一、解构赋值
解构赋值语法是一个js表达式,这使得可以将值从数组或属性从对象提取到不同的变量中
1、数组的解构赋值
const arr = [1,2,3,4,5]let [a,b,c,d,e] = arr//1、更复杂的匹配规则const arr = ['a', 'b', ['c', 'd', ['e', 'f', 'g'] ] ]const [ , b ] = arr //b = 'b'const [ , , g ] = ['e', 'f', 'g'] //g = 'g'const [ , , g ] = ['c', 'd', ['e', 'f', 'g'] ] //g = ['e', 'f', 'g']const [ , , [ , , [ , , g ] ] ] = arr //g = 'g'//2、扩展运算符 ...const arr1 = [1, 2, 3]const arr2 = ['a', 'b']const arr3 = ['zz', 1]const arr4 = [...arr1, ...arr2, ...arr3] //arr4 = [7]> [ 1, 2, 3, 'a', 'b', 'zz', 1]const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]const [a, b, ...c] = arr //c = [ 1, 2, 3, 'a', 'b', 'zz', 1]//3、默认值const arr = [1, undefined, null];const [a, b, c, ,d] = arr //a = 1, b = undefined, c = null, d = undefinedconst [a, b = 123, c = 3, d] = arr //a = 1, b = 2, c = null, d = undefinedPS:只有当undefined才会取默认值,null是不行的//4、交换变量[a, b] = [b , a]//5、接收多个 函数返回值function getUserInfo(id){// ...get请求return [true,{name: '小明',gender: '女',id: id},'请求成功']}const [status, data, msg] = getUserInfo(123)//output=> status = true, data = { name: '小明', gender: '女', id: id }, msg = '请求成功'
2、对象的解构赋值
//等号左右两边都为对象结构 - const{ a, b } = {a:1, b:2 } 左边的{}中为需要赋值的变量,右边为需要解构的对象;//1、对象结构赋值的用法const obj = {saber: '阿尔',archer: '卫宫',};const { saber, archer} = obj //output: saber="阿尔",archer="卫宫" 注意:属性名称要一致,否则拿不到值;//2、稍微复杂的解构条件const player = {nickname: '感情的戏',skill: [{skillName: '龙吟',mp: '100',time: 3000,},{skillName: '龙腾',mp: '400',time: 20000,}]};const { nickname } = player //output: nickname="感情的戏"const { skill } = player //output: skill=[{skillName: '龙吟',mp: '100',time: 3000,},{skillName: '龙腾',mp: '400',time: 20000,}]const {skill: [ skill1, { skillName } ] } = player; //output: skillName="龙吟"//3、扩展运算符const obj = {saber: '阿尔',archer: '卫宫',lancher: '呼呼呼',};const { saber, ...oth } = obj //output:saber="阿尔", oth="{archer:"卫宫"},{lancher:"呼呼呼"}"//4、如何对已经申明的变量进行对象的解构赋值let age;const obj = {name: '阿尔',age: 22,};({ age } = obj ); //output:age = 22//5、默认值const obj = {name: 'name',age: undefined,};const { name, age = 24, hobby = ['学习'] } = obj //output: age = 24//6、提取对象const { name, hobby:[hobby1], hobby } = {name: '小红',hobby: ['学习'],}; //output: name = "小红", hobby1="学习", hobby=["学习"]//7、使用对象传入乱序的函数参数function AJAX({url,data,type='get'}) {console.log(type);};AJAX({url: '/getinfo',data: {a: 1,b: 2,}});//8、获取多个 函数返回值function getUserInfo(){//...ajaxreturn {status: true,data: {name: '小明',gender: '女',id: id},msg: '请求成功'};};const { status, data, msg: message } = getUserInfo(123);//9、动态插入属性名和属性值:for (var i = 1; i < 3; i++) {var app['app' + i] = {text: window.appInfo[i].appName,imageUrl: '/src/assets/images/chihoi/workbench/test.png',...createAction('custom:App', '已选APP', 'app', window.appInfo[i].appName, window.appInfo[i].id),};}console.log(app)//output: 见下图
3、字符串的解构赋值
//1、解构赋值const str = 'I am fy';const [ a, b, c, ...oth ] = str; // a="I",b=" ",c="a",oth=['m',' ','f','y']const [ ...spStr1 ] = strconst spStr2 = str.split('');const spStr3 = [ ...str ]; //output: spStr1=spStr2=spStr3=[7>]['....']//2、提取属性const { length, split } = str
二、ES6扩展
1、字符串扩展
(1)模板字符串
符号:``const xiaoming = {name: 小明',age : 13,say1: function(){console.log('我叫' + this.name + ', 今年' + this.age + '岁');}say2 function(){console.log(`我叫 ${this.name}, 我今年 ${this.age}岁`);}}xiaoming.sya1();xiaoming.say2(); //我叫小明,我今年13岁
(2)部分新的方法
// 1.padStart--从头部补充字符串 padEnd--从尾部补充字符串let str = 'i';let str1 = str.padStart(6, 'mooc');console.log(str1); // str1 = moocmilet str2 = str.padEnd(5, 'mooc');console.log(str2); // str2 = imooc// 2.repeat--相当于复制粘贴(不能写负数,小数的话回自动取整)console.log('i', repeat(10) ); // iiiiiiiiiifunction repeat(str, num){return new Array(num + 1).join(str);}console.log(repeat('s', 5) ); // sssss// 3.startsWith--判断字符串以什么开头 endsWith--判断字符串以什么结尾(输出为布尔值)const str = 'A process'console.log(str.startsWith('B')); //falseconsole.log(str.endsWith('cess')); //true// 4.includesconst str = 'A process'if(str.indexOf('process') !== -1){console.log(" 存在 "); //存在}if(str.includes('process')){console.log(" 存在 "); //存在}
(3)新的Unicode表示法和遍历方式
// 1. 转成数组遍历循环字符串let str = 'PROMISE';var oStr = Array.prototype.slice.call(str);console.log(oStr); //[7>]['P','R','O','M','I','S','E']// 2.扩展运算符实现var oStr = [...str]; //[7>]['P','R','O','M','I','S','E']//需求:有时候需要对字符串加密解密var oStr = 'BD';const map = {A: '100', B: '99', C: '98', D: '97', E: '96'};const words = 'ABCDE';oStr.forEach(function(word, index){if(words.includes(word))oStr[index] = map[word];});console.log(oStr.join('')); // join方法是用来连接字符串,output:9997// 3.for-of遍历字符串实现对字符串加密解密let newStr = '';for(let word of oStr){if(words.includes(word))newStr += map[word];}console.log(newStr); // output:9997// Unicode是一项标准 包括字符集、编码方案等,为了解决传统的字符编码方案的局限二产生的,为每个语言中的每个字符设定了统一并且唯一的二进制编码。'\u{1f436}' //ES6 提供 \u{} 来支持Unicode编码 output:"🐶"// codePointAt() 获取字符串中对应字符的一个码点;"🐶".codePointAt(0);
