TVM编译模型的基本步骤
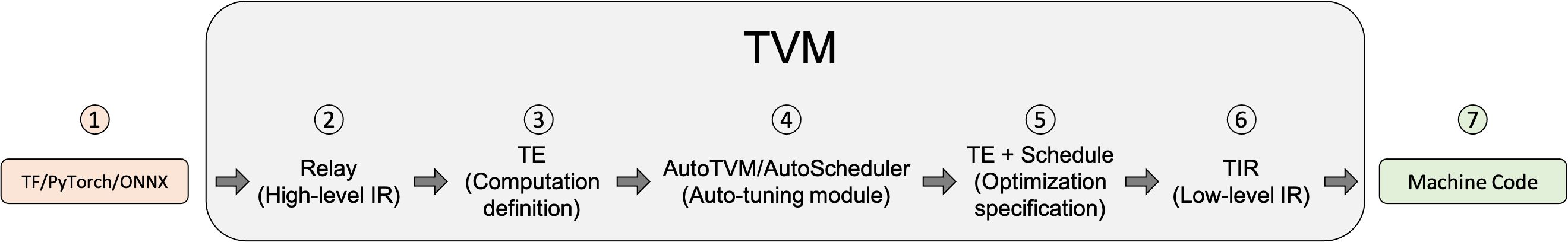
导入其他框架的模型
支持的主要框架:Tensorflow, PyTorch, ONNX将该模型转换成Relay(TVM的高层级IR).
Relay支持特性:
- 传统数据流式的表示
- 函数式语言风格的表示
两种风格的混合
在此步骤中,Relay进行图层次的优化
将Relay转换成更细粒度的Tensor Expression(TE)
Relay使用FuseOps将模型划分成小的子图,在此过程中可以使用一些schedule原语进行优化,
如tiling, vectorization, parallelization, unrolling, and fusion
TOPI包含一些预定义的常用Operator。搜索最佳调度策略(AutoTVM或AutoScheduler)
TVM提供了如下两种自动调优模块。
AutoTVM: 模板化的自动调优模块。
TOPI中提供了通用算子优化后的调度模板
AutoScheduler (a.k.a. Ansor): 无模板的自动调优模块,自动生成搜索空间
选择模型编译的最优配置。
自动调优会生成JSON格式的优化记录.编译生成Tensor IR (TIR, TVM的低层级IR,相对于Relay)。
TVM支持的后端包括:
- LLVM, 通过它可以生成llvm支持的所有硬件如x86, ARM.
- 特定编译器,如NVCC, NVIDIA的编译器.
- 通过BYOC(Bring Your Own Codegen)框架实现
- 编译生成机器代码。
TVM可以将模型编译成可链接的对象模块来通过轻量级的运行时来运行。它提供多种语言的支持。
TVM也支持将模型和运行时统一打包。
Relay的使用
Relay是TVM中定义的High-level IR。
通过TVM中Relay模块,我们可以转换其他框架模型,并生成对应后端代码。
import numpy as npfrom tvm import relayfrom tvm.relay import testingimport tvmfrom tvm import tefrom tvm.contrib import graph_executorimport tvm.testing####################################################################### (1) 导入模型:# 这里我们使用了预编译的resnet_18batch_size = 1num_class = 1000image_shape = (3, 224, 224)data_shape = (batch_size,) + image_shapeout_shape = (batch_size, num_class)mod, params = relay.testing.resnet.get_workload(num_layers=18, batch_size=batch_size, image_shape=image_shape)# set show_meta_data=True if you want to show meta dataprint(mod.astext(show_meta_data=False))####################################################################### (2) 编译# -----------# - 优化等级范围 (0 to 3).# - 优化passes: operator fusion, pre-computation, layout transformation...# Relay进行graph-level优化, TVM进行tensor-level优化#opt_level = 3target = tvm.target.Target(target="llvm", host="llvm") #tvm.target.cuda()with tvm.transform.PassContext(opt_level=opt_level):lib = relay.build(mod, target, params=params)######################################################################(3) 运行dev = tvm.device(target.kind.name, 0) #tvm.cuda()data = np.random.uniform(-1, 1, size=data_shape).astype("float32")module = graph_executor.GraphModule(lib["default"](dev))module.set_input("data", data)module.run()out = module.get_output(0, tvm.nd.empty(out_shape)).numpy()print(out.flatten()[0:10])####################################################################### (4) 保存并加载模型from tvm.contrib import utilstemp = utils.tempdir()path_lib = temp.relpath("deploy_lib.tar")lib.export_library(path_lib)print(temp.listdir())####################################################loaded_lib = tvm.runtime.load_module(path_lib)input_data = tvm.nd.array(data)module = graph_executor.GraphModule(loaded_lib["default"](dev))module.run(data=input_data)out_deploy = module.get_output(0).numpy()print(out_deploy.flatten()[0:10])# 比较结果tvm.testing.assert_allclose(out_deploy, out, atol=1e-5)
TOPI的使用
TOPI 提供了很多实用算子和针对特性后端的调度器。
