进程,线程,协程
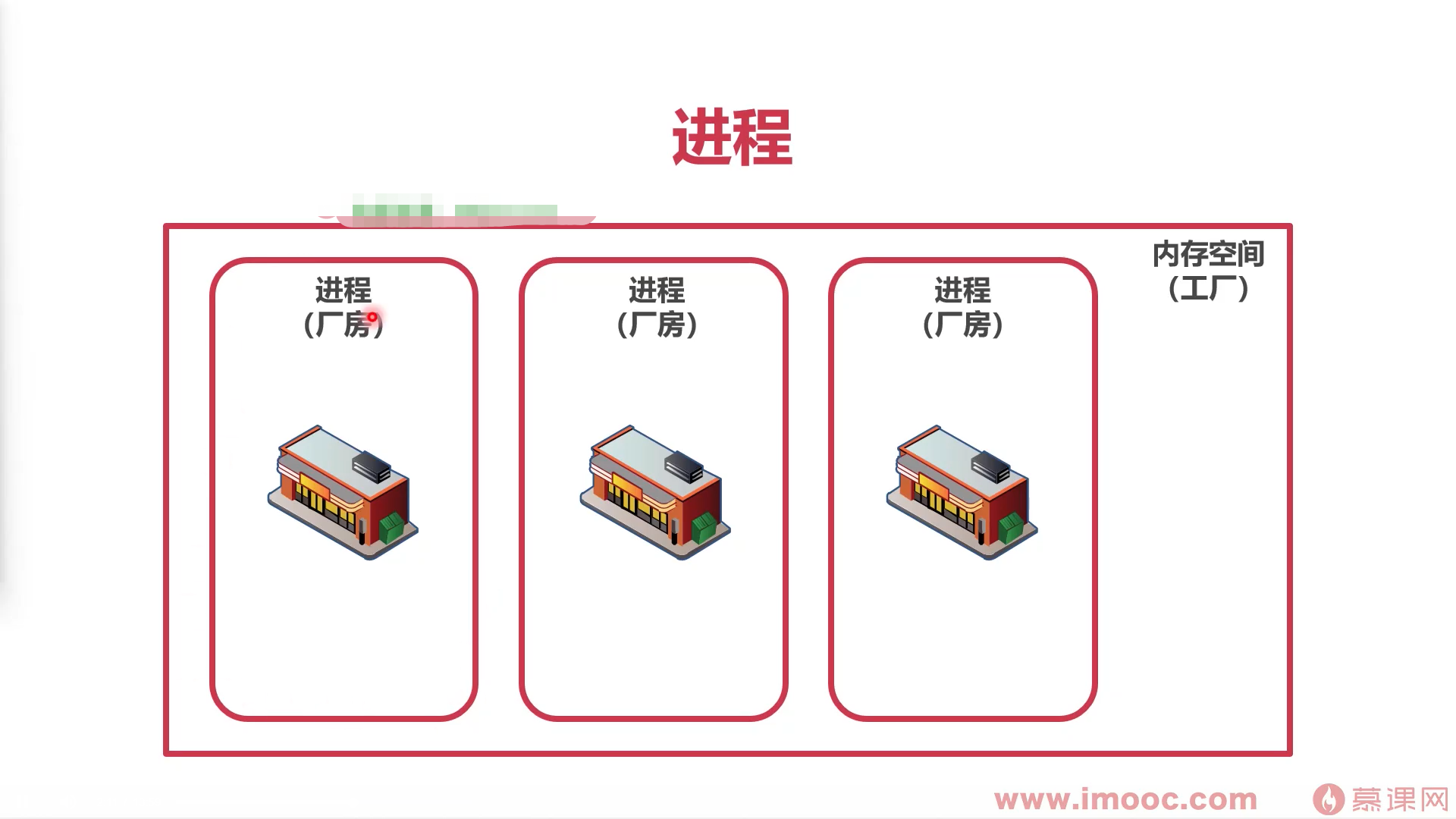
进程:为了占据内存空间
- 操作系统 “程序” 最新小单位
- 进程用来占用空间
- 如果计算机是一个工厂,进程相当于厂房,占用工厂空间
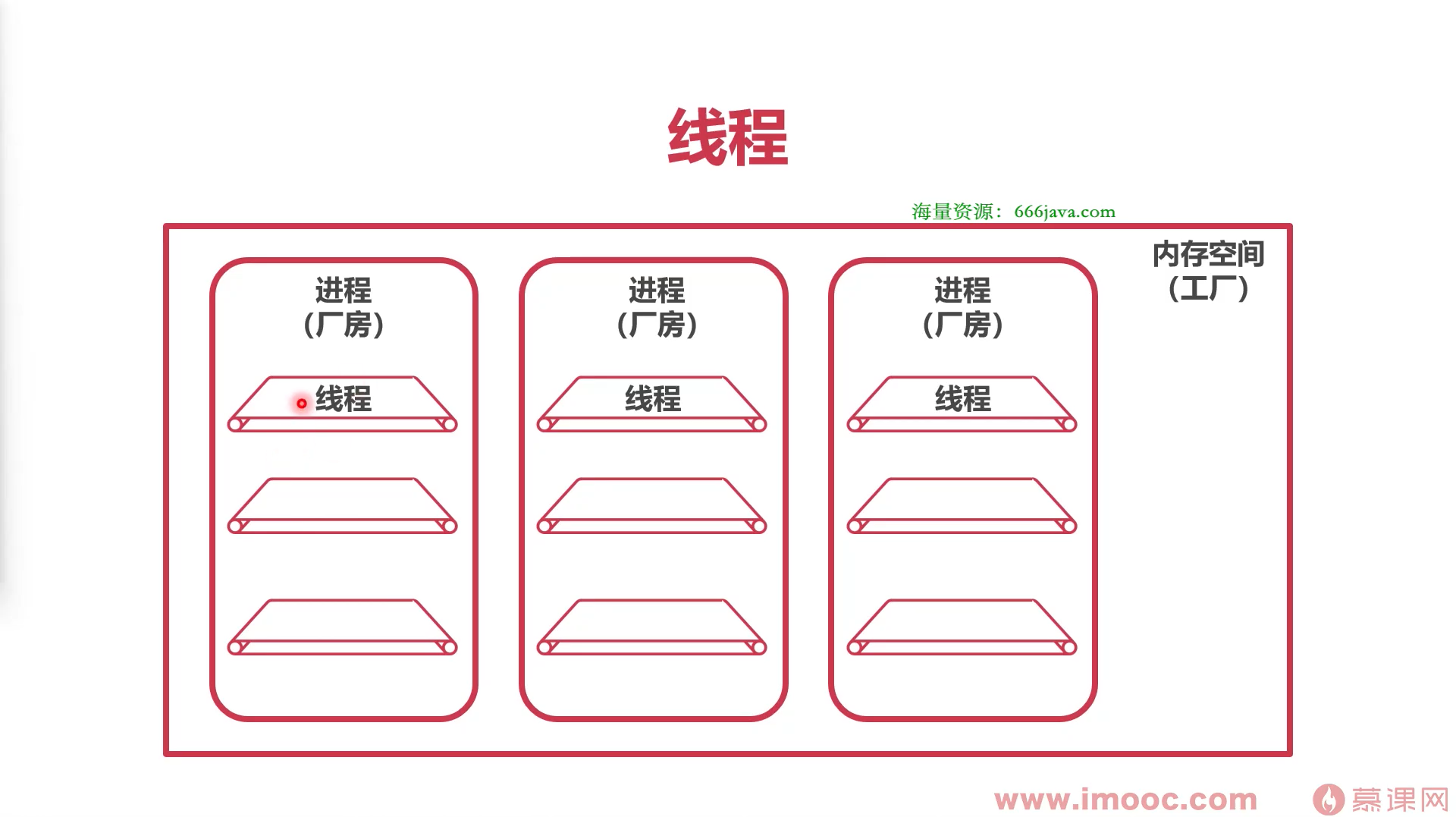
线程:占用工厂(CPU)处理能力
- 每个进程可以有多个线程
- 线程使用系统分配给进程的内存,线程之间共享内存
线程原理
总结
- 进程用徕分配内存空间
- 线程用来分配CPU时间
- 协程用来切换不同的线程
-
协程的本质
协程底层结构
type g struct {// Stack parameters.// stack describes the actual stack memory: [stack.lo, stack.hi).// stackguard0 is the stack pointer compared in the Go stack growth prologue.// It is stack.lo+StackGuard normally, but can be StackPreempt to trigger a preemption.// stackguard1 is the stack pointer compared in the C stack growth prologue.// It is stack.lo+StackGuard on g0 and gsignal stacks.// It is ~0 on other goroutine stacks, to trigger a call to morestackc (and crash).stack stack // offset known to runtime/cgo 协程栈stackguard0 uintptr // offset known to liblinkstackguard1 uintptr // offset known to liblink_panic *_panic // innermost panic - offset known to liblink_defer *_defer // innermost deferm *m // current m; offset known to arm liblinksched gobuf //记录栈指针,和运行到的行数syscallsp uintptr // if status==Gsyscall, syscallsp = sched.sp to use during gcsyscallpc uintptr // if status==Gsyscall, syscallpc = sched.pc to use during gcstktopsp uintptr // expected sp at top of stack, to check in tracebackparam unsafe.Pointer // passed parameter on wakeupatomicstatus uint32 //协程状态stackLock uint32 // sigprof/scang lock; TODO: fold in to atomicstatusgoid int64 //协程的idschedlink guintptrwaitsince int64 // approx time when the g become blockedwaitreason waitReason // if status==Gwaitingpreempt bool // preemption signal, duplicates stackguard0 = stackpreemptpreemptStop bool // transition to _Gpreempted on preemption; otherwise, just deschedulepreemptShrink bool // shrink stack at