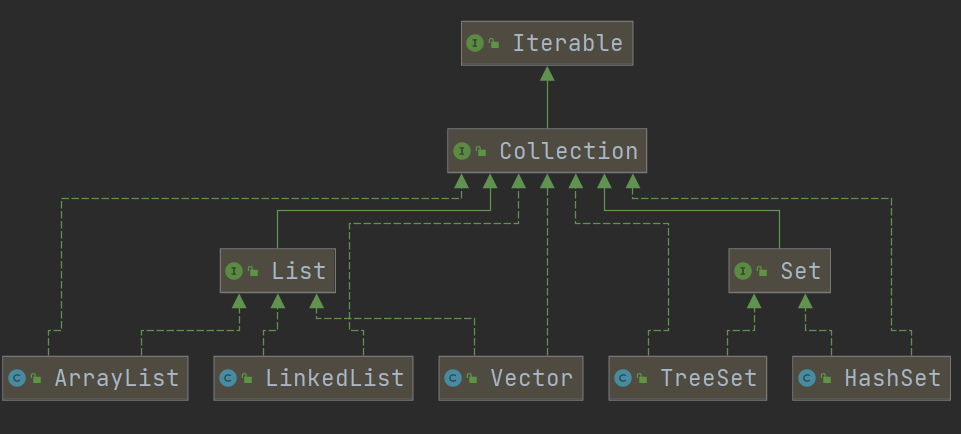
1.集合框架
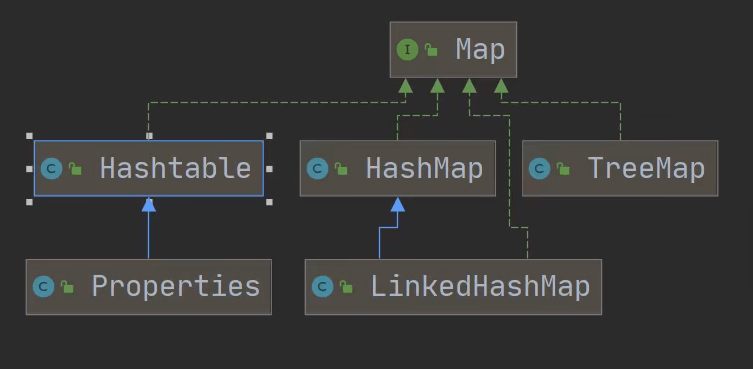
Map
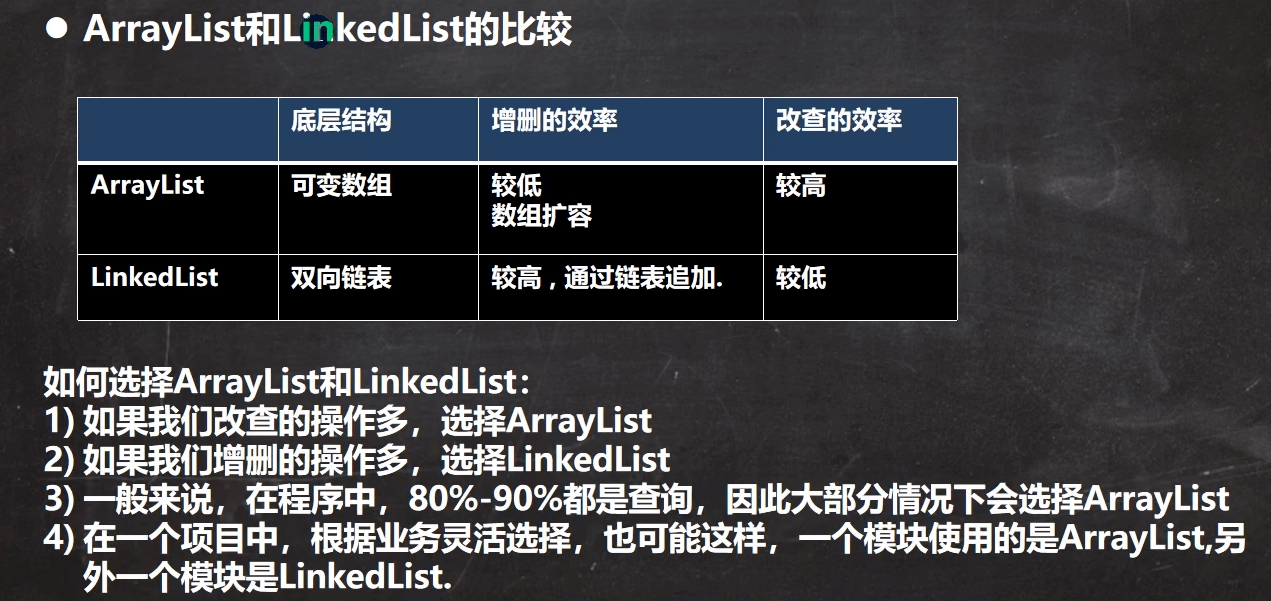
1.ArrayList

1.ArrayList的底层是一个Object的数组第一次初始化是一个长度为0的空数组transient Object[] elementData 不被序列化private int size 每次存入一一个元素,size就会+12.默认的初始容量是0第一次添加元素后容量为10private void grow(int minCapacity) {// overflow-conscious codeint oldCapacity = elementData.length;int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)newCapacity = minCapacity;if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); --//此处为第一次扩容}private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 103.拥有自动扩容机制,当元素大于当前容量时,会自动扩容,以保证list能够存放添加进去的元素。每次扩容都是原来的(1.5)倍int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);由于底层是一个数组,因而get和set方法都较为简单·size() 方法可以获取list的容量·set() 方法直接对指定位置进行赋值,且赋值前会进行角标越界检查·get() 方法通过角标获得值,由于List是一个Object数组,故而获取后进行转换·add() 方法可以添加一个元素
2.LinkedList
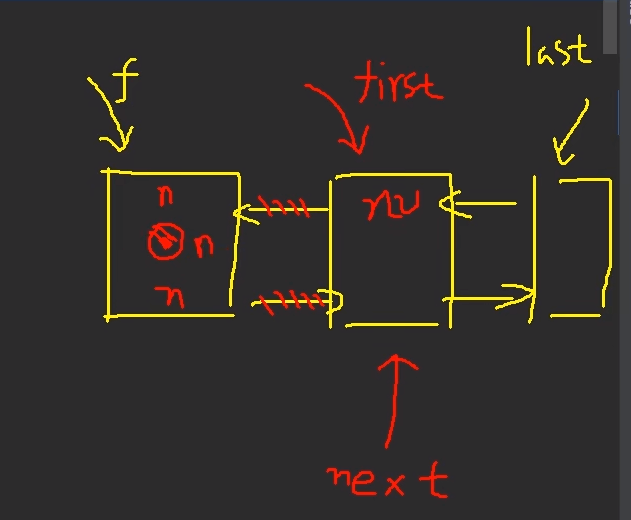
1.LinkedList是一个双向链表transient Node<E> first;transient Node<E> last;private static class Node<E> {E item;Node<E> next;Node<E> prev;节点Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {this.item = element;this.next = next;this.prev = prev;}}····添加void linkLast(E e) {final Node<E> l = last;final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);last = newNode;if (l == null)first = newNode;elsel.next = newNode;size++;modCount++;}····删除第一个private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) {// assert f == first && f != null;final E element = f.item;final Node<E> next = f.next;f.item = null;f.next = null; // help GCfirst = next;if (next == null)last = null;elsenext.prev = null;size--;modCount++;return element;}2.初始为0transient int size = 0;transient Node<E> first;transient Node<E> last;
删除
3.HashMap

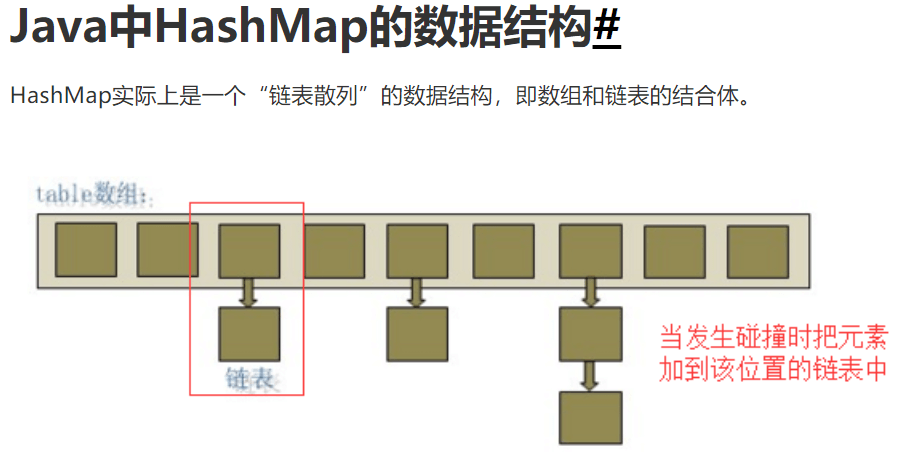
1.HashMap的默认容量为16底层维护了一个transient Node<K,V>[] table; node数组采用的数组+链表每次扩容都是原来的(2)倍2.加载因子为0.75,当元素大于等于容量的0.75倍时,就会进行扩容,是为了既要减少元素的碰撞,又充分利用空间提高空间利用率和减少查询成本的折中,主要是泊松分布,0.75的话碰撞最小3.如果key相同,后者的value就会覆盖掉前者的value,等价于替换4.key-value中,key放在一个set集合,value放在一个collection集合set不可重复,collection可重复但是实际上key-value是存放在Node<hash,key,value,Node<K,V> next>中的key,value中set和collection只是创建了一个引用指向了他们两个主要是为了方便遍历key和value,还会创建一个EntrySet集合,这个集合存放的类型是Entry而一个Entry对象就有有k,v EntrySet<Entry<key,value>> 即transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet而Entry就是一个Node节点详见HashSet