"""TVM Operator Inventory (TOPI)提供了numpy风格的高级抽象算子."""from __future__ import absolute_import, print_functionimport tvmimport tvm.testingfrom tvm import tefrom tvm import topiimport numpy as np####################################################################### 基础实例:按行求和(等价numpy代码:`B = numpy.sum(A, axis=1)`)#n = te.var("n")m = te.var("m")A = te.placeholder((n, m), name="A")k = te.reduce_axis((0, m), "k")B = te.compute((n,), lambda i: te.sum(A[i, k], axis=k), name="B")s = te.create_schedule(B.op)####################################################################### 查看生成的IRprint(tvm.lower(s, [A], simple_mode=True))####################################################################### 使用预定义topi方法C = topi.sum(A, axis=1)ts = te.create_schedule(C.op)print(tvm.lower(ts, [A], simple_mode=True))####################################################################### Numpy-style 广播操作x, y = 100, 10a = te.placeholder((x, y, y), name="a")b = te.placeholder((y, y), name="b")c = a + b # same as topi.broadcast_addd = a * b # same as topi.broadcast_mul####################################################################### Overloaded with the same syntax, TOPI handles broadcasting a primitive (`int`, `float`) to a tensor :code:`d - 3.14`.####################################################################### TOPI定义了针对不同平台的调度器,如CUDA,x86...#e = topi.elemwise_sum([c, d])f = e / 2.0g = topi.sum(f)with tvm.target.Target(target="llvm", host="llvm"):# sg = topi.cuda.schedule_reduce(g)sg = topi.x86.schedule_reduce(g)print(tvm.lower(sg, [a, b], simple_mode=True))####################################################################### As you can see, scheduled stages of computation have been accumulated and we can examine them byprint(sg.stages)####################################################################### 和numpy运算结果做比较func = tvm.build(sg, [a, b, g], "llvm")dev = tvm.device("llvm", 0)a_np = np.random.uniform(size=(x, y, y)).astype(a.dtype)b_np = np.random.uniform(size=(y, y)).astype(b.dtype)g_np = np.sum(np.add(a_np + b_np, a_np * b_np) / 2.0)a_nd = tvm.nd.array(a_np, dev)b_nd = tvm.nd.array(b_np, dev)g_nd = tvm.nd.array(np.zeros(g_np.shape, dtype=g_np.dtype), dev)func(a_nd, b_nd, g_nd)tvm.testing.assert_allclose(g_nd.numpy(), g_np, rtol=1e-5)####################################################################### TOPI 提供了常用的神经网络算子,如softmax,conv####################################################################### NOTE: TOPI的实现因后端而异,目标平台和调度器必须一致tarray = te.placeholder((512, 512), name="tarray")softmax_topi = topi.nn.softmax(tarray)with tvm.target.Target(target="llvm", host="llvm"):# sst = topi.cuda.schedule_softmax(softmax_topi)sst = topi.x86.schedule_softmax(softmax_topi)print(tvm.lower(sst, [tarray], simple_mode=True))data = te.placeholder((1, 3, 224, 224))kernel = te.placeholder((10, 3, 5, 5))with tvm.target.Target(target="llvm", host="llvm"):conv = topi.nn.conv2d_nchw(data, kernel, 1, 2, 1)out = topi.nn.relu(conv)# sconv = topi.cuda.schedule_conv2d_nchw([out])sconv = topi.x86.schedule_conv2d_nchw([out])print(tvm.lower(sconv, [data, kernel], simple_mode=True))
模型的编译、运行和优化
