@TOC
基础知识概述
基础知识:集合、泛型、异常、反射、注解、内部类、序列化。
集合框架概述
接口:Collection接口、Map接口。Java集合框架图,如下:
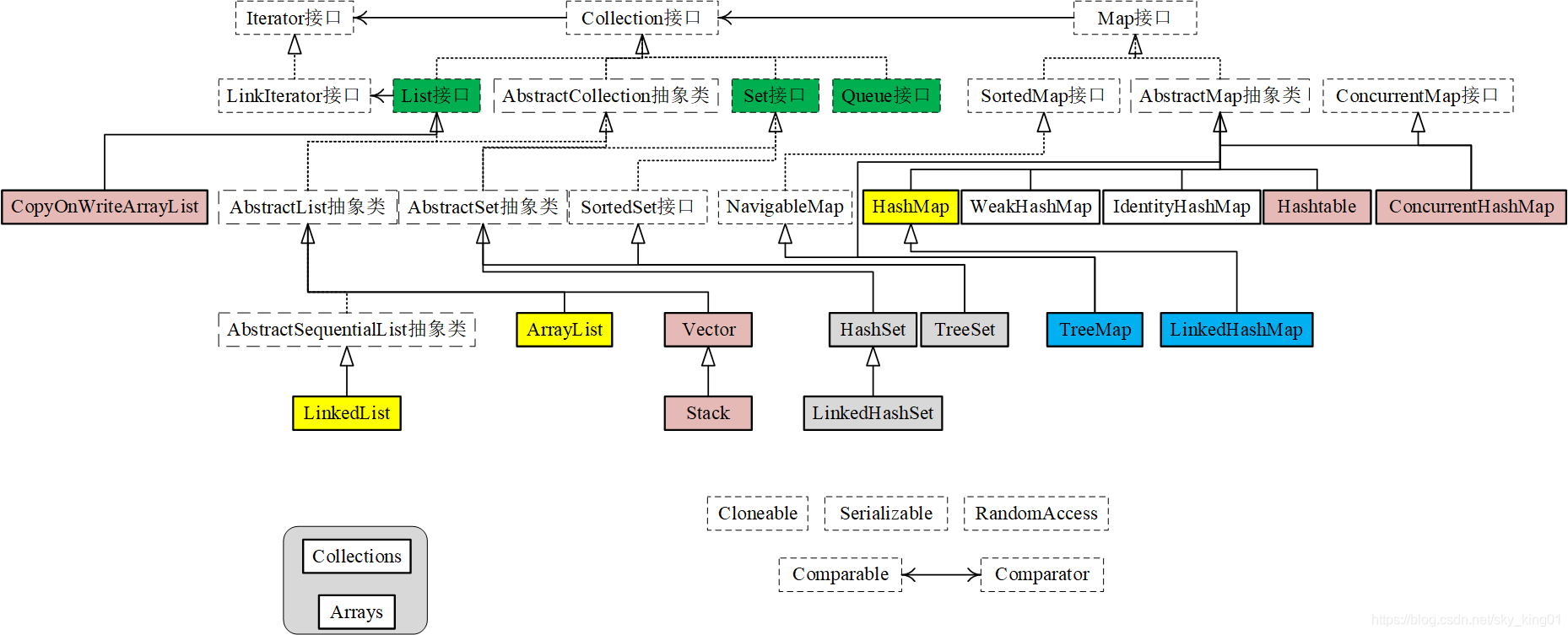
Collections,提供了对集合进行排序、遍历等多种算法实现;
Arrays,提供了大量的静态方法,用来实现数组常见的操作;
自定义的集合类型,那么类需要有Comparable或者Comparator接口的支持;
Iterator(迭代器)不是一个集合,它是一种用于访问集合的方法;
ListIterator 是 Collection API 中的接口, 它扩展了 Iterator 接口;
Iterator接口
迭代器(Iterator)主要用来操作java中的集合对象(Collection),迭代器提供了统一的语法进行集合对象(Collection)遍历操作,无需关心集合对象内部的实现方式,
Iterator只能向前移,无法后退;
public interface Iterator<E> {boolean hasNext();//判断是否还有下一个对象,如果有,则返回true,否则falseE next();//返回集合的下个值,此方法只能在hasNext方法返回true时调用void remove();//删除集合的当前值,此方法也只能在hasNext方法返回true时调用}
Iterable接口
jdk1.5之后新增了Iterable接口用于支持foreach循环,所有实现Iterable接口的对象都可以实现foreach循环操作。
public interface Iterable<T> {Iterator<T> iterator();//返回集合的Iterator对象default void forEach(Consumer<? super T> action) {// JDK1.8 新增遍历方式Objects.requireNonNull(action);for (T t : this) {action.accept(t);}}default Spliterator<T> spliterator() {// 可分割迭代器return Spliterators.spliteratorUnknownSize(iterator(), 0);}}
Collection接口
Collection接口是所有集合类的根节点,Collection表示一种规则,所有实现了Collection接口的类遵循这种规则。
一个Collection代表一组Object,即Collection的元素(Elements)。一些Collection允许有重复的元素(例如List),但是另一些则不允许有重复的元素,即可为无序的(如Set)。
所有实现Collection接口的类都必须提供两个标准的构造函数:无参数的构造函数用于创建一个空的Collection,有参数的构造函数用于创建一个具有与其参数相同元素的新的Collection。实际上,后者允许用户复制任何Collection,以生产所需实现类型的一个等效Collection。尽管无法强制执行此约定(因为接口不能包含构造方法),但是Java平台库中所有通用的Collection实现都遵从它。
JDK不提供此接口的任何直接实现—-它会提供更为具体的子接口(如Set和List)。
public interface Collection<E> extends Iterable<E> {// Query Operationsint size();//返回集合中元素的个数boolean isEmpty();//判断集合是否为空集合,为空返回trueboolean contains(Object o);//判断集合中是否存在指定元素,存在返回trueIterator<E> iterator();//返回集合遍历的迭代器Object[] toArray();//集合转变成数组<T> T[] toArray(T[] a);//将指定集合转变成相应的数组// Modification Operationsboolean add(E e);//往集合中添加元素,添加成功返回trueboolean remove(Object o);//从集合中删除指定的元素,删除成功返回true// Bulk Operationsboolean containsAll(Collection<?> c);//判断集合中是否包含集合c,包含则返回trueboolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c);//将集合c添加到集合中,添加成功返回trueboolean removeAll(Collection<?> c);//从集合中删除集合c,删除成功返回truedefault boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) {//删除集合中符合条件的元素,删除成功返回true(从1.8开始提供)Objects.requireNonNull(filter);boolean removed = false;final Iterator<E> each = iterator();while (each.hasNext()) {if (filter.test(each.next())) {each.remove();removed = true;}}return removed;}boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c);//保留集合中集合c从中的元素void clear();//清空集合中的所有元素// Comparison and hashingboolean equals(Object o);//判断对象是否和对象o内容一致,是则返回trueint hashCode();//计算对象的哈希码值@Overridedefault Spliterator<E> spliterator() {//(从1.8开始提供)return Spliterators.spliterator(this, 0);}default Stream<E> stream() {//(从1.8开始提供)return StreamSupport.stream(spliterator(), false);}default Stream<E> parallelStream() {//(从1.8开始提供)return StreamSupport.stream(spliterator(), true);}}
AbstractCollection抽象类,Collection接口的骨架实现类,最小化实现了Collection接口所需要实现的工作量,主要作用是方便其他类实现Collection。
AbstractCollection抽象类,实现了Collection中除了iterator()和size()之外的所有(公共)方法。其他集合想要实现Collection,通过继承AbstractCollection抽象类,以及覆写iterator()和size() 即可。
Map接口
Map接口,储存一键-值对的对象接口,提供key(键)到value(值)的映射,Map中的key不要求有序,不允许重复。value同样不要求有序,但可以重复。
给定一个键和一个值,你可以将该值存储在一个Map对象。可以通过键来访问对应的值。
当访问的值不存在的时候,方法就会抛出一个 NoSuchElementException 异常。
当对象的类型和 Map 里元素类型不兼容的时候,就会抛出一个 ClassCastException 异常。
当在不允许使用 Null 对象的 Map (例如,TreeMap)中使用 Null 对象,会抛出一个 NullPointerException 异常。
当尝试修改一个只读的 Map 时,会抛出一个 UnsupportedOperationException 异常。
基本上所有的 Map 接口实现类都使用 put() 方法存入数据、用get() 方法去除数据,使用 entrySet/keySet 迭代获取 Map 数据。
public interface Map<K,V> {// Query Operationsint size();//返回map中Map.Entry的个数boolean isEmpty();//判断map是否为空map,为空返回trueboolean containsKey(Object key);//判断map中是否存在指定key,存在返回trueboolean containsValue(Object value);//判断map中是否存在指定value,存在返回trueV get(Object key);//获取指定键(key)所对应的值(value)// Modification Operations/**若指定的键(key)在集合中没有,则没有这个键对应的值,返回null,并把指定的键值添加到集合中*若指定的键(key)在集合中存在,则返回值为集合中键对应的值(该值为替换前的值),并把指定键所对应的值,替换成指定的新值*/V put(K key, V value);//将指定的键与值对应起来,并添加到集合中V remove(Object key);//根据指定的键(key)删除元素,返回被删除元素的值(value)// Bulk Operationsvoid putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m);//从指定映射中将所有映射关系复制到此映射中(可选操作)void clear();//移除map的所有映射// Views/**通过键找值,来实现的遍历*1.调用 Map 集合的方法 keySet,将所有的键(key对象)存储到Set集合中*2.遍历 Set 集合,获取出 Set 集合中的所有元素 ( Map 中的键(key对象))*3.调用 Map 集合 get 方法,通过键(key对象)获取到值(value对象)*/Set<K> keySet();//将所有的键(key对象)存储到Set集合中Collection<V> values();//将所有的值(value对象)存储到集合数组中Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> entrySet();//将所有的Map.Entry存储到Set集合中,interface Entry<K,V> {//1.2,嵌套接口,将键值对的对应关系封装成了对象,即键值对对象K getKey();//获取map的键(key对象)V getValue();//获取map的值(value对象)V setValue(V value);//存储map的值(value对象)boolean equals(Object o);//判断键(key对象)或值(value对象)是否与对象o内容一致int hashCode();//计算键(key对象)的哈希码值public static <K extends Comparable<? super K>, V> Comparator<Map.Entry<K,V>> comparingByKey() {//1.8,compareTo(),key对象比较return (Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> & Serializable)(c1, c2) -> c1.getKey().compareTo(c2.getKey());}public static <K, V extends Comparable<? super V>> Comparator<Map.Entry<K,V>> comparingByValue() {//1.8,compareTo(),value对象比较return (Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> & Serializable)(c1, c2) -> c1.getValue().compareTo(c2.getValue());}public static <K, V> Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> comparingByKey(Comparator<? super K> cmp) {//1.8,(比较器cmp).compare(),key对象比较Objects.requireNonNull(cmp);return (Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> & Serializable)(c1, c2) -> cmp.compare(c1.getKey(), c2.getKey());}public static <K, V> Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> comparingByValue(Comparator<? super V> cmp) {//1.8,(比较器cmp).compare(),value对象比较Objects.requireNonNull(cmp);return (Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> & Serializable)(c1, c2) -> cmp.compare(c1.getValue(), c2.getValue());}}// Comparison and hashingboolean equals(Object o);//比较指定对象与此 Map 的等价性int hashCode();//返回此 Map 的哈希码// Defaultable methodsdefault V getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) {//1.8,V v;return (((v = get(key)) != null) || containsKey(key))? v: defaultValue;}default void forEach(BiConsumer<? super K, ? super V> action) {//1.8,Objects.requireNonNull(action);for (Map.Entry<K, V> entry : entrySet()) {K k;V v;try {k = entry.getKey();v = entry.getValue();} catch(IllegalStateException ise) {// this usually means the entry is no longer in the map.throw new ConcurrentModificationException(ise);}action.accept(k, v);}}default void replaceAll(BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> function) {//1.8Objects.requireNonNull(function);for (Map.Entry<K, V> entry : entrySet()) {K k;V v;try {k = entry.getKey();v = entry.getValue();} catch(IllegalStateException ise) {// this usually means the entry is no longer in the map.throw new ConcurrentModificationException(ise);}// ise thrown from function is not a cme.v = function.apply(k, v);try {entry.setValue(v);} catch(IllegalStateException ise) {// this usually means the entry is no longer in the map.throw new ConcurrentModificationException(ise);}}}default V putIfAbsent(K key, V value) {//1.8V v = get(key);if (v == null) {v = put(key, value);}return v;}default boolean remove(Object key, Object value) {//1.8,从 Map 中删除键和关联的值Object curValue = get(key);if (!Objects.equals(curValue, value) ||(curValue == null && !containsKey(key))) {return false;}remove(key);return true;}default boolean replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) {//1.8Object curValue = get(key);if (!Objects.equals(curValue, oldValue) ||(curValue == null && !containsKey(key))) {return false;}put(key, newValue);return true;}default V replace(K key, V value) {//1.8V curValue;if (((curValue = get(key)) != null) || containsKey(key)) {curValue = put(key, value);}return curValue;}default V computeIfAbsent(K key,Function<? super K, ? extends V> mappingFunction) {//1.8Objects.requireNonNull(mappingFunction);V v;if ((v = get(key)) == null) {V newValue;if ((newValue = mappingFunction.apply(key)) != null) {put(key, newValue);return newValue;}}return v;}default V computeIfPresent(K key,BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {//1.8Objects.requireNonNull(remappingFunction);V oldValue;if ((oldValue = get(key)) != null) {V newValue = remappingFunction.apply(key, oldValue);if (newValue != null) {put(key, newValue);return newValue;} else {remove(key);return null;}} else {return null;}}default V compute(K key,BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {//1.8Objects.requireNonNull(remappingFunction);V oldValue = get(key);V newValue = remappingFunction.apply(key, oldValue);if (newValue == null) {// delete mappingif (oldValue != null || containsKey(key)) {// something to removeremove(key);return null;} else {// nothing to do. Leave things as they were.return null;}} else {// add or replace old mappingput(key, newValue);return newValue;}}default V merge(K key, V value,BiFunction<? super V, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {//(从1.8提供)Objects.requireNonNull(remappingFunction);Objects.requireNonNull(value);V oldValue = get(key);V newValue = (oldValue == null) ? value :remappingFunction.apply(oldValue, value);if(newValue == null) {remove(key);} else {put(key, newValue);}return newValue;}}
AbstractMap抽象类,除了entrySet()这个方法定义为抽象的,Map接口中的其它方法(公共方法)都已经给出实现。需要注意的是,实现了keySet()方法,巧妙使用entrySet()的迭代器遍历,不需要每次新增都遍历所有entry。
AbstractMap抽象类,包含了Map.Entry接口的两个静态内部实现类:SimpleEntry和SimpleImmutableEntry。不可变,为事实不可变,因为它不提供setValue方法。
AbstractMap抽象类,包含两个字段:keySet和values,分别存储键集合和值集合。这两个字段是transient修饰的,子类决定如何去序列化。
Collections工具类
Collections是一个操作集合的工具类。
常见方法:
1.对list集合排序:sort(list);sort(list,comparator);
2.对list进行二分法查找:int binarySearch(list,key);int binarySearch(list,key,Comparator);
3.按照指定比较器进行排序:max(Collection); max(Collection,comparator); min(Collection); min(Collection,comparator);
4.对list集合进行反转: reverse(list);
5.将不同步的集合变为同步的集合: Set synchronizedSet(SET s); Map synchronizedMaP(Map
public class Collections {private Collections() {}// Algorithmsprivate static final int BINARYSEARCH_THRESHOLD = 5000;private static final int REVERSE_THRESHOLD = 18;private static final int SHUFFLE_THRESHOLD = 5;private static final int FILL_THRESHOLD = 25;private static final int ROTATE_THRESHOLD = 100;private static final int COPY_THRESHOLD = 10;private static final int REPLACEALL_THRESHOLD = 11;private static final int INDEXOFSUBLIST_THRESHOLD = 35;@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> void sort(List<T> list) {list.sort(null);}@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes"})public static <T> void sort(List<T> list, Comparator<? super T> c) {list.sort(c);}public static <T>int binarySearch(List<? extends Comparable<? super T>> list, T key) {if (list instanceof RandomAccess || list.size()<BINARYSEARCH_THRESHOLD)return Collections.indexedBinarySearch(list, key);elsereturn Collections.iteratorBinarySearch(list, key);}private static <T>int indexedBinarySearch(List<? extends Comparable<? super T>> list, T key) {int low = 0;int high = list.size()-1;while (low <= high) {int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;Comparable<? super T> midVal = list.get(mid);int cmp = midVal.compareTo(key);if (cmp < 0)low = mid + 1;else if (cmp > 0)high = mid - 1;elsereturn mid; // key found}return -(low + 1); // key not found}private static <T>int iteratorBinarySearch(List<? extends Comparable<? super T>> list, T key){int low = 0;int high = list.size()-1;ListIterator<? extends Comparable<? super T>> i = list.listIterator();while (low <= high) {int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;Comparable<? super T> midVal = get(i, mid);int cmp = midVal.compareTo(key);if (cmp < 0)low = mid + 1;else if (cmp > 0)high = mid - 1;elsereturn mid; // key found}return -(low + 1); // key not found}/*** Gets the ith element from the given list by repositioning the specified* list listIterator.*/private static <T> T get(ListIterator<? extends T> i, int index) {T obj = null;int pos = i.nextIndex();if (pos <= index) {do {obj = i.next();} while (pos++ < index);} else {do {obj = i.previous();} while (--pos > index);}return obj;}/*** Searches the specified list for the specified object using the binary* search algorithm. The list must be sorted into ascending order* according to the specified comparator (as by the* {@link #sort(List, Comparator) sort(List, Comparator)}* method), prior to making this call. If it is* not sorted, the results are undefined. If the list contains multiple* elements equal to the specified object, there is no guarantee which one* will be found.** <p>This method runs in log(n) time for a "random access" list (which* provides near-constant-time positional access). If the specified list* does not implement the {@link RandomAccess} interface and is large,* this method will do an iterator-based binary search that performs* O(n) link traversals and O(log n) element comparisons.** @param <T> the class of the objects in the list* @param list the list to be searched.* @param key the key to be searched for.* @param c the comparator by which the list is ordered.* A <tt>null</tt> value indicates that the elements'* {@linkplain Comparable natural ordering} should be used.* @return the index of the search key, if it is contained in the list;* otherwise, <tt>(-(<i>insertion point</i>) - 1)</tt>. The* <i>insertion point</i> is defined as the point at which the* key would be inserted into the list: the index of the first* element greater than the key, or <tt>list.size()</tt> if all* elements in the list are less than the specified key. Note* that this guarantees that the return value will be >= 0 if* and only if the key is found.* @throws ClassCastException if the list contains elements that are not* <i>mutually comparable</i> using the specified comparator,* or the search key is not mutually comparable with the* elements of the list using this comparator.*/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public static <T> int binarySearch(List<? extends T> list, T key, Comparator<? super T> c) {if (c==null)return binarySearch((List<? extends Comparable<? super T>>) list, key);if (list instanceof RandomAccess || list.size()<BINARYSEARCH_THRESHOLD)return Collections.indexedBinarySearch(list, key, c);elsereturn Collections.iteratorBinarySearch(list, key, c);}private static <T> int indexedBinarySearch(List<? extends T> l, T key, Comparator<? super T> c) {int low = 0;int high = l.size()-1;while (low <= high) {int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;T midVal = l.get(mid);int cmp = c.compare(midVal, key);if (cmp < 0)low = mid + 1;else if (cmp > 0)high = mid - 1;elsereturn mid; // key found}return -(low + 1); // key not found}private static <T> int iteratorBinarySearch(List<? extends T> l, T key, Comparator<? super T> c) {int low = 0;int high = l.size()-1;ListIterator<? extends T> i = l.listIterator();while (low <= high) {int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;T midVal = get(i, mid);int cmp = c.compare(midVal, key);if (cmp < 0)low = mid + 1;else if (cmp > 0)high = mid - 1;elsereturn mid; // key found}return -(low + 1); // key not found}/*** Reverses the order of the elements in the specified list.<p>** This method runs in linear time.** @param list the list whose elements are to be reversed.* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the specified list or* its list-iterator does not support the <tt>set</tt> operation.*/@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes", "unchecked"})public static void reverse(List<?> list) {int size = list.size();if (size < REVERSE_THRESHOLD || list instanceof RandomAccess) {for (int i=0, mid=size>>1, j=size-1; i<mid; i++, j--)swap(list, i, j);} else {// instead of using a raw type here, it's possible to capture// the wildcard but it will require a call to a supplementary// private methodListIterator fwd = list.listIterator();ListIterator rev = list.listIterator(size);for (int i=0, mid=list.size()>>1; i<mid; i++) {Object tmp = fwd.next();fwd.set(rev.previous());rev.set(tmp);}}}/*** Randomly permutes the specified list using a default source of* randomness. All permutations occur with approximately equal* likelihood.** <p>The hedge "approximately" is used in the foregoing description because* default source of randomness is only approximately an unbiased source* of independently chosen bits. If it were a perfect source of randomly* chosen bits, then the algorithm would choose permutations with perfect* uniformity.** <p>This implementation traverses the list backwards, from the last* element up to the second, repeatedly swapping a randomly selected element* into the "current position". Elements are randomly selected from the* portion of the list that runs from the first element to the current* position, inclusive.** <p>This method runs in linear time. If the specified list does not* implement the {@link RandomAccess} interface and is large, this* implementation dumps the specified list into an array before shuffling* it, and dumps the shuffled array back into the list. This avoids the* quadratic behavior that would result from shuffling a "sequential* access" list in place.** @param list the list to be shuffled.* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the specified list or* its list-iterator does not support the <tt>set</tt> operation.*/public static void shuffle(List<?> list) {Random rnd = r;if (rnd == null)r = rnd = new Random(); // harmless race.shuffle(list, rnd);}private static Random r;/*** Randomly permute the specified list using the specified source of* randomness. All permutations occur with equal likelihood* assuming that the source of randomness is fair.<p>** This implementation traverses the list backwards, from the last element* up to the second, repeatedly swapping a randomly selected element into* the "current position". Elements are randomly selected from the* portion of the list that runs from the first element to the current* position, inclusive.<p>** This method runs in linear time. If the specified list does not* implement the {@link RandomAccess} interface and is large, this* implementation dumps the specified list into an array before shuffling* it, and dumps the shuffled array back into the list. This avoids the* quadratic behavior that would result from shuffling a "sequential* access" list in place.** @param list the list to be shuffled.* @param rnd the source of randomness to use to shuffle the list.* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the specified list or its* list-iterator does not support the <tt>set</tt> operation.*/@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes", "unchecked"})public static void shuffle(List<?> list, Random rnd) {int size = list.size();if (size < SHUFFLE_THRESHOLD || list instanceof RandomAccess) {for (int i=size; i>1; i--)swap(list, i-1, rnd.nextInt(i));} else {Object arr[] = list.toArray();// Shuffle arrayfor (int i=size; i>1; i--)swap(arr, i-1, rnd.nextInt(i));// Dump array back into list// instead of using a raw type here, it's possible to capture// the wildcard but it will require a call to a supplementary// private methodListIterator it = list.listIterator();for (int i=0; i<arr.length; i++) {it.next();it.set(arr[i]);}}}/*** Swaps the elements at the specified positions in the specified list.* (If the specified positions are equal, invoking this method leaves* the list unchanged.)** @param list The list in which to swap elements.* @param i the index of one element to be swapped.* @param j the index of the other element to be swapped.* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if either <tt>i</tt> or <tt>j</tt>* is out of range (i < 0 || i >= list.size()* || j < 0 || j >= list.size()).* @since 1.4*/@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes", "unchecked"})public static void swap(List<?> list, int i, int j) {// instead of using a raw type here, it's possible to capture// the wildcard but it will require a call to a supplementary// private methodfinal List l = list;l.set(i, l.set(j, l.get(i)));}/*** Swaps the two specified elements in the specified array.*/private static void swap(Object[] arr, int i, int j) {Object tmp = arr[i];arr[i] = arr[j];arr[j] = tmp;}/*** Replaces all of the elements of the specified list with the specified* element. <p>** This method runs in linear time.** @param <T> the class of the objects in the list* @param list the list to be filled with the specified element.* @param obj The element with which to fill the specified list.* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the specified list or its* list-iterator does not support the <tt>set</tt> operation.*/public static <T> void fill(List<? super T> list, T obj) {int size = list.size();if (size < FILL_THRESHOLD || list instanceof RandomAccess) {for (int i=0; i<size; i++)list.set(i, obj);} else {ListIterator<? super T> itr = list.listIterator();for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {itr.next();itr.set(obj);}}}/*** Copies all of the elements from one list into another. After the* operation, the index of each copied element in the destination list* will be identical to its index in the source list. The destination* list must be at least as long as the source list. If it is longer, the* remaining elements in the destination list are unaffected. <p>** This method runs in linear time.