上一篇文章跟踪了Listen、Accept接口的实现流程,本文将继续分析 epoll 在 runtime 层的运作,文中内容会集中在 runtime 层,若有不当之处请指出。
poll
runtime/netpoll.go是 poll 的抽象,它规范 poll 层和 runtime 层之间的交互接口。
poll_runtime_pollServerInit
func poll_runtime_pollServerInit() {netpollinit()atomic.Store(&netpollInited, 1)}
poll 初始化,初始化网络轮询器。
poll_runtime_isPollServerDescriptor
判断给定的 fd 是否是当前 epoll 中使用的 fd。
poll_runtime_pollOpen
func poll_runtime_pollOpen(fd uintptr) (*pollDesc, int) {pd := pollcache.alloc()// ...var errno int32errno = netpollopen(fd, pd)return pd, int(errno)}
开启网络轮询器。pollcache.alloc()从pollcache创建pollDesc,pollDesc在pollcache中以链表的方式存储。将pollDesc和 fd 绑定起来,netpollopen将在下面解释。
poll_runtime_pollClose
关闭某个连接,需当前连接无读写行为。
poll_runtime_pollReset
重置某个连接,即重置pollDesc。
poll_runtime_pollWait
就地等待读信号或者写信号,该函数在前一篇文章详解过。
poll_runtime_pollSetDeadline
设置到期时间。网络请求过程中存在很高的不确定性,大部分情况我们需要有到期时间来标记某个操作已截止。
func poll_runtime_pollSetDeadline(pd *pollDesc, d int64, mode int) {// 并发访问加锁lock(&pd.lock)if pd.closing {unlock(&pd.lock)return}rd0, wd0 := pd.rd, pd.wdcombo0 := rd0 > 0 && rd0 == wd0// 计算过期时间点if d > 0 {d += nanotime()if d <= 0 {d = 1<<63 - 1}}// 将过期时间根据mode存到rd和wd上if mode == 'r' || mode == 'r'+'w' {pd.rd = d}if mode == 'w' || mode == 'r'+'w' {pd.wd = d}combo := pd.rd > 0 && pd.rd == pd.wd// timer回调函数rtf := netpollReadDeadlineif combo {rtf = netpollDeadline}// 读timerif pd.rt.f == nil {if pd.rd > 0 {pd.rt.f = rtfpd.rt.when = pd.rd// seq的作用就是在timer到期的时候,和原pollDesc.rseq比较,// 如果不同,则重用描述符或重置计时器pd.rt.arg = pdpd.rt.seq = pd.rseqaddtimer(&pd.rt)}} else if pd.rd != rd0 || combo != combo0 {// 重置当前正在进行中的计时器pd.rseq++if pd.rd > 0 { // 修改计时器modtimer(&pd.rt, pd.rd, 0, rtf, pd, pd.rseq)} else { // 删除计时器deltimer(&pd.rt)pd.rt.f = nil}}// 写计时器// ...// 获取正在进行IO操作的读goroutine地址或写goroutine地址var rg, wg *gif pd.rd < 0 || pd.wd < 0 {// 内存操作atomic.StorepNoWB(noescape(unsafe.Pointer(&wg)), nil)// 获取已被阻塞的goroutine地址if pd.rd < 0 {rg = netpollunblock(pd, 'r', false)}if pd.wd < 0 {wg = netpollunblock(pd, 'w', false)}}unlock(&pd.lock)// 唤醒对应的goroutineif rg != nil {netpollgoready(rg, 3)}if wg != nil {netpollgoready(wg, 3)}}
还有另外一个类似实现接口netpolldeadlineimpl,实际上大多数情况下都是调用netpollDeadline,netpollReadDeadline,netpollWriteDeadline完成。
netpollready
func netpollready(toRun *gList, pd *pollDesc, mode int32) {var rg, wg *gif mode == 'r' || mode == 'r'+'w' {rg = netpollunblock(pd, 'r', true)}if mode == 'w' || mode == 'r'+'w' {wg = netpollunblock(pd, 'w', true)}if rg != nil {toRun.push(rg)}if wg != nil {toRun.push(wg)}}
netpollready是 epoll 上报事件的接口,通过 mode 取到当前读写 goroutine 地址将之推送到即将执行队列。
netpollunblock
// ioready为false表示此次调用并非底层epoll事件上报func netpollunblock(pd *pollDesc, mode int32, ioready bool) *g {gpp := &pd.rgif mode == 'w' {gpp = &pd.wg}for {// (1)old := *gppif old == pdReady {return nil}// (2)if old == 0 && !ioready {// Only set READY for ioready. runtime_pollWait// will check for timeout/cancel before waiting.return nil}var new uintptrif ioready {new = pdReady}// (3)if atomic.Casuintptr(gpp, old, new) {if old == pdReady || old == pdWait {old = 0}return (*g)(unsafe.Pointer(old))}}}