synchronous safe point// asyncSafePoint is set if g is stopped at an asynchronous// safe point. This means there are frames on the stack// without precise pointer information.asyncSafePoint boolpaniconfault bool // panic (instead of crash) on unexpected fault addressgcscandone bool // g has scanned stack; protected by _Gscan bit in statusthrowsplit bool // must not split stack// activeStackChans indicates that there are unlocked channels// pointing into this goroutine's stack. If true, stack// copying needs to acquire channel locks to protect these// areas of the stack.activeStackChans bool// parkingOnChan indicates that the goroutine is about to// park on a chansend or chanrecv. Used to signal an unsafe point// for stack shrinking. It's a boolean value, but is updated atomically.parkingOnChan uint8raceignore int8 // ignore race detection eventssysblocktraced bool // StartTrace has emitted EvGoInSyscall about this goroutinesysexitticks int64 // cputicks when syscall has returned (for tracing)traceseq uint64 // trace event sequencertracelastp puintptr // last P emitted an event for this goroutinelockedm muintptrsig uint32writebuf []bytesigcode0 uintptrsigcode1 uintptrsigpc uintptrgopc uintptr // pc of go statement that created this goroutineancestors *[]ancestorInfo // ancestor information goroutine(s) that created this goroutine (only used if debug.tracebackancestors)startpc uintptr // pc of goroutine functionracectx uintptrwaiting *sudog // sudog structures this g is waiting on (that have a valid elem ptr); in lock ordercgoCtxt []uintptr // cgo traceback contextlabels unsafe.Pointer // profiler labelstimer *timer // cached timer for time.SleepselectDone uint32 // are we participating in a select and did someone win the race?