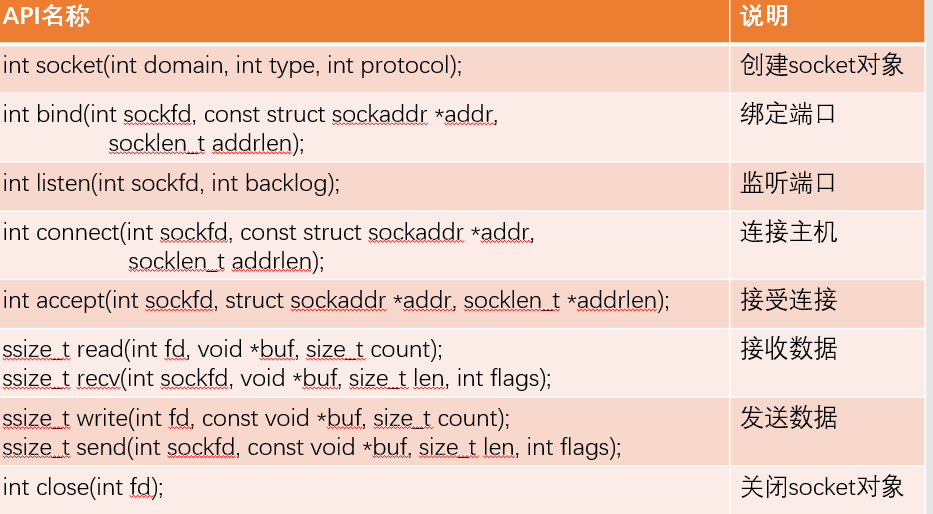
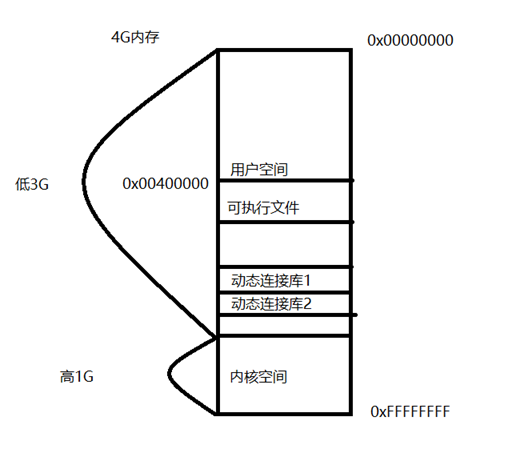
1. 进程操作
1.1 环境变量
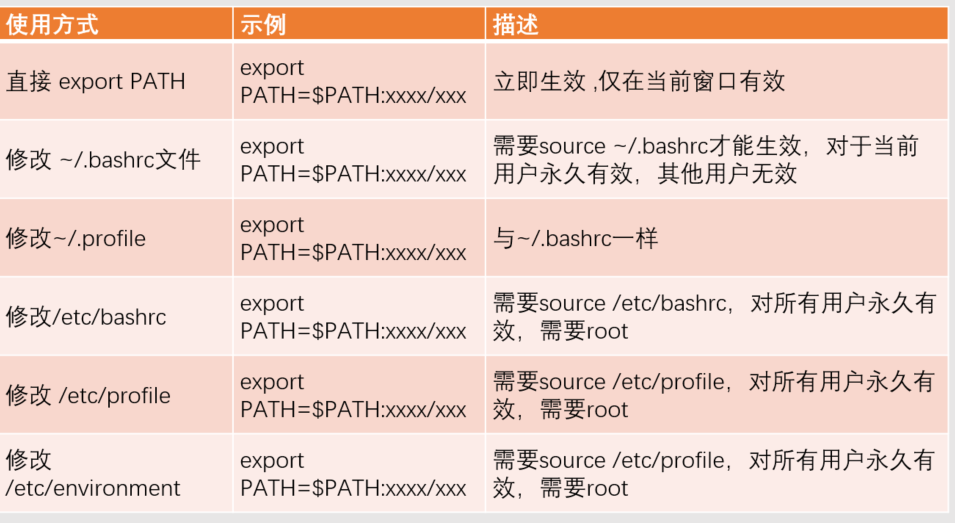
1.1.1 关于环境变量 修改方式
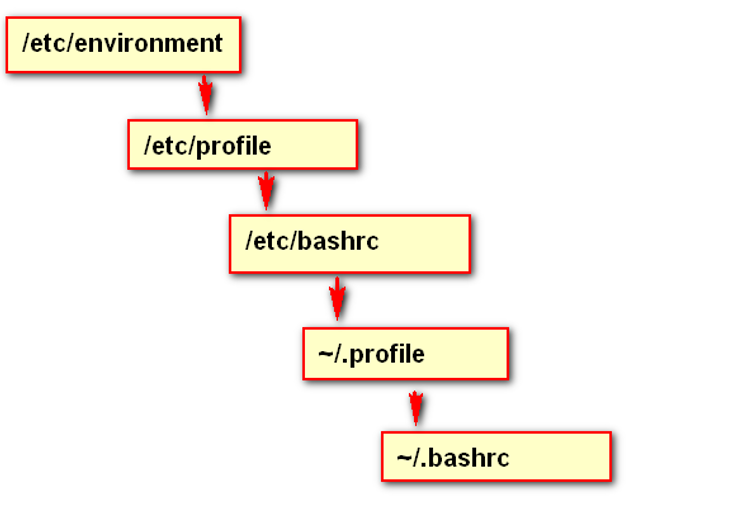
1.1.2 环境变量加载的顺序
1.1.3 Linux下操作环境变量的函数
include
//这个全局变量是直接导出的,能够直接访问到所有的环境变量
extern char **environ;
//这个全局变量是直接导出的,能够直接访问到所有的环境变量
extern char **environ;
void showallenviron()
{
for (char *ptr = environ; ptr != NULL; ++ptr)
puts(ptr);
}
//设置环境变量
void getenvirton()
{
// 设置环境变量 key:value
setenv(“TEST”,”12345678”,1);
// 获取环境变量内容
char test = getenv(“TEST”);
puts(test);
}
int main()
{
//showallenviron();
getenvirton();
return 0;
}
1.2 进程相关
1.2.1 基本信息
1.2.2 命令
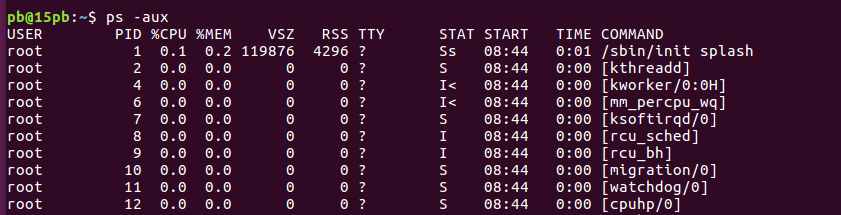
- ps命令 ps -aux
如果想要查看某个进程的信息
grep 进行一个过滤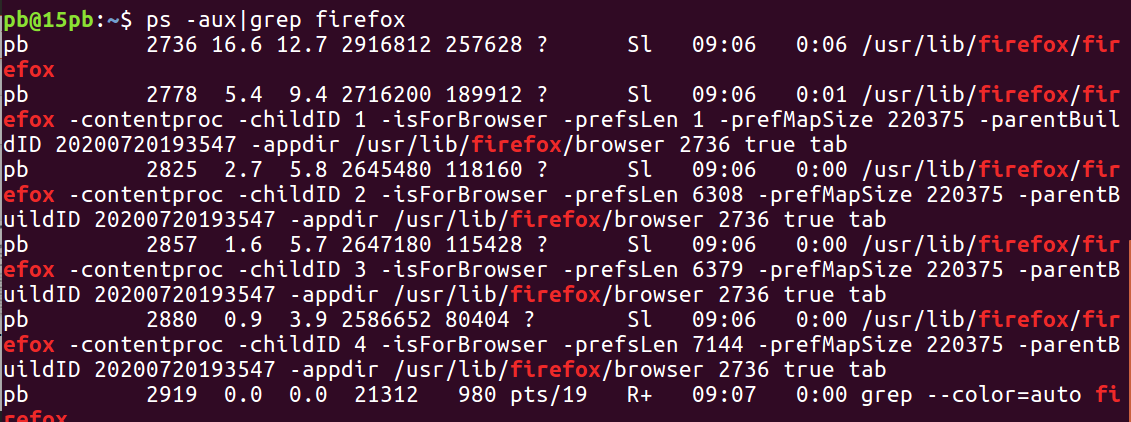
上面这个命令,不是动态
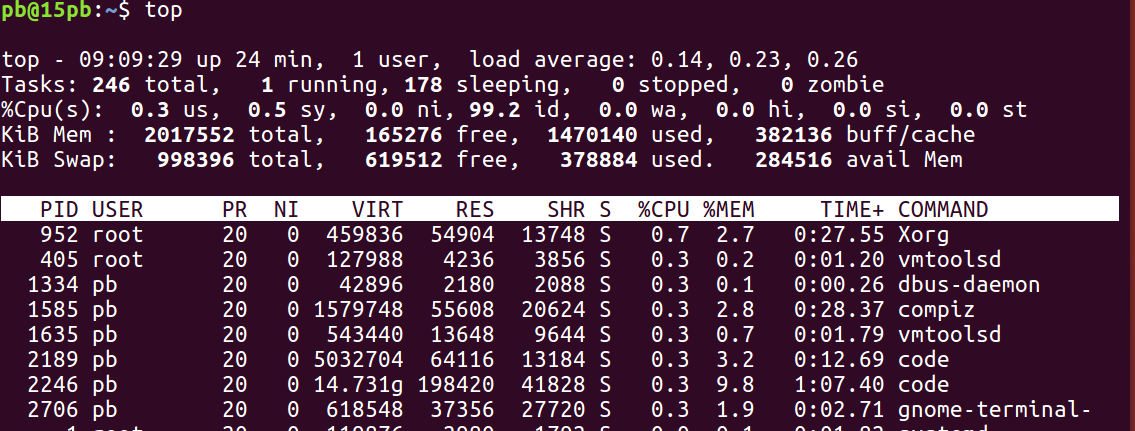
- Linux版本的任务管理器-top命令
- 另外一个比较好用的进程查看工具
htop 默认是不安装的
apt-get install htop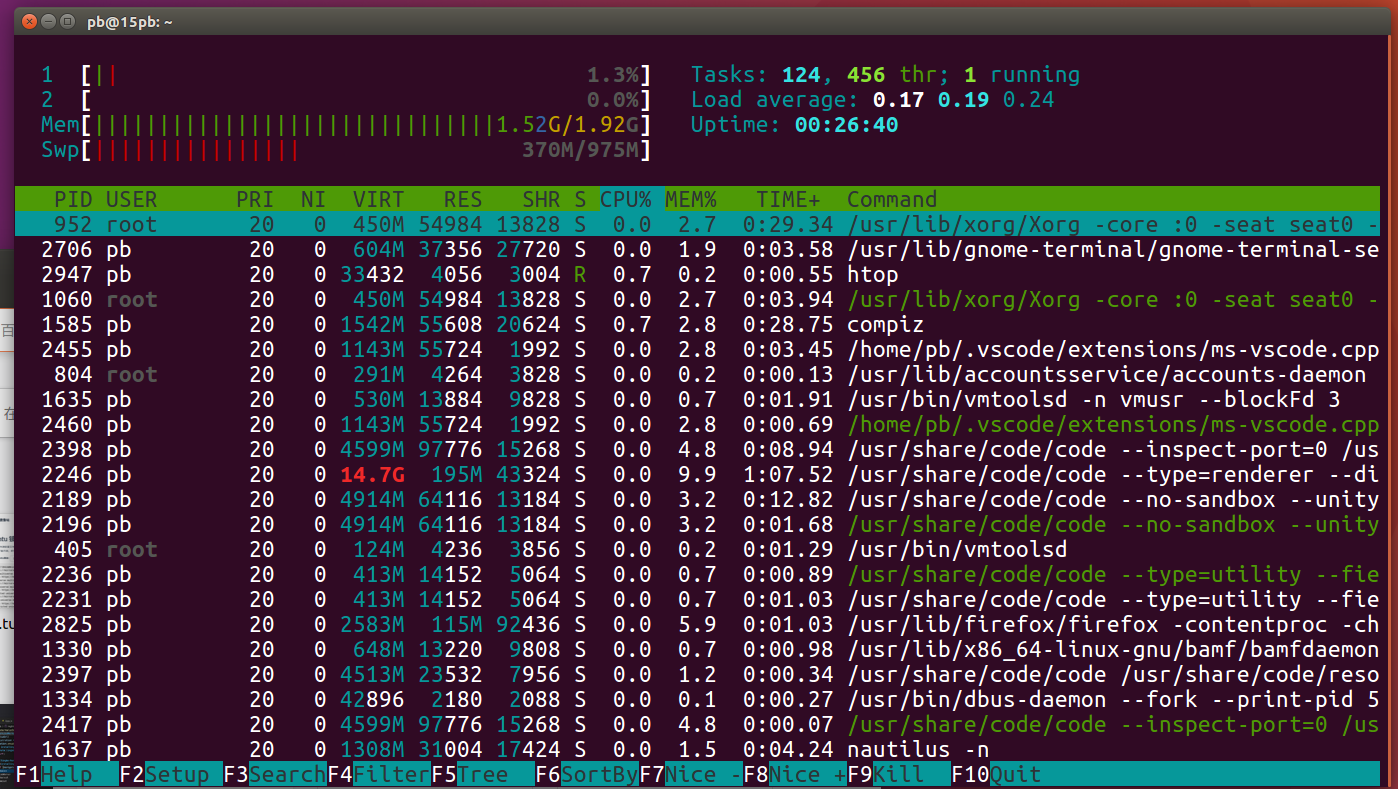
如果想要结束一个进程
按 F9 选择9号 结束进程
也可以
- 结束进程
kill -9 进程的ID 也可以
killall 进程名
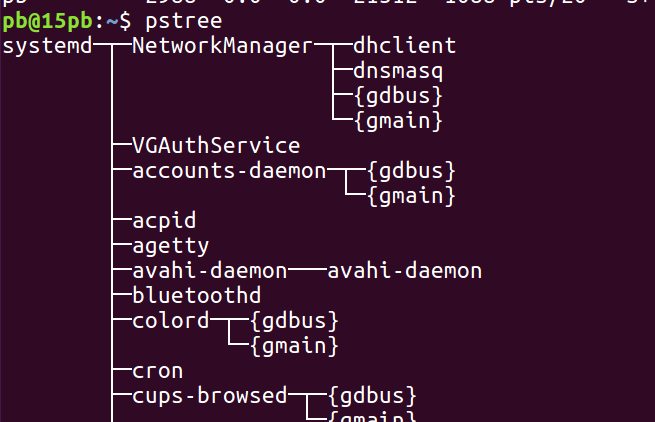
- 查看进程树
1.2.3 proc文件系统
我们去1645中查看
这些文件就是进程相关的信息
比如:
cat maps 查看进程的内存布局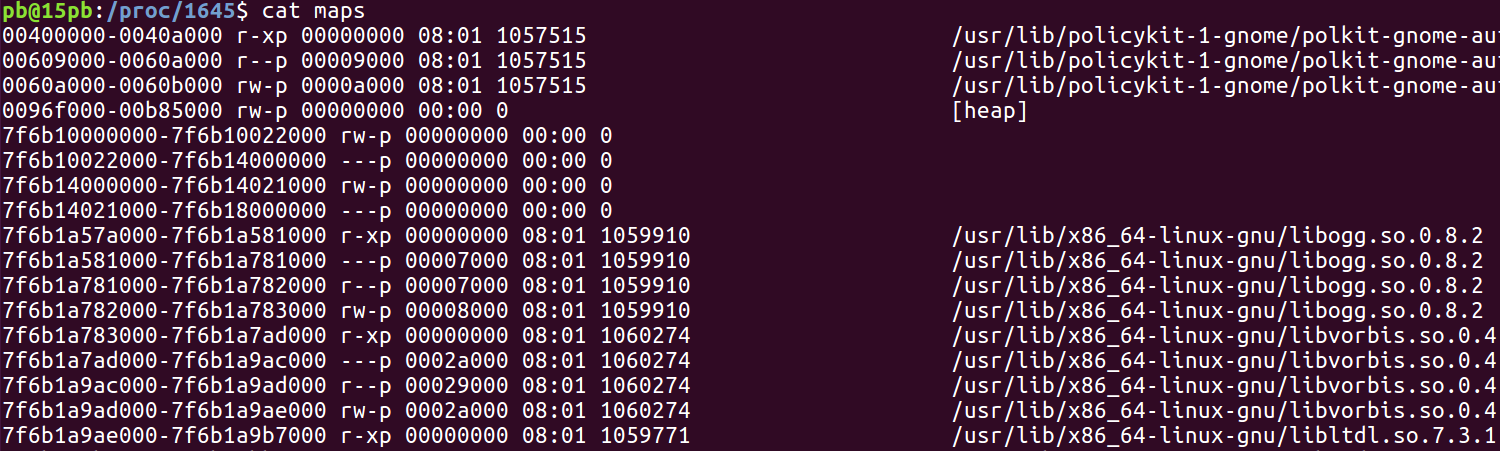
cat cmdline查看命令行参数
cat status 查看进程的一些状态信息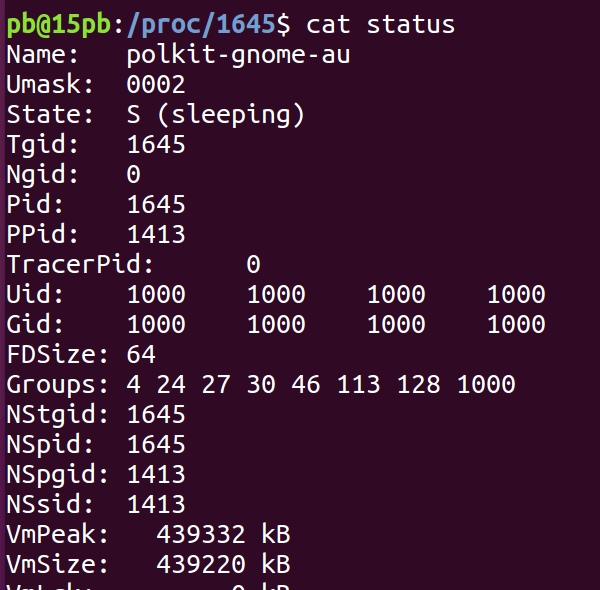
还有一个进程信息的查看方式
cat stat 对于我们来说 可读性比较差 对于软件来说,可以按照一定的格式去读取他们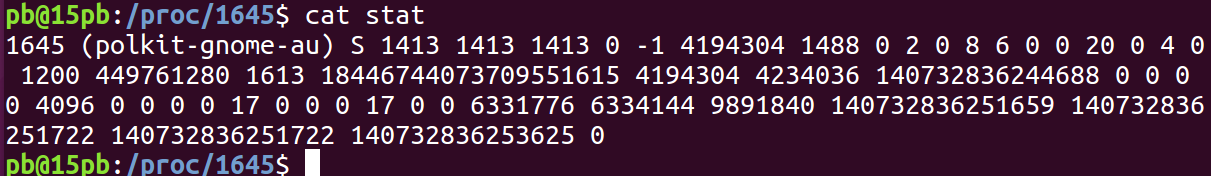