netpollunblock尝试获取在netpollblock中被gopark的 goroutine,通过抽象数据结构g返回。
(1) old == pdReady即已唤醒,可以直接使用遂直接返回nil。
(2) 初始化状态时候,当前既没 Ready 的 goroutine 也没有 Wait 的 goroutine 也直接返回nil。
(3) 通过原子操作重置并拿到当前正在被gopark的 goroutine 地址,抽象数据结构g返回。
runtime-epoll
epoll 在 runtime 中的部分在runtime/netpoll_epoll.go文件中实现。上文中涉及到两个函数:netpollinit,netpollopen,实际上是调用到了 epoll 中。
netpollinit
func netpollinit() {epfd = epollcreate1(_EPOLL_CLOEXEC)if epfd >= 0 {return}epfd = epollcreate(1024)if epfd >= 0 {closeonexec(epfd)return}println("runtime: epollcreate failed with", -epfd)throw("runtime: netpollinit failed")}
首先调用 epoll_create1 创建 epoll handle,若epoll_create1失败再调用epoll_create。
netpollopen
func netpollopen(fd uintptr, pd *pollDesc) int32 {var ev epolleventev.events = _EPOLLIN | _EPOLLOUT | _EPOLLRDHUP | _EPOLLET*(**pollDesc)(unsafe.Pointer(&ev.data)) = pdreturn -epollctl(epfd, _EPOLL_CTL_ADD, int32(fd), &ev)}
epoll 事件注册,注册这个 epoll 里关心的事件,并将 user data 设置为runtime.pollDesc,这也就是为什么 netpoll 系列函数均以pollDesc为参数。
netpollclose
func netpollclose(fd uintptr) int32 {var ev epolleventreturn -epollctl(epfd, _EPOLL_CTL_DEL, int32(fd), &ev)}
从 epoll 中剔除某个不再关心的 fd,应用于主动关闭或超时关闭。
netpoll
netpoll中调用了 epoll 中第三个 API:epoll_wait。
func netpoll(block bool) gList {if epfd == -1 {return gList{}}waitms := int32(-1)if !block {waitms = 0}var events [128]epolleventretry:// (1)n := epollwait(epfd, &events[0], int32(len(events)), waitms)if n < 0 {if n != -_EINTR {println("runtime: epollwait on fd", epfd, "failed with", -n)throw("runtime: netpoll failed")}goto retry}// (2)var toRun gListfor i := int32(0); i < n; i++ {ev := &events[i]if ev.events == 0 {continue}var mode int32// 通过netpollopen注册的epoll关心事件确定是否读写事件if ev.events&(_EPOLLIN|_EPOLLRDHUP|_EPOLLHUP|_EPOLLERR) != 0 {mode += 'r'}if ev.events&(_EPOLLOUT|_EPOLLHUP|_EPOLLERR) != 0 {mode += 'w'}if mode != 0 {// 由netpollopen可知,此处的&ev.data是pollDescpd := *(**pollDesc)(unsafe.Pointer(&ev.data))pd.everr = falseif ev.events == _EPOLLERR {pd.everr = true}// 唤醒goroutinenetpollready(&toRun, pd, mode)}}if block && toRun.empty() {goto retry}// 返回可以执行事件的goroutine地址集合return toRun}
(1) 调用epoll_wait获取事件,当次最多获取 128 个 epoll 事件。
(2) 根据事件类型唤醒读写 goroutine。
从整个流程上来看,分别调用了 epoll 中的三个 API:epoll_create,epoll_ctl以及epoll_wait,通过层级化的封装使用 epoll 完成 IO 多路复用。这里很多人可能会好奇,netpoll是在哪里调用的?
实际上netpoll是在runtime.proc.go被底层多处调用,以 Go1.13 为例,runtime.proc.go中有四处调用netpoll,分别是:
func startTheWorldWithSema(emitTraceEvent bool) int64
func findrunnable() (gp *g, inheritTime bool)
func pollWork() bool
func sysmon()
以上均涉及到底层轮询器和调度器。
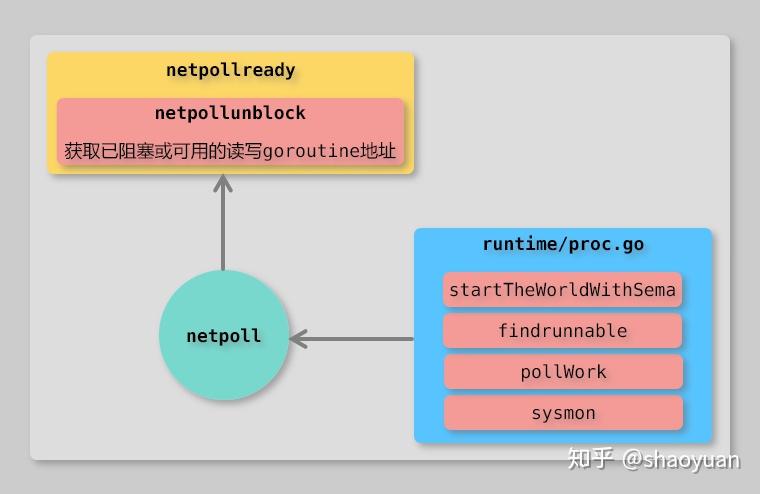
netpoll 调用
小结
通过前面的内容,我们清楚了 epoll 在 Go 中是如何封装的,对用户接口层简化了Listen、Accept、Read、Write等接口,简单友好的接口给用户层的逻辑代码提供相当大的便利。
而从 net 包的整体实现来看,对于用户而言:net 的实现是基于 epoll 的 nonblock 模式的一些列 fd 操作。网络操作未 Ready 时切换 goroutine,Ready 后等待调度的 goroutine 加入运行队列,实现了网络操作既不阻塞又是同步执行,这也就是前一篇文章所说的 epoll+goroutine。
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/109559267