// Per-G GC state// gcAssistBytes is this G's GC assist credit in terms of// bytes allocated. If this is positive, then the G has credit// to allocate gcAssistBytes bytes without assisting. If this// is negative, then the G must correct this by performing// scan work. We track this in bytes to make it fast to update// and check for debt in the malloc hot path. The assist ratio// determines how this corresponds to scan work debt.gcAssistBytes int64}
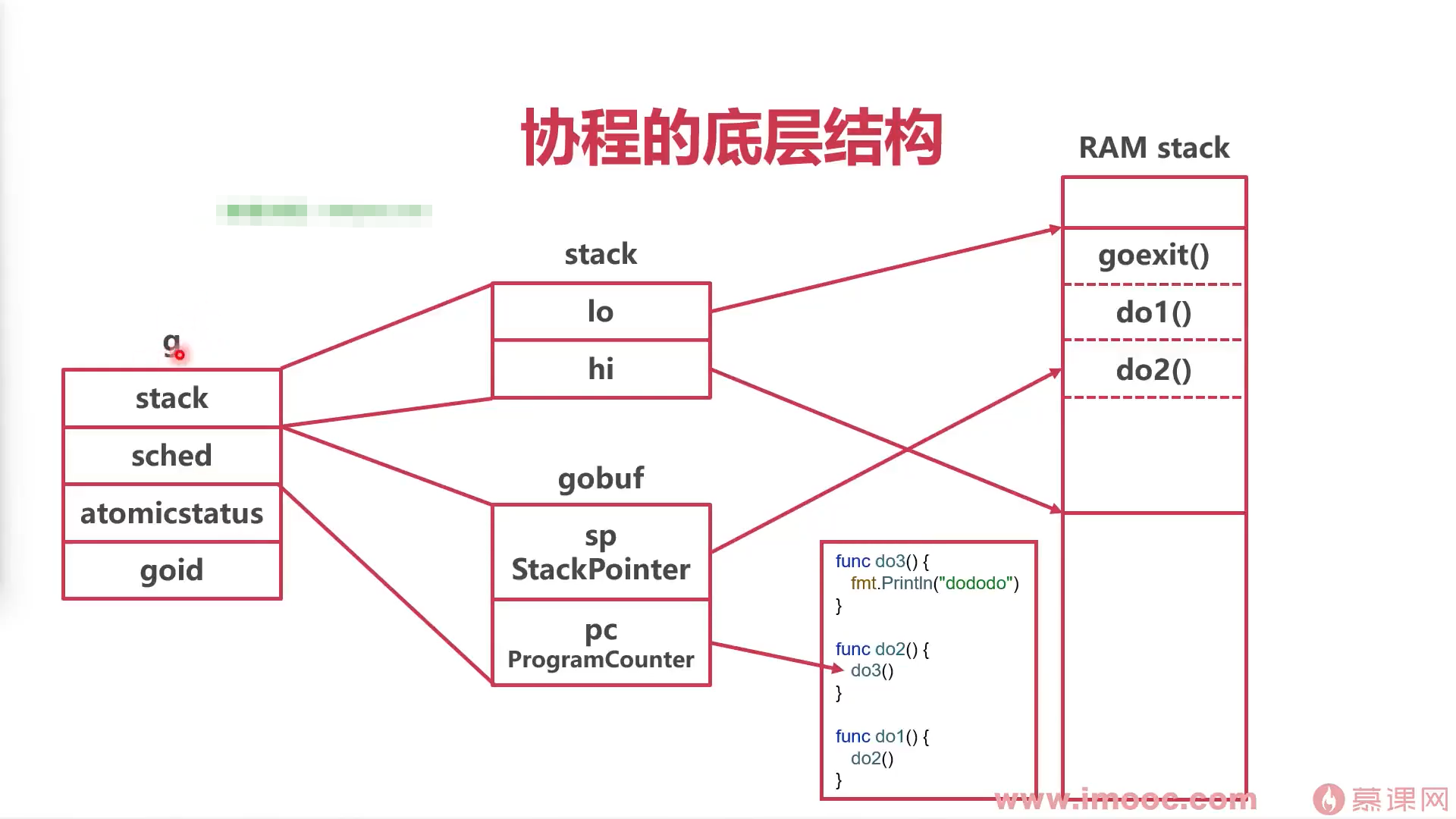
runtime中,协程本质是一个g结构体
- stack:堆栈地址
- gobuf:目前协程运行状态(sp,协程栈。pc 程序运行行数)
-
golang将系统线程抽象表达出
type m struct {g0 *g // 初始协程,启动其他协程的协程morebuf gobuf // gobuf arg to morestackdivmod uint32 // div/mod denominator for arm - known to liblink// Fields not known to debuggers.procid uint64 // for debuggers, but offset not hard-codedgsignal *g // signal-handling ggoSigStack gsignalStack // Go-allocated signal handling stacksigmask sigset // storage for saved signal masktls [6]uintptr // thread-local storage (for x86 extern register)mstartfn func()curg *g // current running goroutine 正在运行的协程结构体gcaughtsig guintptr // goroutine running during fatal signalp puintptr // attached p for executing go code (nil if not executing go code)nextp puintptroldp puintptr // the p that was attached before executing a syscallid int64 线程idmallocing int32throwing int32preemptoff string // if != "", keep curg running on this mlocks int32dying int32profilehz int32spinning bool // m is out of work and is actively looking for workblocked bool // m is blocked on a notenewSigstack bool // minit on C thread called sigaltstackprintlock int8incgo bool // m is executing a cgo callfreeWait uint32 // if == 0, safe to free g0 and delete m (atomic)fastrand [2]uint32needextram booltraceback uint8ncgocall uint64 // number of cgo calls