队列的应用
41:滑动窗口的平均值
:::info 请实现如下类型MovingAverage,计算滑动窗口中所有数字的平均值,该类型构造函数的参数确定滑动窗口的大小,每次调用成员函数next时都会在滑动窗口中添加一个整数,并返回滑动窗口中所有数字的平均值。 :::
public class MovingAverage {private Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();int sum = 0;int capcity = 0;public MovingAverage(int capacity) {this.capcity = capacity;}public double next(int val) {if (queue.size() == capcity) {int deletedNum = queue.poll();sum -= deletedNum;}sum += val;queue.add(val);return (double) sum / queue.size();}public static void main(String[] args) {MovingAverage movingAverage = new MovingAverage(3);System.out.println(movingAverage.next(1));System.out.println(movingAverage.next(2));System.out.println(movingAverage.next(3));System.out.println(movingAverage.next(4));}}
42:最近请求次数
:::info 题目:请实现如下类型RecentCounter,它是统计过去3000ms内的请求次数的计数器。该类型的构造函数RecentCounter初始化计数器,请求数初始化为0;函数ping(int t)在时间t添加一个新请求(t表示以毫秒为单位的时间),并返回过去3000ms内(时间范围为[t-3000,t])发生的所有请求数。假设每次调用函数ping的参数t都比之前调用的参数值大。 :::
public cleass RecentCounter {private int windowSize = 3000;private Queue<Integer> times = new LinkedList<>();public RecentCounter42() {}public int ping(int time) {times.offer(time);while(times.peek() + windowSize < time) {times.poll();}return times.size();}}
二叉树的广度优先搜索
BFS
:::info 二叉树的广度优先遍历 :::
public class TreeNode {public int val;public TreeNode left;public TreeNode right;public TreeNode(int val) {this.val = val;}}
public class BFS {public void bfd(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();if(root == null) {return result;}queue.add(root);while(queue.isNotEmpty()) {TreeNode node = queue.poll();result.add(node.val);if(node.left != null) {queue.offer(left);}if(node.right != null) {queue.offer(right);}}return result;}public static void main(String[] args) {TreeNode node5 = new TreeNode(5);TreeNode node7 = new TreeNode(7);TreeNode node6 = new TreeNode(6, node5, node7);TreeNode node9 = new TreeNode(9);TreeNode node11 = new TreeNode(11);TreeNode node10 = new TreeNode(10, node9, node11);TreeNode node8 = new TreeNode(8, node6, node10);System.out.println(bfs(node8));}}
:::info
笔记:
队列的特点是先进先出,所以每一层的元素先进队列之后,一定会先被遍历到,才会开始遍历后进的子节点。
:::
43:在完全二叉树中添加节点
:::info
题目:在完全二叉树中,除最后一层之外其他层的节点都是满的(第n层有2n-1个节点)。最后一层的节点可能不满,该层所有的节点尽可能向左边靠拢。例如,图7.3中的4棵二叉树均为完全二叉树。实现数据结构CBTInserter有如下3种方法。
● 构造函数CBTInserter(TreeNode root),用一棵完全二叉树的根节点初始化该数据结构。