1.2.4 遍历进程的思路
我们可以遍历 proc目录下的 所有数字文件夹,然后就能够得到所有的进程ID,之后,进入ID文件夹,通过读取文件,就能够获取到进程的信息。
我们可以参考PS命令的实现方式:
下载源码:
PS的源码:int main(int argc, char *argv[]){arg_parse(argc, argv);#if 0choose_dimensions();#endifif(!old_h_option){const char *head;switch(ps_format){default: /* can't happen */case 0: head = " PID TTY TIME CMD"; break;case 'l': head = "F S UID PID PPID C PRI NI ADDR SZ WCHAN TTY TIME CMD"; break;case 'f': head = "USER PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD"; break;case 'j': head = " PID PGID SID TTY TIME CMD"; break;case 'u'|0x80: head = "USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY S START TIME COMMAND"; break;case 'v'|0x80: head = " PID TTY S TIME MAJFL TRS DRS RSS %MEM COMMAND"; break;case 'j'|0x80: head = " PPID PID PGID SID TTY TPGID S UID TIME COMMAND"; break;case 'l'|0x80: head = "F UID PID PPID PRI NI VSZ RSS WCHAN S TTY TIME COMMAND"; break;}printf("%s\n",head);}if(want_one_pid){if(stat2proc(want_one_pid)) print_proc();else exit(1);}else{struct dirent *ent; /* dirent handle */DIR *dir;int ouruid;int found_a_proc;found_a_proc = 0;ouruid = getuid();dir = opendir("/proc");while(( ent = readdir(dir) )){if(*ent->d_name<'0' || *ent->d_name>'9') continue;if(!stat2proc(atoi(ent->d_name))) continue;if(want_one_command){if(strcmp(want_one_command,P_cmd)) continue;}else{if(!select_notty && P_tty_num==NO_TTY_VALUE) continue;if(!select_all && P_euid!