in totalncgo int32 // number of cgo calls currently in progresscgoCallersUse uint32 // if non-zero, cgoCallers in use temporarilycgoCallers *cgoCallers // cgo traceback if crashing in cgo calldoesPark bool // non-P running threads: sysmon and newmHandoff never use .parkpark notealllink *m // on allmschedlink muintptrlockedg guintptrcreatestack [32]uintptr // stack that created this thread.lockedExt uint32 // tracking for external LockOSThreadlockedInt uint32 // tracking for internal lockOSThreadnextwaitm muintptr // next m waiting for lockwaitunlockf func(*g, unsafe.Pointer) boolwaitlock unsafe.Pointerwaittraceev bytewaittraceskip intstartingtrace boolsyscalltick uint32freelink *m // on sched.freem// mFixup is used to synchronize OS related m state// (credentials etc) use mutex to access. To avoid deadlocks// an atomic.Load() of used being zero in mDoFixupFn()// guarantees fn is nil.mFixup struct {lock mutexused uint32fn func(bool) bool}// these are here because they are too large to be on the stack// of low-level NOSPLIT functions.libcall libcalllibcallpc uintptr // for cpu profilerlibcallsp uintptrlibcallg guintptrsyscall libcall // stores syscall parameters on windowsvdsoSP uintptr // SP for traceback while in VDSO call (0 if not in call)vdsoPC uintptr // PC for traceback while in VDSO call// preemptGen counts the number of completed preemption// signals. This is used to detect when a preemption is// requested, but fails. Accessed atomically.preemptGen uint32// Whether this is a pending preemption signal on this M.// Accessed atomically.signalPending uint32dlogPerMmOS// Up to 10 locks held by this m, maintained by the lock ranking code.locksHeldLen intlocksHeld [10]heldLockInfo}
将系统线程抽象为结构体m
- g0:g0协程,操作调度器
- curg:current g,目前运行的g
-