** @param <T> the class of the objects in the lists* @param dest The destination list.* @param src The source list.* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if the destination list is too small* to contain the entire source List.* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the destination list's* list-iterator does not support the <tt>set</tt> operation.*/public static <T> void copy(List<? super T> dest, List<? extends T> src) {int srcSize = src.size();if (srcSize > dest.size())throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Source does not fit in dest");if (srcSize < COPY_THRESHOLD ||(src instanceof RandomAccess && dest instanceof RandomAccess)) {for (int i=0; i<srcSize; i++)dest.set(i, src.get(i));} else {ListIterator<? super T> di=dest.listIterator();ListIterator<? extends T> si=src.listIterator();for (int i=0; i<srcSize; i++) {di.next();di.set(si.next());}}}/*** Returns the minimum element of the given collection, according to the* <i>natural ordering</i> of its elements. All elements in the* collection must implement the <tt>Comparable</tt> interface.* Furthermore, all elements in the collection must be <i>mutually* comparable</i> (that is, <tt>e1.compareTo(e2)</tt> must not throw a* <tt>ClassCastException</tt> for any elements <tt>e1</tt> and* <tt>e2</tt> in the collection).<p>** This method iterates over the entire collection, hence it requires* time proportional to the size of the collection.** @param <T> the class of the objects in the collection* @param coll the collection whose minimum element is to be determined.* @return the minimum element of the given collection, according* to the <i>natural ordering</i> of its elements.* @throws ClassCastException if the collection contains elements that are* not <i>mutually comparable</i> (for example, strings and* integers).* @throws NoSuchElementException if the collection is empty.* @see Comparable*/public static <T extends Object & Comparable<? super T>> T min(Collection<? extends T> coll) {Iterator<? extends T> i = coll.iterator();T candidate = i.next();while (i.hasNext()) {T next = i.next();if (next.compareTo(candidate) < 0)candidate = next;}return candidate;}/*** Returns the minimum element of the given collection, according to the* order induced by the specified comparator. All elements in the* collection must be <i>mutually comparable</i> by the specified* comparator (that is, <tt>comp.compare(e1, e2)</tt> must not throw a* <tt>ClassCastException</tt> for any elements <tt>e1</tt> and* <tt>e2</tt> in the collection).<p>** This method iterates over the entire collection, hence it requires* time proportional to the size of the collection.** @param <T> the class of the objects in the collection* @param coll the collection whose minimum element is to be determined.* @param comp the comparator with which to determine the minimum element.* A <tt>null</tt> value indicates that the elements' <i>natural* ordering</i> should be used.* @return the minimum element of the given collection, according* to the specified comparator.* @throws ClassCastException if the collection contains elements that are* not <i>mutually comparable</i> using the specified comparator.* @throws NoSuchElementException if the collection is empty.* @see Comparable*/@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes"})public static <T> T min(Collection<? extends T> coll, Comparator<? super T> comp) {if (comp==null)return (T)min((Collection) coll);Iterator<? extends T> i = coll.iterator();T candidate = i.next();while (i.hasNext()) {T next = i.next();if (comp.compare(next, candidate) < 0)candidate = next;}return candidate;}/*** Returns the maximum element of the given collection, according to the* <i>natural ordering</i> of its elements. All elements in the* collection must implement the <tt>Comparable</tt> interface.* Furthermore, all elements in the collection must be <i>mutually* comparable</i> (that is, <tt>e1.compareTo(e2)</tt> must not throw a* <tt>ClassCastException</tt> for any elements <tt>e1</tt> and* <tt>e2</tt> in the collection).<p>** This method iterates over the entire collection, hence it requires* time proportional to the size of the collection.** @param <T> the class of the objects in the collection* @param coll the collection whose maximum element is to be determined.* @return the maximum element of the given collection, according* to the <i>natural ordering</i> of its elements.* @throws ClassCastException if the collection contains elements that are* not <i>mutually comparable</i> (for example, strings and* integers).* @throws NoSuchElementException if the collection is empty.* @see Comparable*/public static <T extends Object & Comparable<? super T>> T max(Collection<? extends T> coll) {Iterator<? extends T> i = coll.iterator();T candidate = i.next();while (i.hasNext()) {T next = i.next();if (next.compareTo(candidate) > 0)candidate = next;}return candidate;}/*** Returns the maximum element of the given collection, according to the* order induced by the specified comparator. All elements in the* collection must be <i>mutually comparable</i> by the specified* comparator (that is, <tt>comp.compare(e1, e2)</tt> must not throw a* <tt>ClassCastException</tt> for any elements <tt>e1</tt> and* <tt>e2</tt> in the collection).<p>** This method iterates over the entire collection, hence it requires* time proportional to the size of the collection.** @param <T> the class of the objects in the collection* @param coll the collection whose maximum element is to be determined.* @param comp the comparator with which to determine the maximum element.* A <tt>null</tt> value indicates that the elements' <i>natural* ordering</i> should be used.* @return the maximum element of the given collection, according* to the specified comparator.* @throws ClassCastException if the collection contains elements that are* not <i>mutually comparable</i> using the specified comparator.* @throws NoSuchElementException if the collection is empty.* @see Comparable*/@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes"})public static <T> T max(Collection<? extends T> coll, Comparator<? super T> comp) {if (comp==null)return (T)max((Collection) coll);Iterator<? extends T> i = coll.iterator();T candidate = i.next();while (i.hasNext()) {T next = i.next();if (comp.compare(next, candidate) > 0)candidate = next;}return candidate;}/*** Rotates the elements in the specified list by the specified distance.* After calling this method, the element at index <tt>i</tt> will be* the element previously at index <tt>(i - distance)</tt> mod* <tt>list.size()</tt>, for all values of <tt>i</tt> between <tt>0</tt>* and <tt>list.size()-1</tt>, inclusive. (This method has no effect on* the size of the list.)** <p>For example, suppose <tt>list</tt> comprises<tt> [t, a, n, k, s]</tt>.* After invoking <tt>Collections.rotate(list, 1)</tt> (or* <tt>Collections.rotate(list, -4)</tt>), <tt>list</tt> will comprise* <tt>[s, t, a, n, k]</tt>.** <p>Note that this method can usefully be applied to sublists to* move one or more elements within a list while preserving the* order of the remaining elements. For example, the following idiom* moves the element at index <tt>j</tt> forward to position* <tt>k</tt> (which must be greater than or equal to <tt>j</tt>):*<pre>* Collections.rotate(list.subList(j, k+1), -1);* </pre>* To make this concrete, suppose <tt>list</tt> comprises* <tt>[a, b, c, d, e]</tt>. To move the element at index <tt>1</tt>* (<tt>b</tt>) forward two positions, perform the following invocation:*<pre>* Collections.rotate(l.subList(1, 4), -1);* </pre>* The resulting list is <tt>[a, c, d, b, e]</tt>.** <p>To move more than one element forward, increase the absolute value* of the rotation distance. To move elements backward, use a positive* shift distance.** <p>If the specified list is small or implements the {@link* RandomAccess} interface, this implementation exchanges the first* element into the location it should go, and then repeatedly exchanges* the displaced element into the location it should go until a displaced* element is swapped into the first element. If necessary, the process* is repeated on the second and successive elements, until the rotation* is complete. If the specified list is large and doesn't implement the* <tt>RandomAccess</tt> interface, this implementation breaks the* list into two sublist views around index <tt>-distance mod size</tt>.* Then the {@link #reverse(List)} method is invoked on each sublist view,* and finally it is invoked on the entire list. For a more complete* description of both algorithms, see Section 2.3 of Jon Bentley's* <i>Programming Pearls</i> (Addison-Wesley, 1986).** @param list the list to be rotated.* @param distance the distance to rotate the list. There are no* constraints on this value; it may be zero, negative, or* greater than <tt>list.size()</tt>.* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the specified list or* its list-iterator does not support the <tt>set</tt> operation.* @since 1.4*/public static void rotate(List<?> list, int distance) {if (list instanceof RandomAccess || list.size() < ROTATE_THRESHOLD)rotate1(list, distance);elserotate2(list, distance);}private static <T> void rotate1(List<T> list, int distance) {int size = list.size();if (size == 0)return;distance = distance % size;if (distance < 0)distance += size;if (distance == 0)return;for (int cycleStart = 0, nMoved = 0; nMoved != size; cycleStart++) {T displaced = list.get(cycleStart);int i = cycleStart;do {i += distance;if (i >= size)i -= size;displaced = list.set(i, displaced);nMoved ++;} while (i != cycleStart);}}private static void rotate2(List<?> list, int distance) {int size = list.size();if (size == 0)return;int mid = -distance % size;if (mid < 0)mid += size;if (mid == 0)return;reverse(list.subList(0, mid));reverse(list.subList(mid, size));reverse(list);}/*** Replaces all occurrences of one specified value in a list with another.* More formally, replaces with <tt>newVal</tt> each element <tt>e</tt>* in <tt>list</tt> such that* <tt>(oldVal==null ? e==null : oldVal.equals(e))</tt>.* (This method has no effect on the size of the list.)** @param <T> the class of the objects in the list* @param list the list in which replacement is to occur.* @param oldVal the old value to be replaced.* @param newVal the new value with which <tt>oldVal</tt> is to be* replaced.* @return <tt>true</tt> if <tt>list</tt> contained one or more elements* <tt>e</tt> such that* <tt>(oldVal==null ? e==null : oldVal.equals(e))</tt>.* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the specified list or* its list-iterator does not support the <tt>set</tt> operation.* @since 1.4*/public static <T> boolean replaceAll(List<T> list, T oldVal, T newVal) {boolean result = false;int size = list.size();if (size < REPLACEALL_THRESHOLD || list instanceof RandomAccess) {if (oldVal==null) {for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {if (list.get(i)==null) {list.set(i, newVal);result = true;}}} else {for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {if (oldVal.equals(list.get(i))) {list.set(i, newVal);result = true;}}}} else {ListIterator<T> itr=list.listIterator();if (oldVal==null) {for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {if (itr.next()==null) {itr.set(newVal);result = true;}}} else {for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {if (oldVal.equals(itr.next())) {itr.set(newVal);result = true;}}}}return result;}/*** Returns the starting position of the first occurrence of the specified* target list within the specified source list, or -1 if there is no* such occurrence. More formally, returns the lowest index <tt>i</tt>* such that {@code source.subList(i, i+target.size()).equals(target)},* or -1 if there is no such index. (Returns -1 if* {@code target.size() > source.size()})** <p>This implementation uses the "brute force" technique of scanning* over the source list, looking for a match with the target at each* location in turn.** @param source the list in which to search for the first occurrence* of <tt>target</tt>.* @param target the list to search for as a subList of <tt>source</tt>.* @return the starting position of the first occurrence of the specified* target list within the specified source list, or -1 if there* is no such occurrence.* @since 1.4*/public static int indexOfSubList(List<?> source, List<?> target) {int sourceSize = source.size();int targetSize = target.size();int maxCandidate = sourceSize - targetSize;if (sourceSize < INDEXOFSUBLIST_THRESHOLD ||(source instanceof RandomAccess&&target instanceof RandomAccess)) {nextCand:for (int candidate = 0; candidate <= maxCandidate; candidate++) {for (int i=0, j=candidate; i<targetSize; i++, j++)if (!eq(target.get(i), source.get(j)))continue nextCand; // Element mismatch, try next candreturn candidate; // All elements of candidate matched target}} else { // Iterator version of above algorithmListIterator<?> si = source.listIterator();nextCand:for (int candidate = 0; candidate <= maxCandidate; candidate++) {ListIterator<?> ti = target.listIterator();for (int i=0; i<targetSize; i++) {if (!eq(ti.next(), si.next())) {// Back up source iterator to next candidatefor (int j=0; j<i; j++)si.previous();continue nextCand;}}return candidate;}}return -1; // No candidate matched the target}/*** Returns the starting position of the last occurrence of the specified* target list within the specified source list, or -1 if there is no such* occurrence. More formally, returns the highest index <tt>i</tt>* such that {@code source.subList(i, i+target.size()).equals(target)},* or -1 if there is no such index. (Returns -1 if* {@code target.size() > source.size()})** <p>This implementation uses the "brute force" technique of iterating* over the source list, looking for a match with the target at each* location in turn.** @param source the list in which to search for the last occurrence* of <tt>target</tt>.* @param target the list to search for as a subList of <tt>source</tt>.* @return the starting position of the last occurrence of the specified* target list within the specified source list, or -1 if there* is no such occurrence.* @since 1.4*/public static int lastIndexOfSubList(List<?> source, List<?> target) {int sourceSize = source.size();int targetSize = target.size();int maxCandidate = sourceSize - targetSize;if (sourceSize < INDEXOFSUBLIST_THRESHOLD ||source instanceof RandomAccess) { // Index access versionnextCand:for (int candidate = maxCandidate; candidate >= 0; candidate--) {for (int i=0, j=candidate; i<targetSize; i++, j++)if (!eq(target.get(i), source.get(j)))continue nextCand; // Element mismatch, try next candreturn candidate; // All elements of candidate matched target}} else { // Iterator version of above algorithmif (maxCandidate < 0)return -1;ListIterator<?> si = source.listIterator(maxCandidate);nextCand:for (int candidate = maxCandidate; candidate >= 0; candidate--) {ListIterator<?> ti = target.listIterator();for (int i=0; i<targetSize; i++) {if (!eq(ti.next(), si.next())) {if (candidate != 0) {// Back up source iterator to next candidatefor (int j=0; j<=i+1; j++)si.previous();}continue nextCand;}}return candidate;}}return -1; // No candidate matched the target}// Unmodifiable Wrappers/*** Returns an unmodifiable view of the specified collection. This method* allows modules to provide users with "read-only" access to internal* collections. Query operations on the returned collection "read through"* to the specified collection, and attempts to modify the returned* collection, whether direct or via its iterator, result in an* <tt>UnsupportedOperationException</tt>.<p>** The returned collection does <i>not</i> pass the hashCode and equals* operations through to the backing collection, but relies on* <tt>Object</tt>'s <tt>equals</tt> and <tt>hashCode</tt> methods. This* is necessary to preserve the contracts of these operations in the case* that the backing collection is a set or a list.<p>** The returned collection will be serializable if the specified collection* is serializable.** @param <T> the class of the objects in the collection* @param c the collection for which an unmodifiable view is to be* returned.* @return an unmodifiable view of the specified collection.*/public static <T> Collection<T> unmodifiableCollection(Collection<? extends T> c) {return new UnmodifiableCollection<>(c);}/*** @serial include*/static class UnmodifiableCollection<E> implements Collection<E>, Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = 1820017752578914078L;final Collection<? extends E> c;UnmodifiableCollection(Collection<? extends E> c) {if (c==null)throw new NullPointerException();this.c = c;}public int size() {return c.size();}public boolean isEmpty() {return c.isEmpty();}public boolean contains(Object o) {return c.contains(o);}public Object[] toArray() {return c.toArray();}public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {return c.toArray(a);}public String toString() {return c.toString();}public Iterator<E> iterator() {return new Iterator<E>() {private final Iterator<? extends E> i = c.iterator();public boolean hasNext() {return i.hasNext();}public E next() {return i.next();}public void remove() {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}@Overridepublic void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {// Use backing collection versioni.forEachRemaining(action);}};}public boolean add(E e) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}public boolean remove(Object o) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}public boolean containsAll(Collection<?> coll) {return c.containsAll(coll);}public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> coll) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> coll) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> coll) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}public void clear() {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}// Override default methods in Collection@Overridepublic void forEach(Consumer<? super E> action) {c.forEach(action);}@Overridepublic boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")@Overridepublic Spliterator<E> spliterator() {return (Spliterator<E>)c.spliterator();}@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")@Overridepublic Stream<E> stream() {return (Stream<E>)c.stream();}@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")@Overridepublic Stream<E> parallelStream() {return (Stream<E>)c.parallelStream();}}/*** Returns an unmodifiable view of the specified set. This method allows* modules to provide users with "read-only" access to internal sets.* Query operations on the returned set "read through" to the specified* set, and attempts to modify the returned set, whether direct or via its* iterator, result in an <tt>UnsupportedOperationException</tt>.<p>** The returned set will be serializable if the specified set* is serializable.** @param <T> the class of the objects in the set* @param s the set for which an unmodifiable view is to be returned.* @return an unmodifiable view of the specified set.*/public static <T> Set<T> unmodifiableSet(Set<? extends T> s) {return new UnmodifiableSet<>(s);}/*** @serial include*/static class UnmodifiableSet<E> extends UnmodifiableCollection<E>implements Set<E>, Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = -9215047833775013803L;UnmodifiableSet(Set<? extends E> s) {super(s);}public boolean equals(Object o) {return o == this || c.equals(o);}public int hashCode() {return c.hashCode();}}/*** Returns an unmodifiable view of the specified sorted set. This method* allows modules to provide users with "read-only" access to internal* sorted sets. Query operations on the returned sorted set "read* through" to the specified sorted set. Attempts to modify the returned* sorted set, whether direct, via its iterator, or via its* <tt>subSet</tt>, <tt>headSet</tt>, or <tt>tailSet</tt> views, result in* an <tt>UnsupportedOperationException</tt>.<p>** The returned sorted set will be serializable if the specified sorted set* is serializable.** @param <T> the class of the objects in the set* @param s the sorted set for which an unmodifiable view is to be* returned.* @return an unmodifiable view of the specified sorted set.