4.HashSet
1.HashSet底层是HashMappublic HashSet() {map = new HashMap<>();}2.元素不重复,可以存放空3.数据无序,存放顺序和取出顺序可能不同,因为获得hash值后,在确定元素的索引4.扩容2倍扩容5.为何相同元素添加不进去?set.add("java")1.执行addprivate static final Object PRESENT = new Object()PRESENT占位符因为hashSet存放的并不是键值对,所以,map的value处都默认添加一个PRESENT占位符public boolean add(E e) { e "java"return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;}2.put方法public V put(K key, V value) { key = "java" value = PRESENT key是变化的,value不变,因为底层用的hashmap属于键值对,而这里相当于只添加键故而值value为固定值return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);}2.1·hash()方法先调用hashcode方法算出hash值h,再亦或其hash值并且无符号右移16位此处为字符串的hashCode方法public int hashCode() {int h = hash;if (h == 0 && value.length > 0) {char val[] = value;for (int i = 0; i < value.length; i++) {h = 31 * h + val[i];}hash = h;}return h;}return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16)因此,putVal()方法中的int hash并不是hashCode计算出的值这样主要是为了减少数据的碰撞3.putVal()方法final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,boolean evict) {Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i; --辅助变量if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)--如果当前table是null,或者大小为0,进行第一次扩容--table就是map的一个属性,是一个数组,用来存放节点n = (tab = resize()).length;--resize()后 tab和n就变成了16if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)1.--根据传入的key,计算key的hash值,确认这个key该存放到table的那个索引--并且把这个位置的对象,赋给辅助变量p2.--判断这个p是不是空 "java" PRESENT--如果为空:表示还没有存放数据,就创建一个Node->tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null)真正存放数据的节点--不为空:tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);else {Node<K,V> e; K k;if (p.hash == hash && --1..如果当前索引位置链表的第一个元素的hash==和准备添加的key的hash之一样,到2--2.若满足以下两个条件之一--(1)准备加入的key和p指向的Node节点的Key是同一个对象--(2)不是用一个对象,但是内容相同--不能加入((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))e = p;--判断p是不是一颗红黑树else if (p instanceof TreeNode)e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);else {--如果索引3是一个链表,有多个值,那么待添加的元素就和他们依次比较内容,如果不同就添加在最后一个的后面--添加后判断节点数量是否为8,如果为8, 使用treeifyBin(tab, hash)把链表转为红黑树--红黑树化时:如果数组长度<64不会进行树化,而是继续reSize,扩容后,再转化为红黑树for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {if ((e = p.next) == null) {p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1sttreeifyBin(tab, hash);break;}--如果值一样,退出循环,比较下一个if (e.hash == hash &&((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))break;p = e;}}if (e != null) { // existing mapping for keyV oldValue = e.value;if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)e.value = value;afterNodeAccess(e);return oldValue;--返回空代表成功了}}++modCount;if (++size > threshold)--首次扩容时的临界值threshold=12--如果++size后大于当前临界值,就进行resize()进行扩容resize();afterNodeInsertion(evict);return null;}4.reSize()方法final Node<K,V>[] resize() {第一次时,table为空Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table;int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;int oldThr = threshold;--threshold是下一次更变大小的值,或者0int newCap, newThr = 0; --辅助变量oldCap首次为0,不进入该方法if (oldCap > 0) {if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;return oldTab;}else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold}else if (oldThr > 0) --需要更变大小的值newCap = oldThr;else { --初始值为0newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;--首次容量->DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY,为1<<<4 即初始容量为16newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY); --他是扩容需要的临界值--DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY 加载因子,为0.75--临界值->newThr = 16*0.75}if (newThr == 0) {float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);}threshold = newThr;@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap];--(Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap] 创建一个长度为16的数组,并转成Node,并且把Node赋给newTab节点table = newTab;--把newTab赋值给table,此时table就有16个容量if (oldTab != null) {for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {Node<K,V> e;if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {oldTab[j] = null;if (e.next == null)newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;else if (e instanceof TreeNode)((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);else { // preserve orderNode<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;Node<K,V> next;do {next = e.next;if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {if (loTail == null)loHead = e;elseloTail.next = e;loTail = e;}else {if (hiTail == null)hiHead = e;elsehiTail.next = e;hiTail = e;}} while ((e = next) != null);if (loTail != null) {loTail.next = null;newTab[j] = loHead;}if (hiTail != null) {hiTail.next = null;newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;}}}}}return newTab;}