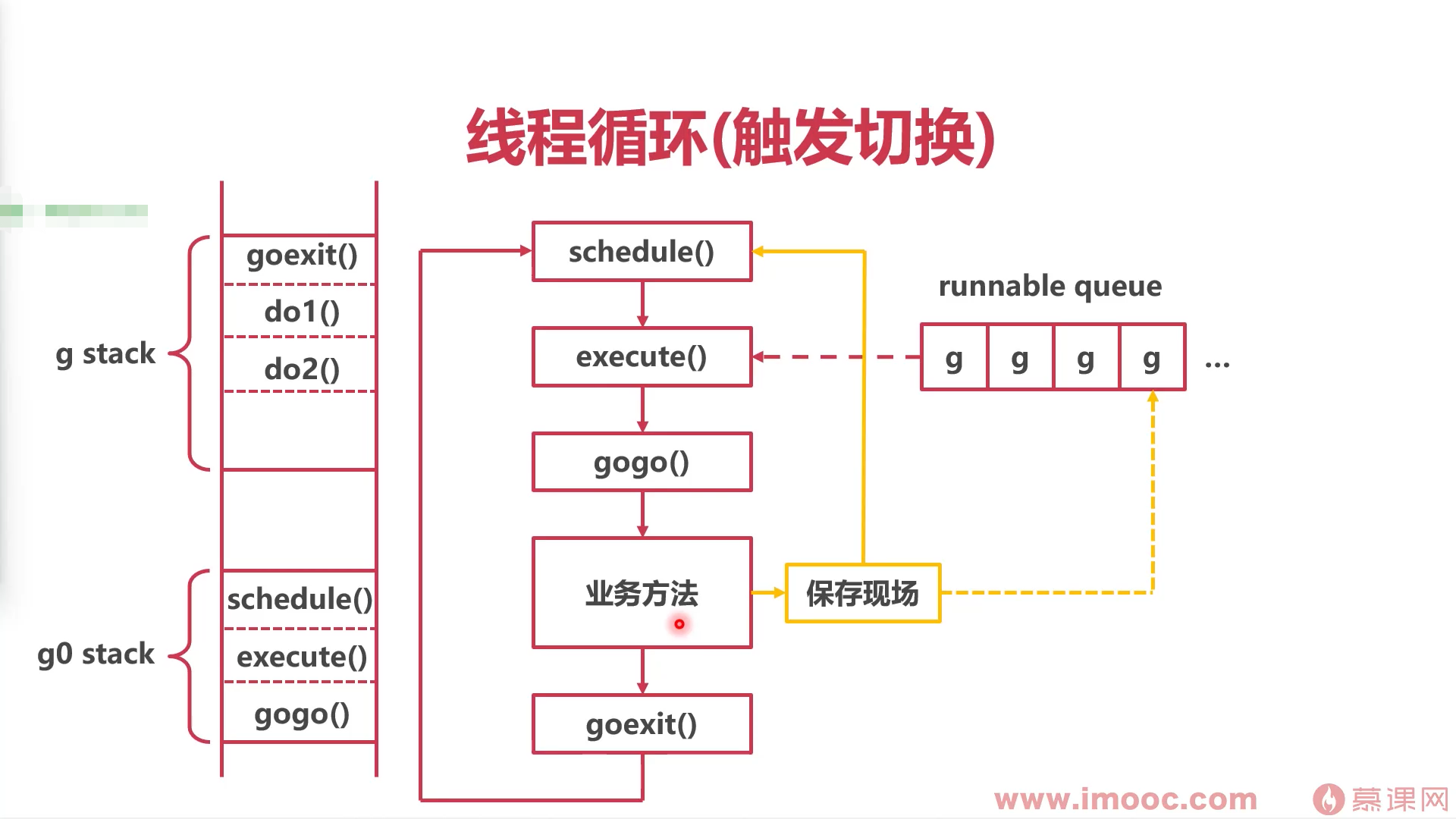
协程如何执行的
在go1.0版本,启动了多线程循环抢占式调用全局协程队列中的协程,要先通过全局协程队列的锁,才能调用协程
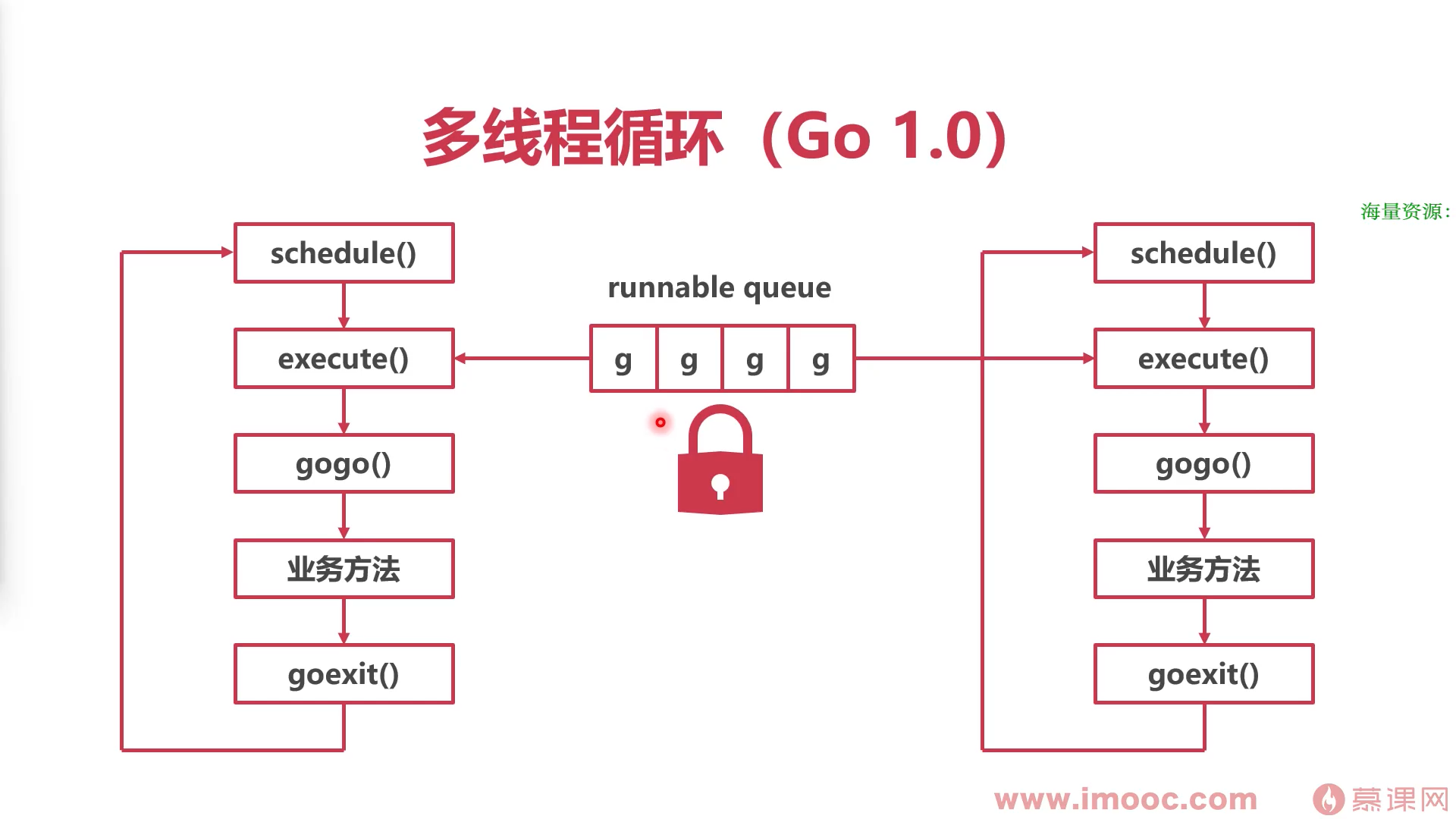
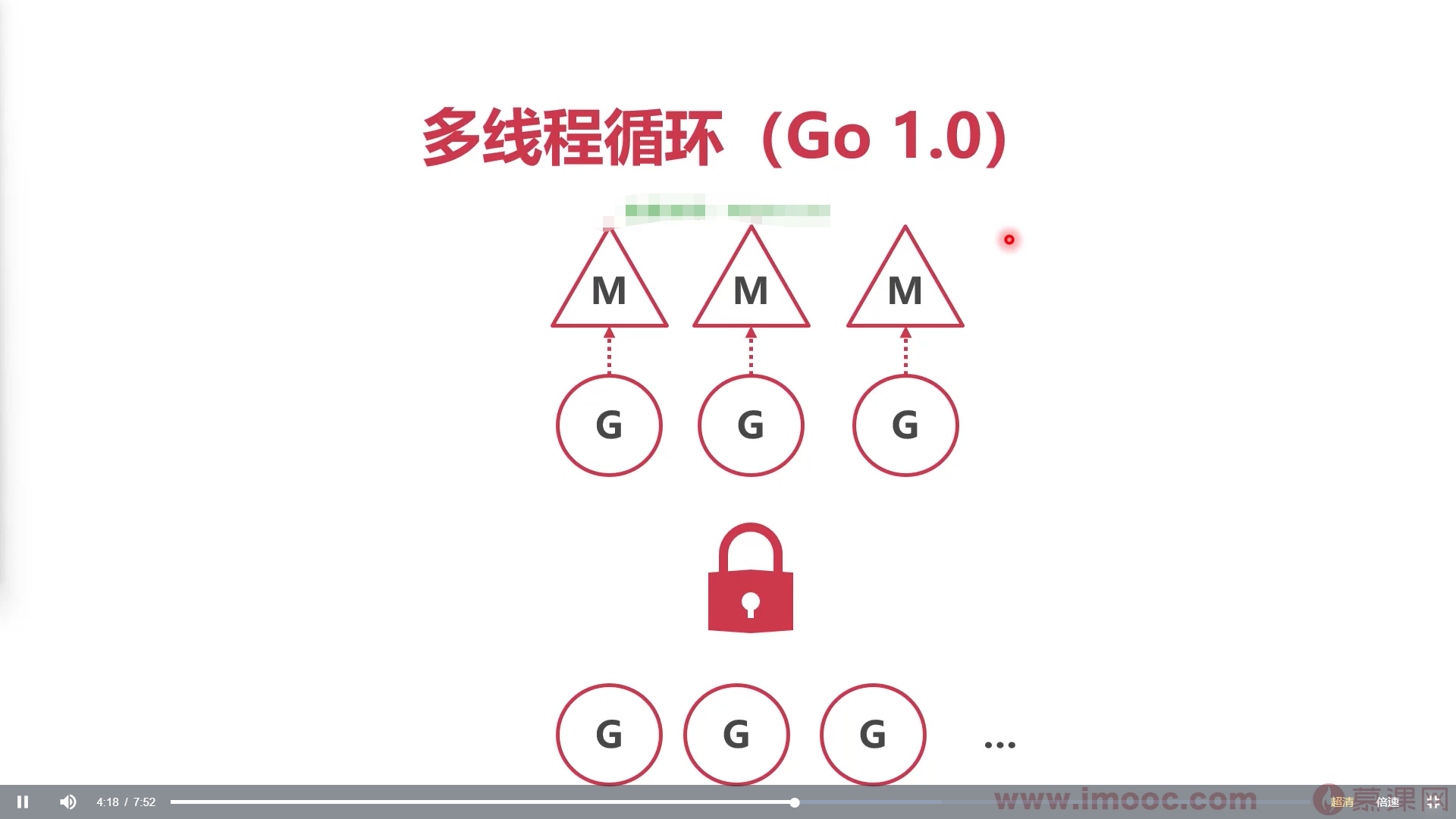
操作系统不知道协程goroutine的存在
- 操作系统线程执行一个调度循环,顺序执行goroutine
-
总结
协程本质是一个g结构体
- g结构体记录了sp(协程栈),pc(程序运行行数)
- 最简情况下,线程执行标准调度循环,执行协程
G-M-P调度模型
解决的问题
多线程并发时,会抢夺全局协程队里的锁,造成锁的冲突和锁的等待
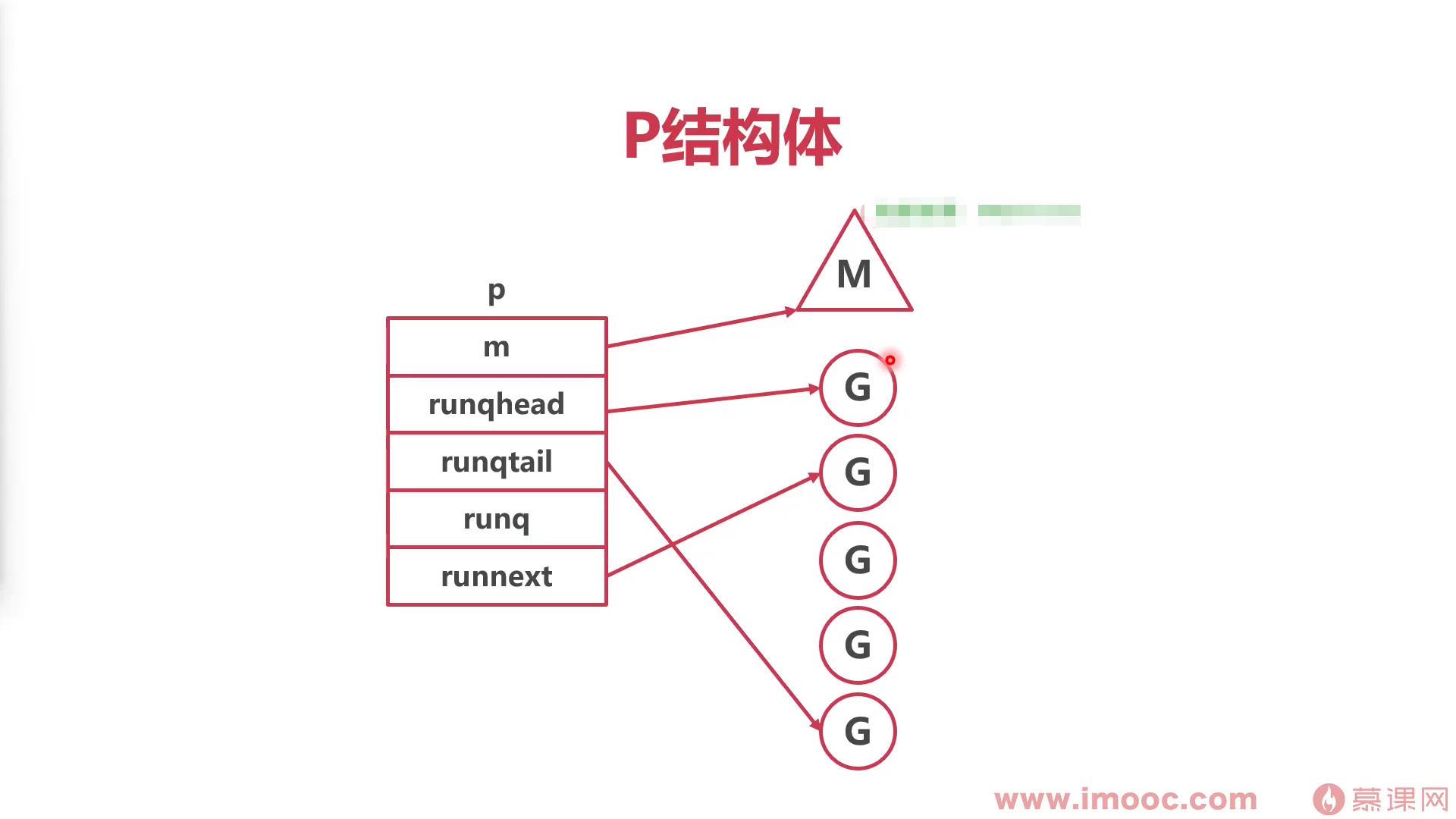
p(本地队列)的结构体
type p struct {id int32status uint32 // one of pidle/prunning/...link puintptrschedtick uint32 // incremented on every scheduler callsyscalltick uint32 // incremented on every system callsysmontick sysmontick // last tick observed by sysmonm muintptr // 指向的服务的mmcache *mcachepcache pageCacheraceprocctx uintptrdeferpool [5][]*_defer // pool of available defer structs of different sizes (see panic.go)deferpoolbuf [5][32]*_defer// Cache of goroutine ids, amortizes accesses to runtime·sched.goidgen.goidcache uint64goidcacheend uint64// Queue of runnable goroutines. Accessed without lock.//本地队列,可以无锁访问runqhead uint32runqtail uint32runq [256]guintptr// runnext, if non-nil, is a runnable G that was ready'd by// the current G and should be run next instead of what's in// runq if there's time remaining in the running G's time// slice. It will inherit the time left in the current time// slice. If a set of goroutines is locked in a// communicate-and-wait pattern, this schedules that set as a// unit and eliminates the (potentially large) scheduling// latency that otherwise arises from adding the ready'd// goroutines to the end of the run queue.runnext guintptr //下一个可用协程的指针// Available G's (status == Gdead)gFree struct {gListn int32}sudogcache []*sudogsudogbuf [128]*sudog// Cache of mspan objects from the heap.mspancache struct {// We need an explicit length here