● 函数insert(int v)在完全二叉树中添加一个值为v的节点,并返回被插入节点的父节点。例如,在如图7.3(a)所示的完全二叉树中添加一个值为7的节点之后,二叉树如图7.3(b)所示,并返回节点3。在如图7.3(b)所示的完全二叉树中添加一个值为8的节点之后,二叉树如图7.3(c)所示,并返回节点4。在如图7.3(c)所示的完全二叉树中添加节点9会得到如图7.3(d)所示的二叉树并返回节点4。
● 函数get_root()返回完全二叉树的根节点。
:::
public class CBTInserter {// 保存所有左右子节点不完全的节点private Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();private TreeNode root;public CBTInserter(TreeNode treeNode) {this.root = treeNode;if (treeNode != null) {queue.offer(treeNode);// 遍历直到找到最后一层不满的节点while (queue.peek().left != null && queue.peek().right != null) {TreeNode node = queue.poll();queue.offer(node.left);queue.offer(node.right);}}}public int insert(TreeNode node) {queue.offer(node);TreeNode parent = queue.peek();if (parent.left == null) {parent.left = node;} else {parent.right = node;// 右节点补齐了,要把这个节点从queue里面删掉了queue.poll();queue.offer(parent.left);queue.offer(parent.right);}return parent.val;}public TreeNode getRoot() {return root;}public static void main(String[] args) {TreeNode node4 = new TreeNode(4);TreeNode node5 = new TreeNode(5);TreeNode node2 = new TreeNode(2, node4, node5);TreeNode node6 = new TreeNode(6);TreeNode node7 = new TreeNode(7);TreeNode node3 = new TreeNode(3, node6, node7);TreeNode node1 = new TreeNode(1, node2, node3);CBTInserter inserter = new CBTInserter(node1);System.out.println(inserter.insert(new TreeNode(8)));System.out.println(inserter.insert(new TreeNode(9)));System.out.println(inserter.insert(new TreeNode(10)));}}
44:二叉树中每层的最大值
:::info 题目:输入一棵二叉树,请找出二叉树中每层的最大值。例如,输入图7.4中的二叉树,返回各层节点的最大值[3,4,9]。
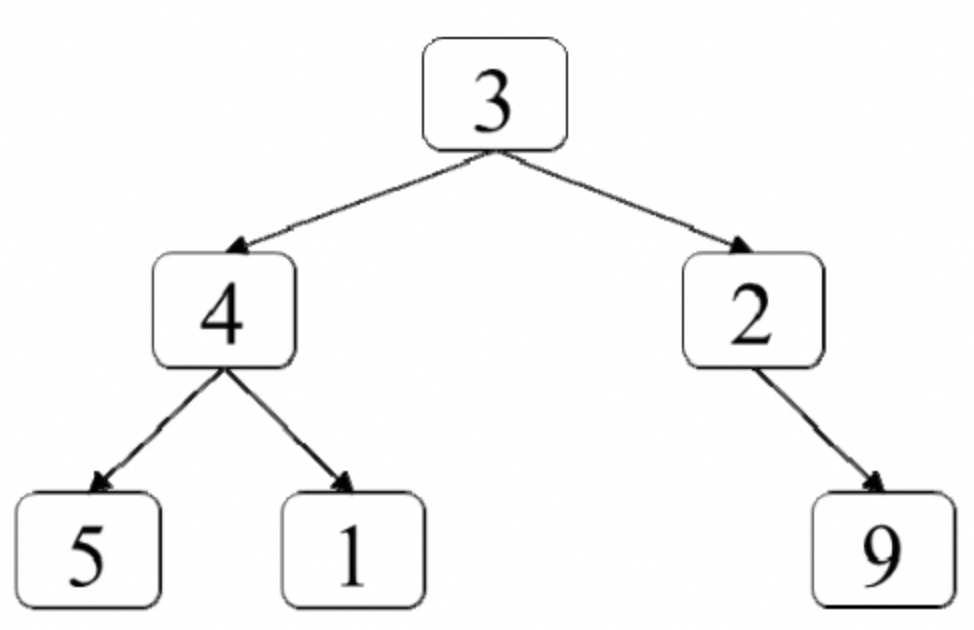 :::
:::
public class LargestValues{public static List<Integer> findLargestValues(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) {return new ArrayList<>();}List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);int current = 1;int next = 0;int maxValue = Integer.MIN_VALUE;while (!queue.isEmpty()) {TreeNode node = queue.poll();maxValue = Math.max(maxValue, node.val);current--;if (node.left != null) {queue.offer(node.left);next++;}if (node.right != null) {queue.offer(node.right);next++;}// 这个if条件需要放在最后,否则next的计数会不准确if (current == 0) {result.add(maxValue);// 重置计数器maxValue = Integer.MIN_VALUE;current = next;next = 0;}}return result;}public static List<Integer> findLargestValuesWith2Queue(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) {return new ArrayList<>();}List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();// 用来存当前层Queue<TreeNode> queue1 = new LinkedList<>();queue1.offer(root);// 