*/public static <T> SortedSet<T> unmodifiableSortedSet(SortedSet<T> s) {return new UnmodifiableSortedSet<>(s);}/*** @serial include*/static class UnmodifiableSortedSet<E>extends UnmodifiableSet<E>implements SortedSet<E>, Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = -4929149591599911165L;private final SortedSet<E> ss;UnmodifiableSortedSet(SortedSet<E> s) {super(s); ss = s;}public Comparator<? super E> comparator() {return ss.comparator();}public SortedSet<E> subSet(E fromElement, E toElement) {return new UnmodifiableSortedSet<>(ss.subSet(fromElement,toElement));}public SortedSet<E> headSet(E toElement) {return new UnmodifiableSortedSet<>(ss.headSet(toElement));}public SortedSet<E> tailSet(E fromElement) {return new UnmodifiableSortedSet<>(ss.tailSet(fromElement));}public E first() {return ss.first();}public E last() {return ss.last();}}/*** Returns an unmodifiable view of the specified navigable set. This method* allows modules to provide users with "read-only" access to internal* navigable sets. Query operations on the returned navigable set "read* through" to the specified navigable set. Attempts to modify the returned* navigable set, whether direct, via its iterator, or via its* {@code subSet}, {@code headSet}, or {@code tailSet} views, result in* an {@code UnsupportedOperationException}.<p>** The returned navigable set will be serializable if the specified* navigable set is serializable.** @param <T> the class of the objects in the set* @param s the navigable set for which an unmodifiable view is to be* returned* @return an unmodifiable view of the specified navigable set* @since 1.8*/public static <T> NavigableSet<T> unmodifiableNavigableSet(NavigableSet<T> s) {return new UnmodifiableNavigableSet<>(s);}/*** Wraps a navigable set and disables all of the mutative operations.** @param <E> type of elements* @serial include*/static class UnmodifiableNavigableSet<E>extends UnmodifiableSortedSet<E>implements NavigableSet<E>, Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = -6027448201786391929L;/*** A singleton empty unmodifiable navigable set used for* {@link #emptyNavigableSet()}.** @param <E> type of elements, if there were any, and bounds*/private static class EmptyNavigableSet<E> extends UnmodifiableNavigableSet<E>implements Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = -6291252904449939134L;public EmptyNavigableSet() {super(new TreeSet<E>());}private Object readResolve() { return EMPTY_NAVIGABLE_SET; }}@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")private static final NavigableSet<?> EMPTY_NAVIGABLE_SET =new EmptyNavigableSet<>();/*** The instance we are protecting.*/private final NavigableSet<E> ns;UnmodifiableNavigableSet(NavigableSet<E> s) {super(s); ns = s;}public E lower(E e) { return ns.lower(e); }public E floor(E e) { return ns.floor(e); }public E ceiling(E e) { return ns.ceiling(e); }public E higher(E e) { return ns.higher(e); }public E pollFirst() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); }public E pollLast() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); }public NavigableSet<E> descendingSet(){ return new UnmodifiableNavigableSet<>(ns.descendingSet()); }public Iterator<E> descendingIterator(){ return descendingSet().iterator(); }public NavigableSet<E> subSet(E fromElement, boolean fromInclusive, E toElement, boolean toInclusive) {return new UnmodifiableNavigableSet<>(ns.subSet(fromElement, fromInclusive, toElement, toInclusive));}public NavigableSet<E> headSet(E toElement, boolean inclusive) {return new UnmodifiableNavigableSet<>(ns.headSet(toElement, inclusive));}public NavigableSet<E> tailSet(E fromElement, boolean inclusive) {return new UnmodifiableNavigableSet<>(ns.tailSet(fromElement, inclusive));}}/*** Returns an unmodifiable view of the specified list. This method allows* modules to provide users with "read-only" access to internal* lists. Query operations on the returned list "read through" to the* specified list, and attempts to modify the returned list, whether* direct or via its iterator, result in an* <tt>UnsupportedOperationException</tt>.<p>** The returned list will be serializable if the specified list* is serializable. Similarly, the returned list will implement* {@link RandomAccess} if the specified list does.** @param <T> the class of the objects in the list* @param list the list for which an unmodifiable view is to be returned.* @return an unmodifiable view of the specified list.*/public static <T> List<T> unmodifiableList(List<? extends T> list) {return (list instanceof RandomAccess ?new UnmodifiableRandomAccessList<>(list) :new UnmodifiableList<>(list));}/*** @serial include*/static class UnmodifiableList<E> extends UnmodifiableCollection<E>implements List<E> {private static final long serialVersionUID = -283967356065247728L;final List<? extends E> list;UnmodifiableList(List<? extends E> list) {super(list);this.list = list;}public boolean equals(Object o) {return o == this || list.equals(o);}public int hashCode() {return list.hashCode();}public E get(int index) {return list.get(index);}public E set(int index, E element) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}public void add(int index, E element) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}public E remove(int index) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}public int indexOf(Object o) {return list.indexOf(o);}public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {return list.lastIndexOf(o);}public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}@Overridepublic void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<E> operator) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}@Overridepublic void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}public ListIterator<E> listIterator() {return listIterator(0);}public ListIterator<E> listIterator(final int index) {return new ListIterator<E>() {private final ListIterator<? extends E> i= list.listIterator(index);public boolean hasNext() {return i.hasNext();}public E next() {return i.next();}public boolean hasPrevious() {return i.hasPrevious();}public E previous() {return i.previous();}public int nextIndex() {return i.nextIndex();}public int previousIndex() {return i.previousIndex();}public void remove() {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}public void set(E e) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}public void add(E e) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}@Overridepublic void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {i.forEachRemaining(action);}};}public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {return new UnmodifiableList<>(list.subList(fromIndex, toIndex));}/*** UnmodifiableRandomAccessList instances are serialized as* UnmodifiableList instances to allow them to be deserialized* in pre-1.4 JREs (which do not have UnmodifiableRandomAccessList).* This method inverts the transformation. As a beneficial* side-effect, it also grafts the RandomAccess marker onto* UnmodifiableList instances that were serialized in pre-1.4 JREs.** Note: Unfortunately, UnmodifiableRandomAccessList instances* serialized in 1.4.1 and deserialized in 1.4 will become* UnmodifiableList instances, as this method was missing in 1.4.*/private Object readResolve() {return (list instanceof RandomAccess? new UnmodifiableRandomAccessList<>(list): this);}}/*** @serial include*/static class UnmodifiableRandomAccessList<E> extends UnmodifiableList<E>implements RandomAccess{UnmodifiableRandomAccessList(List<? extends E> list) {super(list);}public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {return new UnmodifiableRandomAccessList<>(list.subList(fromIndex, toIndex));}private static final long serialVersionUID = -2542308836966382001L;/*** Allows instances to be deserialized in pre-1.4 JREs (which do* not have UnmodifiableRandomAccessList). UnmodifiableList has* a readResolve method that inverts this transformation upon* deserialization.*/private Object writeReplace() {return new UnmodifiableList<>(list);}}/*** Returns an unmodifiable view of the specified map. This method* allows modules to provide users with "read-only" access to internal* maps. Query operations on the returned map "read through"* to the specified map, and attempts to modify the returned* map, whether direct or via its collection views, result in an* <tt>UnsupportedOperationException</tt>.<p>** The returned map will be serializable if the specified map* is serializable.** @param <K> the class of the map keys* @param <V> the class of the map values* @param m the map for which an unmodifiable view is to be returned.* @return an unmodifiable view of the specified map.*/public static <K,V> Map<K,V> unmodifiableMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {return new UnmodifiableMap<>(m);}/*** @serial include*/private static class UnmodifiableMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V>, Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = -1034234728574286014L;private final Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m;UnmodifiableMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {if (m==null)throw new NullPointerException();this.m = m;}public int size() {return m.size();}public boolean isEmpty() {return m.isEmpty();}public boolean containsKey(Object key) {return m.containsKey(key);}public boolean containsValue(Object val) {return m.containsValue(val);}public V get(Object key) {return m.get(key);}public V put(K key, V value) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}public V remove(Object key) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}public void clear() {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}private transient Set<K> keySet;private transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet;private transient Collection<V> values;public Set<K> keySet() {if (keySet==null)keySet = unmodifiableSet(m.keySet());return keySet;}public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() {if (entrySet==null)entrySet = new UnmodifiableEntrySet<>(m.entrySet());return entrySet;}public Collection<V> values() {if (values==null)values = unmodifiableCollection(m.values());return values;}public boolean equals(Object o) {return o == this || m.equals(o);}public int hashCode() {return m.hashCode();}public String toString() {return m.toString();}// Override default methods in Map@Override@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public V getOrDefault(Object k, V defaultValue) {// Safe cast as we don't change the valuereturn ((Map<K, V>)m).getOrDefault(k, defaultValue);}@Overridepublic void forEach(BiConsumer<? super K, ? super V> action) {m.forEach(action);}@Overridepublic void replaceAll(BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> function) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}@Overridepublic V putIfAbsent(K key, V value) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}@Overridepublic boolean remove(Object key, Object value) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}@Overridepublic boolean replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}@Overridepublic V replace(K key, V value) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}@Overridepublic V computeIfAbsent(K key, Function<? super K, ? extends V> mappingFunction) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}@Overridepublic V computeIfPresent(K key,BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}@Overridepublic V compute(K key,BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}@Overridepublic V merge(K key, V value,BiFunction<? super V, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}/*** We need this class in addition to UnmodifiableSet as* Map.Entries themselves permit modification of the backing Map* via their setValue operation. This class is subtle: there are* many possible attacks that must be thwarted.** @serial include*/static class UnmodifiableEntrySet<K,V>extends UnmodifiableSet<Map.Entry<K,V>> {private static final long serialVersionUID = 7854390611657943733L;@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes"})UnmodifiableEntrySet(Set<? extends Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V>> s) {// Need to cast to raw in order to work around a limitation in the type systemsuper((Set)s);}static <K, V> Consumer<Map.Entry<K, V>> entryConsumer(Consumer<? super Entry<K, V>> action) {return e -> action.accept(new UnmodifiableEntry<>(e));}public void forEach(Consumer<? super Entry<K, V>> action) {Objects.requireNonNull(action);c.forEach(entryConsumer(action));}static final class UnmodifiableEntrySetSpliterator<K, V>implements Spliterator<Entry<K,V>> {final Spliterator<Map.Entry<K, V>> s;UnmodifiableEntrySetSpliterator(Spliterator<Entry<K, V>> s) {this.s = s;}@Overridepublic boolean tryAdvance(Consumer<? super Entry<K, V>> action) {Objects.requireNonNull(action);return s.tryAdvance(entryConsumer(action));}@Overridepublic void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super Entry<K, V>> action) {Objects.requireNonNull(action);s.forEachRemaining(entryConsumer(action));}@Overridepublic Spliterator<Entry<K, V>> trySplit() {Spliterator<Entry<K, V>> split = s.trySplit();return split == null? null: new UnmodifiableEntrySetSpliterator<>(split);}@Overridepublic long estimateSize() {return s.estimateSize();}@Overridepublic long getExactSizeIfKnown() {return s.getExactSizeIfKnown();}@Overridepublic int characteristics() {return s.characteristics();}@Overridepublic boolean hasCharacteristics(int characteristics) {return s.hasCharacteristics(characteristics);}@Overridepublic Comparator<? super Entry<K, V>> getComparator() {return s.getComparator();}}@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public Spliterator<Entry<K,V>> spliterator() {return new UnmodifiableEntrySetSpliterator<>((Spliterator<Map.Entry<K, V>>) c.spliterator());}@Overridepublic Stream<Entry<K,V>> stream() {return StreamSupport.stream(spliterator(), false);}@Overridepublic Stream<Entry<K,V>> parallelStream() {return StreamSupport.stream(spliterator(), true);}public Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() {return new Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>>() {private final Iterator<? extends Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V>> i = c.iterator();public boolean hasNext() {return i.hasNext();}public Map.Entry<K,V> next() {return new UnmodifiableEntry<>(i.next());}public void remove() {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}};}@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public Object[] toArray() {Object[] a = c.toArray();for (int i=0; i<a.length; i++)a[i] = new UnmodifiableEntry<>((Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V>)a[i]);return a;}@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {// We don't pass a to c.toArray, to avoid window of// vulnerability wherein an unscrupulous multithreaded client// could get his hands on raw (unwrapped) Entries from c.Object[] arr = c.toArray(a.length==0 ? a : Arrays.copyOf(a, 0));for (int i=0; i<arr.length; i++)arr[i] = new UnmodifiableEntry<>((Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V>)arr[i]);if (arr.length > a.length)return (T[])arr;System.arraycopy(arr, 0, a, 0, arr.length);if (a.length > arr.length)a[arr.length] = null;return a;}/*** This method is overridden to protect the backing set against* an object with a nefarious equals function that senses* that the equality-candidate is Map.Entry and calls its* setValue method.*/public boolean contains(Object o) {if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))return false;return c.contains(new UnmodifiableEntry<>((Map.Entry<?,?>) o));}/*** The next two methods are overridden to protect against* an unscrupulous List whose contains(Object o) method senses* when o is a Map.Entry, and calls o.setValue.*/public boolean containsAll(Collection<?> coll) {for (Object e : coll) {if (!contains(e)) // Invokes safe contains() abovereturn false;}return true;}public boolean equals(Object o) {if (o == this)return true;if (!(o instanceof Set))return false;Set<?> s = (Set<?>) o;if (s.size() != c.size())return false;return containsAll(s); // Invokes safe containsAll() above}/*** This "wrapper class" serves two purposes: it prevents* the client from modifying the backing Map, by short-circuiting* the setValue method, and it protects the backing Map against* an ill-behaved Map.Entry that attempts to modify another* Map Entry when asked to perform an equality check.*/private static class UnmodifiableEntry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {private Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e;UnmodifiableEntry(Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e){this.e = Objects.requireNonNull(e);}public K getKey() {return e.getKey();}public V getValue() {return e.getValue();}public V setValue(V value) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}public int hashCode() {return e.hashCode();}public boolean equals(Object o) {if (this == o)return true;if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))return false;Map.Entry<?,?> t = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;return eq(e.getKey(), t.getKey()) &&eq(e.getValue(), t.getValue());}public String toString() {return e.toString();}}}}/*** Returns an unmodifiable view of the specified sorted map. This method* allows modules to provide users with "read-only" access to internal* sorted maps. Query operations on the returned sorted map "read through"* to the specified sorted map. Attempts to modify the returned* sorted map, whether direct, via its collection views, or via its* <tt>subMap</tt>, <tt>headMap</tt>, or <tt>tailMap</tt> views, result in* an <tt>UnsupportedOperationException</tt>.<p>** The returned sorted map will be serializable if the specified sorted map* is serializable.** @param <K> the class of the map keys* @param <V> the class of the map values* @param m the sorted map for which an unmodifiable view is to be* returned.* @return an unmodifiable view of the specified sorted map.*/public static <K,V> SortedMap<K,V> unmodifiableSortedMap(SortedMap<K, ? extends V> m) {return new UnmodifiableSortedMap<>(m);}/*** @serial include*/static class UnmodifiableSortedMap<K,V>extends UnmodifiableMap<K,V>implements SortedMap<K,V>, Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = -8806743815996713206L;private final SortedMap<K, ? extends V> sm;UnmodifiableSortedMap(SortedMap<K, ? extends V> m) {super(m); sm = m; }public Comparator<? super K> comparator() { return sm.comparator(); }public SortedMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, K toKey){ return new UnmodifiableSortedMap<>(sm.subMap(fromKey, toKey)); }public SortedMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey){ return new UnmodifiableSortedMap<>(sm.headMap(toKey)); }public SortedMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey){ return new UnmodifiableSortedMap<>(sm.tailMap(fromKey)); }public K firstKey() { return sm.firstKey(); }public K lastKey() { return sm.lastKey(); }}/*** Returns an unmodifiable view of the specified navigable map. This method* allows modules to provide users with "read-only" access to internal* navigable maps. Query operations on the returned navigable map "read* through" to the specified navigable map. Attempts to modify the returned* navigable map, whether direct, via its collection views, or via its* {@code subMap}, {@code headMap}, or {@code tailMap} views, result in* an {@code UnsupportedOperationException}.<p>** The returned navigable map will be serializable if the specified* navigable map is serializable.** @param <K> the class of the map keys* @param <V> the class of the map values* @param m the navigable map for which an unmodifiable view is to be* returned* @return an unmodifiable view of the specified navigable map* @since 1.8*/public static <K,V> NavigableMap<K,V> unmodifiableNavigableMap(NavigableMap<K, ? extends V> m) {return new UnmodifiableNavigableMap<>(m);}/*** @serial include*/static class UnmodifiableNavigableMap<K,V>extends UnmodifiableSortedMap<K,V>implements NavigableMap<K,V>, Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = -4858195264774772197L;/*** A class for the {@link EMPTY_NAVIGABLE_MAP} which needs readResolve* to preserve singleton property.** @param <K> type of keys, if there were any, and of bounds* @param <V> type of values, if there were any*/private static class EmptyNavigableMap<K,V> extends UnmodifiableNavigableMap<K,V>implements Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = -2239321462712562324L;EmptyNavigableMap() { super(new TreeMap<K,V>()); }@Overridepublic NavigableSet<K> navigableKeySet(){ return emptyNavigableSet(); }private Object readResolve() { return EMPTY_NAVIGABLE_MAP; }}/*** Singleton for {@link emptyNavigableMap()} which is also immutable.*/private static final EmptyNavigableMap<?,?> EMPTY_NAVIGABLE_MAP =new EmptyNavigableMap<>();/*** The instance we wrap and protect.