一、概述
queue:一个队列就是一个先入先出(FIFO)的数据结构,queue接口与list、set同一级别,都是集成Collection接口。
二、queue类图
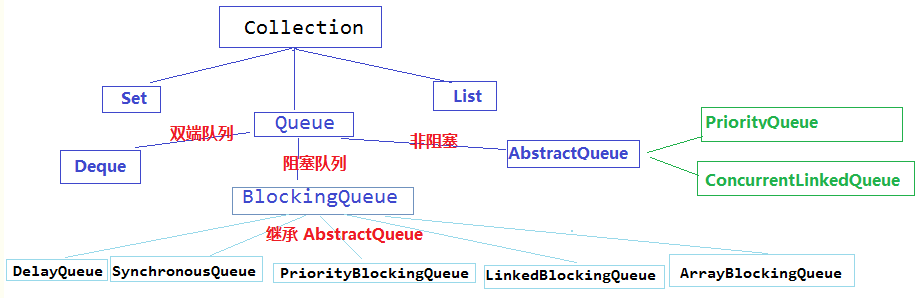
常用的队列分为两类:阻塞队列和非阻塞队列
- 常用阻塞队列
ArrayBlockingQueue - 基于数组实现的有界阻塞队列
LinkedBlockingQueue - 基于链表实现的有界阻塞队列
PriorityBlockingQueue - 一个具有优先级的无限阻塞队列,默认情况下元素采用自然顺序升序排列。基于最 小 二叉堆实现,使用CAS实现的自旋锁来控制队列的动态扩容
SynchronousQueue - 一个不存储元素的阻塞队列,每个插入操作必须等到另一个线程调用移除 操作,否则插 入操作处于阻塞状态
- 常用非阻塞队列
LinkedList - 除了实现了List接口,也实现了Deque接口,可以当做双端队列来使用
PriorityQueue - 无界有序队列,按照自然顺序排列。Object数组实现
ConcurrentLinkedQueue - 基于连接节点(链表)、线程安全的队列(CAS)。
三、常用方法
-- 尾部添加add() - 增加一个元素,如果队列已满,则抛出异常队列满 notFull.awaitnotEmpty.signal()offer() - 添加一个元素并返回true,如果队列已满,则返回false-- 删除并返回头部元素remove() - 移除并返回队列头部的元素 如果队列为空,则抛出异常notFull.single() 取元素调用notEmpty.await() 当队列长度为 0poll() - 移除并返回队列头部的元素,如果队列为空,则返回null-- 获取头部元素但不删除element() - 返回队列的头部元素,如果队列为空,则抛出异常peek() - 返回队列头部的元素,如果队列为空,则返回null-- 阻塞添加删除队列满 notFull.awaitnotEmpty.signal()put() - 添加一个元素,如果队列满,则阻塞notFull.single()notEmpty.await() 当队列长度为 0take() - 移除并返回队列头部的元素,如果队列为空,则阻塞
四、ArrayBlockingQueue
- 通过数组实现的有界阻塞队列,此队列按照先进先出的原则对元素进行排序
- 锁没有分离(只有一把锁),生产和消费用的是同一把锁
- 数组队列在生产和消费(出队入队)时直接将对象从数组中插入或移除,效率较高
- 因为是数组队列,所以初始化时必须指定队列大小。 ```java final Object[] items; / Main lock guarding all access */ final ReentrantLock lock; / Condition for waiting takes / private final Condition notEmpty; /** Condition for waiting puts / private final Condition notFull; / items index for next take, poll, peek or remove */ int takeIndex; / items index for next put, offer, or add / int putIndex; /** Number of elements in the queue / int count;
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair) { if (capacity <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); this.items = new Object[capacity]; lock = new ReentrantLock(fair); //非空条件等待队列 notEmpty = lock.newCondition(); //非满条件等待队列 notFull = lock.newCondition(); }
public boolean offer(E e) { checkNotNull(e); final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; lock.lock(); try { //如果队列已满,发挥false if (count == items.length) return false; else { enqueue(e); return true; } } finally { lock.unlock(); } }
private void enqueue(E x) { // assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1; // assert items[putIndex] == null; final Object[] items = this.items; items[putIndex] = x; if (++putIndex == items.length) putIndex = 0; count++; notEmpty.signal(); }
public E take() throws InterruptedException { final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; lock.lockInterruptibly(); try { //当队列元素个数等于0时,阻塞等待 while (count == 0) notEmpty.await(); //不等于0,添加元素 return dequeue(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } private E dequeue() { // assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1; // assert items[takeIndex] != null; final Object[] items = this.items; @SuppressWarnings(“unchecked”) E x = (E) items[takeIndex]; items[takeIndex] = null; if (++takeIndex == items.length) takeIndex = 0; count—; if (itrs != null) itrs.elementDequeued(); notFull.signal(); return x; }
<a name="QLfN8"></a># 五、LinkedBlockingQueue- 通过链表实现可选容量阻塞队列- 有两把锁,一把用于put(生产),一把用户take(消费)- 队列在生产和消费的时候,需要把数据对象封装到Node节点中,相对效率没有那么高- 队列容量限制是可选的,如果在初始化时没有指定容量,那么默认使用int的最大值作为队列容量```java/** 执行take, poll等操作时候需要获取该锁 */private final ReentrantLock takeLock = new ReentrantLock();/** 当队列为空时候执行出队操作(比如take)的线程会被放入这个条件队列进行等待 */private final Condition notEmpty = takeLock.newCondition();/** 执行put, offer等操作时候需要获取该锁*/private final ReentrantLock putLock = new ReentrantLock();/**当队列满时候执行进队操作(比如put)的线程会被放入这个条件队列进行等待 */private final Condition notFull = putLock.newCondition();/** 当前队列元素个数 ArrayBlockingQueue用的是int*/private final AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(0);
public LinkedBlockingQueue(int capacity) {if (capacity <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();this.capacity = capacity;last = head = new Node<E>(null);}public boolean offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)throws InterruptedException {if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);int c = -1;final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;final AtomicInteger count = this.count;putLock.lockInterruptibly();try {while (count.get() == capacity) {if (nanos <= 0)return false;nanos = notFull.awaitNanos(nanos);}enqueue(new Node<E>(e));c = count.getAndIncrement();if (c + 1 < capacity)notFull.signal();} finally {putLock.unlock();}if (c == 0)signalNotEmpty();return true;}private void enqueue(Node<E> node) {// assert putLock.isHeldByCurrentThread();// assert last.next == null;last = last.next = node;}public E take() throws InterruptedException {E x;int c = -1;final AtomicInteger count = this.count;final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;takeLock.lockInterruptibly();try {while (count.get() == 0) {notEmpty.await();}x = dequeue();c = count.getAndDecrement();if (c > 1)notEmpty.signal();} finally {takeLock.unlock();}if (c == capacity)signalNotFull();return x;}private E dequeue() {// assert takeLock.isHeldByCurrentThread();// assert head.item == null;Node<E> h = head;Node<E> first = h.next;h.next = h; // help GChead = first;E x = first.item;first.item = null;return x;}