"""使用TVM的python API来进行模型的编译、运行和优化"""import onnxfrom tvm.contrib.download import download_testdatafrom PIL import Imageimport numpy as npimport tvm.relay as relayimport tvmfrom tvm.contrib import graph_executor################################################################################ 获取一个预训练的模型(使用了一个ONNX格式的模型)和测试图片model_url = "".join(["https://github.com/onnx/models/raw/","master/vision/classification/resnet/model/","resnet50-v2-7.onnx",])model_path = download_testdata(model_url, "resnet50-v2-7.onnx", module="onnx")onnx_model = onnx.load(model_path)img_url = "https://s3.amazonaws.com/model-server/inputs/kitten.jpg"img_path = download_testdata(img_url, "imagenet_cat.png", module="data")# Resize it to 224x224resized_image = Image.open(img_path).resize((224, 224))img_data = np.asarray(resized_image).astype("float32")# Our input image is in HWC layout while ONNX expects CHW input, so convert the arrayimg_data = np.transpose(img_data, (2, 0, 1))# Normalize according to the ImageNet input specificationimagenet_mean = np.array([0.485, 0.456, 0.406]).reshape((3, 1, 1))imagenet_stddev = np.array([0.229, 0.224, 0.225]).reshape((3, 1, 1))norm_img_data = (img_data / 255 - imagenet_mean) / imagenet_stddev# Add the batch dimension, as we are expecting 4-dimensional input: NCHW.img_data = np.expand_dims(norm_img_data, axis=0)################################################################################ 使用Relay来编译模型target = "llvm"input_name = "data"shape_dict = {input_name: img_data.shape}mod, params = relay.frontend.from_onnx(onnx_model, shape_dict)with tvm.transform.PassContext(opt_level=3):lib = relay.build(mod, target=target, params=params)dev = tvm.device(str(target), 0)module = graph_executor.GraphModule(lib["default"](dev))####################################################################### 使用TVM Runtime运行模型dtype = "float32"module.set_input(input_name, img_data)module.run()output_shape = (1, 1000)tvm_output = module.get_output(0, tvm.nd.empty(output_shape)).numpy()#~~~~~~~~~~~# 评估基本的性能数据import timeittiming_number = 10timing_repeat = 10unoptimized = (np.array(timeit.Timer(lambda: module.run()).repeat(repeat=timing_repeat, number=timing_number))* 1000/ timing_number)unoptimized = {"mean": np.mean(unoptimized),"median": np.median(unoptimized),"std": np.std(unoptimized),}print(unoptimized)#~~~~~~~~~~# 后处理from scipy.special import softmax# Download a list of labelslabels_url = "https://s3.amazonaws.com/onnx-model-zoo/synset.txt"labels_path = download_testdata(labels_url, "synset.txt", module="data")with open(labels_path, "r") as f:labels = [l.rstrip() for l in f]# Open the output and read the output tensorscores = softmax(tvm_output)scores = np.squeeze(scores)ranks = np.argsort(scores)[::-1]for rank in ranks[0:5]:print("class='%s' with probability=%f" % (labels[rank], scores[rank]))#~~~~~~~~~~~# 输出结果## # class='n02123045 tabby, tabby cat' with probability=0.610553# # class='n02123159 tiger cat' with probability=0.367179# # class='n02124075 Egyptian cat' with probability=0.019365# # class='n02129604 tiger, Panthera tigris' with probability=0.001273# # class='n04040759 radiator' with probability=0.000261################################################################################# 使用autotvm来优化模型#import tvm.auto_scheduler as auto_schedulerfrom tvm.autotvm.tuner import XGBTunerfrom tvm import autotvm#~~~~~~~~~~~# 基本配置参数number = 10 # 尝试的不同优化配置的数目repeat = 1 # 每个配置重复测量的次数min_repeat_ms = 0 # 最小运行时间,影响GPU精度调优,CPU设置为0timeout = 10 # 超时时间# create a TVM runnerrunner = autotvm.LocalRunner(number=number,repeat=repeat,timeout=timeout,min_repeat_ms=min_repeat_ms,enable_cpu_cache_flush=True,)#~~~~~~~~~~~~# 优化选项# tuner: 这里使用xgboost作为优化算法# trials:对于产品级的模型,trials推荐值为CPU 1500, GPU 3000-4000. 