*/private final NavigableMap<K, ? extends V> nm;UnmodifiableNavigableMap(NavigableMap<K, ? extends V> m){super(m); nm = m;}public K lowerKey(K key) { return nm.lowerKey(key); }public K floorKey(K key) { return nm.floorKey(key); }public K ceilingKey(K key) { return nm.ceilingKey(key); }public K higherKey(K key) { return nm.higherKey(key); }@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public Entry<K, V> lowerEntry(K key) {Entry<K,V> lower = (Entry<K, V>) nm.lowerEntry(key);return (null != lower)? new UnmodifiableEntrySet.UnmodifiableEntry<>(lower): null;}@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public Entry<K, V> floorEntry(K key) {Entry<K,V> floor = (Entry<K, V>) nm.floorEntry(key);return (null != floor)? new UnmodifiableEntrySet.UnmodifiableEntry<>(floor): null;}@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public Entry<K, V> ceilingEntry(K key) {Entry<K,V> ceiling = (Entry<K, V>) nm.ceilingEntry(key);return (null != ceiling)? new UnmodifiableEntrySet.UnmodifiableEntry<>(ceiling): null;}@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public Entry<K, V> higherEntry(K key) {Entry<K,V> higher = (Entry<K, V>) nm.higherEntry(key);return (null != higher)? new UnmodifiableEntrySet.UnmodifiableEntry<>(higher): null;}@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public Entry<K, V> firstEntry() {Entry<K,V> first = (Entry<K, V>) nm.firstEntry();return (null != first)? new UnmodifiableEntrySet.UnmodifiableEntry<>(first): null;}@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public Entry<K, V> lastEntry() {Entry<K,V> last = (Entry<K, V>) nm.lastEntry();return (null != last)? new UnmodifiableEntrySet.UnmodifiableEntry<>(last): null;}public Entry<K, V> pollFirstEntry(){ throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); }public Entry<K, V> pollLastEntry(){ throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); }public NavigableMap<K, V> descendingMap(){ return unmodifiableNavigableMap(nm.descendingMap()); }public NavigableSet<K> navigableKeySet(){ return unmodifiableNavigableSet(nm.navigableKeySet()); }public NavigableSet<K> descendingKeySet(){ return unmodifiableNavigableSet(nm.descendingKeySet()); }public NavigableMap<K, V> subMap(K fromKey, boolean fromInclusive, K toKey, boolean toInclusive) {return unmodifiableNavigableMap(nm.subMap(fromKey, fromInclusive, toKey, toInclusive));}public NavigableMap<K, V> headMap(K toKey, boolean inclusive){ return unmodifiableNavigableMap(nm.headMap(toKey, inclusive)); }public NavigableMap<K, V> tailMap(K fromKey, boolean inclusive){ return unmodifiableNavigableMap(nm.tailMap(fromKey, inclusive)); }}// Synch Wrappers/*** Returns a synchronized (thread-safe) collection backed by the specified* collection. In order to guarantee serial access, it is critical that* <strong>all</strong> access to the backing collection is accomplished* through the returned collection.<p>** It is imperative that the user manually synchronize on the returned* collection when traversing it via {@link Iterator}, {@link Spliterator}* or {@link Stream}:*<pre>* Collection c = Collections.synchronizedCollection(myCollection);* ...* synchronized (c) {* Iterator i = c.iterator(); // Must be in the synchronized block* while (i.hasNext())* foo(i.next());* }* </pre>* Failure to follow this advice may result in non-deterministic behavior.** <p>The returned collection does <i>not</i> pass the {@code hashCode}* and {@code equals} operations through to the backing collection, but* relies on {@code Object}'s equals and hashCode methods. This is* necessary to preserve the contracts of these operations in the case* that the backing collection is a set or a list.<p>** The returned collection will be serializable if the specified collection* is serializable.** @param <T> the class of the objects in the collection* @param c the collection to be "wrapped" in a synchronized collection.* @return a synchronized view of the specified collection.*/public static <T> Collection<T> synchronizedCollection(Collection<T> c) {return new SynchronizedCollection<>(c);}static <T> Collection<T> synchronizedCollection(Collection<T> c, Object mutex) {return new SynchronizedCollection<>(c, mutex);}/*** @serial include*/static class SynchronizedCollection<E> implements Collection<E>, Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = 3053995032091335093L;final Collection<E> c; // Backing Collectionfinal Object mutex; // Object on which to synchronizeSynchronizedCollection(Collection<E> c) {this.c = Objects.requireNonNull(c);mutex = this;}SynchronizedCollection(Collection<E> c, Object mutex) {this.c = Objects.requireNonNull(c);this.mutex = Objects.requireNonNull(mutex);}public int size() {synchronized (mutex) {return c.size();}}public boolean isEmpty() {synchronized (mutex) {return c.isEmpty();}}public boolean contains(Object o) {synchronized (mutex) {return c.contains(o);}}public Object[] toArray() {synchronized (mutex) {return c.toArray();}}public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {synchronized (mutex) {return c.toArray(a);}}public Iterator<E> iterator() {return c.iterator(); // Must be manually synched by user!}public boolean add(E e) {synchronized (mutex) {return c.add(e);}}public boolean remove(Object o) {synchronized (mutex) {return c.remove(o);}}public boolean containsAll(Collection<?> coll) {synchronized (mutex) {return c.containsAll(coll);}}public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> coll) {synchronized (mutex) {return c.addAll(coll);}}public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> coll) {synchronized (mutex) {return c.removeAll(coll);}}public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> coll) {synchronized (mutex) {return c.retainAll(coll);}}public void clear() {synchronized (mutex) {c.clear();}}public String toString() {synchronized (mutex) {return c.toString();}}// Override default methods in Collection@Overridepublic void forEach(Consumer<? super E> consumer) {synchronized (mutex) {c.forEach(consumer);}}@Overridepublic boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) {synchronized (mutex) {return c.removeIf(filter);}}@Overridepublic Spliterator<E> spliterator() {return c.spliterator(); // Must be manually synched by user!}@Overridepublic Stream<E> stream() {return c.stream(); // Must be manually synched by user!}@Overridepublic Stream<E> parallelStream() {return c.parallelStream(); // Must be manually synched by user!}private void writeObject(ObjectOutputStream s) throws IOException {synchronized (mutex) {s.defaultWriteObject();}}}/*** Returns a synchronized (thread-safe) set backed by the specified* set. In order to guarantee serial access, it is critical that* <strong>all</strong> access to the backing set is accomplished* through the returned set.<p>** It is imperative that the user manually synchronize on the returned* set when iterating over it:*<pre>* Set s = Collections.synchronizedSet(new HashSet());* ...* synchronized (s) {* Iterator i = s.iterator(); // Must be in the synchronized block* while (i.hasNext())* foo(i.next());* }* </pre>* Failure to follow this advice may result in non-deterministic behavior.** <p>The returned set will be serializable if the specified set is* serializable.** @param <T> the class of the objects in the set* @param s the set to be "wrapped" in a synchronized set.* @return a synchronized view of the specified set.*/public static <T> Set<T> synchronizedSet(Set<T> s) {return new SynchronizedSet<>(s);}static <T> Set<T> synchronizedSet(Set<T> s, Object mutex) {return new SynchronizedSet<>(s, mutex);}/*** @serial include*/static class SynchronizedSet<E>extends SynchronizedCollection<E>implements Set<E> {private static final long serialVersionUID = 487447009682186044L;SynchronizedSet(Set<E> s) {super(s);}SynchronizedSet(Set<E> s, Object mutex) {super(s, mutex);}public boolean equals(Object o) {if (this == o)return true;synchronized (mutex) {return c.equals(o);}}public int hashCode() {synchronized (mutex) {return c.hashCode();}}}/*** Returns a synchronized (thread-safe) sorted set backed by the specified* sorted set. In order to guarantee serial access, it is critical that* <strong>all</strong> access to the backing sorted set is accomplished* through the returned sorted set (or its views).<p>** It is imperative that the user manually synchronize on the returned* sorted set when iterating over it or any of its <tt>subSet</tt>,* <tt>headSet</tt>, or <tt>tailSet</tt> views.*<pre>* SortedSet s = Collections.synchronizedSortedSet(new TreeSet());* ...* synchronized (s) {* Iterator i = s.iterator(); // Must be in the synchronized block* while (i.hasNext())* foo(i.next());* }* </pre>* or:*<pre>* SortedSet s = Collections.synchronizedSortedSet(new TreeSet());* SortedSet s2 = s.headSet(foo);* ...* synchronized (s) { // Note: s, not s2!!!* Iterator i = s2.iterator(); // Must be in the synchronized block* while (i.hasNext())* foo(i.next());* }* </pre>* Failure to follow this advice may result in non-deterministic behavior.** <p>The returned sorted set will be serializable if the specified* sorted set is serializable.** @param <T> the class of the objects in the set* @param s the sorted set to be "wrapped" in a synchronized sorted set.* @return a synchronized view of the specified sorted set.*/public static <T> SortedSet<T> synchronizedSortedSet(SortedSet<T> s) {return new SynchronizedSortedSet<>(s);}/*** @serial include*/static class SynchronizedSortedSet<E>extends SynchronizedSet<E>implements SortedSet<E>{private static final long serialVersionUID = 8695801310862127406L;private final SortedSet<E> ss;SynchronizedSortedSet(SortedSet<E> s) {super(s);ss = s;}SynchronizedSortedSet(SortedSet<E> s, Object mutex) {super(s, mutex);ss = s;}public Comparator<? super E> comparator() {synchronized (mutex) {return ss.comparator();}}public SortedSet<E> subSet(E fromElement, E toElement) {synchronized (mutex) {return new SynchronizedSortedSet<>(ss.subSet(fromElement, toElement), mutex);}}public SortedSet<E> headSet(E toElement) {synchronized (mutex) {return new SynchronizedSortedSet<>(ss.headSet(toElement), mutex);}}public SortedSet<E> tailSet(E fromElement) {synchronized (mutex) {return new SynchronizedSortedSet<>(ss.tailSet(fromElement),mutex);}}public E first() {synchronized (mutex) {return ss.first();}}public E last() {synchronized (mutex) {return ss.last();}}}/*** Returns a synchronized (thread-safe) navigable set backed by the* specified navigable set. In order to guarantee serial access, it is* critical that <strong>all</strong> access to the backing navigable set is* accomplished through the returned navigable set (or its views).<p>** It is imperative that the user manually synchronize on the returned* navigable set when iterating over it or any of its {@code subSet},* {@code headSet}, or {@code tailSet} views.*<pre>* NavigableSet s = Collections.synchronizedNavigableSet(new TreeSet());* ...* synchronized (s) {* Iterator i = s.iterator(); // Must be in the synchronized block* while (i.hasNext())* foo(i.next());* }* </pre>* or:*<pre>* NavigableSet s = Collections.synchronizedNavigableSet(new TreeSet());* NavigableSet s2 = s.headSet(foo, true);* ...* synchronized (s) { // Note: s, not s2!!!* Iterator i = s2.iterator(); // Must be in the synchronized block* while (i.hasNext())* foo(i.next());* }* </pre>* Failure to follow this advice may result in non-deterministic behavior.** <p>The returned navigable set will be serializable if the specified* navigable set is serializable.** @param <T> the class of the objects in the set* @param s the navigable set to be "wrapped" in a synchronized navigable* set* @return a synchronized view of the specified navigable set* @since 1.8*/public static <T> NavigableSet<T> synchronizedNavigableSet(NavigableSet<T> s) {return new SynchronizedNavigableSet<>(s);}/*** @serial include*/static class SynchronizedNavigableSet<E>extends SynchronizedSortedSet<E>implements NavigableSet<E>{private static final long serialVersionUID = -5505529816273629798L;private final NavigableSet<E> ns;SynchronizedNavigableSet(NavigableSet<E> s) {super(s);ns = s;}SynchronizedNavigableSet(NavigableSet<E> s, Object mutex) {super(s, mutex);ns = s;}public E lower(E e) { synchronized (mutex) {return ns.lower(e);} }public E floor(E e) { synchronized (mutex) {return ns.floor(e);} }public E ceiling(E e) { synchronized (mutex) {return ns.ceiling(e);} }public E higher(E e) { synchronized (mutex) {return ns.higher(e);} }public E pollFirst() { synchronized (mutex) {return ns.pollFirst();} }public E pollLast() { synchronized (mutex) {return ns.pollLast();} }public NavigableSet<E> descendingSet() {synchronized (mutex) {return new SynchronizedNavigableSet<>(ns.descendingSet(), mutex);}}public Iterator<E> descendingIterator(){ synchronized (mutex) { return descendingSet().iterator(); } }public NavigableSet<E> subSet(E fromElement, E toElement) {synchronized (mutex) {return new SynchronizedNavigableSet<>(ns.subSet(fromElement, true, toElement, false), mutex);}}public NavigableSet<E> headSet(E toElement) {synchronized (mutex) {return new SynchronizedNavigableSet<>(ns.headSet(toElement, false), mutex);}}public NavigableSet<E> tailSet(E fromElement) {synchronized (mutex) {return new SynchronizedNavigableSet<>(ns.tailSet(fromElement, true), mutex);}}public NavigableSet<E> subSet(E fromElement, boolean fromInclusive, E toElement, boolean toInclusive) {synchronized (mutex) {return new SynchronizedNavigableSet<>(ns.subSet(fromElement, fromInclusive, toElement, toInclusive), mutex);}}public NavigableSet<E> headSet(E toElement, boolean inclusive) {synchronized (mutex) {return new SynchronizedNavigableSet<>(ns.headSet(toElement, inclusive), mutex);}}public NavigableSet<E> tailSet(E fromElement, boolean inclusive) {synchronized (mutex) {return new SynchronizedNavigableSet<>(ns.tailSet(fromElement, inclusive), mutex);}}}/*** Returns a synchronized (thread-safe) list backed by the specified* list. In order to guarantee serial access, it is critical that* <strong>all</strong> access to the backing list is accomplished* through the returned list.<p>** It is imperative that the user manually synchronize on the returned* list when iterating over it:*<pre>* List list = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList());* ...* synchronized (list) {* Iterator i = list.iterator(); // Must be in synchronized block* while (i.hasNext())* foo(i.next());* }* </pre>* Failure to follow this advice may result in non-deterministic behavior.** <p>The returned list will be serializable if the specified list is* serializable.** @param <T> the class of the objects in the list* @param list the list to be "wrapped" in a synchronized list.* @return a synchronized view of the specified list.*/public static <T> List<T> synchronizedList(List<T> list) {return (list instanceof RandomAccess ?new SynchronizedRandomAccessList<>(list) :new SynchronizedList<>(list));}static <T> List<T> synchronizedList(List<T> list, Object mutex) {return (list instanceof RandomAccess ?new SynchronizedRandomAccessList<>(list, mutex) :new SynchronizedList<>(list, mutex));}/*** @serial include*/static class SynchronizedList<E>extends SynchronizedCollection<E>implements List<E> {private static final long serialVersionUID = -7754090372962971524L;final List<E> list;SynchronizedList(List<E> list) {super(list);this.list = list;}SynchronizedList(List<E> list, Object mutex) {super(list, mutex);this.list = list;}public boolean equals(Object o) {if (this == o)return true;synchronized (mutex) {return list.equals(o);}}public int hashCode() {synchronized (mutex) {return list.hashCode();}}public E get(int index) {synchronized (mutex) {return list.get(index);}}public E set(int index, E element) {synchronized (mutex) {return list.set(index, element);}}public void add(int index, E element) {synchronized (mutex) {list.add(index, element);}}public E remove(int index) {synchronized (mutex) {return list.remove(index);}}public int indexOf(Object o) {synchronized (mutex) {return list.indexOf(o);}}public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {synchronized (mutex) {return list.lastIndexOf(o);}}public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {synchronized (mutex) {return list.addAll(index, c);}}public ListIterator<E> listIterator() {return list.listIterator(); // Must be manually synched by user}public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) {return list.listIterator(index); // Must be manually synched by user}public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {synchronized (mutex) {return new SynchronizedList<>(list.subList(fromIndex, toIndex),mutex);}}@Overridepublic void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<E> operator) {synchronized (mutex) {list.replaceAll(operator);}}@Overridepublic void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) {synchronized (mutex) {list.sort(c);}}/*** SynchronizedRandomAccessList instances are serialized as* SynchronizedList instances to allow them to be deserialized* in pre-1.4 JREs (which do not have SynchronizedRandomAccessList).* This method inverts the transformation. As a beneficial* side-effect, it also grafts the RandomAccess marker onto* SynchronizedList instances that were serialized in pre-1.4 JREs.** Note: Unfortunately, SynchronizedRandomAccessList instances* serialized in 1.4.1 and deserialized in 1.4 will become* SynchronizedList instances, as this method was missing in 1.4.*/private Object readResolve() {return (list instanceof RandomAccess? new SynchronizedRandomAccessList<>(list): this);}}/*** @serial include*/static class SynchronizedRandomAccessList<E>extends SynchronizedList<E>implements RandomAccess {SynchronizedRandomAccessList(List<E> list) {super(list);}SynchronizedRandomAccessList(List<E> list, Object mutex) {super(list, mutex);}public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {synchronized (mutex) {return new SynchronizedRandomAccessList<>(list.subList(fromIndex, toIndex), mutex);}}private static final long serialVersionUID = 1530674583602358482L;/*** Allows instances to be deserialized in pre-1.4 JREs (which do* not have SynchronizedRandomAccessList). SynchronizedList has* a readResolve method that inverts this transformation upon* deserialization.*/private Object writeReplace() {return new SynchronizedList<>(list);}}/*** Returns a synchronized (thread-safe) map backed by the specified* map. In order to guarantee serial access, it is critical that* <strong>all</strong> access to the backing map is accomplished* through the returned map.<p>** It is imperative that the user manually synchronize on the returned* map when iterating over any of its collection views:*<pre>* Map m = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap());* ...* Set s = m.keySet(); // Needn't be in synchronized block* ...* synchronized (m) { // Synchronizing on m, not s!* Iterator i = s.iterator(); // Must be in synchronized block* while (i.hasNext())* foo(i.next());* }* </pre>* Failure to follow this advice may result in non-deterministic behavior.** <p>The returned map will be serializable if the specified map is* serializable.** @param <K> the class of the map keys* @param <V> the class of the map values* @param m the map to be "wrapped" in a synchronized map.* @return a synchronized view of the specified map.*/public static <K,V> Map<K,V> synchronizedMap(Map<K,V> m) {return new SynchronizedMap<>(m);}/*** @serial include*/private static class SynchronizedMap<K,V>implements Map<K,V>, Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = 1978198479659022715L;private final Map<K,V> m; // Backing Mapfinal Object mutex; // Object on which to synchronizeSynchronizedMap(Map<K,V> m) {this.m = Objects.requireNonNull(m);mutex = this;}SynchronizedMap(Map<K,V> m, Object mutex) {this.m = m;this.mutex = mutex;}public int size() {synchronized (mutex) {return m.size();}}public boolean isEmpty() {synchronized (mutex) {return m.isEmpty();}}public boolean containsKey(Object key) {synchronized (mutex) {return m.containsKey(key);}}public boolean containsValue(Object value) {synchronized (mutex) {return m.containsValue(value);}}public V get(Object key) {synchronized (mutex) {return m.get(key);}}public V put(K key, V value) {synchronized (mutex) {return m.put(key, value);}}public V remove(Object key) {synchronized (mutex) {return m.remove(key);}}public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> map) {synchronized (mutex) {m.putAll(map);}}public void clear() {synchronized (mutex) {m.clear();}}private transient Set<K> keySet;private transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet;private transient Collection<V> values;public Set<K> keySet() {synchronized (mutex) {if (keySet==null)keySet = new SynchronizedSet<>(m.keySet(), mutex);return keySet;}}public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() {synchronized (mutex) {if (entrySet==null)entrySet = new SynchronizedSet<>(m.entrySet(), mutex);return entrySet;}}public Collection<V> values() {synchronized (mutex) {if (values==null)values = new SynchronizedCollection<>(m.values(), mutex);return values;}}public boolean equals(Object o) {if (this == o)return true;synchronized (mutex) {return m.equals(o);}}public int hashCode() {synchronized (mutex) {return m.hashCode();}}public String toString() {synchronized (mutex) {return m.toString();}}// Override default methods in Map@Overridepublic V getOrDefault(Object k, V defaultValue) {synchronized (mutex) {return m.getOrDefault(k, defaultValue);}}@Overridepublic void forEach(BiConsumer<? super K, ? super V> action) {synchronized (mutex) {m.forEach(action);}}@Overridepublic void replaceAll(BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> function) {synchronized (mutex) {m.replaceAll(function);}}@Overridepublic V putIfAbsent(K key, V value) {synchronized (mutex) {return m.putIfAbsent(key, value);}}@Overridepublic boolean remove(Object key, Object value) {synchronized (mutex) {return m.remove(key, value);}}@Overridepublic boolean replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) {synchronized (mutex) {return m.replace(key, oldValue, newValue);}}@Overridepublic V replace(K key, V value) {synchronized (mutex) {return m.replace(key, value);}}@Overridepublic V computeIfAbsent(K key,Function<? super K, ? extends V> mappingFunction) {synchronized (mutex) {return m.computeIfAbsent(key, mappingFunction);}}@Overridepublic V computeIfPresent(K key,BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {synchronized (mutex) {return m.computeIfPresent(key, remappingFunction);}}@Overridepublic V compute(K key,BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {synchronized (mutex) {return m.compute(key, remappingFunction);}}@Overridepublic V merge(K key, V value,BiFunction<? super V, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {synchronized (mutex) {return m.merge(key, value, remappingFunction);}}private void writeObject(ObjectOutputStream s) throws IOException {synchronized (mutex) {s.defaultWriteObject();}}}/*** Returns a synchronized (thread-safe) sorted map backed by the specified* sorted map. In order to guarantee serial access, it is critical that* <strong>all</strong> access to the backing sorted map is accomplished* through the returned sorted map (or its views).