=ouruid) continue;}found_a_proc++;print_proc();}}}另外一段static int stat2proc(int pid) {char buf[800]; /* about 40 fields, 64-bit decimal is about 20 chars */int num;int fd;char* tmp;struct stat sb; /* stat() used to get EUID */snprintf(buf, 32, "/proc/%d/stat", pid);if ( (fd = open(buf, O_RDONLY, 0) ) == -1 ) return 0;num = read(fd, buf, sizeof buf - 1);fstat(fd, &sb);P_euid = sb.st_uid;close(fd);if(num<80) return 0;buf[num] = '\0';tmp = strrchr(buf, ')'); /* split into "PID (cmd" and "<rest>" */*tmp = '\0'; /* replace trailing ')' with NUL *//* parse these two strings separately, skipping the leading "(". */memset(P_cmd, 0, sizeof P_cmd); /* clear */sscanf(buf, "%d (%15c", &P_pid, P_cmd); /* comm[16] in kernel */num = sscanf(tmp + 2, /* skip space after ')' too */"%c ""%d %d %d %d %d ""%lu %lu %lu %lu %lu %lu %lu ""%ld %ld %ld %ld %ld %ld ""%lu %lu ""%ld ""%lu %lu %lu %lu %lu %lu ""%u %u %u %u " /* no use for RT signals */"%lu %lu %lu",&P_state,&P_ppid, &P_pgrp, &P_session, &P_tty_num, &P_tpgid,&P_flags, &P_min_flt, &P_cmin_flt, &P_maj_flt, &P_cmaj_flt, &P_utime, &P_stime,&P_cutime, &P_cstime, &P_priority, &P_nice, &P_timeout, &P_alarm,&P_start_time, &P_vsize,&P_rss,&P_rss_rlim, &P_start_code, &P_end_code, &P_start_stack, &P_kstk_esp, &P_kstk_eip,&P_signal, &P_blocked, &P_sigignore, &P_sigcatch,&P_wchan, &P_nswap, &P_cnswap);/* fprintf(stderr, "stat2proc