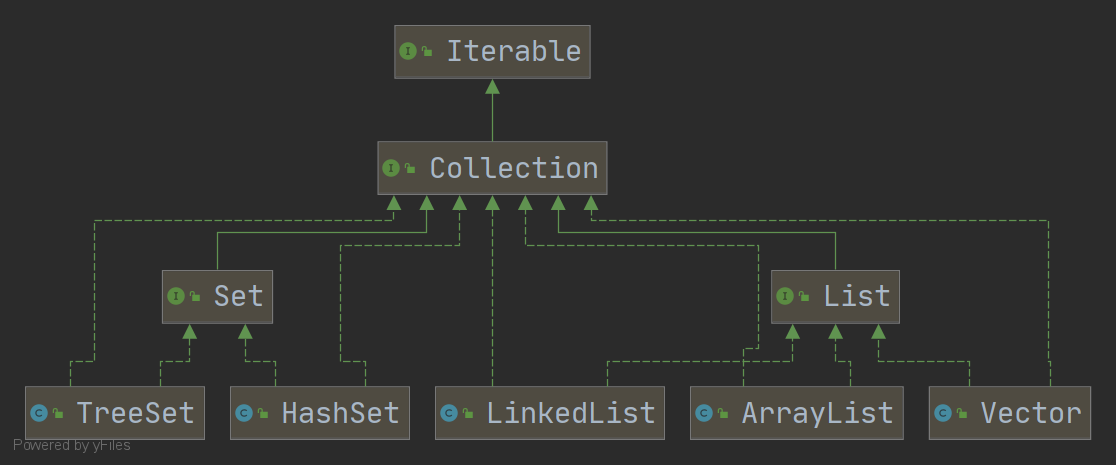
1.1 Collection
1.1常用的方法
public class CollectionMethod { @SuppressWarnings({"all"}) public static void main(String[] args) { List list = new ArrayList();// add:添加单个元素 list.add("jack"); list.add(10);//list.add(new Integer(10)) list.add(true); System.out.println("list=" + list);// remove:删除指定元素 //list.remove(0);//删除第一个元素 list.remove(true);//指定删除某个元素 System.out.println("list=" + list);// contains:查找元素是否存在 System.out.println(list.contains("jack"));//T// size:获取元素个数 System.out.println(list.size());//2// isEmpty:判断是否为空 System.out.println(list.isEmpty());//F// clear:清空 list.clear(); System.out.println("list=" + list);// addAll:添加多个元素 ArrayList list2 = new ArrayList(); list2.add("红楼梦"); list2.add("三国演义"); list.addAll(list2); System.out.println("list=" + list);// containsAll:查找多个元素是否都存在 System.out.println(list.containsAll(list2));//T// removeAll:删除多个元素 list.add("聊斋"); list.removeAll(list2); System.out.println("list=" + list);//[聊斋]// 说明:以ArrayList实现类来演示. }
1.2 迭代器(Iterator)
public class CollectionIterator { @SuppressWarnings({"all"}) public static void main(String[] args) { Collection col = new ArrayList(); col.add(new Book("三国演义", "罗贯中", 10.1)); col.add(new Book("小李飞刀", "古龙", 5.1)); col.add(new Book("红楼梦", "曹雪芹", 34.6)); //1. 先得到 col 对应的 迭代器 Iterator iterator = col.iterator(); //2. 使用while循环遍历// while (iterator.hasNext()) {//判断是否还有数据// //返回下一个元素,类型是Object// Object obj = iterator.next();// System.out.println("obj=" + obj);// } //快速生成 while => itit while (iterator.hasNext()) { Object obj = iterator.next(); System.out.println("obj=" + obj); } //3. 当退出while循环后 , 这时iterator迭代器,指向最后的元素 // iterator.next();//NoSuchElementException //4. 如果希望再次遍历,需要重置迭代器 iterator = col.iterator(); System.out.println("===第二次遍历==="); while (iterator.hasNext()) { Object obj = iterator.next(); System.out.println("obj=" + obj); } }}class Book { private String name; private String author; private double price; public Book(String name, String author, double price) { this.name = name; this.author = author; this.price = price; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getAuthor() { return author; } public void setAuthor(String author) { this.author = author; } public double getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(double price) { this.price = price; } @Override public String toString() { return "Book{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", author='" + author + '\'' + ", price=" + price + '}'; }