<p>** It is imperative that the user manually synchronize on the returned* sorted map when iterating over any of its collection views, or the* collections views of any of its <tt>subMap</tt>, <tt>headMap</tt> or* <tt>tailMap</tt> views.*<pre>* SortedMap m = Collections.synchronizedSortedMap(new TreeMap());* ...* Set s = m.keySet(); // Needn't be in synchronized block* ...* synchronized (m) { // Synchronizing on m, not s!* Iterator i = s.iterator(); // Must be in synchronized block* while (i.hasNext())* foo(i.next());* }* </pre>* or:*<pre>* SortedMap m = Collections.synchronizedSortedMap(new TreeMap());* SortedMap m2 = m.subMap(foo, bar);* ...* Set s2 = m2.keySet(); // Needn't be in synchronized block* ...* synchronized (m) { // Synchronizing on m, not m2 or s2!* Iterator i = s.iterator(); // Must be in synchronized block* while (i.hasNext())* foo(i.next());* }* </pre>* Failure to follow this advice may result in non-deterministic behavior.** <p>The returned sorted map will be serializable if the specified* sorted map is serializable.** @param <K> the class of the map keys* @param <V> the class of the map values* @param m the sorted map to be "wrapped" in a synchronized sorted map.* @return a synchronized view of the specified sorted map.*/public static <K,V> SortedMap<K,V> synchronizedSortedMap(SortedMap<K,V> m) {return new SynchronizedSortedMap<>(m);}/*** @serial include*/static class SynchronizedSortedMap<K,V>extends SynchronizedMap<K,V>implements SortedMap<K,V>{private static final long serialVersionUID = -8798146769416483793L;private final SortedMap<K,V> sm;SynchronizedSortedMap(SortedMap<K,V> m) {super(m);sm = m;}SynchronizedSortedMap(SortedMap<K,V> m, Object mutex) {super(m, mutex);sm = m;}public Comparator<? super K> comparator() {synchronized (mutex) {return sm.comparator();}}public SortedMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, K toKey) {synchronized (mutex) {return new SynchronizedSortedMap<>(sm.subMap(fromKey, toKey), mutex);}}public SortedMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey) {synchronized (mutex) {return new SynchronizedSortedMap<>(sm.headMap(toKey), mutex);}}public SortedMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey) {synchronized (mutex) {return new SynchronizedSortedMap<>(sm.tailMap(fromKey),mutex);}}public K firstKey() {synchronized (mutex) {return sm.firstKey();}}public K lastKey() {synchronized (mutex) {return sm.lastKey();}}}/*** Returns a synchronized (thread-safe) navigable map backed by the* specified navigable map. In order to guarantee serial access, it is* critical that <strong>all</strong> access to the backing navigable map is* accomplished through the returned navigable map (or its views).<p>** It is imperative that the user manually synchronize on the returned* navigable map when iterating over any of its collection views, or the* collections views of any of its {@code subMap}, {@code headMap} or* {@code tailMap} views.*<pre>* NavigableMap m = Collections.synchronizedNavigableMap(new TreeMap());* ...* Set s = m.keySet(); // Needn't be in synchronized block* ...* synchronized (m) { // Synchronizing on m, not s!* Iterator i = s.iterator(); // Must be in synchronized block* while (i.hasNext())* foo(i.next());* }* </pre>* or:*<pre>* NavigableMap m = Collections.synchronizedNavigableMap(new TreeMap());* NavigableMap m2 = m.subMap(foo, true, bar, false);* ...* Set s2 = m2.keySet(); // Needn't be in synchronized block* ...* synchronized (m) { // Synchronizing on m, not m2 or s2!* Iterator i = s.iterator(); // Must be in synchronized block* while (i.hasNext())* foo(i.next());* }* </pre>* Failure to follow this advice may result in non-deterministic behavior.** <p>The returned navigable map will be serializable if the specified* navigable map is serializable.** @param <K> the class of the map keys* @param <V> the class of the map values* @param m the navigable map to be "wrapped" in a synchronized navigable* map* @return a synchronized view of the specified navigable map.* @since 1.8*/public static <K,V> NavigableMap<K,V> synchronizedNavigableMap(NavigableMap<K,V> m) {return new SynchronizedNavigableMap<>(m);}/*** A synchronized NavigableMap.** @serial include*/static class SynchronizedNavigableMap<K,V>extends SynchronizedSortedMap<K,V>implements NavigableMap<K,V>{private static final long serialVersionUID = 699392247599746807L;private final NavigableMap<K,V> nm;SynchronizedNavigableMap(NavigableMap<K,V> m) {super(m);nm = m;}SynchronizedNavigableMap(NavigableMap<K,V> m, Object mutex) {super(m, mutex);nm = m;}public Entry<K, V> lowerEntry(K key){ synchronized (mutex) { return nm.lowerEntry(key); } }public K lowerKey(K key){ synchronized (mutex) { return nm.lowerKey(key); } }public Entry<K, V> floorEntry(K key){ synchronized (mutex) { return nm.floorEntry(key); } }public K floorKey(K key){ synchronized (mutex) { return nm.floorKey(key); } }public Entry<K, V> ceilingEntry(K key){ synchronized (mutex) { return nm.ceilingEntry(key); } }public K ceilingKey(K key){ synchronized (mutex) { return nm.ceilingKey(key); } }public Entry<K, V> higherEntry(K key){ synchronized (mutex) { return nm.higherEntry(key); } }public K higherKey(K key){ synchronized (mutex) { return nm.higherKey(key); } }public Entry<K, V> firstEntry(){ synchronized (mutex) { return nm.firstEntry(); } }public Entry<K, V> lastEntry(){ synchronized (mutex) { return nm.lastEntry(); } }public Entry<K, V> pollFirstEntry(){ synchronized (mutex) { return nm.pollFirstEntry(); } }public Entry<K, V> pollLastEntry(){ synchronized (mutex) { return nm.pollLastEntry(); } }public NavigableMap<K, V> descendingMap() {synchronized (mutex) {returnnew SynchronizedNavigableMap<>(nm.descendingMap(), mutex);}}public NavigableSet<K> keySet() {return navigableKeySet();}public NavigableSet<K> navigableKeySet() {synchronized (mutex) {return new SynchronizedNavigableSet<>(nm.navigableKeySet(), mutex);}}public NavigableSet<K> descendingKeySet() {synchronized (mutex) {return new SynchronizedNavigableSet<>(nm.descendingKeySet(), mutex);}}public SortedMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, K toKey) {synchronized (mutex) {return new SynchronizedNavigableMap<>(nm.subMap(fromKey, true, toKey, false), mutex);}}public SortedMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey) {synchronized (mutex) {return new SynchronizedNavigableMap<>(nm.headMap(toKey, false), mutex);}}public SortedMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey) {synchronized (mutex) {return new SynchronizedNavigableMap<>(nm.tailMap(fromKey, true),mutex);}}public NavigableMap<K, V> subMap(K fromKey, boolean fromInclusive, K toKey, boolean toInclusive) {synchronized (mutex) {return new SynchronizedNavigableMap<>(nm.subMap(fromKey, fromInclusive, toKey, toInclusive), mutex);}}public NavigableMap<K, V> headMap(K toKey, boolean inclusive) {synchronized (mutex) {return new SynchronizedNavigableMap<>(nm.headMap(toKey, inclusive), mutex);}}public NavigableMap<K, V> tailMap(K fromKey, boolean inclusive) {synchronized (mutex) {return new SynchronizedNavigableMap<>(nm.tailMap(fromKey, inclusive), mutex);}}}// Dynamically typesafe collection wrappers/*** Returns a dynamically typesafe view of the specified collection.* Any attempt to insert an element of the wrong type will result in an* immediate {@link ClassCastException}. Assuming a collection* contains no incorrectly typed elements prior to the time a* dynamically typesafe view is generated, and that all subsequent* access to the collection takes place through the view, it is* <i>guaranteed</i> that the collection cannot contain an incorrectly* typed element.** <p>The generics mechanism in the language provides compile-time* (static) type checking, but it is possible to defeat this mechanism* with unchecked casts. Usually this is not a problem, as the compiler* issues warnings on all such unchecked operations. There are, however,* times when static type checking alone is not sufficient. For example,* suppose a collection is passed to a third-party library and it is* imperative that the library code not corrupt the collection by* inserting an element of the wrong type.** <p>Another use of dynamically typesafe views is debugging. Suppose a* program fails with a {@code ClassCastException}, indicating that an* incorrectly typed element was put into a parameterized collection.* Unfortunately, the exception can occur at any time after the erroneous* element is inserted, so it typically provides little or no information* as to the real source of the problem. If the problem is reproducible,* one can quickly determine its source by temporarily modifying the* program to wrap the collection with a dynamically typesafe view.* For example, this declaration:*<pre> {@code* Collection<String> c = new HashSet<>();* }</pre>* may be replaced temporarily by this one:*<pre> {@code* Collection<String> c = Collections.checkedCollection(* new HashSet<>(), String.class);* }</pre>* Running the program again will cause it to fail at the point where* an incorrectly typed element is inserted into the collection, clearly* identifying the source of the problem. Once the problem is fixed, the* modified declaration may be reverted back to the original.** <p>The returned collection does <i>not</i> pass the hashCode and equals* operations through to the backing collection, but relies on* {@code Object}'s {@code equals} and {@code hashCode} methods. This* is necessary to preserve the contracts of these operations in the case* that the backing collection is a set or a list.** <p>The returned collection will be serializable if the specified* collection is serializable.** <p>Since {@code null} is considered to be a value of any reference* type, the returned collection permits insertion of null elements* whenever the backing collection does.** @param <E> the class of the objects in the collection* @param c the collection for which a dynamically typesafe view is to be* returned* @param type the type of element that {@code c} is permitted to hold* @return a dynamically typesafe view of the specified collection* @since 1.5*/public static <E> Collection<E> checkedCollection(Collection<E> c,Class<E> type) {return new CheckedCollection<>(c, type);}@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")static <T> T[] zeroLengthArray(Class<T> type) {return (T[]) Array.newInstance(type, 0);}/*** @serial include*/static class CheckedCollection<E> implements Collection<E>, Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = 1578914078182001775L;final Collection<E> c;final Class<E> type;@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")E typeCheck(Object o) {if (o != null && !type.isInstance(o))throw new ClassCastException(badElementMsg(o));return (E) o;}private String badElementMsg(Object o) {return "Attempt to insert " + o.getClass() +" element into collection with element type " + type;}CheckedCollection(Collection<E> c, Class<E> type) {this.c = Objects.requireNonNull(c, "c");this.type = Objects.requireNonNull(type, "type");}public int size() { return c.size(); }public boolean isEmpty() { return c.isEmpty(); }public boolean contains(Object o) { return c.contains(o); }public Object[] toArray() { return c.toArray(); }public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) { return c.toArray(a); }public String toString() { return c.toString(); }public boolean remove(Object o) { return c.remove(o); }public void clear() { c.clear(); }public boolean containsAll(Collection<?> coll) {return c.containsAll(coll);}public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> coll) {return c.removeAll(coll);}public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> coll) {return c.retainAll(coll);}public Iterator<E> iterator() {// JDK-6363904 - unwrapped iterator could be typecast to// ListIterator with unsafe set()final Iterator<E> it = c.iterator();return new Iterator<E>() {public boolean hasNext() { return it.hasNext(); }public E next() { return it.next(); }public void remove() { it.remove(); }};}public boolean add(E e) { return c.add(typeCheck(e)); }private E[] zeroLengthElementArray; // Lazily initializedprivate E[] zeroLengthElementArray() {return zeroLengthElementArray != null ? zeroLengthElementArray :(zeroLengthElementArray = zeroLengthArray(type));}@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")Collection<E> checkedCopyOf(Collection<? extends E> coll) {Object[] a;try {E[] z = zeroLengthElementArray();a = coll.toArray(z);// Defend against coll violating the toArray contractif (a.getClass() != z.getClass())a = Arrays.copyOf(a, a.length, z.getClass());} catch (ArrayStoreException ignore) {// To get better and consistent diagnostics,// we call typeCheck explicitly on each element.// We call clone() to defend against coll retaining a// reference to the returned array and storing a bad// element into it after it has been type checked.a = coll.toArray().clone();for (Object o : a)typeCheck(o);}// A slight abuse of the type system, but safe here.return (Collection<E>) Arrays.asList(a);}public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> coll) {// Doing things this way insulates us from concurrent changes// in the contents of coll and provides all-or-nothing// semantics (which we wouldn't get if we type-checked each// element as we added it)return c.addAll(checkedCopyOf(coll));}// Override default methods in Collection@Overridepublic void forEach(Consumer<? super E> action) {c.forEach(action);}@Overridepublic boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) {return c.removeIf(filter);}@Overridepublic Spliterator<E> spliterator() {return c.spliterator();}@Overridepublic Stream<E> stream() {return c.stream();}@Overridepublic Stream<E> parallelStream() {return c.parallelStream();}}/*** Returns a dynamically typesafe view of the specified queue.* Any attempt to insert an element of the wrong type will result in* an immediate {@link ClassCastException}. Assuming a queue contains* no incorrectly typed elements prior to the time a dynamically typesafe* view is generated, and that all subsequent access to the queue* takes place through the view, it is <i>guaranteed</i> that the* queue cannot contain an incorrectly typed element.** <p>A discussion of the use of dynamically typesafe views may be* found in the documentation for the {@link #checkedCollection* checkedCollection} method.** <p>The returned queue will be serializable if the specified queue* is serializable.** <p>Since {@code null} is considered to be a value of any reference* type, the returned queue permits insertion of {@code null} elements* whenever the backing queue does.** @param <E> the class of the objects in the queue* @param queue the queue for which a dynamically typesafe view is to be* returned* @param type the type of element that {@code queue} is permitted to hold* @return a dynamically typesafe view of the specified queue* @since 1.8*/public static <E> Queue<E> checkedQueue(Queue<E> queue, Class<E> type) {return new CheckedQueue<>(queue, type);}/*** @serial include*/static class CheckedQueue<E>extends CheckedCollection<E>implements Queue<E>, Serializable{private static final long serialVersionUID = 1433151992604707767L;final Queue<E> queue;CheckedQueue(Queue<E> queue, Class<E> elementType) {super(queue, elementType);this.queue = queue;}public E element() {return queue.element();}public boolean equals(Object o) {return o == this || c.equals(o);}public int hashCode() {return c.hashCode();}public E peek() {return queue.peek();}public E poll() {return queue.poll();}public E remove() {return queue.remove();}public boolean offer(E e) {return queue.offer(typeCheck(e));}}/*** Returns a dynamically typesafe view of the specified set.* Any attempt to insert an element of the wrong type will result in* an immediate {@link ClassCastException}. Assuming a set contains* no incorrectly typed elements prior to the time a dynamically typesafe* view is generated, and that all subsequent access to the set* takes place through the view, it is <i>guaranteed</i> that the* set cannot contain an incorrectly typed element.** <p>A discussion of the use of dynamically typesafe views may be* found in the documentation for the {@link #checkedCollection* checkedCollection} method.** <p>The returned set will be serializable if the specified set is* serializable.** <p>Since {@code null} is considered to be a value of any reference* type, the returned set permits insertion of null elements whenever* the backing set does.** @param <E> the class of the objects in the set* @param s the set for which a dynamically typesafe view is to be* returned* @param type the type of element that {@code s} is permitted to hold* @return a dynamically typesafe view of the specified set* @since 1.5*/public static <E> Set<E> checkedSet(Set<E> s, Class<E> type) {return new CheckedSet<>(s, type);}/*** @serial include*/static class CheckedSet<E> extends CheckedCollection<E>implements Set<E>, Serializable{private static final long serialVersionUID = 4694047833775013803L;CheckedSet(Set<E> s, Class<E> elementType) { super(s, elementType); }public boolean equals(Object o) { return o == this || c.equals(o); }public int hashCode() { return c.hashCode(); }}/*** Returns a dynamically typesafe view of the specified sorted set.* Any attempt to insert an element of the wrong type will result in an* immediate {@link ClassCastException}. Assuming a sorted set* contains no incorrectly typed elements prior to the time a* dynamically typesafe view is generated, and that all subsequent* access to the sorted set takes place through the view, it is* <i>guaranteed</i> that the sorted set cannot contain an incorrectly* typed element.** <p>A discussion of the use of dynamically typesafe views may be* found in the documentation for the {@link #checkedCollection* checkedCollection} method.** <p>The returned sorted set will be serializable if the specified sorted* set is serializable.** <p>Since {@code null} is considered to be a value of any reference* type, the returned sorted set permits insertion of null elements* whenever the backing sorted set does.** @param <E> the class of the objects in the set* @param s the sorted set for which a dynamically typesafe view is to be* returned* @param type the type of element that {@code s} is permitted to hold* @return a dynamically typesafe view of the specified sorted set* @since 1.5*/public static <E> SortedSet<E> checkedSortedSet(SortedSet<E> s,Class<E> type) {return new CheckedSortedSet<>(s, type);}/*** @serial include*/static class CheckedSortedSet<E> extends CheckedSet<E>implements SortedSet<E>, Serializable{private static final long serialVersionUID = 1599911165492914959L;private final SortedSet<E> ss;CheckedSortedSet(SortedSet<E> s, Class<E> type) {super(s, type);ss = s;}public Comparator<? super E> comparator() { return ss.comparator(); }public E first() { return ss.first(); }public E last() { return ss.last(); }public SortedSet<E> subSet(E fromElement, E toElement) {return checkedSortedSet(ss.subSet(fromElement,toElement), type);}public SortedSet<E> headSet(E toElement) {return checkedSortedSet(ss.headSet(toElement), type);}public SortedSet<E> tailSet(E fromElement) {return checkedSortedSet(ss.tailSet(fromElement), type);}}/*** Returns a dynamically typesafe view of the specified navigable set.