converted %d fields.\n",num); */P_vsize /= 1024;P_rss *= (PAGE_SIZE/1024);memcpy(P_tty_text, " ? ", 8);if (P_tty_num != NO_TTY_VALUE) {int tty_maj = (P_tty_num>>8)&0xfff;int tty_min = (P_tty_num&0xff) | ((P_tty_num>>12)&0xfff00);snprintf(P_tty_text, sizeof P_tty_text, "%3d,%-3d", tty_maj, tty_min);}if(num < 30) return 0;if(P_pid != pid) return 0;return 1;}遍历进程的实现#include <stdio.h>#include <dirent.h>#include <string.h>#include <sys/stat.h>#include <errno.h>// 显示进程名称void proc_show_name(int pid){// 打开文件char path[266];sprintf(path, "/proc/%d/status", pid);FILE *fd = fopen(path, "r");if (fd == NULL){printf("无法打开文件 :%s\n", path);return;}fscanf(fd, "Name: %s\n", path);printf(" %s ", path);// 关闭文件.fclose(fd);}// 显示进程模块名称void proc_show_module(int pid){char path[266];sprintf(path, "/proc/%d/maps", pid);FILE *fd = fopen(path, "r");if (fd == NULL){printf("无法打开文件 :%s\n", path);}// %llx-%llx %4s %x %5s %d %sunsigned long long base = 0, end = 0;char pageatt[5];int offset;char time[6];unsigned int inode;while (7 ==fscanf(fd, "%llx-%llx %4s %x %5s %d %s",&base, &end, pageatt, &offset, time, &inode, path)){if (offset == 0){printf("\t%llx-%llx %4s %x %5s %d %s\n",base, end, pageatt, offset, time, inode, path);}}// 关闭文件.fclose(fd);return;}int main(){//1.