三、扩展
1、正则扩展
const regexp1 = /^a/g; //g代表全局意思,全局匹配开头为 a 的字符串const regexp2 = new RegExp('^a', 'g');const regexp3 = new RegExp(/^a/g); //全局匹配 a 的字符串console.log('aaabbccdd'.match(regexp1)); // ['a'];console.log('aaabbccdd'.match(regexp3)); // ['a', 'a', 'a'];// u(unicode)修饰符作用将两个字符当作一个字符console.log(/^\ud83d/u.test('\ud83d\udc36')); // false;// y 粘连修饰符const r1 = /imooc/g;const r2 = /imooc/y;const str = 'imoocimooc-imooc';console.log(r1.exec(str)); // ['imooc', 'imooc', 'imooc']console.log(r2.exec(str)); // ['imooc', 'imooc']
2、数值扩展
(1)新的进制表示法
//八进制以 0o(0O)开头//二进制以 0b(0B)开头
(2)新的方法与安全数
//Number.parseInt() 转换整数; Number.parseFloat()//Number.isNaN() 判断是不是NaN//Number.isFinite() 判断是不是有限的//Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER() 判断是不是安全数,范围 (2^53) -1 ~ (- 2^53) + 1//Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER()//Number.isSafeInteger()//幂运算(默认右边开始计算)let a = (2 ** 10) ** 0;console.log( a ) = 1024
3、函数扩展之默认参数
(1)默认参数
function add(a, b=999){//如果不给b传值,默认为999}
(2)与扩展运算符的结合(剩余参数…)
function sun(){let args = Array.prototype.slice.call(argu); // 转换成数组//等价于 let args = [...agru]console.log(argu);}sum(1,2,3,'345');function op(type, ...nums){console.log(type); // type = 'sum'console.log(nums); // nums = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]}op('sun', 1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
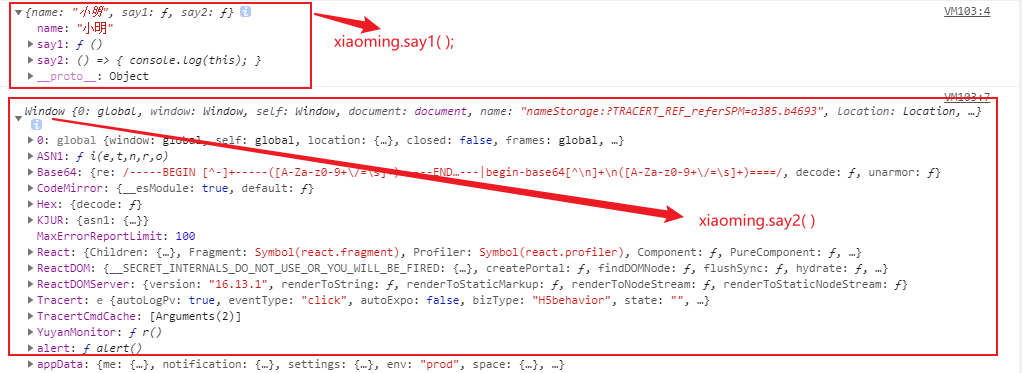
(3)箭头函数(=>)
const add1 = (a, b) => a + b;//等价于 :const add2 = function(a, b){return a + b;}//函数不返回值const pop = arr => void arr.pop();console.log(pop([1, 2, 3])); // arr = undefine//与普通函数的区别:箭头函数没有arguments参数,需要使用扩展运算符...argsconst log = () => {console.log(arguments);};log(1, 2, 3); // 控制台报错。修改为:const log = (...args) =>//箭头函数没有自己的thisconst xiaoming = {name: '小明',say1: function(){console.log(this);},say2: () => {console.log(this);},}xiaoming.say1();xiaoming.say2(); //结果见下图;
4、对象扩展
(1)简洁表示法
//老式写法const getUserInfo = (id = 1) =>{const name = 'xiaoming';age = age;return {name: name,age: age,say: function(){console.log(this.name + this.age);}}}const xiaoming = getUserInfo();//ES6写法const getUserInfo = (id = 1) =>{const name = 'xiaoming';age = age;return {name, //会自动去找同名变量age,say(){console.log(this.name + this.age);}}}const xiaoming = getUserInfo();// 属性名表达式const obj = {a: 1,$abc: 2,'uiasfuafyhahfio': 3,}// 可以通过obj.a拿到a的值// 但是乱码的就不能通过这种形式拿到对应的值,需要通过obj['属性名']的方式取到值
(2)扩展运算符
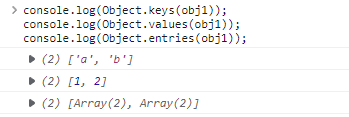