because this field is used// in allocation codepaths where write barriers are not allowed,// and eliminating the write barrier/keeping it eliminated from// slice updates is tricky, moreso than just managing the length// ourselves.len intbuf [128]*mspan}tracebuf traceBufPtr// traceSweep indicates the sweep events should be traced.// This is used to defer the sweep start event until a span// has actually been swept.traceSweep bool// traceSwept and traceReclaimed track the number of bytes// swept and reclaimed by sweeping in the current sweep loop.traceSwept, traceReclaimed uintptrpalloc persistentAlloc // per-P to avoid mutex_ uint32 // Alignment for atomic fields below// The when field of the first entry on the timer heap.// This is updated using atomic functions.// This is 0 if the timer heap is empty.timer0When uint64// The earliest known nextwhen field of a timer with// timerModifiedEarlier status. Because the timer may have been// modified again, there need not be any timer with this value.// This is updated using atomic functions.// This is 0 if the value is unknown.timerModifiedEarliest uint64// Per-P GC stategcAssistTime int64 // Nanoseconds in assistAllocgcFractionalMarkTime int64 // Nanoseconds in fractional mark worker (atomic)// gcMarkWorkerMode is the mode for the next mark worker to run in.// That is, this is used to communicate with the worker goroutine// selected for immediate execution by// gcController.findRunnableGCWorker. When scheduling other goroutines,// this field must be set to gcMarkWorkerNotWorker.gcMarkWorkerMode gcMarkWorkerMode// gcMarkWorkerStartTime is the nanotime() at which the most recent// mark worker started.gcMarkWorkerStartTime int64// gcw is this P's GC work buffer cache. The work buffer is// filled by write barriers, drained by mutator assists, and// disposed on certain GC state transitions.gcw gcWork// wbBuf is this P's GC write barrier buffer.