* Any attempt to insert an element of the wrong type will result in an* immediate {@link ClassCastException}. Assuming a navigable set* contains no incorrectly typed elements prior to the time a* dynamically typesafe view is generated, and that all subsequent* access to the navigable set takes place through the view, it is* <em>guaranteed</em> that the navigable set cannot contain an incorrectly* typed element.** <p>A discussion of the use of dynamically typesafe views may be* found in the documentation for the {@link #checkedCollection* checkedCollection} method.** <p>The returned navigable set will be serializable if the specified* navigable set is serializable.** <p>Since {@code null} is considered to be a value of any reference* type, the returned navigable set permits insertion of null elements* whenever the backing sorted set does.** @param <E> the class of the objects in the set* @param s the navigable set for which a dynamically typesafe view is to be* returned* @param type the type of element that {@code s} is permitted to hold* @return a dynamically typesafe view of the specified navigable set* @since 1.8*/public static <E> NavigableSet<E> checkedNavigableSet(NavigableSet<E> s,Class<E> type) {return new CheckedNavigableSet<>(s, type);}/*** @serial include*/static class CheckedNavigableSet<E> extends CheckedSortedSet<E>implements NavigableSet<E>, Serializable{private static final long serialVersionUID = -5429120189805438922L;private final NavigableSet<E> ns;CheckedNavigableSet(NavigableSet<E> s, Class<E> type) {super(s, type);ns = s;}public E lower(E e) { return ns.lower(e); }public E floor(E e) { return ns.floor(e); }public E ceiling(E e) { return ns.ceiling(e); }public E higher(E e) { return ns.higher(e); }public E pollFirst() { return ns.pollFirst(); }public E pollLast() {return ns.pollLast(); }public NavigableSet<E> descendingSet(){ return checkedNavigableSet(ns.descendingSet(), type); }public Iterator<E> descendingIterator(){return checkedNavigableSet(ns.descendingSet(), type).iterator(); }public NavigableSet<E> subSet(E fromElement, E toElement) {return checkedNavigableSet(ns.subSet(fromElement, true, toElement, false), type);}public NavigableSet<E> headSet(E toElement) {return checkedNavigableSet(ns.headSet(toElement, false), type);}public NavigableSet<E> tailSet(E fromElement) {return checkedNavigableSet(ns.tailSet(fromElement, true), type);}public NavigableSet<E> subSet(E fromElement, boolean fromInclusive, E toElement, boolean toInclusive) {return checkedNavigableSet(ns.subSet(fromElement, fromInclusive, toElement, toInclusive), type);}public NavigableSet<E> headSet(E toElement, boolean inclusive) {return checkedNavigableSet(ns.headSet(toElement, inclusive), type);}public NavigableSet<E> tailSet(E fromElement, boolean inclusive) {return checkedNavigableSet(ns.tailSet(fromElement, inclusive), type);}}/*** Returns a dynamically typesafe view of the specified list.* Any attempt to insert an element of the wrong type will result in* an immediate {@link ClassCastException}. Assuming a list contains* no incorrectly typed elements prior to the time a dynamically typesafe* view is generated, and that all subsequent access to the list* takes place through the view, it is <i>guaranteed</i> that the* list cannot contain an incorrectly typed element.** <p>A discussion of the use of dynamically typesafe views may be* found in the documentation for the {@link #checkedCollection* checkedCollection} method.** <p>The returned list will be serializable if the specified list* is serializable.** <p>Since {@code null} is considered to be a value of any reference* type, the returned list permits insertion of null elements whenever* the backing list does.** @param <E> the class of the objects in the list* @param list the list for which a dynamically typesafe view is to be* returned* @param type the type of element that {@code list} is permitted to hold* @return a dynamically typesafe view of the specified list* @since 1.5*/public static <E> List<E> checkedList(List<E> list, Class<E> type) {return (list instanceof RandomAccess ?new CheckedRandomAccessList<>(list, type) :new CheckedList<>(list, type));}/*** @serial include*/static class CheckedList<E>extends CheckedCollection<E>implements List<E>{private static final long serialVersionUID = 65247728283967356L;final List<E> list;CheckedList(List<E> list, Class<E> type) {super(list, type);this.list = list;}public boolean equals(Object o) { return o == this || list.equals(o); }public int hashCode() { return list.hashCode(); }public E get(int index) { return list.get(index); }public E remove(int index) { return list.remove(index); }public int indexOf(Object o) { return list.indexOf(o); }public int lastIndexOf(Object o) { return list.lastIndexOf(o); }public E set(int index, E element) {return list.set(index, typeCheck(element));}public void add(int index, E element) {list.add(index, typeCheck(element));}public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {return list.addAll(index, checkedCopyOf(c));}public ListIterator<E> listIterator() { return listIterator(0); }public ListIterator<E> listIterator(final int index) {final ListIterator<E> i = list.listIterator(index);return new ListIterator<E>() {public boolean hasNext() { return i.hasNext(); }public E next() { return i.next(); }public boolean hasPrevious() { return i.hasPrevious(); }public E previous() { return i.previous(); }public int nextIndex() { return i.nextIndex(); }public int previousIndex() { return i.previousIndex(); }public void remove() { i.remove(); }public void set(E e) {i.set(typeCheck(e));}public void add(E e) {i.add(typeCheck(e));}@Overridepublic void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {i.forEachRemaining(action);}};}public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {return new CheckedList<>(list.subList(fromIndex, toIndex), type);}/*** {@inheritDoc}** @throws ClassCastException if the class of an element returned by the* operator prevents it from being added to this collection. The* exception may be thrown after some elements of the list have* already been replaced.*/@Overridepublic void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<E> operator) {Objects.requireNonNull(operator);list.replaceAll(e -> typeCheck(operator.apply(e)));}@Overridepublic void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) {list.sort(c);}}/*** @serial include*/static class CheckedRandomAccessList<E> extends CheckedList<E>implements RandomAccess{private static final long serialVersionUID = 1638200125423088369L;CheckedRandomAccessList(List<E> list, Class<E> type) {super(list, type);}public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {return new CheckedRandomAccessList<>(list.subList(fromIndex, toIndex), type);}}/*** Returns a dynamically typesafe view of the specified map.* Any attempt to insert a mapping whose key or value have the wrong* type will result in an immediate {@link ClassCastException}.* Similarly, any attempt to modify the value currently associated with* a key will result in an immediate {@link ClassCastException},* whether the modification is attempted directly through the map* itself, or through a {@link Map.Entry} instance obtained from the* map's {@link Map#entrySet() entry set} view.** <p>Assuming a map contains no incorrectly typed keys or values* prior to the time a dynamically typesafe view is generated, and* that all subsequent access to the map takes place through the view* (or one of its collection views), it is <i>guaranteed</i> that the* map cannot contain an incorrectly typed key or value.** <p>A discussion of the use of dynamically typesafe views may be* found in the documentation for the {@link #checkedCollection* checkedCollection} method.** <p>The returned map will be serializable if the specified map is* serializable.** <p>Since {@code null} is considered to be a value of any reference* type, the returned map permits insertion of null keys or values* whenever the backing map does.** @param <K> the class of the map keys* @param <V> the class of the map values* @param m the map for which a dynamically typesafe view is to be* returned* @param keyType the type of key that {@code m} is permitted to hold* @param valueType the type of value that {@code m} is permitted to hold* @return a dynamically typesafe view of the specified map* @since 1.5*/public static <K, V> Map<K, V> checkedMap(Map<K, V> m,Class<K> keyType,Class<V> valueType) {return new CheckedMap<>(m, keyType, valueType);}/*** @serial include*/private static class CheckedMap<K,V>implements Map<K,V>, Serializable{private static final long serialVersionUID = 5742860141034234728L;private final Map<K, V> m;final Class<K> keyType;final Class<V> valueType;private void typeCheck(Object key, Object value) {if (key != null && !keyType.isInstance(key))throw new ClassCastException(badKeyMsg(key));if (value != null && !valueType.isInstance(value))throw new ClassCastException(badValueMsg(value));}private BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> typeCheck(BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> func) {Objects.requireNonNull(func);return (k, v) -> {V newValue = func.apply(k, v);typeCheck(k, newValue);return newValue;};}private String badKeyMsg(Object key) {return "Attempt to insert " + key.getClass() +" key into map with key type " + keyType;}private String badValueMsg(Object value) {return "Attempt to insert " + value.getClass() +" value into map with value type " + valueType;}CheckedMap(Map<K, V> m, Class<K> keyType, Class<V> valueType) {this.m = Objects.requireNonNull(m);this.keyType = Objects.requireNonNull(keyType);this.valueType = Objects.requireNonNull(valueType);}public int size() { return m.size(); }public boolean isEmpty() { return m.isEmpty(); }public boolean containsKey(Object key) { return m.containsKey(key); }public boolean containsValue(Object v) { return m.containsValue(v); }public V get(Object key) { return m.get(key); }public V remove(Object key) { return m.remove(key); }public void clear() { m.clear(); }public Set<K> keySet() { return m.keySet(); }public Collection<V> values() { return m.values(); }public boolean equals(Object o) { return o == this || m.equals(o); }public int hashCode() { return m.hashCode(); }public String toString() { return m.toString(); }public V put(K key, V value) {typeCheck(key, value);return m.put(key, value);}@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> t) {// Satisfy the following goals:// - good diagnostics in case of type mismatch// - all-or-nothing semantics// - protection from malicious t// - correct behavior if t is a concurrent mapObject[] entries = t.entrySet().toArray();List<Map.Entry<K,V>> checked = new ArrayList<>(entries.length);for (Object o : entries) {Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>) o;Object k = e.getKey();Object v = e.getValue();typeCheck(k, v);checked.add(new AbstractMap.SimpleImmutableEntry<>((K)k, (V)v));}for (Map.Entry<K,V> e : checked)m.put(e.getKey(), e.getValue());}private transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet;public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() {if (entrySet==null)entrySet = new CheckedEntrySet<>(m.entrySet(), valueType);return entrySet;}// Override default methods in Map@Overridepublic void forEach(BiConsumer<? super K, ? super V> action) {m.forEach(action);}@Overridepublic void replaceAll(BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> function) {m.replaceAll(typeCheck(function));}@Overridepublic V putIfAbsent(K key, V value) {typeCheck(key, value);return m.putIfAbsent(key, value);}@Overridepublic boolean remove(Object key, Object value) {return m.remove(key, value);}@Overridepublic boolean replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) {typeCheck(key, newValue);return m.replace(key, oldValue, newValue);}@Overridepublic V replace(K key, V value) {typeCheck(key, value);return m.replace(key, value);}@Overridepublic V computeIfAbsent(K key,Function<? super K, ? extends V> mappingFunction) {Objects.requireNonNull(mappingFunction);return m.computeIfAbsent(key, k -> {V value = mappingFunction.apply(k);typeCheck(k, value);return value;});}@Overridepublic V computeIfPresent(K key,BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {return m.computeIfPresent(key, typeCheck(remappingFunction));}@Overridepublic V compute(K key,BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {return m.compute(key, typeCheck(remappingFunction));}@Overridepublic V merge(K key, V value,BiFunction<? super V, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {Objects.requireNonNull(remappingFunction);return m.merge(key, value, (v1, v2) -> {V newValue = remappingFunction.apply(v1, v2);typeCheck(null, newValue);return newValue;});}/*** We need this class in addition to CheckedSet as Map.Entry permits* modification of the backing Map via the setValue operation. This* class is subtle: there are many possible attacks that must be* thwarted.** @serial exclude*/static class CheckedEntrySet<K,V> implements Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> {private final Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> s;private final Class<V> valueType;CheckedEntrySet(Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> s, Class<V> valueType) {this.s = s;this.valueType = valueType;}public int size() { return s.size(); }public boolean isEmpty() { return s.isEmpty(); }public String toString() { return s.toString(); }public int hashCode() { return s.hashCode(); }public void clear() { s.clear(); }public boolean add(Map.Entry<K, V> e) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends Map.Entry<K, V>> coll) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}public Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() {final Iterator<Map.Entry<K, V>> i = s.iterator();final Class<V> valueType = this.valueType;return new Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>>() {public boolean hasNext() { return i.hasNext(); }public void remove() { i.remove(); }public Map.Entry<K,V> next() {return checkedEntry(i.next(), valueType);}};}@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public Object[] toArray() {Object[] source = s.toArray();/** Ensure that we don't get an ArrayStoreException even if* s.toArray returns an array of something other than Object*/Object[] dest = (CheckedEntry.class.isInstance(source.getClass().getComponentType()) ? source :new Object[source.length]);for (int i = 0; i < source.length; i++)dest[i] = checkedEntry((Map.Entry<K,V>)source[i],valueType);return dest;}@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {// We don't pass a to s.toArray, to avoid window of// vulnerability wherein an unscrupulous multithreaded client// could get his hands on raw (unwrapped) Entries from s.T[] arr = s.toArray(a.length==0 ? a : Arrays.copyOf(a, 0));for (int i=0; i<arr.length; i++)arr[i] = (T) checkedEntry((Map.Entry<K,V>)arr[i],valueType);if (arr.length > a.length)return arr;System.arraycopy(arr, 0, a, 0, arr.length);if (a.length > arr.length)a[arr.length] = null;return a;}/*** This method is overridden to protect the backing set against* an object with a nefarious equals function that senses* that the equality-candidate is Map.Entry and calls its* setValue method.*/public boolean contains(Object o) {if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))return false;Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>) o;return s.contains((e instanceof CheckedEntry) ? e : checkedEntry(e, valueType));}/*** The bulk collection methods are overridden to protect* against an unscrupulous collection whose contains(Object o)* method senses when o is a Map.Entry, and calls o.setValue.*/public boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) {for (Object o : c)if (!contains(o)) // Invokes safe contains() abovereturn false;return true;}public boolean remove(Object o) {if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))return false;return s.remove(new AbstractMap.SimpleImmutableEntry<>((Map.Entry<?,?>)o));}public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {return batchRemove(c, false);}public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) {return batchRemove(c, true);}private boolean batchRemove(Collection<?> c, boolean complement) {Objects.requireNonNull(c);boolean modified = false;Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> it = iterator();while (it.hasNext()) {if (c.contains(it.next()) != complement) {it.remove();modified = true;}}return modified;}public boolean equals(Object o) {if (o == this)return true;if (!(o instanceof Set))return false;Set<?> that = (Set<?>) o;return that.size() == s.size()&& containsAll(that); // Invokes safe containsAll() above}static <K,V,T> CheckedEntry<K,V,T> checkedEntry(Map.Entry<K,V> e,Class<T> valueType) {return new CheckedEntry<>(e, valueType);}/*** This "wrapper class" serves two purposes: it prevents* the client from modifying the backing Map, by short-circuiting* the setValue method, and it protects the backing Map against* an ill-behaved Map.Entry that attempts to modify another* Map.Entry when asked to perform an equality check.*/private static class CheckedEntry<K,V,T> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {private final Map.Entry<K, V> e;private final Class<T> valueType;CheckedEntry(Map.Entry<K, V> e, Class<T> valueType) {this.e = Objects.requireNonNull(e);this.valueType = Objects.requireNonNull(valueType);}public K getKey() { return e.getKey(); }public V getValue() { return e.getValue(); }public int hashCode() { return e.hashCode(); }public String toString() { return e.toString(); }public V setValue(V value) {if (value != null && !valueType.isInstance(value))throw new ClassCastException(badValueMsg(value));return e.setValue(value);}private String badValueMsg(Object value) {return "Attempt to insert " + value.getClass() +" value into map with value type " + valueType;}public boolean equals(Object o) {if (o == this)return true;if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))return false;return e.equals(new AbstractMap.SimpleImmutableEntry<>((Map.Entry<?,?>)o));}}}}/*** Returns a dynamically typesafe view of the specified sorted map.* Any attempt to insert a mapping whose key or value have the wrong* type will result in an immediate {@link ClassCastException}.* Similarly, any attempt to modify the value currently associated with* a key will result in an immediate {@link ClassCastException},* whether the modification is attempted directly through the map* itself, or through a {@link Map.Entry} instance obtained from the* map's {@link Map#entrySet() entry set} view.** <p>Assuming a map contains no incorrectly typed keys or values* prior to the time a dynamically typesafe view is generated, and* that all subsequent access to the map takes place through the view* (or one of its collection views), it is <i>guaranteed</i> that the* map cannot contain an incorrectly typed key or value.** <p>A discussion of the use of dynamically typesafe views may be* found in the documentation for the {@link #checkedCollection* checkedCollection} method.** <p>The returned map will be serializable if the specified map is* serializable.** <p>Since {@code null} is considered to be a value of any reference* type, the returned map permits insertion of null keys or values* whenever the backing map does.** @param <K> the class of the map keys* @param <V> the class of the map values* @param m the map for which a dynamically typesafe view is to be* returned* @param keyType the type of key that {@code m} is permitted to hold* @param valueType the type of value that {@code m} is permitted to hold* @return a dynamically typesafe view of the specified map* @since 1.5*/public static <K,V> SortedMap<K,V> checkedSortedMap(SortedMap<K, V> m,Class<K> keyType,Class<V> valueType) {return new CheckedSortedMap<>(m, keyType, valueType);}/*** @serial include*/static class CheckedSortedMap<K,V> extends CheckedMap<K,V>implements SortedMap<K,V>, Serializable{private static final long serialVersionUID = 1599671320688067438L;private final SortedMap<K, V> sm;CheckedSortedMap(SortedMap<K, V> m,Class<K> keyType, Class<V> valueType) {super(m, keyType, valueType);sm = m;}public Comparator<? super K> comparator() { return sm.comparator(); }public K firstKey() { return sm.firstKey(); }public K lastKey() { return sm.lastKey(); }public SortedMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, K toKey) {return checkedSortedMap(sm.subMap(fromKey, toKey),keyType, valueType);}public SortedMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey) {return checkedSortedMap(sm.headMap(toKey), keyType, valueType);}public SortedMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey) {return checkedSortedMap(sm.tailMap(fromKey), keyType, valueType);}}/*** Returns a dynamically typesafe view of the specified navigable map.* Any attempt to insert a mapping whose key or value have the wrong* type will result in an immediate {@link ClassCastException}.