// 复制对象-- 浅拷贝(拷贝后对象值改变也会修改被拷贝的对象)const obj = {a: 1,b: 2,d:{ a: 3 },}const cobj = { ...obj } // 这样可以完成对象的复制cobj.d.a = 999; // 此时obj和cobj的 d.a 的值都会被修改为999// 合并对象(也是浅拷贝)-- 同名属性时取后一个为最终结果(与合并写的顺序有关)const obj1 = {a: 1,b: 2,}const obj2 = {a: 9,c: 3,}const newObj = { ...obj1, ...obj2 } // 此刻输出{ a=9,b=2,c=3 }// 部分新的方法和属性// Object.is()-- 浅拷贝console.log(Object.is(+0, -0)) // falseconsole.log(+0 === -0) // trueconsole.log(Object.is(NaN, NaN)) // trueconsole.log(NaN === NaN) // false// Object.assignconst o = Object.assign({a: 1}, {b: 2}) // o就是合并后的结果;// Object.keys-- 返回数组, 返回自身对应的key// Object.values-- 返回数组, 返回自身对应的value// Object.entries-- 返回数组, 每个数组包括key和value效果如下:console.log(Object.keys(obj1));console.log(Object.values(obj1));console.log(Object.entries(obj1));
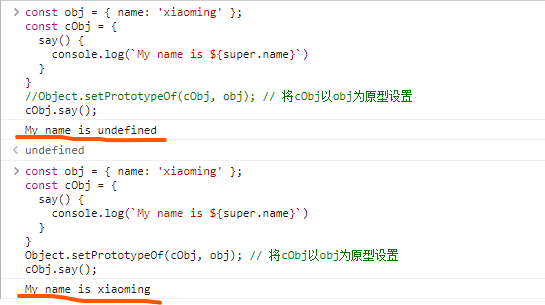
// Object.setPrototypeOf 设置对象的原型// Object.getPrototypeOf 获取对象的原型// super 一个关键字,可以拿到原型对象const obj = { name: 'xiaoming' };const cObj = {say() {console.log(`My name is ${super.name}`)}}Object.setPrototypeOf(cObj, obj); // 将cObj以obj为原型设置cObj.say();// 结果见下:
5、数组扩展
(1)结合扩展运算符使用
function foo (a, b, c) {console.log(a);console.log(b);console.log(c);}foo(...[1, 2, 3]);// apply的使用const arr = [1, 255, 5];console.log(Math.max(...arr));console.log(Math.max.apply(null, arr)); // 输出结果一致,都是255// 生成器函数-- 生成迭代器函数function *g() {console.log(1);yield 'hi~';console.log(2);yield 'lethe';}const arr = [...g()]; // arr = ['hi~', 'lethe'] ;// new Set() -- 可以实现数组去重let set = new Set([1, 2, 2, 3]);console.log(set); // { 1, 2, 3 }
(2)数组新的方法
// Array.from-- 把类数组(ArrayLike)或者Iterable对象转换成数组形式const obj1 = {0: 1,1: 'jj',2: false,length: 3};console.log(Array.from(obj, item => item*2)); // 输出 [2, 44]// Array.of-- 连接为数组console.log(Array.of(1, 2, 3); // 输出 [1, 2, 3]// Array#fill-- 用来填充数组值,会覆盖数组原有的值const arr = new Array(10).fill(0) // 创建一个长度为10并填充为0数组// Array.includes()-- 用来箭簇数组中包含什么指定的值,成功true,失败false// Array.find()-- 根据条件(回调)按顺序遍历数组,当回调返回true时,返回的当前遍历到的值const arr = [1, 2, 3]const res = arr.find((value, index, arr) => value % 2 === 0 ); // 输出6// Array.findIndex()-- 根据条件(回调)按顺序遍历数组,当回调返回true时,返回的当前遍历到的下标const res = arr.findIndex((value, index, arr) => value % 2 === 0 ); // 输出1// Array.keys-- 返回数组, 需要通过for-of遍历返回自身对应的key(下标)// Array.values-- 返回数组, 需要通过for-of遍历返回自身对应的value// Array.entries-- 返回数组, 需要通过for-of遍历每个数组包括key和valueconst arr = [1, 2, 3]console.log(arr.keys());console.log(arr.values());console.log(arr.entries());