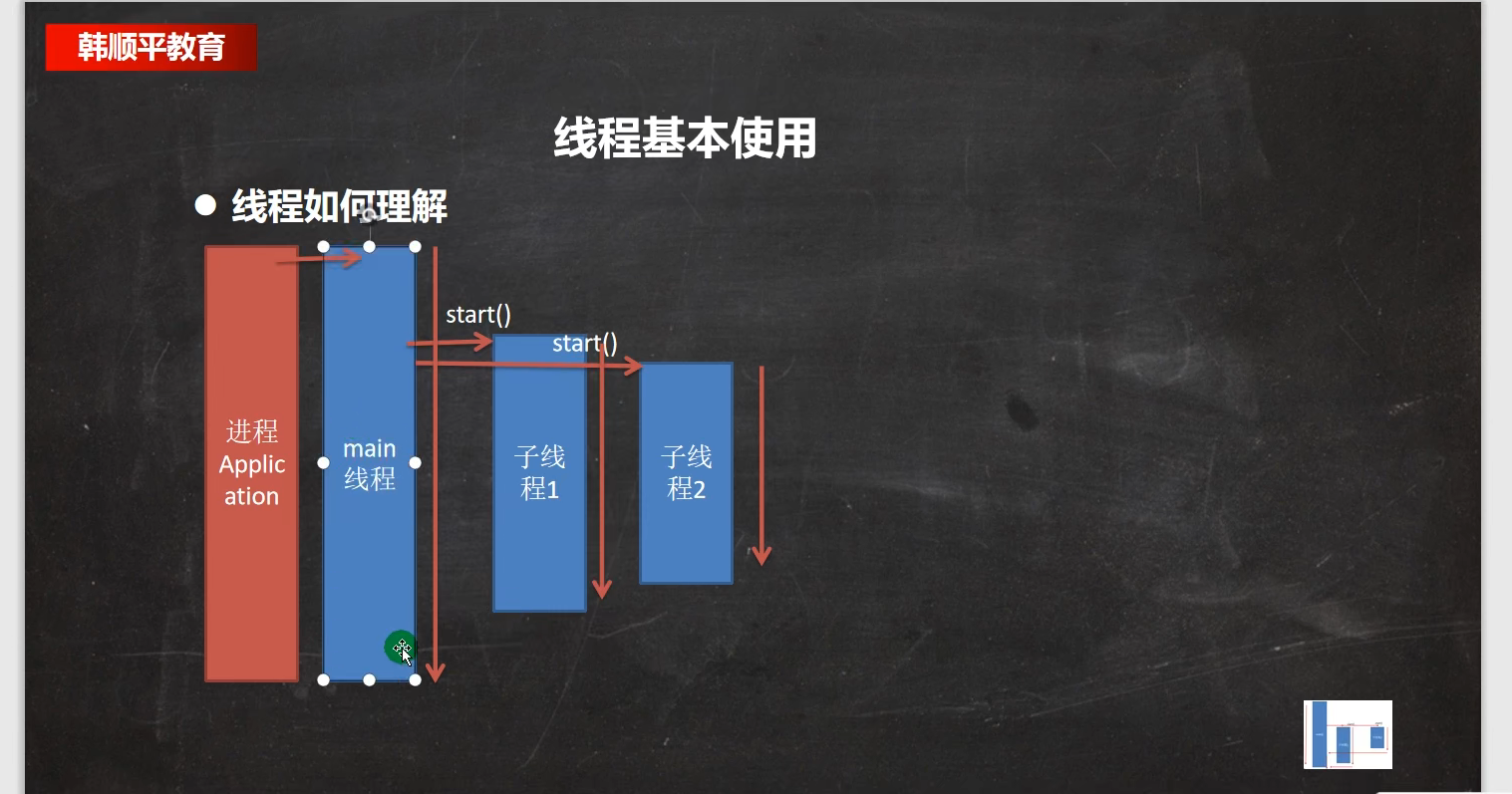


线程的终止

public class Exit { public static void main(String[] args) { T t = new T(); t.start(); try { System.out.println("休眠5s..."); Thread.sleep(10*500); t.setLoop(false);//设置loop的值 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }}class T extends Thread{ private int count = 0; //设置一个boolean 类型的对象,后面好赋值条件 private Boolean loop = true; //提供set方法给loop赋值 public void setLoop(Boolean loop) { this.loop = loop; } @Override public void run() { while (loop){ System.out.println("T 运行中...."); try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }}
线程的常用方法