//// TODO: Consider caching this in the running G.wbBuf wbBufrunSafePointFn uint32 // if 1, run sched.safePointFn at next safe point// statsSeq is a counter indicating whether this P is currently// writing any stats. Its value is even when not, odd when it is.statsSeq uint32// Lock for timers. We normally access the timers while running// on this P, but the scheduler can also do it from a different P.timersLock mutex// Actions to take at some time. This is used to implement the// standard library's time package.// Must hold timersLock to access.timers []*timer// Number of timers in P's heap.// Modified using atomic instructions.numTimers uint32// Number of timerModifiedEarlier timers on P's heap.// This should only be modified while holding timersLock,// or while the timer status is in a transient state// such as timerModifying.adjustTimers uint32// Number of timerDeleted timers in P's heap.// Modified using atomic instructions.deletedTimers uint32// Race context used while executing timer functions.timerRaceCtx uintptr// preempt is set to indicate that this P should be enter the// scheduler ASAP (regardless of what G is running on it).preempt boolpad cpu.CacheLinePad}
- p结构体中的m:指向线程
- 队列的 runqhead:头部队列
- runqtail:尾队列
- runq:最大长度为256协程队列
- runnext:队列中下一个运行的协程
g-m-p的执行细节
m每次获取协程执行的时候,会先在本地队列p中去调用g,调用完之后释放,然后开始调用下一个g,当本地队列p中的g消耗完之后,会去获取全局队列的锁,然后拿去一部分g,放到本地队列p中。如果全局队列的g没了,就会去其他p中获取g。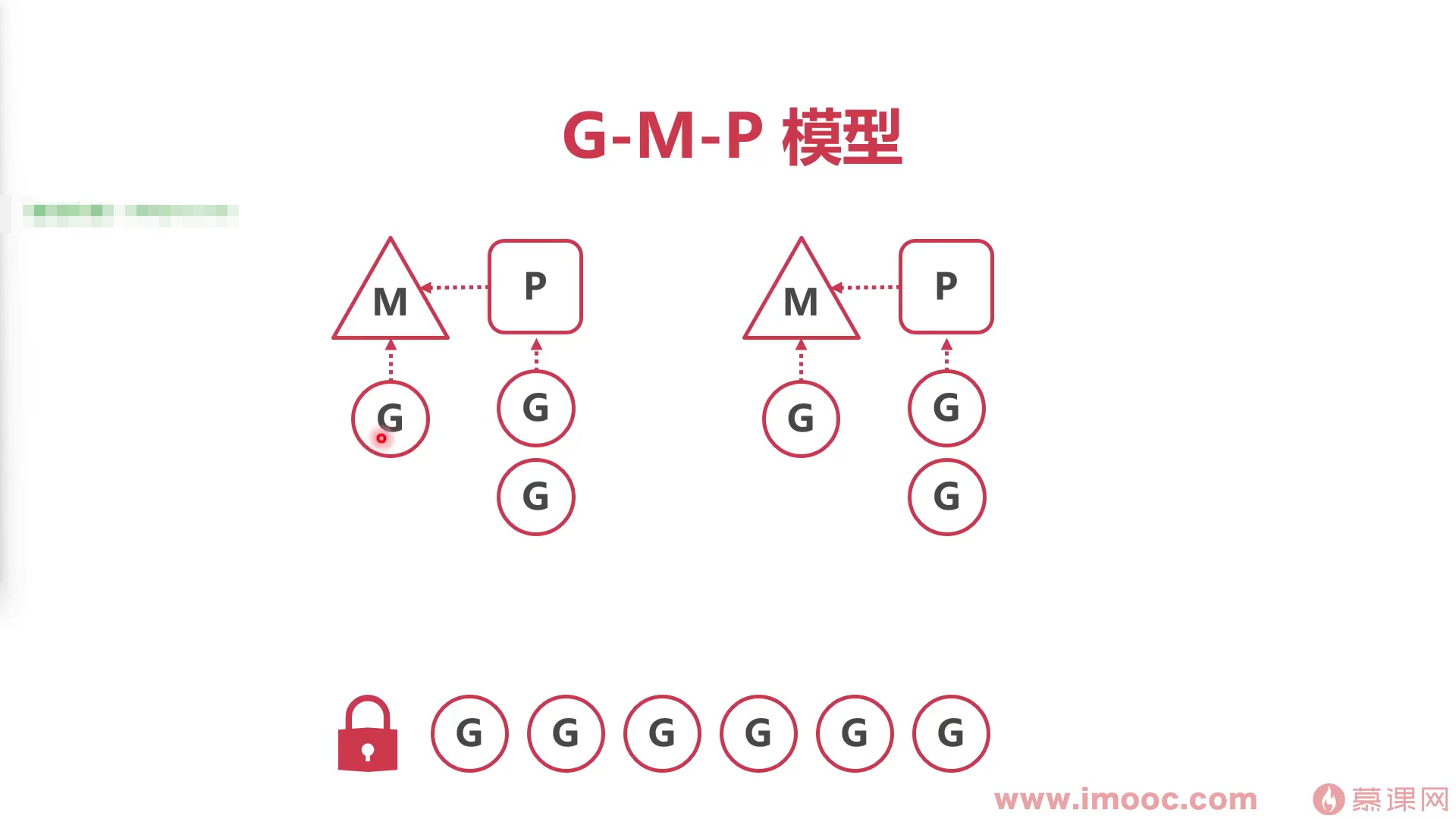
源码分析本地队列无G后
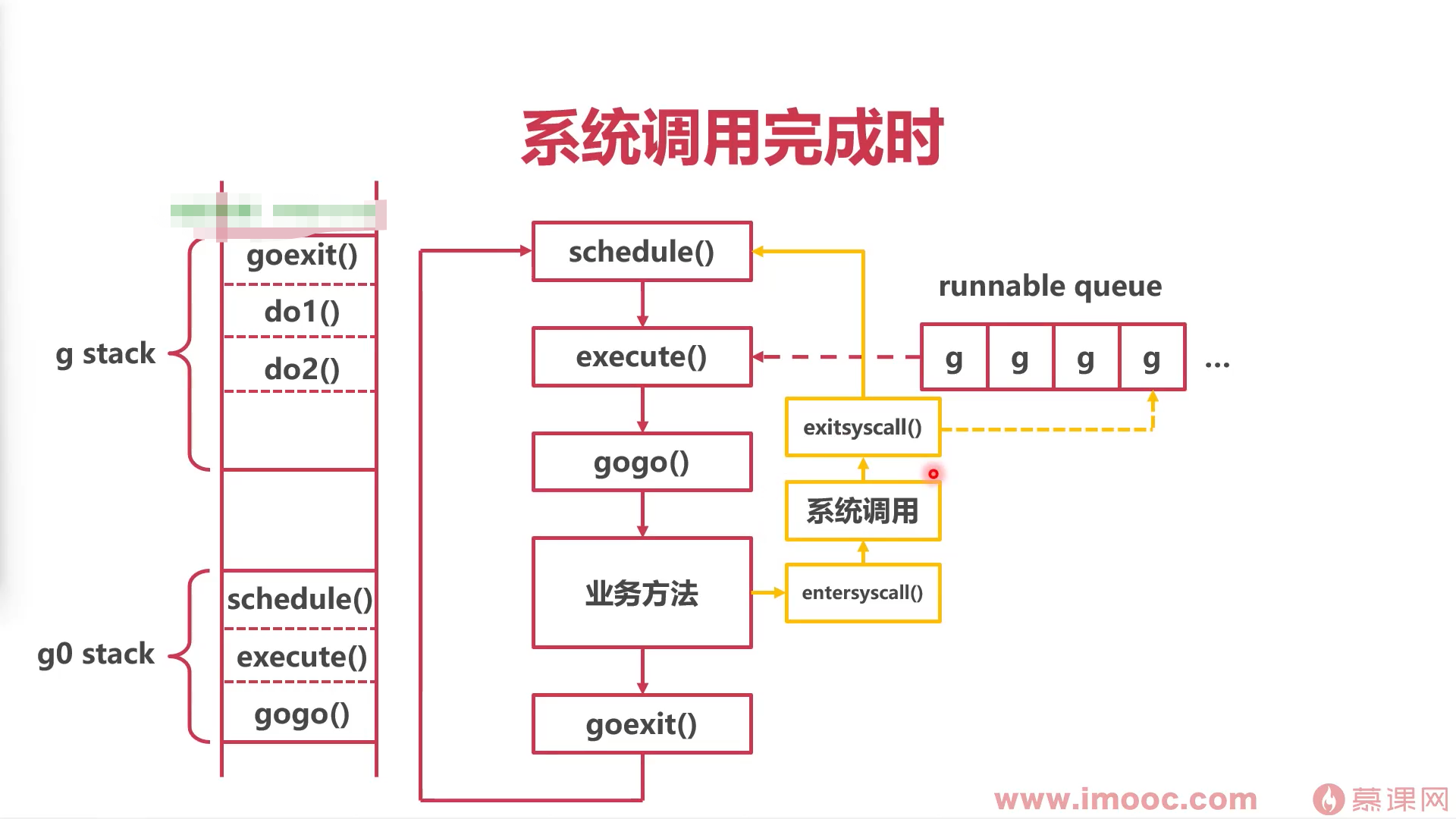