首次添加元素Java,计算出hash值后,放在索引为3的位置
5.LinkedHashSet
链表的物理结构不一定和链表的逻辑结构一样,不同于顺序表
6.数据结构-简单二叉树的实现
package datatest;/*** @author 舞遍邓城一条街*/public class MyTreeTest {public static void main(String[] args) {TestTree testTree = new TestTree();testTree.setRoot(new TestNode(22,"小宝"));testTree.insert(new TestNode(18,"哈哈"));testTree.insert(new TestNode(50,"小宝大大"));testTree.insert(new TestNode(15,"小宝大大"));testTree.insert(new TestNode(19,"小宝大大"));testTree.delete(18);testTree.preList();System.out.println();System.out.println(testTree.getNode(50));}}@SuppressWarnings("all")class TestTree{private TestNode root;// 查找节点public TestNode getNode(int id){TestNode node = this.root;while (node.getId()!=id){if (node.getId()==id) {return node;}if (id>node.getId()) {node = node.getRight();} else {node = node.getLeft();}if (node==null) {break;}}return node;}// 插入节点public void insert(TestNode node){if (this.root==null){root = node;}else {TestNode cur = this.root;TestNode parent;while (true){parent = cur;if (node.getId() < parent.getId()){ // 是否去左子树cur = cur.getLeft();if (cur == null){parent.left = node;return;}}else{ // 是否去右子树cur = cur.getRight();if (cur == null){parent.right = node;return;}}}}}// 查找最值public TestNode getMin(){TestNode last = null;TestNode cur = this.root;while (cur!=null){last = cur;cur = cur.left;}return last;}public TestNode getMax(){TestNode last = null;TestNode cur = this.root;while (cur!=null){last = cur;cur = cur.getRight();}return last;}// 删除节点public boolean delete(int id){TestNode current = root;TestNode parent = root; // 记录要删除节点的父节点boolean isLeft = true; // 判断这个节点在父节点的左边还是右边while (current.getId()!=id){parent = current;if (id < current.getId()){isLeft = true;current = current.getLeft();}else{isLeft = false;current = current.getRight();}if (current == null) {return false; // 没有找到节点}}// 找到了该节点if (current.getLeft()==null && current.getRight()==null){if (current == root){ // 如果是根节点root = null;}else if (isLeft){ // 如果是左节点parent.left = null;}else { // 如果是右节点parent.right = null;}// 该节点没有右子节点,就让他的左子节点代当前节点}else if (current.getRight()==null){if (current == root){root = current.getLeft();}else if (isLeft){parent.left = current.getLeft();}else {parent.right = current.getLeft();}// 