这个是模型和处理器相关的。# 需要多花时间实验。这里作为简单测试,仅设置为10# Tearly_stopping:尝试最小次数# measure_option: 构建运行选项# tuning_records: 输出的优化记录文件tuning_option = {"tuner": "xgb","trials": 10,"early_stopping": 100,"measure_option": autotvm.measure_option(builder=autotvm.LocalBuilder(build_func="default"), runner=runner),"tuning_records": "resnet-50-v2-autotuning.json",}# begin by extracting the taks from the onnx modeltasks = autotvm.task.extract_from_program(mod["main"], target=target, params=params)# Tune the extracted tasks sequentially.for i, task in enumerate(tasks):prefix = "[Task %2d/%2d] " % (i + 1, len(tasks))tuner_obj = XGBTuner(task, loss_type="rank")tuner_obj.tune(n_trial=min(tuning_option["trials"], len(task.config_space)),early_stopping=tuning_option["early_stopping"],measure_option=tuning_option["measure_option"],callbacks=[autotvm.callback.progress_bar(tuning_option["trials"], prefix=prefix),autotvm.callback.log_to_file(tuning_option["tuning_records"]),],)#~~~~~~~# 输出实例:# # [Task 1/24] Current/Best: 10.71/ 21.08 GFLOPS | Progress: (60/1000) | 111.77 s Done.# # [Task 1/24] Current/Best: 9.32/ 24.18 GFLOPS | Progress: (192/1000) | 365.02 s Done.# # [Task 2/24] Current/Best: 22.39/ 177.59 GFLOPS | Progress: (960/1000) | 976.17 s Done.# # [Task 3/24] Current/Best: 32.03/ 153.34 GFLOPS | Progress: (800/1000) | 776.84 s Done.# ....# # [Task 24/24] Current/Best: 25.03/ 146.14 GFLOPS | Progress: (1000/1000) | 1112.55 s Done.################################################################################# 编译优化后的模型with autotvm.apply_history_best(tuning_option["tuning_records"]):with tvm.transform.PassContext(opt_level=3, config={}):lib = relay.build(mod, target=target, params=params)dev = tvm.device(str(target), 0)module = graph_executor.GraphModule(lib["default"](dev))#~~~~~~~~~# 校验优化模型的结果dtype = "float32"module.set_input(input_name, img_data)module.run()output_shape = (1, 1000)tvm_output = module.get_output(0, tvm.nd.empty(output_shape)).numpy()scores = softmax(tvm_output)scores = np.squeeze(scores)ranks = np.argsort(scores)[::-1]for rank in ranks[0:5]:print("class='%s' with probability=%f" % (labels[rank], scores[rank]))#~~~~~~~~~# 评估性能import timeittiming_number = 10timing_repeat = 10optimized = (np.array(timeit.Timer(lambda: module.run()).repeat(repeat=timing_repeat, number=timing_number))* 1000/ timing_number)optimized = {"mean": np.mean(optimized), "median": np.median(optimized), "std": np.std(optimized)}print("optimized: %s" % (optimized))print("unoptimized: %s" % (unoptimized))
使用Ansor优化模型