* Similarly, any attempt to modify the value currently associated with* a key will result in an immediate {@link ClassCastException},* whether the modification is attempted directly through the map* itself, or through a {@link Map.Entry} instance obtained from the* map's {@link Map#entrySet() entry set} view.** <p>Assuming a map contains no incorrectly typed keys or values* prior to the time a dynamically typesafe view is generated, and* that all subsequent access to the map takes place through the view* (or one of its collection views), it is <em>guaranteed</em> that the* map cannot contain an incorrectly typed key or value.** <p>A discussion of the use of dynamically typesafe views may be* found in the documentation for the {@link #checkedCollection* checkedCollection} method.** <p>The returned map will be serializable if the specified map is* serializable.** <p>Since {@code null} is considered to be a value of any reference* type, the returned map permits insertion of null keys or values* whenever the backing map does.** @param <K> type of map keys* @param <V> type of map values* @param m the map for which a dynamically typesafe view is to be* returned* @param keyType the type of key that {@code m} is permitted to hold* @param valueType the type of value that {@code m} is permitted to hold* @return a dynamically typesafe view of the specified map* @since 1.8*/public static <K,V> NavigableMap<K,V> checkedNavigableMap(NavigableMap<K, V> m,Class<K> keyType,Class<V> valueType) {return new CheckedNavigableMap<>(m, keyType, valueType);}/*** @serial include*/static class CheckedNavigableMap<K,V> extends CheckedSortedMap<K,V>implements NavigableMap<K,V>, Serializable{private static final long serialVersionUID = -4852462692372534096L;private final NavigableMap<K, V> nm;CheckedNavigableMap(NavigableMap<K, V> m,Class<K> keyType, Class<V> valueType) {super(m, keyType, valueType);nm = m;}public Comparator<? super K> comparator() { return nm.comparator(); }public K firstKey() { return nm.firstKey(); }public K lastKey() { return nm.lastKey(); }public Entry<K, V> lowerEntry(K key) {Entry<K,V> lower = nm.lowerEntry(key);return (null != lower)? new CheckedMap.CheckedEntrySet.CheckedEntry<>(lower, valueType): null;}public K lowerKey(K key) { return nm.lowerKey(key); }public Entry<K, V> floorEntry(K key) {Entry<K,V> floor = nm.floorEntry(key);return (null != floor)? new CheckedMap.CheckedEntrySet.CheckedEntry<>(floor, valueType): null;}public K floorKey(K key) { return nm.floorKey(key); }public Entry<K, V> ceilingEntry(K key) {Entry<K,V> ceiling = nm.ceilingEntry(key);return (null != ceiling)? new CheckedMap.CheckedEntrySet.CheckedEntry<>(ceiling, valueType): null;}public K ceilingKey(K key) { return nm.ceilingKey(key); }public Entry<K, V> higherEntry(K key) {Entry<K,V> higher = nm.higherEntry(key);return (null != higher)? new CheckedMap.CheckedEntrySet.CheckedEntry<>(higher, valueType): null;}public K higherKey(K key) { return nm.higherKey(key); }public Entry<K, V> firstEntry() {Entry<K,V> first = nm.firstEntry();return (null != first)? new CheckedMap.CheckedEntrySet.CheckedEntry<>(first, valueType): null;}public Entry<K, V> lastEntry() {Entry<K,V> last = nm.lastEntry();return (null != last)? new CheckedMap.CheckedEntrySet.CheckedEntry<>(last, valueType): null;}public Entry<K, V> pollFirstEntry() {Entry<K,V> entry = nm.pollFirstEntry();return (null == entry)? null: new CheckedMap.CheckedEntrySet.CheckedEntry<>(entry, valueType);}public Entry<K, V> pollLastEntry() {Entry<K,V> entry = nm.pollLastEntry();return (null == entry)? null: new CheckedMap.CheckedEntrySet.CheckedEntry<>(entry, valueType);}public NavigableMap<K, V> descendingMap() {return checkedNavigableMap(nm.descendingMap(), keyType, valueType);}public NavigableSet<K> keySet() {return navigableKeySet();}public NavigableSet<K> navigableKeySet() {return checkedNavigableSet(nm.navigableKeySet(), keyType);}public NavigableSet<K> descendingKeySet() {return checkedNavigableSet(nm.descendingKeySet(), keyType);}@Overridepublic NavigableMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, K toKey) {return checkedNavigableMap(nm.subMap(fromKey, true, toKey, false),keyType, valueType);}@Overridepublic NavigableMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey) {return checkedNavigableMap(nm.headMap(toKey, false), keyType, valueType);}@Overridepublic NavigableMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey) {return checkedNavigableMap(nm.tailMap(fromKey, true), keyType, valueType);}public NavigableMap<K, V> subMap(K fromKey, boolean fromInclusive, K toKey, boolean toInclusive) {return checkedNavigableMap(nm.subMap(fromKey, fromInclusive, toKey, toInclusive), keyType, valueType);}public NavigableMap<K, V> headMap(K toKey, boolean inclusive) {return checkedNavigableMap(nm.headMap(toKey, inclusive), keyType, valueType);}public NavigableMap<K, V> tailMap(K fromKey, boolean inclusive) {return checkedNavigableMap(nm.tailMap(fromKey, inclusive), keyType, valueType);}}// Empty collections/*** Returns an iterator that has no elements. More precisely,** <ul>* <li>{@link Iterator#hasNext hasNext} always returns {@code* false}.</li>* <li>{@link Iterator#next next} always throws {@link* NoSuchElementException}.</li>* <li>{@link Iterator#remove remove} always throws {@link* IllegalStateException}.</li>* </ul>** <p>Implementations of this method are permitted, but not* required, to return the same object from multiple invocations.** @param <T> type of elements, if there were any, in the iterator* @return an empty iterator* @since 1.7*/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public static <T> Iterator<T> emptyIterator() {return (Iterator<T>) EmptyIterator.EMPTY_ITERATOR;}private static class EmptyIterator<E> implements Iterator<E> {static final EmptyIterator<Object> EMPTY_ITERATOR= new EmptyIterator<>();public boolean hasNext() { return false; }public E next() { throw new NoSuchElementException(); }public void remove() { throw new IllegalStateException(); }@Overridepublic void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {Objects.requireNonNull(action);}}/*** Returns a list iterator that has no elements. More precisely,** <ul>* <li>{@link Iterator#hasNext hasNext} and {@link* ListIterator#hasPrevious hasPrevious} always return {@code* false}.</li>* <li>{@link Iterator#next next} and {@link ListIterator#previous* previous} always throw {@link NoSuchElementException}.</li>* <li>{@link Iterator#remove remove} and {@link ListIterator#set* set} always throw {@link IllegalStateException}.</li>* <li>{@link ListIterator#add add} always throws {@link* UnsupportedOperationException}.</li>* <li>{@link ListIterator#nextIndex nextIndex} always returns* {@code 0}.</li>* <li>{@link ListIterator#previousIndex previousIndex} always* returns {@code -1}.</li>* </ul>** <p>Implementations of this method are permitted, but not* required, to return the same object from multiple invocations.** @param <T> type of elements, if there were any, in the iterator* @return an empty list iterator* @since 1.7*/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public static <T> ListIterator<T> emptyListIterator() {return (ListIterator<T>) EmptyListIterator.EMPTY_ITERATOR;}private static class EmptyListIterator<E>extends EmptyIterator<E>implements ListIterator<E>{static final EmptyListIterator<Object> EMPTY_ITERATOR= new EmptyListIterator<>();public boolean hasPrevious() { return false; }public E previous() { throw new NoSuchElementException(); }public int nextIndex() { return 0; }public int previousIndex() { return -1; }public void set(E e) { throw new IllegalStateException(); }public void add(E e) { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); }}/*** Returns an enumeration that has no elements. More precisely,** <ul>* <li>{@link Enumeration#hasMoreElements hasMoreElements} always* returns {@code false}.</li>* <li> {@link Enumeration#nextElement nextElement} always throws* {@link NoSuchElementException}.</li>* </ul>** <p>Implementations of this method are permitted, but not* required, to return the same object from multiple invocations.** @param <T> the class of the objects in the enumeration* @return an empty enumeration* @since 1.7*/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public static <T> Enumeration<T> emptyEnumeration() {return (Enumeration<T>) EmptyEnumeration.EMPTY_ENUMERATION;}private static class EmptyEnumeration<E> implements Enumeration<E> {static final EmptyEnumeration<Object> EMPTY_ENUMERATION= new EmptyEnumeration<>();public boolean hasMoreElements() { return false; }public E nextElement() { throw new NoSuchElementException(); }}/*** The empty set (immutable). This set is serializable.** @see #emptySet()*/@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")public static final Set EMPTY_SET = new EmptySet<>();/*** Returns an empty set (immutable). This set is serializable.* Unlike the like-named field, this method is parameterized.** <p>This example illustrates the type-safe way to obtain an empty set:*<pre>* Set<String> s = Collections.emptySet();* </pre>* @implNote Implementations of this method need not create a separate* {@code Set} object for each call. Using this method is likely to have* comparable cost to using the like-named field. (Unlike this method, the* field does not provide type safety.)** @param <T> the class of the objects in the set* @return the empty set** @see #EMPTY_SET* @since 1.5*/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public static final <T> Set<T> emptySet() {return (Set<T>) EMPTY_SET;}/*** @serial include*/private static class EmptySet<E>extends AbstractSet<E>implements Serializable{private static final long serialVersionUID = 1582296315990362920L;public Iterator<E> iterator() { return emptyIterator(); }public int size() {return 0;}public boolean isEmpty() {return true;}public boolean contains(Object obj) {return false;}public boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) { return c.isEmpty(); }public Object[] toArray() { return new Object[0]; }public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {if (a.length > 0)a[0] = null;return a;}// Override default methods in Collection@Overridepublic void forEach(Consumer<? super E> action) {Objects.requireNonNull(action);}@Overridepublic boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) {Objects.requireNonNull(filter);return false;}@Overridepublic Spliterator<E> spliterator() { return Spliterators.emptySpliterator(); }// Preserves singleton propertyprivate Object readResolve() {return EMPTY_SET;}}/*** Returns an empty sorted set (immutable). This set is serializable.** <p>This example illustrates the type-safe way to obtain an empty* sorted set:*<pre> {@code* SortedSet<String> s = Collections.emptySortedSet();* }</pre>** @implNote Implementations of this method need not create a separate* {@code SortedSet} object for each call.** @param <E> type of elements, if there were any, in the set* @return the empty sorted set* @since 1.8*/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public static <E> SortedSet<E> emptySortedSet() {return (SortedSet<E>) UnmodifiableNavigableSet.EMPTY_NAVIGABLE_SET;}/*** Returns an empty navigable set (immutable). This set is serializable.** <p>This example illustrates the type-safe way to obtain an empty* navigable set:*<pre> {@code* NavigableSet<String> s = Collections.emptyNavigableSet();* }</pre>** @implNote Implementations of this method need not* create a separate {@code NavigableSet} object for each call.** @param <E> type of elements, if there were any, in the set* @return the empty navigable set* @since 1.8*/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public static <E> NavigableSet<E> emptyNavigableSet() {return (NavigableSet<E>) UnmodifiableNavigableSet.EMPTY_NAVIGABLE_SET;}/*** The empty list (immutable). This list is serializable.** @see #emptyList()*/@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")public static final List EMPTY_LIST = new EmptyList<>();/*** Returns an empty list (immutable). This list is serializable.** <p>This example illustrates the type-safe way to obtain an empty list:*<pre>* List<String> s = Collections.emptyList();* </pre>** @implNote* Implementations of this method need not create a separate <tt>List</tt>* object for each call. Using this method is likely to have comparable* cost to using the like-named field. (Unlike this method, the field does* not provide type safety.)** @param <T> type of elements, if there were any, in the list* @return an empty immutable list** @see #EMPTY_LIST* @since 1.5*/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public static final <T> List<T> emptyList() {return (List<T>) EMPTY_LIST;}/*** @serial include*/private static class EmptyList<E>extends AbstractList<E>implements RandomAccess, Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = 8842843931221139166L;public Iterator<E> iterator() {return emptyIterator();}public ListIterator<E> listIterator() {return emptyListIterator();}public int size() {return 0;}public boolean isEmpty() {return true;}public boolean contains(Object obj) {return false;}public boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) { return c.isEmpty(); }public Object[] toArray() { return new Object[0]; }public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {if (a.length > 0)a[0] = null;return a;}public E get(int index) {throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index);}public boolean equals(Object o) {return (o instanceof List) && ((List<?>)o).isEmpty();}public int hashCode() { return 1; }@Overridepublic boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) {Objects.requireNonNull(filter);return false;}@Overridepublic void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<E> operator) {Objects.requireNonNull(operator);}@Overridepublic void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) {}// Override default methods in Collection@Overridepublic void forEach(Consumer<? super E> action) {Objects.requireNonNull(action);}@Overridepublic Spliterator<E> spliterator() { return Spliterators.emptySpliterator(); }// Preserves singleton propertyprivate Object readResolve() {return EMPTY_LIST;}}/*** The empty map (immutable). This map is serializable.** @see #emptyMap()* @since 1.3*/@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")public static final Map EMPTY_MAP = new EmptyMap<>();/*** Returns an empty map (immutable). This map is serializable.** <p>This example illustrates the type-safe way to obtain an empty map:*<pre>* Map<String, Date> s = Collections.emptyMap();* </pre>* @implNote Implementations of this method need not create a separate* {@code Map} object for each call. Using this method is likely to have* comparable cost to using the like-named field. (Unlike this method, the* field does not provide type safety.)** @param <K> the class of the map keys* @param <V> the class of the map values* @return an empty map* @see #EMPTY_MAP* @since 1.5*/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public static final <K,V> Map<K,V> emptyMap() {return (Map<K,V>) EMPTY_MAP;}/*** Returns an empty sorted map (immutable). This map is serializable.** <p>This example illustrates the type-safe way to obtain an empty map:*<pre> {@code* SortedMap<String, Date> s = Collections.emptySortedMap();* }</pre>** @implNote Implementations of this method need not create a separate* {@code SortedMap} object for each call.** @param <K> the class of the map keys* @param <V> the class of the map values* @return an empty sorted map* @since 1.8*/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public static final <K,V> SortedMap<K,V> emptySortedMap() {return (SortedMap<K,V>) UnmodifiableNavigableMap.EMPTY_NAVIGABLE_MAP;}/*** Returns an empty navigable map (immutable). This map is serializable.** <p>This example illustrates the type-safe way to obtain an empty map:*<pre> {@code* NavigableMap<String, Date> s = Collections.emptyNavigableMap();* }</pre>** @implNote Implementations of this method need not create a separate* {@code NavigableMap} object for each call.** @param <K> the class of the map keys* @param <V> the class of the map values* @return an empty navigable map* @since 1.8*/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public static final <K,V> NavigableMap<K,V> emptyNavigableMap() {return (NavigableMap<K,V>) UnmodifiableNavigableMap.EMPTY_NAVIGABLE_MAP;}/*** @serial include*/private static class EmptyMap<K,V>extends AbstractMap<K,V>implements Serializable{private static final long serialVersionUID = 6428348081105594320L;public int size() {return 0;}public boolean isEmpty() {return true;}public boolean containsKey(Object key) {return false;}public boolean containsValue(Object value) {return false;}public V get(Object key) {return null;}public Set<K> keySet() {return emptySet();}public Collection<V> values() {return emptySet();}public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() {return emptySet();}public boolean equals(Object o) {return (o instanceof Map) && ((Map<?,?>)o).isEmpty();}public int hashCode() {return 0;}// Override default methods in Map@Override@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public V getOrDefault(Object k, V defaultValue) {return defaultValue;}@Overridepublic void forEach(BiConsumer<? super K, ? super V> action) {Objects.requireNonNull(action);}@Overridepublic void replaceAll(BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> function) {Objects.requireNonNull(function);}@Overridepublic V putIfAbsent(K key, V value) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}@Overridepublic boolean remove(Object key, Object value) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}@Overridepublic boolean replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}@Overridepublic V replace(K key, V value) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}@Overridepublic V computeIfAbsent(K key,Function<? super K, ? extends V> mappingFunction) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}@Overridepublic V computeIfPresent(K key,BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}@Overridepublic V compute(K key,BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}@Overridepublic V merge(K key, V value,BiFunction<? super V, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}// Preserves singleton propertyprivate Object readResolve() {return EMPTY_MAP;}}// Singleton collections/*** Returns an immutable set containing only the specified object.* The returned set is serializable.** @param <T> the class of the objects in the set* @param o the sole object to be stored in the returned set.* @return an immutable set containing only the specified object.*/public static <T> Set<T> singleton(T o) {return new SingletonSet<>(o);}static <E> Iterator<E> singletonIterator(final E e) {return new Iterator<E>() {private boolean hasNext = true;public boolean hasNext() {return hasNext;}public E next() {if (hasNext) {hasNext = false;return e;}throw new NoSuchElementException();}public void remove() {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}@Overridepublic void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {Objects.requireNonNull(action);if (hasNext) {action.accept(e);hasNext = false;}}};}/*** Creates a {@code Spliterator} with only the specified element** @param <T> Type of elements* @return A singleton {@code Spliterator}*/static <T> Spliterator<T> singletonSpliterator(final T element) {return new Spliterator<T>() {long est = 1;@Overridepublic Spliterator<T> trySplit() {return null;}@Overridepublic boolean tryAdvance(Consumer<? super T> consumer) {Objects.requireNonNull(consumer);if (est > 0) {est--;consumer.accept(element);return true;}return false;}@Overridepublic void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super T> consumer) {tryAdvance(consumer);}@Overridepublic long estimateSize() {return est;}@Overridepublic int characteristics() {int value = (element != null) ? Spliterator.NONNULL : 0;return value | Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.SUBSIZED | Spliterator.IMMUTABLE |Spliterator.DISTINCT | Spliterator.ORDERED;}};}/*** @serial include*/private static class SingletonSet<E>extends AbstractSet<E>implements Serializable{private static final long serialVersionUID = 3193687207550431679L;private final E element;SingletonSet(E e) {element = e;}public Iterator<E> iterator() {return singletonIterator(element);}public int size() {return 1;}public boolean contains(Object o) {return eq(o, element);}// Override default methods for Collection@Overridepublic void forEach(Consumer<? super E> action) {action.accept(element);}@Overridepublic Spliterator<E> spliterator() {return singletonSpliterator(element);}@Overridepublic boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}}/*** Returns an immutable list containing only the specified object.* The returned list is serializable.** @param <T> the class of the objects in the list* @param o the sole object to be stored in the returned list.