// One round of scheduler: find a runnable goroutine and execute it.// Never returns.// 线程循环的方法func schedule() {_g_ := getg().....var gp *g.....// 先到本地队列获取协程if gp == nil {gp, inheritTime = runqget(_g_.m.p.ptr())// We can see gp != nil here even if the M is spinning,// if checkTimers added a local goroutine via goready.}// 上面的本地队列没有g,就会去全局队列或者其他本地队列获取gif gp == nil {gp, inheritTime = findrunnable() // blocks until work is available}......}
p的作用
- M与G之间的中间(送料器)
- p持有一些G,使得每次获取G的时候不用从全局找
-
新建的协程
随机寻找一个p
- 将协程房屋p的runnext,go的调度户优先执行新的协程
-
实现协程并发
协程顺序执行容易产生饥饿问题
当下只有两个M,其中正在执行的G需要较长时间,在本地队列P的G都无法执行,无法进行本地队列循环。
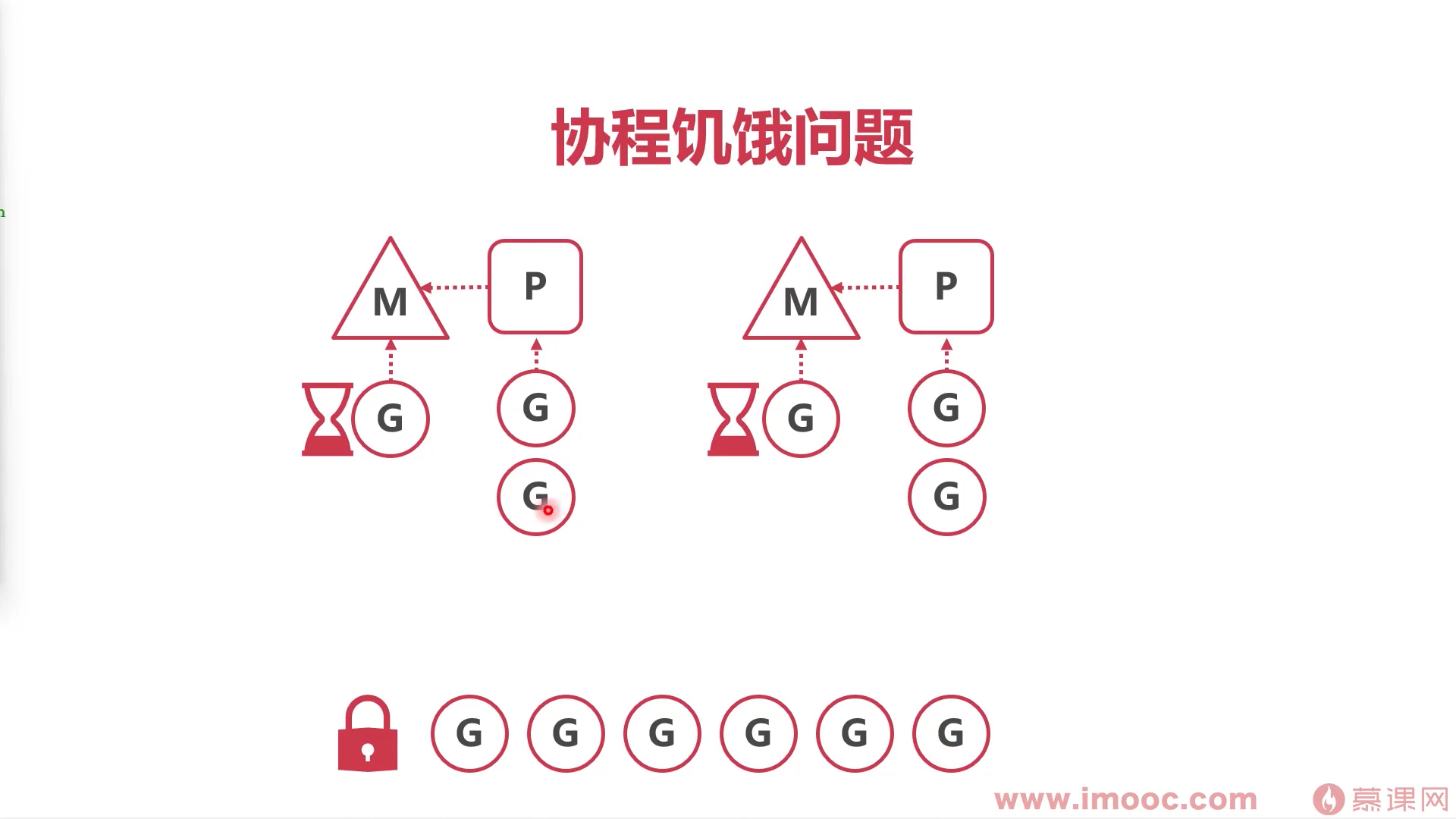
解决本地队列协程饥饿问题
将正在执行的协程存起来,并停止
- 将停止的协程放到runnablue队列的尾部,
- 协程机型循环,重新运行新的G
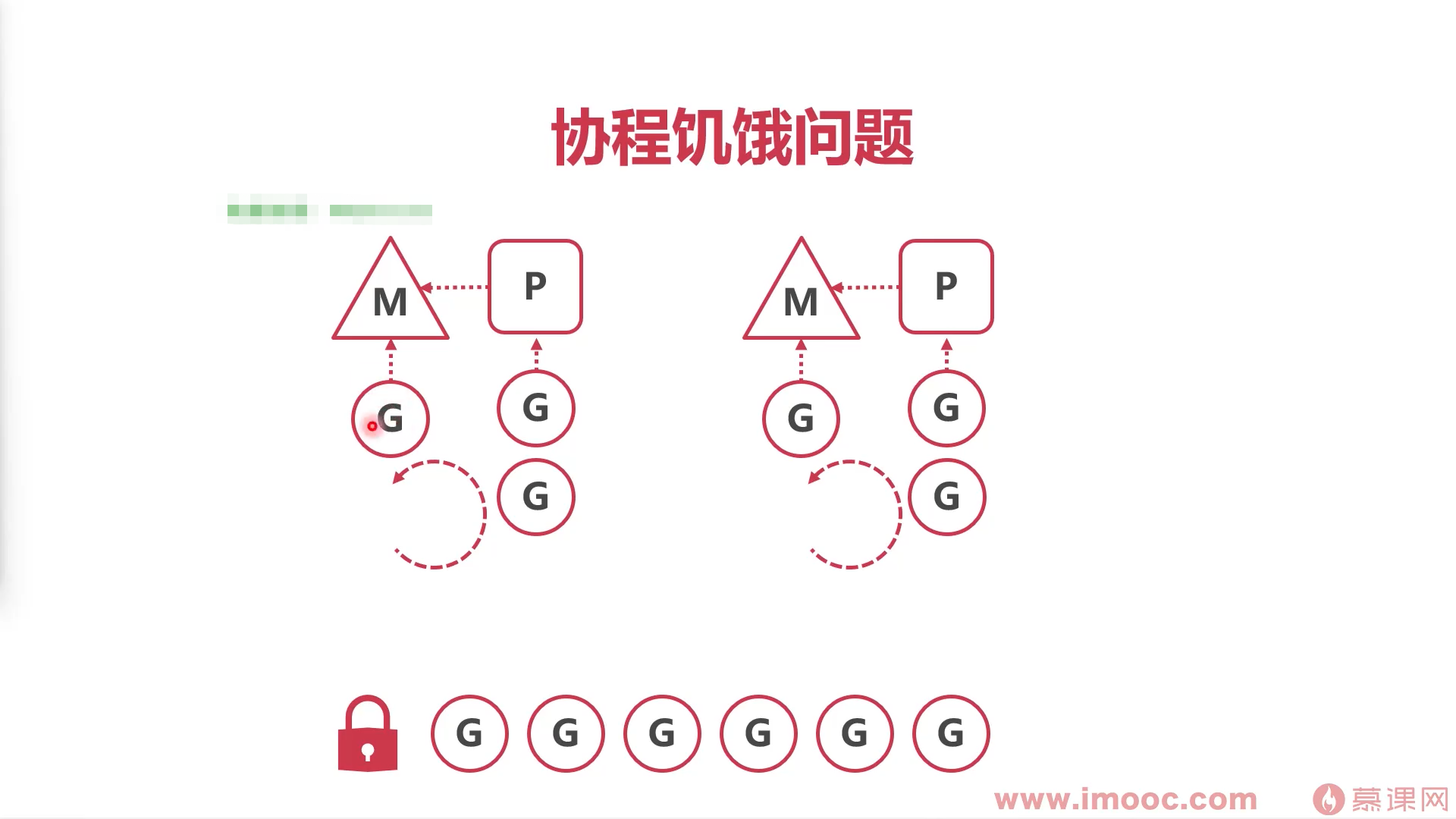
该方法:可能会造成全局队列的协程饥饿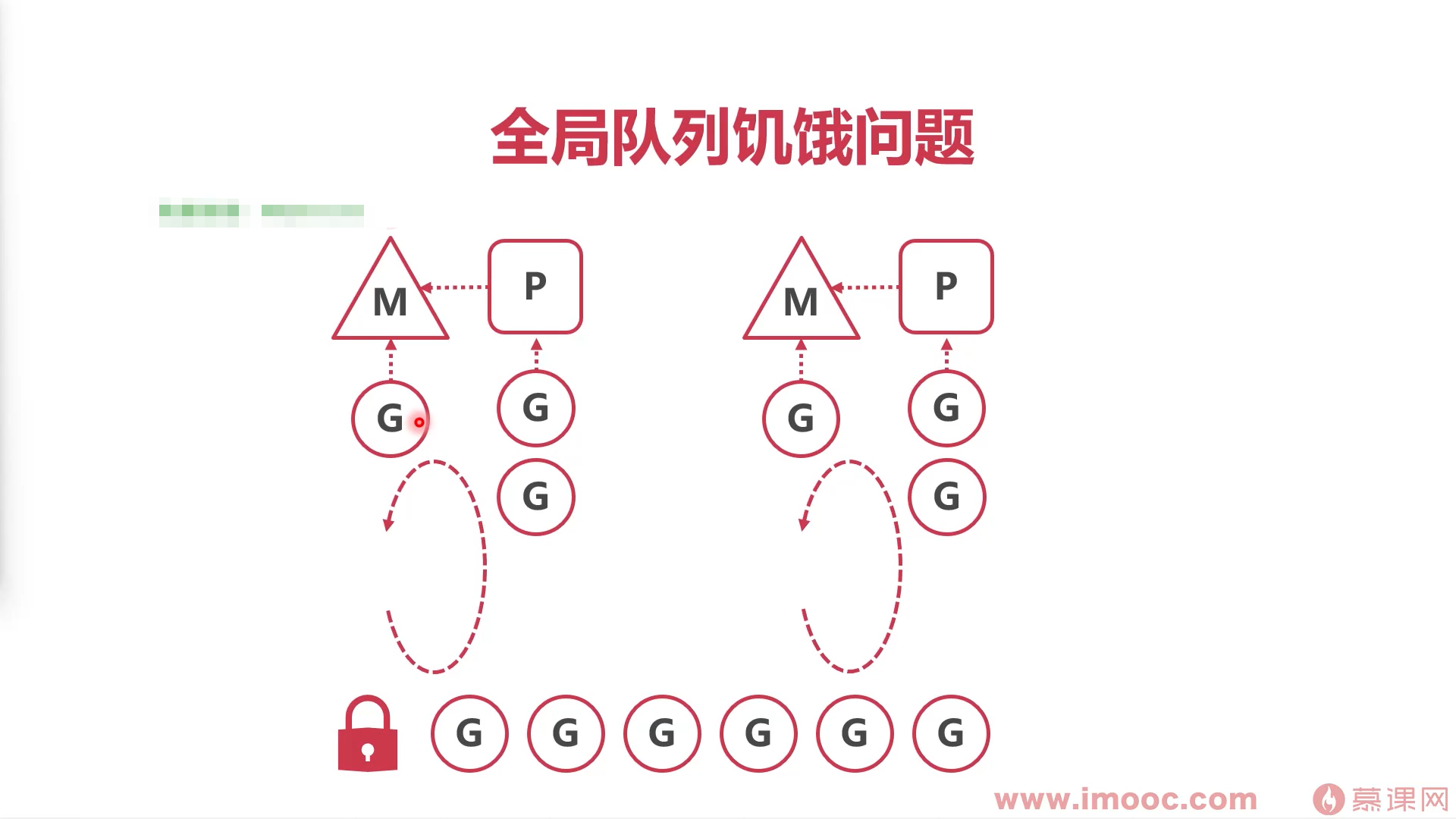
- 解决全局队列协程饥饿
go解决饥饿问题的方法:每执行61次协程循环,就会从全局队列中拿一个协程放到本地队列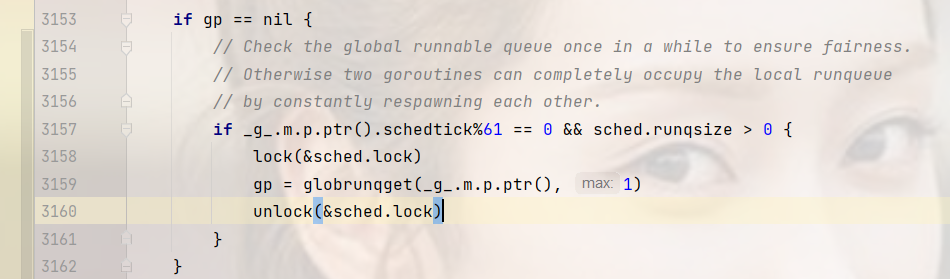
切换时机(切换协程的方案)
主动挂起
调用sleep,channel时会主动挂起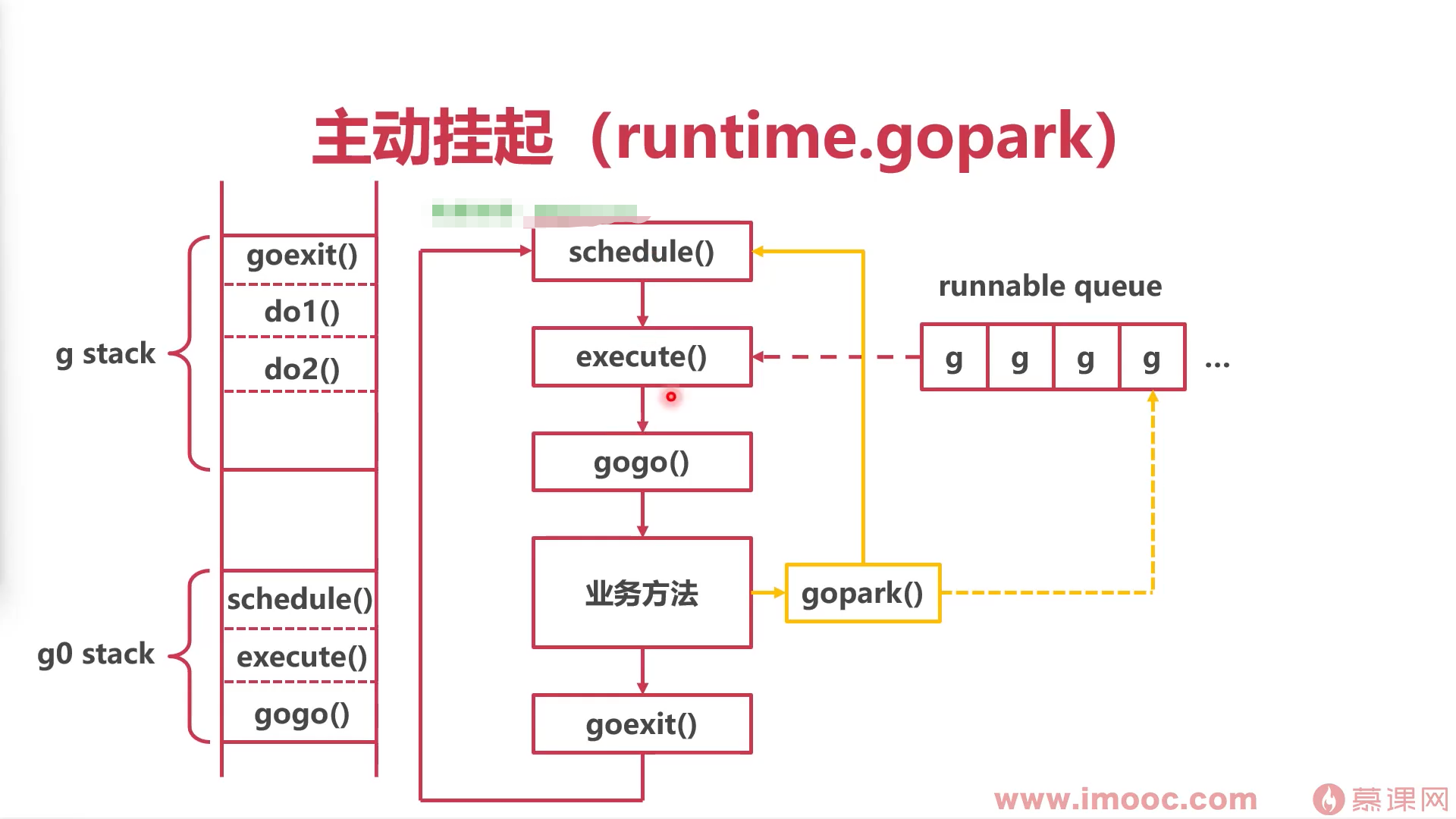
系统条用完成时
总结
- 如果协程顺序执行,会有饥饿问题
- 协程执行超时,协程执行中间,将协程挂起,执行其他协程
- 完成系统调用时挂起,也可以主动挂起
-
抢占式调度
协作抢占
解决的问题
永远不主动挂起
-
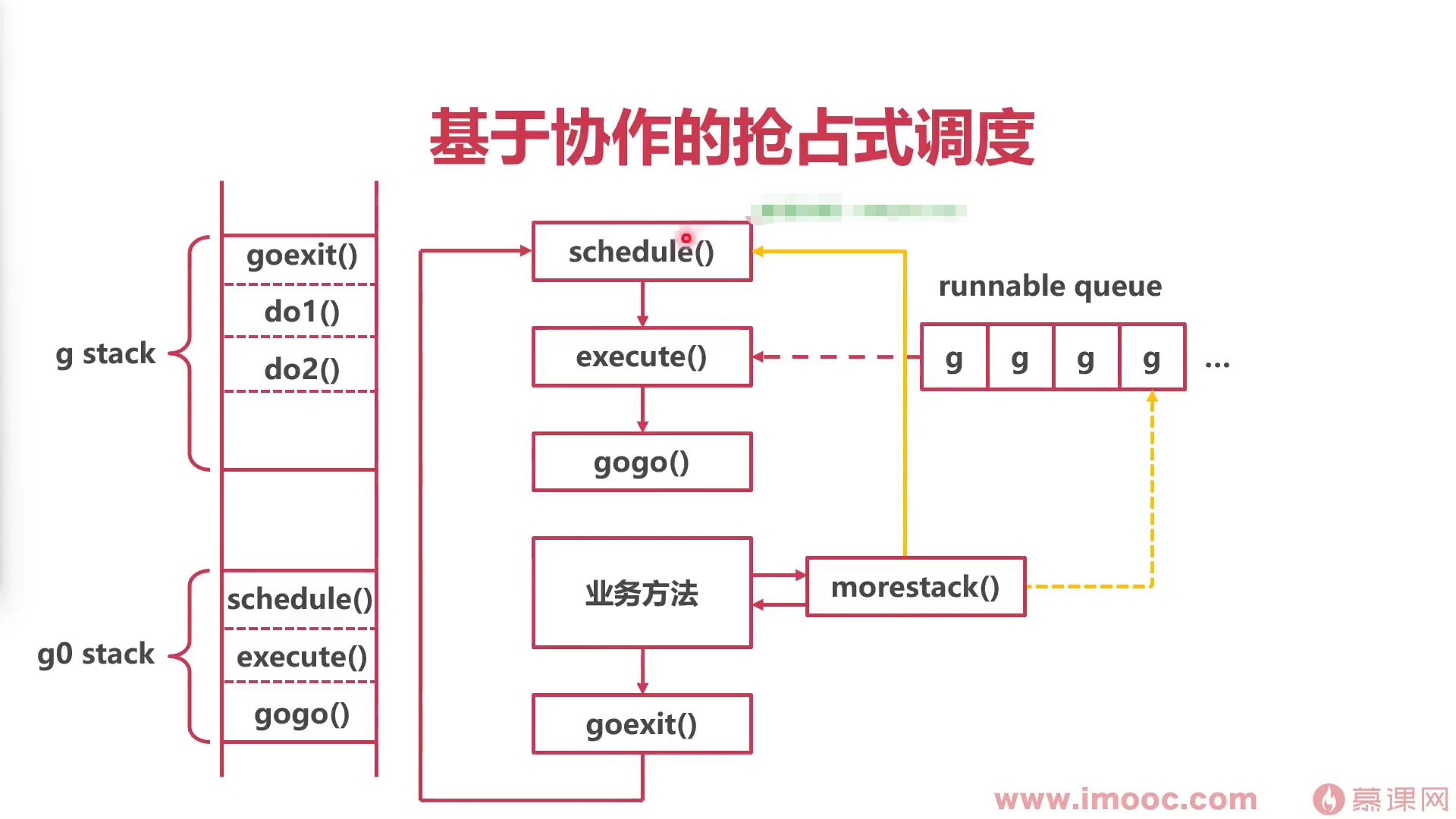
抢占
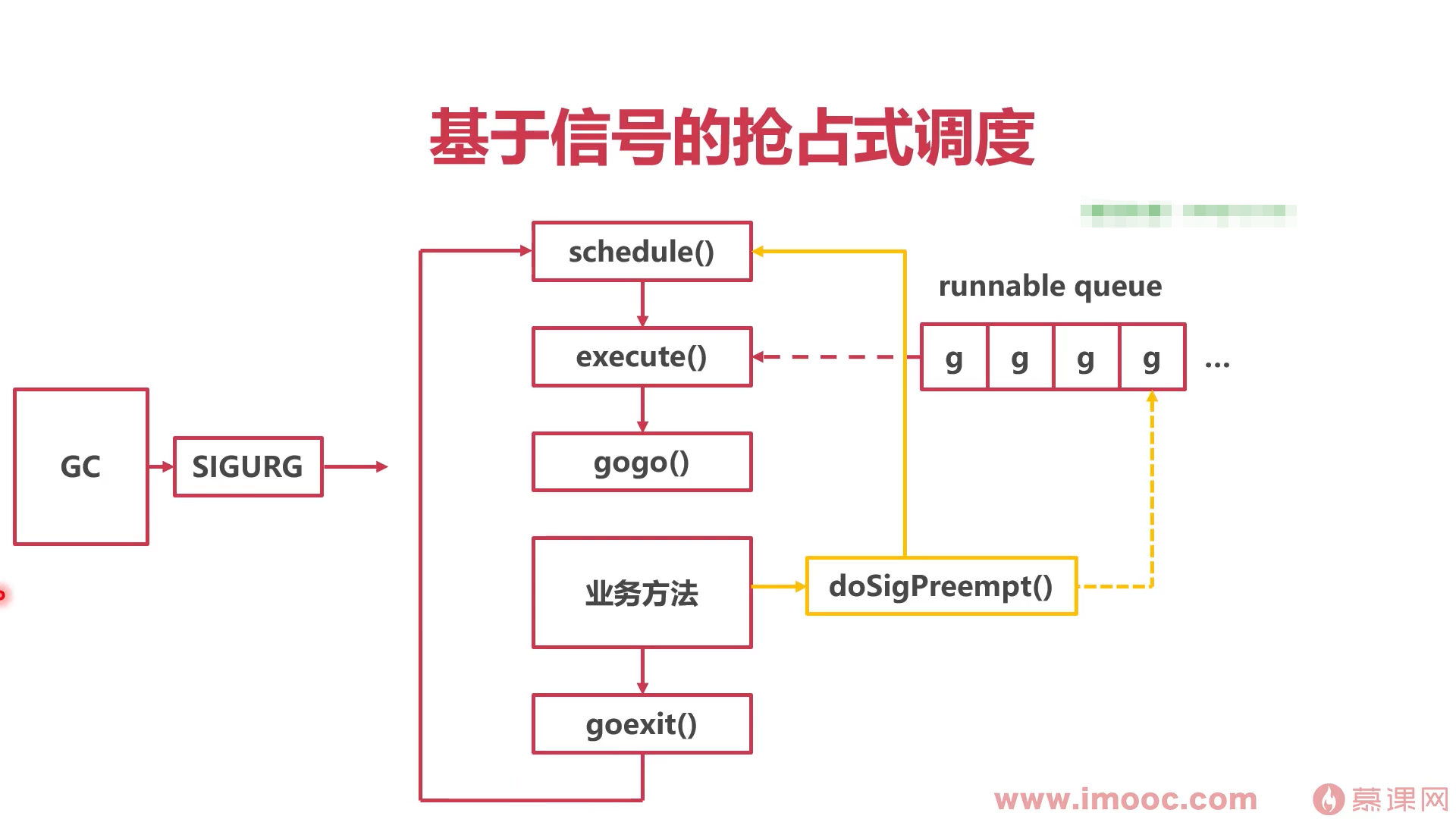
在go中,方法do1调用方法do2时,总会被系统插入一个方法 runtime.morestack

- 基于morestack方法,进行标记抢占


- 如果协程循环中的业务方法,执行了morestack方法,会检查协程是不是标记了抢占(系统监控器标记的),标记后就会出现调用schedule(协程循环重新开始)
总结
- 基于系统调用和主动挂起,协程可能无法调度
- 基于协作的抢占式调度:业务主动调用morestack()
基于信号的抢占式调度:强制线程调用doSigPreempt()
协程太多
造成的问题
文件打开数太大
- 超过内存限制
-
处理协程太多的方案
优化业务逻辑
- 利用channel的缓冲
- 利用channel的缓冲区
- 启动协程前向channel发送一个空结构体
- 协程结束取出一个结构体
- 适用于构建一大批系统的协程 ```go func do(i int,ch chan struct{}) { fmt.Println(i) time.Sleep(time.Second) <-ch }
func main() { ch := make(chan struct{},3000) for i := 0; i < math.MaxInt32; i++ { ch<- struct{}{} go do(i,ch) } time.Sleep(time.Hour) } ```
- 协程池 (tunny)
- 预创建一定数量协程
- 将任务送入协程池队列
- 协程池不断取出可用协程,执行任务
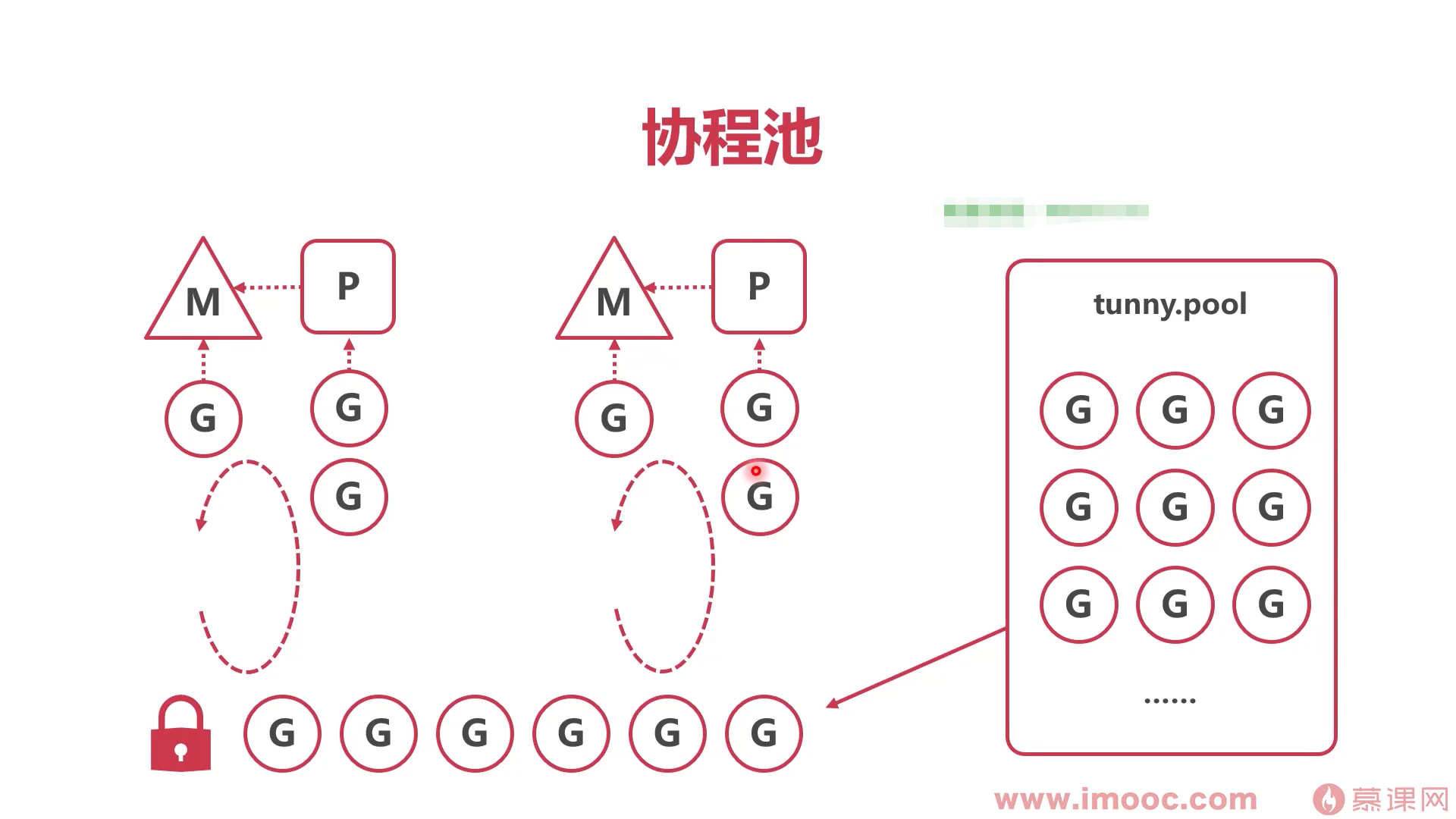
- 调度系统资源