用来存下一层Queue<TreeNode> queue2 = new LinkedList<>();Integer maxValue = Integer.MIN_VALUE;while (!queue1.isEmpty()) {TreeNode node = queue1.poll();maxValue = Math.max(maxValue, node.val);if (node.left != null) {queue2.offer(node.left);}if (node.right != null) {queue2.offer(node.right);}// 这个if条件需要放在最后if (queue1.isEmpty()) {result.add(maxValue);queue1 = queue2;queue2 = new LinkedList<>();}}return result;}public static void main(String[] args) {TreeNode root = TreeNode.buildCBT();System.out.println(findLargestValues(root));System.out.println(findLargestValuesWith2Queue(root));}}
45:二叉树最低层最左边的值
:::info
题目:如何在一棵二叉树中找出它最低层最左边节点的值?假设二叉树中最少有一个节点。例如,在如图7.5所示的二叉树中最低层最左边一个节点的值是5。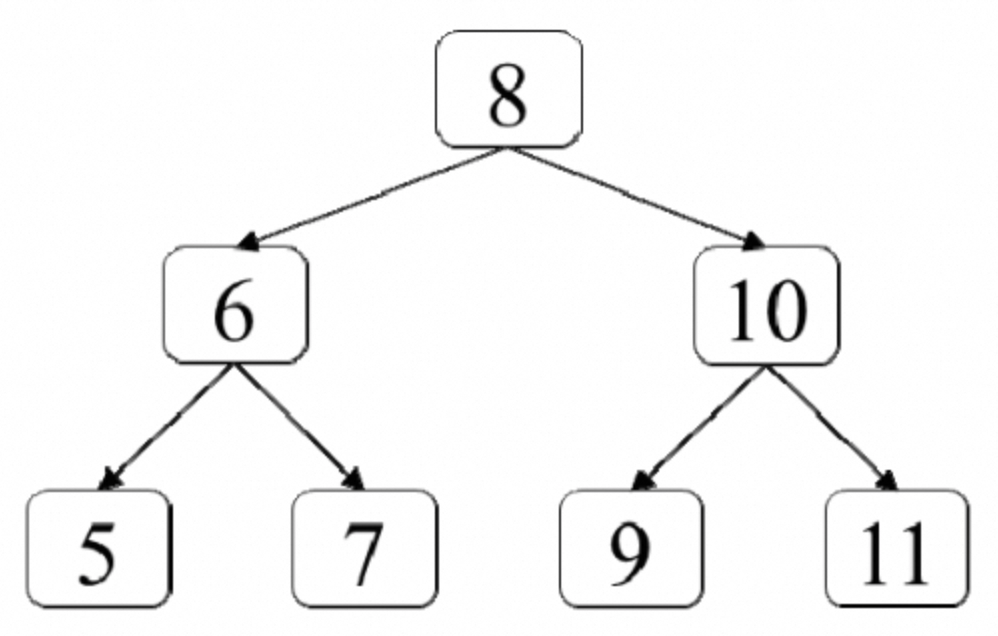 :::
:::
public class BottomLeft {public static TreeNode findBottomLeftNode(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) {return null;}List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();// 用来存当前层Queue<TreeNode> queue1 = new LinkedList<>();queue1.offer(root);// 用来存下一层Queue<TreeNode> queue2 = new LinkedList<>();TreeNode bottomLeftNode = root;while (!queue1.isEmpty()) {TreeNode node = queue1.poll();if (node.left != null) {queue2.offer(node.left);}if (node.right != null) {queue2.offer(node.right);}// 这个if条件需要放在最后if (queue1.isEmpty()) {if (!queue2.isEmpty()) {bottomLeftNode = queue2.peek();}queue1 = queue2;queue2 = new LinkedList<>();}}return bottomLeftNode;}public static void main(String[] args) {TreeNode root = TreeNode.buildCBT();System.out.println(findBottomLeftNode(root).val);}}
46:二叉树的右侧视图
:::info
题目:给定一棵二叉树,如果站在该二叉树的右侧,那么从上到下看到的节点构成二叉树的右侧视图。例如,图7.6中二叉树的右侧视图包含节点8、节点10和节点7。请写一个函数返回二叉树的右侧视图节点的值。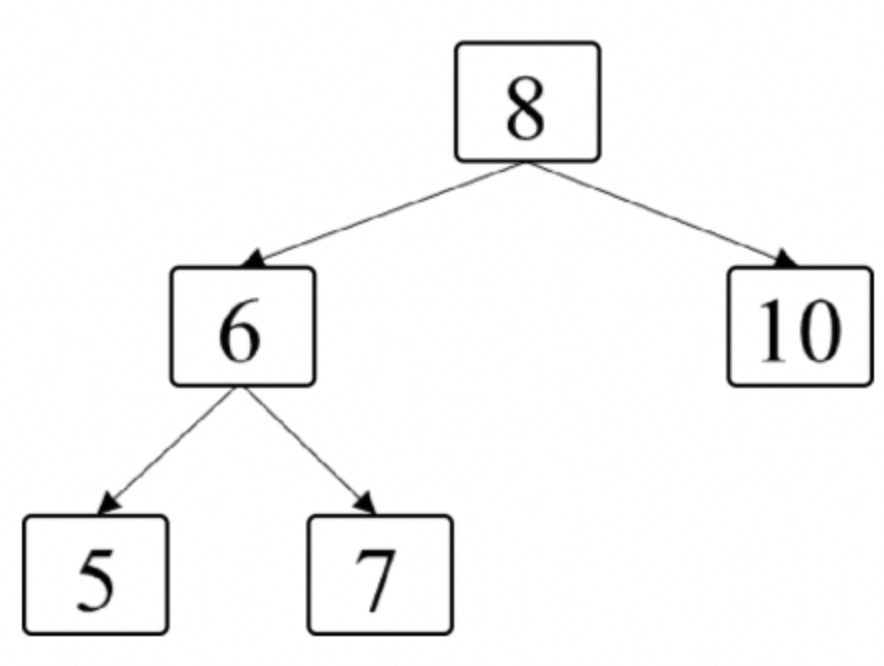 :::
:::
public class RightView {public static List<Integer> rightView(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) {return new ArrayList<>();}List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();// 用来存当前层Queue<TreeNode> queue1 = new LinkedList<>();queue1.offer(root);// 用来存下一层Queue<TreeNode> queue2 = new LinkedList<>();while (!queue1.isEmpty()) {TreeNode node = queue1.poll();if (node.left != null) {queue2.offer(node.left);}if (node.right != null) {queue2.offer(node.right);}// 这个if条件需要放在最后if (queue1.isEmpty()) {result.add(node.val);queue1 = queue2;queue2 = new LinkedList<>();}}return result;}public static void main(String[] args) {TreeNode root = TreeNode.buildCBT();System.out.println(rightView(root));}