遍历/proc目录struct DIR *pdir = opendir("/proc");if (pdir == NULL){printf("无法打开/proc目录\n");return;};// 2.遍历目录下所有数字的目录int pid;char path[266] = {0};char proc_name[100];struct dirent *ent = NULL;while (ent = readdir(pdir)){// 得到进程id,如果无法将字符串转换成数字,说明目录名不是进程idif (1 != sscanf(ent->d_name, "%d", &pid))continue;// 进程信息(包括进程名)保存在status文件中中proc_show_name(pid);// 进程pidprintf("%6d \n", pid);proc_show_module(pid);}// 3.关闭目录流clclosedir(pdir);}
1.2.5 创建进程
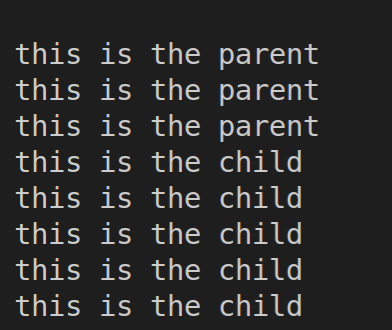
void CreateChild() { pid_t pid; const char *message = NULL; int n = 0; int i =0; pid = fork(); // 创建进程,子进程代码也是从这个地方开始执行 if(pid<0) { // pid大于0时表示当前处于父进程 perror(“fork failed\n”); return; } if (pid == 0){ //pid为0时时子进程 message = “this is the child\n”; n = 6; } else{ // pid是-1时错误 message = “this is the parent\n”; n=3; } for(i =0;i<n;i++) { printf(message); sleep(1); } return; } int main() { CreateChild(); return 0; }
<a name="D8mhq"></a>### **1.2.6 创建进程并且能够 执行一个其他程序**```cpp#include <unistd.h>#include <stdio.h>pid_t CreateProcess(char *name){pid_t pid;pid = fork(); // 创建子进程if(pid<0){perror("fork failed\n");return -1;}if (pid == 0){execl(name,NULL); // 让子进程执行新程序}else{return pid;}return pid;}int main(){CreateProcess("/home/pb/app");return 0;}