2 List接口
- List集合类中的元素是有序的,可重复
- List集合中每个元素都有对应的索引,可用get()得到
List常用方法
public class ListMethod { @SuppressWarnings({"all"}) public static void main(String[] args) { List list = new ArrayList(); list.add("张三丰"); list.add("贾宝玉");// void add(int index, Object ele):在index位置插入ele元素 //在index = 1的位置插入一个对象 list.add(1, "Curry"); System.out.println("list=" + list);// boolean addAll(int index, Collection eles):从index位置开始将eles中的所有元素添加进来 List list2 = new ArrayList(); list2.add("jack"); list2.add("tom"); list.addAll(1, list2); System.out.println("list=" + list);// Object get(int index):获取指定index位置的元素 //说过// int indexOf(Object obj):返回obj在集合中首次出现的位置 System.out.println(list.indexOf("tom"));//2// int lastIndexOf(Object obj):返回obj在当前集合中末次出现的位置 list.add("Curry"); System.out.println("list=" + list); System.out.println(list.lastIndexOf("Curry"));// Object remove(int index):移除指定index位置的元素,并返回此元素 list.remove(0); System.out.println("list=" + list);// Object set(int index, Object ele):设置指定index位置的元素为ele , 相当于是替换. list.set(1, "玛丽"); System.out.println("list=" + list);// List subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex):返回从fromIndex到toIndex位置的子集合 // 注意返回的子集合 fromIndex <= subList < toIndex List returnlist = list.subList(0, 2); System.out.println("returnlist=" + returnlist); }}
3 ArrayList
- ArrayList: 维护了一个Object[]数组。
- 扩容机制:
1.如果使用无参构造器,则数组初始容量为0,第一次添加后容量为10,再次扩容就会变成1.5倍
2.如果使用指定大小的构造器,则初始为指定大小,扩容就变成1.5倍。
4 Vector
- Vector底层也是一个Object[]数组,但Vector是线程安全的,效率没有ArrayListg高
- 扩容机制:
1.如果使用无参构造器,则数组初始容量为10,再次扩容就会变成2倍
2.如果使用指定大小的构造器,则初始为指定大小,扩容就变成2倍。
5 LinkedList
6 Set接口
7 HashSet
- 实现了Set接口
- 底层是HashMap(数组+链表)
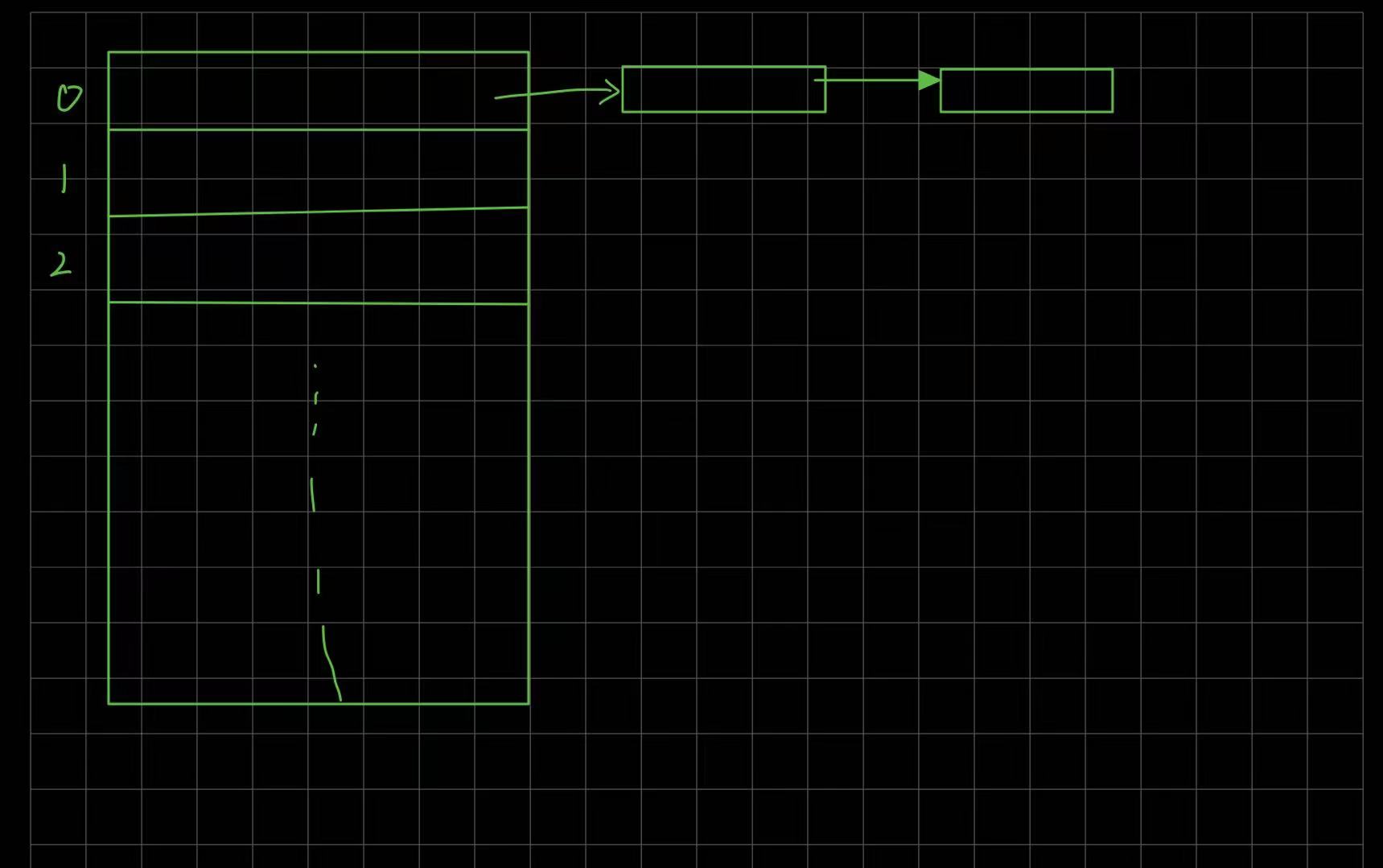
7.1 HashSet添加元素的步骤
- 添加一个元素时,会先得到Hash值,然后转成索引值
- 在存储数据表中的索引上调用equals方法比较,如果有相同元素,就放弃添加,没有就添加的链表尾部
- jdk8中,如果链表元素超过阈值(16),且索引表的大小>=设定的值(64),就会进行树化(红黑树)
8 LinkedHashSet
- 底层是LinkedHashMap(数组+双向链表)
9 Collections工具类