该节点没有左子节点,就让他的右子节点代当前节点}else if (current.getLeft() == null) {if (current == root) {root = current.getRight();}else if (isLeft){parent.left = current.getRight();}else {parent.right = current.getRight();}// 该节点有两个节点,就需要判断再决定让那个节点代替他} else {// 先查找该节点的后继节点TestNode success = getSuccess(current);if (current == root) {root = success;} else if (isLeft) {parent.left = success;}else {parent.right = success;}// 让该后继节点的左子树指向原来节点的左子树success.left = current.getLeft();}return true;}// 找要删除节点的后继节点private TestNode getSuccess(TestNode delnode){TestNode successParent = delnode;TestNode success = delnode;// 去右子树查找后继节点TestNode current = delnode.getRight();while (current!=null){// 记录当前节点的父节点successParent = success;// 记录当前节点success = current;current = current.getLeft();}if (success != delnode.getRight()){successParent.left = success.getRight();successParent.right = success.getRight();}return success;}// 遍历树public void preList(){if (this.root!=null){this.root.preList();}else {System.out.println("树为空");}}public void midList(){if (this.root!=null){this.root.midList();}else {System.out.println("树为空");}}public void postList(){if (this.root!=null){this.root.postList();}else {System.out.println("树为空");}}public TestTree() {}public TestNode getRoot() {return root;}public void setRoot(TestNode root) {this.root = root;}}@SuppressWarnings("all")class TestNode{public int id;public String name;public TestNode left;public TestNode right;// 前序遍历public void preList(){System.out.println(this);if (this.left!=null) {this.left.preList();}if (this.right!=null) {this.right.preList();}}// 中序遍历public void midList(){if (this.left!=null) {this.left.midList();}System.out.println(this);if (this.right!=null) {this.right.midList();}}// 后序遍历public void postList(){if (this.left!=null) {this.left.postList();}if (this.right!=null) {this.right.postList();}System.out.println(this);}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "TestNode{" +"id=" + id +", name='" + name + '\'' +'}';}public TestNode() {}public TestNode(int id, String name) {this.id = id;this.name = name;}public int getId() {return id;}public void setId(int id) {this.id = id;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public TestNode getLeft() {return left;}public TestNode getRight() {return right;}}