1.2.7 关于子进程的等待
子进程是需要被父进程等待,才能够清理完全,
#include <sys/types.h>#include <sys/wait.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>int main(void){pid_t pid;pid = fork(); // 创建子进程if (pid < 0){ // -1时错误perror("fork failed");exit(1);}if (pid == 0) { // 子进程int i;for (i = 3; i > 0; i--) {printf("This is the child\n");sleep(1);}exit(3);}else{ //父进程int stat_val;waitpid(pid, &stat_val, 0); // 等待指定的子进程结束,否则子进程会变成僵尸进程if (WIFEXITED(stat_val))// 如果子进程正常结束则为非0值。printf("Child exited with code %d\n", WEXITSTATUS(stat_val));else if (WIFSIGNALED(stat_val)) // 进程是因为信号而结束则此宏值为真printf("Child terminated abnormally, signal %d\n", WTERMSIG(stat_val));}return 0;}
2. 线程
2.1 创建线程
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <pthread.h>// 线程回调函数void *thread_run(void *arg){int n = (int)arg;for(int i=0;i<10000;i++){printf("child: %d out number%d \n",i,n);}// 释放线程资源pthread_detach(pthread_self());return NULL;}int main(){//1.创建线程pthread_t pthread;pthread_create(&pthread,NULL,thread_run,100);for(int i=0;i<10000;i++){printf("main: %d \n",i);}//2. 等待线程结束pthread_join(pthread,NULL);return 0;}// 编译 gcc 01创建线程.c -g -lpthread -o app总结:子线程结束的时候,一定要调用pthread_detach 这个函数。创建线程的地方,应该调用pthread_join去等待线程结束。
2.2 Linux上的线程同步问题的解决