"""使用TVM的Auto Scheduling feature(Ansor)搜索优化解"""import osimport numpy as npimport tvmfrom tvm import te, auto_scheduler################################################################################# 定义矩阵乘计算# ----------------------------------# 1 函数使用 `auto_sceduler` 装饰器# 2 函数返回input/output tensors列表. Ansor据此构建计算图。@auto_scheduler.register_workload # Note the auto_scheduler decoratordef matmul_add(N, L, M, dtype):A = te.placeholder((N, L), name="A", dtype=dtype)B = te.placeholder((L, M), name="B", dtype=dtype)C = te.placeholder((N, M), name="C", dtype=dtype)k = te.reduce_axis((0, L), name="k")matmul = te.compute((N, M),lambda i, j: te.sum(A[i, k] * B[k, j], axis=k),name="matmul",attrs={"layout_free_placeholders": [B]}, # enable automatic layout transform for tensor B)out = te.compute((N, M), lambda i, j: matmul[i, j] + C[i, j], name="out")return [A, B, C, out]################################################################################# 创建搜索任务# ----------------------# 为了充分利用硬件特性,Target越具体越好# - replace "llvm" below with "llvm -mcpu=core-avx2" to enable AVX2# - replace "llvm" below with "llvm -mcpu=skylake-avx512" to enable AVX-512target = tvm.target.Target("llvm")N = L = M = 1024task = tvm.auto_scheduler.SearchTask(func=matmul_add, args=(N, L, M, "float32"), target=target)# Inspect the computational graphprint("Computational DAG:")print(task.compute_dag)#~~~~~~~~~~~~~# 设置Ansor的参数# ---------------------------------# `num_measure_trials`: 尝试次数,通常可能1000次才能收敛,为测试方便,设为10log_file = "matmul.json"tune_option = auto_scheduler.TuningOptions(num_measure_trials=10,measure_callbacks=[auto_scheduler.RecordToFile(log_file)],verbose=2,)################################################################################# 执行自动搜索任务task.tune(tune_option)# Apply the best schedulesch, args = task.apply_best(log_file)################################################################################# 校验优化后的结果# ---------------------------------# auto-scheduler 执行的优化包括 multi-level tiling, layout transformation, parallelization, vectorization, unrolling, and operator fusion.print("Lowered TIR:")print(tvm.lower(sch, args, simple_mode=True))#~~~~~~~~~~~# 检验正确性,评估性能func = tvm.build(sch, args, target)a_np = np.random.uniform(size=(N, L)).astype(np.float32)b_np = np.random.uniform(size=(L, M)).astype(np.float32)c_np = np.random.uniform(size=(N, M)).astype(np.float32)out_np = a_np.dot(b_np) + c_npdev = tvm.cpu()a_tvm = tvm.nd.array(a_np, device=dev)b_tvm = tvm.nd.array(b_np, device=dev)c_tvm = tvm.nd.array(c_np, device=dev)out_tvm = tvm.nd.empty(out_np.shape, device=dev)func(a_tvm, b_tvm, c_tvm, out_tvm)# Check resultsnp.testing.assert_allclose(out_np, out_tvm.numpy(), rtol=1e-3)# Evaluate execution time.evaluator = func.time_evaluator(func.entry_name, dev, min_repeat_ms=500)print("Execution time of this operator: %.3f ms"% (np.median(evaluator(a_tvm, b_tvm, c_tvm, out_tvm).results) * 1000))# 输出等价的Python schedule API结果print("[~~~~~~Equivalent python schedule:~~~~~]")print(task.print_best(log_file))################################################################################# 恢复搜索def resume_search(task, log_file):print("[~~~~Resume search:~~~~~~~]")cost_model = auto_scheduler.XGBModel()cost_model.update_from_file(log_file)search_policy = auto_scheduler.SketchPolicy(task, cost_model, init_search_callbacks=[auto_scheduler.PreloadMeasuredStates(log_file)])tune_option = auto_scheduler.TuningOptions(num_measure_trials=5, measure_callbacks=[auto_scheduler.RecordToFile(log_file)])task.tune(tune_option, search_policy=search_policy)resume_search(task, log_file)