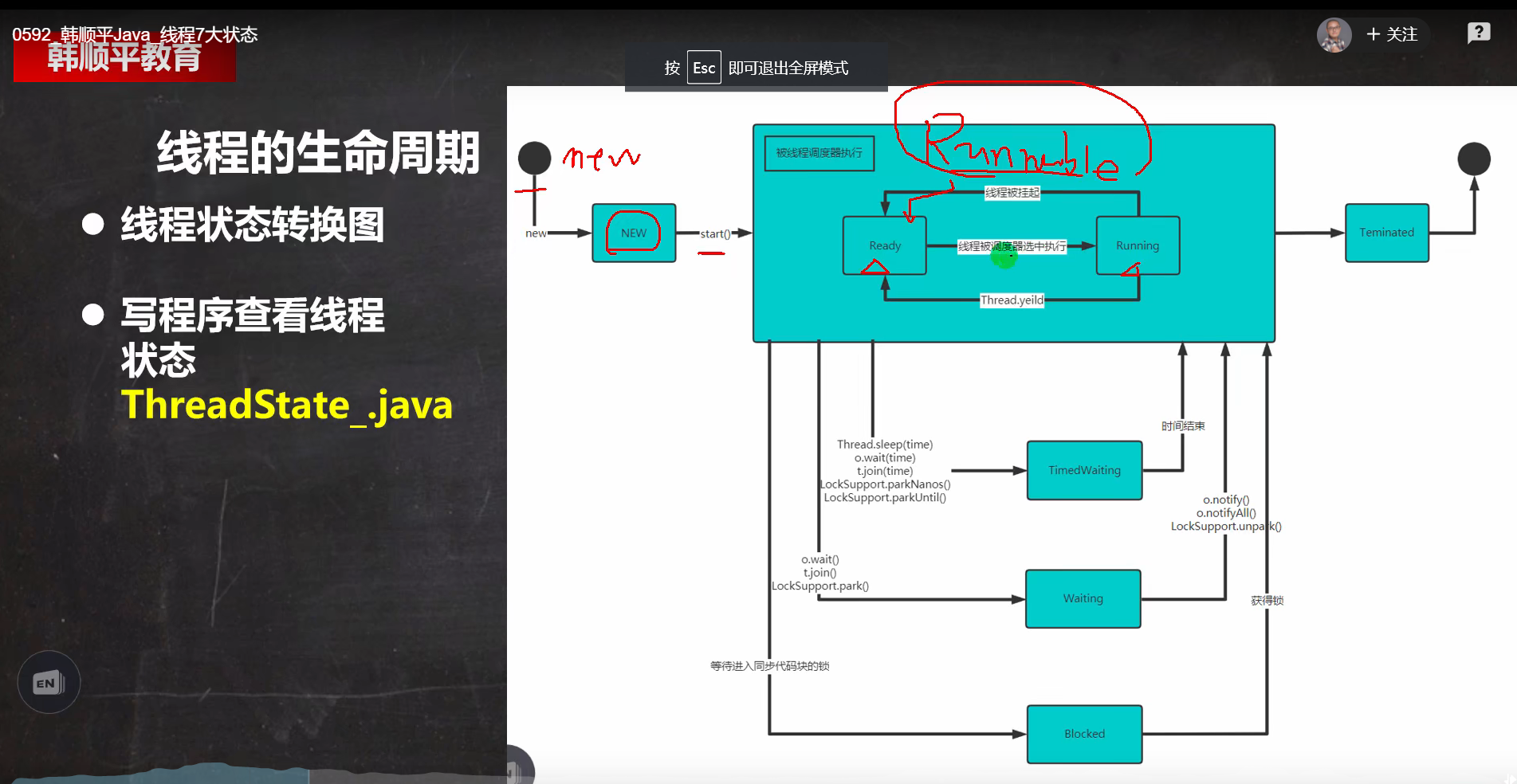
线程生命周期
线程同步

互斥锁





