问题:#include <stdio.h>#include <pthread.h>#include <unistd.h>// 全局变量(共享资源)int g_source = 0;// 线程1void *workthread1(void * param){// 循环增加10000次for (size_t i = 0; i < 10000; i++){g_source += 1;}// 销毁线程pthread_detach(pthread_self());return NULL;}// 线程2void *workthread2(void * param){// 循环增加10000次for (size_t i = 0; i < 10000; i++){g_source += 1;}// 销毁线程pthread_detach(pthread_self());return NULL;}int main(){pthread_t threads[2]={};// 创建两个线程pthread_create(&threads[0],NULL,workthread1,0);pthread_create(&threads[1],NULL,workthread2,0);// 等待线程销毁for (size_t i = 0; i < 2; i++){pthread_join(threads[i],NULL);}// 显示全局变量的内容printf("g_source = %d \n",g_source);return 0;}如何解决这个问题呢???可以使用互斥锁#include <stdio.h>#include <pthread.h>#include <unistd.h>// 全局变量(共享资源)int g_source = 0;pthread_mutex_t counter_mutex=PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;// 线程1void *workthread1(void * param){// 循环增加10000次for (size_t i = 0; i < 100000; i++){pthread_mutex_lock(&counter_mutex); //获取锁g_source += 1;pthread_mutex_unlock(&counter_mutex); //释放锁,其它线程才可以取得锁}// 销毁线程pthread_detach(pthread_self());return NULL;}// 线程2void *workthread2(void * param){// 循环增加10000次for (size_t i = 0; i < 100000; i++){pthread_mutex_lock(&counter_mutex); //获取锁g_source += 1;pthread_mutex_unlock(&counter_mutex); //释放锁,其它线程才可以取得锁}// 销毁线程pthread_detach(pthread_self());return NULL;}int main(){pthread_t