public class Collections_ { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建ArrayList 集合,用于测试. List list = new ArrayList(); list.add("tom"); list.add("smith"); list.add("king"); list.add("milan"); list.add("tom");// reverse(List):反转 List 中元素的顺序 Collections.reverse(list); System.out.println("list=" + list);// shuffle(List):对 List 集合元素进行随机排序// for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {// Collections.shuffle(list);// System.out.println("list=" + list);// }// sort(List):根据元素的自然顺序对指定 List 集合元素按升序排序 Collections.sort(list); System.out.println("自然排序后"); System.out.println("list=" + list);// sort(List,Comparator):根据指定的 Comparator 产生的顺序对 List 集合元素进行排序 //我们希望按照 字符串的长度大小排序 Collections.sort(list, new Comparator() { @Override public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) { //可以加入校验代码. return ((String) o2).length() - ((String) o1).length(); } }); System.out.println("字符串长度大小排序=" + list);// swap(List,int, int):将指定 list 集合中的 i 处元素和 j 处元素进行交换 //比如 Collections.swap(list, 0, 1); System.out.println("交换后的情况"); System.out.println("list=" + list); //Object max(Collection):根据元素的自然顺序,返回给定集合中的最大元素 System.out.println("自然顺序最大元素=" + Collections.max(list)); //Object max(Collection,Comparator):根据 Comparator 指定的顺序,返回给定集合中的最大元素 //比如,我们要返回长度最大的元素 Object maxObject = Collections.max(list, new Comparator() { @Override public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) { return ((String)o1).length() - ((String)o2).length(); } }); System.out.println("长度最大的元素=" + maxObject); //Object min(Collection) //Object min(Collection,Comparator) //上面的两个方法,参考max即可 //int frequency(Collection,Object):返回指定集合中指定元素的出现次数 System.out.println("tom出现的次数=" + Collections.frequency(list, "tom")); //void copy(List dest,List src):将src中的内容复制到dest中 ArrayList dest = new ArrayList(); //为了完成一个完整拷贝,我们需要先给dest 赋值,大小和list.size()一样 for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { dest.add(""); } //拷贝 Collections.copy(dest, list); System.out.println("dest=" + dest); //boolean replaceAll(List list,Object oldVal,Object newVal):使用新值替换 List 对象的所有旧值 //如果list中,有tom 就替换成 汤姆 Collections.replaceAll(list, "tom", "汤姆"); System.out.println("list替换后=" + list); }