threads[2]={};// 创建两个线程pthread_create(&threads[0],NULL,workthread1,0);pthread_create(&threads[1],NULL,workthread2,0);// 等待线程销毁for (size_t i = 0; i < 2; i++){pthread_join(threads[i],NULL);}// 显示全局变量的内容printf("g_source = %d \n",g_source);return 0;}信号量解决问题#include <stdio.h>#include <pthread.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <semaphore.h>// 全局变量(共享资源)int g_source = 0;// 信号量sem_t g_semaphore;// 线程1void *workthread1(void * param){// 循环增加10000次for (size_t i = 0; i < 10000; i++){sem_wait(&g_semaphore); //阻塞,直到获取信号,信号数-1g_source += 1; //访问全局变量,不会被其它线程打断sem_post(&g_semaphore); //释放一个信号数+1,让其它线程可以获取信号}// 销毁线程pthread_detach(pthread_self());return NULL;}// 线程2void *workthread2(void * param){// 循环增加10000次for (size_t i = 0; i < 10000; i++){sem_wait(&g_semaphore); //阻塞,直到获取信号,信号数-1g_source += 1; //访问全局变量,不会被其它线程打断sem_post(&g_semaphore); //释放一个信号数+1,让其它线程可以获取信号}// 销毁线程pthread_detach(pthread_self());return NULL;}int main(){pthread_t threads[2]={};// 创建信号量sem_init(&g_semaphore, //信号量0, //0表示同一进程间线程同步1); //信号最大值// 创建两个线程pthread_create(&threads[0],NULL,workthread1,0);pthread_create(&threads[1],NULL,workthread2,0);// 等待线程销毁for (size_t i = 0; i < 2; i++){pthread_join(threads[i],NULL);}// 显示全局变量的内容printf("g_source = %d \n",g_source);// 销毁信号量sem_destroy(&g_semaphore);return 0;}信号量,比较适合解决生产消费的问题。
3. 网络