* @return an immutable list containing only the specified object.* @since 1.3*/public static <T> List<T> singletonList(T o) {return new SingletonList<>(o);}/*** @serial include*/private static class SingletonList<E>extends AbstractList<E>implements RandomAccess, Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = 3093736618740652951L;private final E element;SingletonList(E obj) {element = obj;}public Iterator<E> iterator() {return singletonIterator(element);}public int size() {return 1;}public boolean contains(Object obj) {return eq(obj, element);}public E get(int index) {if (index != 0)throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index+", Size: 1");return element;}// Override default methods for Collection@Overridepublic void forEach(Consumer<? super E> action) {action.accept(element);}@Overridepublic boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}@Overridepublic void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<E> operator) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}@Overridepublic void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) {}@Overridepublic Spliterator<E> spliterator() {return singletonSpliterator(element);}}/*** Returns an immutable map, mapping only the specified key to the* specified value. The returned map is serializable.** @param <K> the class of the map keys* @param <V> the class of the map values* @param key the sole key to be stored in the returned map.* @param value the value to which the returned map maps <tt>key</tt>.* @return an immutable map containing only the specified key-value* mapping.* @since 1.3*/public static <K,V> Map<K,V> singletonMap(K key, V value) {return new SingletonMap<>(key, value);}/*** @serial include*/private static class SingletonMap<K,V>extends AbstractMap<K,V>implements Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = -6979724477215052911L;private final K k;private final V v;SingletonMap(K key, V value) {k = key;v = value;}public int size() {return 1;}public boolean isEmpty() {return false;}public boolean containsKey(Object key) {return eq(key, k);}public boolean containsValue(Object value) {return eq(value, v);}public V get(Object key) {return (eq(key, k) ? v : null);}private transient Set<K> keySet;private transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet;private transient Collection<V> values;public Set<K> keySet() {if (keySet==null)keySet = singleton(k);return keySet;}public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() {if (entrySet==null)entrySet = Collections.<Map.Entry<K,V>>singleton(new SimpleImmutableEntry<>(k, v));return entrySet;}public Collection<V> values() {if (values==null)values = singleton(v);return values;}// Override default methods in Map@Overridepublic V getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) {return eq(key, k) ? v : defaultValue;}@Overridepublic void forEach(BiConsumer<? super K, ? super V> action) {action.accept(k, v);}@Overridepublic void replaceAll(BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> function) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}@Overridepublic V putIfAbsent(K key, V value) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}@Overridepublic boolean remove(Object key, Object value) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}@Overridepublic boolean replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}@Overridepublic V replace(K key, V value) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}@Overridepublic V computeIfAbsent(K key,Function<? super K, ? extends V> mappingFunction) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}@Overridepublic V computeIfPresent(K key,BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}@Overridepublic V compute(K key,BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}@Overridepublic V merge(K key, V value,BiFunction<? super V, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}}// Miscellaneous/*** Returns an immutable list consisting of <tt>n</tt> copies of the* specified object. The newly allocated data object is tiny (it contains* a single reference to the data object). This method is useful in* combination with the <tt>List.addAll</tt> method to grow lists.* The returned list is serializable.** @param <T> the class of the object to copy and of the objects* in the returned list.* @param n the number of elements in the returned list.* @param o the element to appear repeatedly in the returned list.* @return an immutable list consisting of <tt>n</tt> copies of the* specified object.* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code n < 0}* @see List#addAll(Collection)* @see List#addAll(int, Collection)*/public static <T> List<T> nCopies(int n, T o) {if (n < 0)throw new IllegalArgumentException("List length = " + n);return new CopiesList<>(n, o);}/*** @serial include*/private static class CopiesList<E>extends AbstractList<E>implements RandomAccess, Serializable{private static final long serialVersionUID = 2739099268398711800L;final int n;final E element;CopiesList(int n, E e) {assert n >= 0;this.n = n;element = e;}public int size() {return n;}public boolean contains(Object obj) {return n != 0 && eq(obj, element);}public int indexOf(Object o) {return contains(o) ? 0 : -1;}public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {return contains(o) ? n - 1 : -1;}public E get(int index) {if (index < 0 || index >= n)throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index+", Size: "+n);return element;}public Object[] toArray() {final Object[] a = new Object[n];if (element != null)Arrays.fill(a, 0, n, element);return a;}@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {final int n = this.n;if (a.length < n) {a = (T[])java.lang.reflect.Array.newInstance(a.getClass().getComponentType(), n);if (element != null)Arrays.fill(a, 0, n, element);} else {Arrays.fill(a, 0, n, element);if (a.length > n)a[n] = null;}return a;}public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {if (fromIndex < 0)throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("fromIndex = " + fromIndex);if (toIndex > n)throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("toIndex = " + toIndex);if (fromIndex > toIndex)throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromIndex(" + fromIndex +") > toIndex(" + toIndex + ")");return new CopiesList<>(toIndex - fromIndex, element);}// Override default methods in Collection@Overridepublic Stream<E> stream() {return IntStream.range(0, n).mapToObj(i -> element);}@Overridepublic Stream<E> parallelStream() {return IntStream.range(0, n).parallel().mapToObj(i -> element);}@Overridepublic Spliterator<E> spliterator() {return stream().spliterator();}}/*** Returns a comparator that imposes the reverse of the <em>natural* ordering</em> on a collection of objects that implement the* {@code Comparable} interface. (The natural ordering is the ordering* imposed by the objects' own {@code compareTo} method.) This enables a* simple idiom for sorting (or maintaining) collections (or arrays) of* objects that implement the {@code Comparable} interface in* reverse-natural-order. For example, suppose {@code a} is an array of* strings. Then:<pre>* Arrays.sort(a, Collections.reverseOrder());* </pre> sorts the array in reverse-lexicographic (alphabetical) order.<p>** The returned comparator is serializable.** @param <T> the class of the objects compared by the comparator* @return A comparator that imposes the reverse of the <i>natural* ordering</i> on a collection of objects that implement* the <tt>Comparable</tt> interface.* @see Comparable*/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public static <T> Comparator<T> reverseOrder() {return (Comparator<T>) ReverseComparator.REVERSE_ORDER;}/*** @serial include*/private static class ReverseComparatorimplements Comparator<Comparable<Object>>, Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = 7207038068494060240L;static final ReverseComparator REVERSE_ORDER= new ReverseComparator();public int compare(Comparable<Object> c1, Comparable<Object> c2) {return c2.compareTo(c1);}private Object readResolve() { return Collections.reverseOrder(); }@Overridepublic Comparator<Comparable<Object>> reversed() {return Comparator.naturalOrder();}}/*** Returns a comparator that imposes the reverse ordering of the specified* comparator. If the specified comparator is {@code null}, this method is* equivalent to {@link #reverseOrder()} (in other words, it returns a* comparator that imposes the reverse of the <em>natural ordering</em> on* a collection of objects that implement the Comparable interface).** <p>The returned comparator is serializable (assuming the specified* comparator is also serializable or {@code null}).** @param <T> the class of the objects compared by the comparator* @param cmp a comparator who's ordering is to be reversed by the returned* comparator or {@code null}* @return A comparator that imposes the reverse ordering of the* specified comparator.* @since 1.5*/public static <T> Comparator<T> reverseOrder(Comparator<T> cmp) {if (cmp == null)return reverseOrder();if (cmp instanceof ReverseComparator2)return ((ReverseComparator2<T>)cmp).cmp;return new ReverseComparator2<>(cmp);}/*** @serial include*/private static class ReverseComparator2<T> implements Comparator<T>,Serializable{private static final long serialVersionUID = 4374092139857L;/*** The comparator specified in the static factory. This will never* be null, as the static factory returns a ReverseComparator* instance if its argument is null.** @serial*/final Comparator<T> cmp;ReverseComparator2(Comparator<T> cmp) {assert cmp != null;this.cmp = cmp;}public int compare(T t1, T t2) {return cmp.compare(t2, t1);}public boolean equals(Object o) {return (o == this) ||(o instanceof ReverseComparator2 &&cmp.equals(((ReverseComparator2)o).cmp));}public int hashCode() {return cmp.hashCode() ^ Integer.MIN_VALUE;}@Overridepublic Comparator<T> reversed() {return cmp;}}/*** Returns an enumeration over the specified collection. This provides* interoperability with legacy APIs that require an enumeration* as input.** @param <T> the class of the objects in the collection* @param c the collection for which an enumeration is to be returned.* @return an enumeration over the specified collection.* @see Enumeration*/public static <T> Enumeration<T> enumeration(final Collection<T> c) {return new Enumeration<T>() {private final Iterator<T> i = c.iterator();public boolean hasMoreElements() {return i.hasNext();}public T nextElement() {return i.next();}};}/*** Returns an array list containing the elements returned by the* specified enumeration in the order they are returned by the* enumeration. This method provides interoperability between* legacy APIs that return enumerations and new APIs that require* collections.** @param <T> the class of the objects returned by the enumeration* @param e enumeration providing elements for the returned* array list* @return an array list containing the elements returned* by the specified enumeration.* @since 1.4* @see Enumeration* @see ArrayList*/public static <T> ArrayList<T> list(Enumeration<T> e) {ArrayList<T> l = new ArrayList<>();while (e.hasMoreElements())l.add(e.nextElement());return l;}/*** Returns true if the specified arguments are equal, or both null.** NB: Do not replace with Object.equals until JDK-8015417 is resolved.*/static boolean eq(Object o1, Object o2) {return o1==null ? o2==null : o1.equals(o2);}/*** Returns the number of elements in the specified collection equal to the* specified object. More formally, returns the number of elements* <tt>e</tt> in the collection such that* <tt>(o == null ? e == null : o.equals(e))</tt>.** @param c the collection in which to determine the frequency* of <tt>o</tt>* @param o the object whose frequency is to be determined* @return the number of elements in {@code c} equal to {@code o}* @throws NullPointerException if <tt>c</tt> is null* @since 1.5*/public static int frequency(Collection<?> c, Object o) {int result = 0;if (o == null) {for (Object e : c)if (e == null)result++;} else {for (Object e : c)if (o.equals(e))result++;}return result;}/*** Returns {@code true} if the two specified collections have no* elements in common.** <p>Care must be exercised if this method is used on collections that* do not comply with the general contract for {@code Collection}.* Implementations may elect to iterate over either collection and test* for containment in the other collection (or to perform any equivalent* computation). If either collection uses a nonstandard equality test* (as does a {@link SortedSet} whose ordering is not <em>compatible with* equals</em>, or the key set of an {@link IdentityHashMap}), both* collections must use the same nonstandard equality test, or the* result of this method is undefined.** <p>Care must also be exercised when using collections that have* restrictions on the elements that they may contain. Collection* implementations are allowed to throw exceptions for any operation* involving elements they deem ineligible. For absolute safety the* specified collections should contain only elements which are* eligible elements for both collections.** <p>Note that it is permissible to pass the same collection in both* parameters, in which case the method will return {@code true} if and* only if the collection is empty.** @param c1 a collection* @param c2 a collection* @return {@code true} if the two specified collections have no* elements in common.* @throws NullPointerException if either collection is {@code null}.* @throws NullPointerException if one collection contains a {@code null}* element and {@code null} is not an eligible element for the other collection.* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)* @throws ClassCastException if one collection contains an element that is* of a type which is ineligible for the other collection.* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)* @since 1.5*/public static boolean disjoint(Collection<?> c1, Collection<?> c2) {// The collection to be used for contains(). Preference is given to// the collection who's contains() has lower O() complexity.Collection<?> contains = c2;// The collection to be iterated. If the collections' contains() impl// are of different O() complexity, the collection with slower// contains() will be used for iteration. For collections who's// contains() are of the same complexity then best performance is// achieved by iterating the smaller collection.Collection<?> iterate = c1;// Performance optimization cases. The heuristics:// 1. Generally iterate over c1.// 2. If c1 is a Set then iterate over c2.// 3. If either collection is empty then result is always true.// 4. Iterate over the smaller Collection.if (c1 instanceof Set) {// Use c1 for contains as a Set's contains() is expected to perform// better than O(N/2)iterate = c2;contains = c1;} else if (!(c2 instanceof Set)) {// Both are mere Collections. Iterate over smaller collection.// Example: If c1 contains 3 elements and c2 contains 50 elements and// assuming contains() requires ceiling(N/2) comparisons then// checking for all c1 elements in c2 would require 75 comparisons// (3 * ceiling(50/2)) vs. checking all c2 elements in c1 requiring// 100 comparisons (50 * ceiling(3/2)).int c1size = c1.size();int c2size = c2.size();if (c1size == 0 || c2size == 0) {// At least one collection is empty. Nothing will match.return true;}if (c1size > c2size) {iterate = c2;contains = c1;}}for (Object e : iterate) {if (contains.contains(e)) {// Found a common element. Collections are not disjoint.return false;}}// No common elements were found.return true;}/*** Adds all of the specified elements to the specified collection.* Elements to be added may be specified individually or as an array.* The behavior of this convenience method is identical to that of* <tt>c.addAll(Arrays.asList(elements))</tt>, but this method is likely* to run significantly faster under most implementations.** <p>When elements are specified individually, this method provides a* convenient way to add a few elements to an existing collection:*<pre>* Collections.addAll(flavors, "Peaches 'n Plutonium", "Rocky Racoon");* </pre>** @param <T> the class of the elements to add and of the collection* @param c the collection into which <tt>elements</tt> are to be inserted* @param elements the elements to insert into <tt>c</tt>* @return <tt>true</tt> if the collection changed as a result of the call* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if <tt>c</tt> does not support* the <tt>add</tt> operation* @throws NullPointerException if <tt>elements</tt> contains one or more* null values and <tt>c</tt> does not permit null elements, or* if <tt>c</tt> or <tt>elements</tt> are <tt>null</tt>* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of a value in* <tt>elements</tt> prevents it from being added to <tt>c</tt>* @see Collection#addAll(Collection)* @since 1.5*/@SafeVarargspublic static <T> boolean addAll(Collection<? super T> c, T... elements) {boolean result = false;for (T element : elements)result |= c.add(element);return result;}public static <E> Set<E> newSetFromMap(Map<E, Boolean> map) {//1.6return new SetFromMap<>(map);}private static class SetFromMap<E> extends AbstractSet<E>implements Set<E>, Serializable{private final Map<E, Boolean> m; // The backing mapprivate transient Set<E> s; // Its keySetSetFromMap(Map<E, Boolean> map) {if (!map.isEmpty())throw new IllegalArgumentException("Map is non-empty");m = map;s = map.keySet();}public void clear() { m.clear(); }public int size() { return m.size(); }public boolean isEmpty() { return m.isEmpty(); }public boolean contains(Object o) { return m.containsKey(o); }public boolean remove(Object o) { return m.remove(o) != null; }public boolean add(E e) { return m.put(e, Boolean.TRUE) == null; }public Iterator<E> iterator() { return s.iterator(); }public Object[] toArray() { return s.toArray(); }public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) { return s.toArray(a); }public String toString() { return s.toString(); }public int hashCode() { return s.hashCode(); }public boolean equals(Object o) { return o == this || s.equals(o); }public boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) {return s.containsAll(c);}public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {return s.removeAll(c);}public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) {return s.retainAll(c);}@Overridepublic void forEach(Consumer<? super E> action) {s.forEach(action);}@Overridepublic boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) {return s.removeIf(filter);}@Overridepublic Spliterator<E> spliterator() {return s.spliterator();}@Overridepublic Stream<E> stream() {return s.stream();}@Overridepublic Stream<E> parallelStream() {return s.parallelStream();}private static final long serialVersionUID = 2454657854757543876L;private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream stream)throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException{stream.defaultReadObject();s = m.keySet();}}public static <T> Queue<T> asLifoQueue(Deque<T> deque) {//1.6return new AsLIFOQueue<>(deque);}static class AsLIFOQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E>implements Queue<E>, Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = 1802017725587941708L;private final Deque<E> q;AsLIFOQueue(Deque<E> q) { this.q = q; }public boolean add(E e) { q.addFirst(e); return true; }public boolean offer(E e) { return q.offerFirst(e); }public E poll() { return q.pollFirst(); }public E remove() { return q.removeFirst(); }public E peek() { return q.peekFirst(); }public E element() { return q.getFirst(); }public void clear() { q.clear(); }public int size() { return q.size(); }public boolean isEmpty() { return q.isEmpty(); }public boolean contains(Object o) { return q.contains(o); }public boolean remove(Object o) { return q.remove(o); }public Iterator<E> iterator() { return q.iterator(); }public Object[] toArray() { return q.toArray(); }public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) { return q.toArray(a); }public String toString() { return q.toString(); }public boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) {return q.containsAll(c);}public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {return q.removeAll(c);}public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) {return q.retainAll(c);}@Overridepublic void forEach(Consumer<? super E> action) {q.forEach(action);}@Overridepublic boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) {return q.removeIf(filter);}@Overridepublic Spliterator<E> spliterator() {return q.spliterator();}@Overridepublic Stream<E> stream() {return q.stream();}@Overridepublic Stream<E> parallelStream() {return q.parallelStream();}}}
Arrays工具类
Arrays是一个操作数组的工具类。
常见方法:
1.二分查找:binarySearch(int[]); binarySearch(double[]);
2.数组排序:sort(int []); sort(char[]);
3.将数组变成字符串:toString(int []);
4.复制数组:copyOf(int/boolean…[] original,int newLength);
5.复制部分数组:copyOfRange(int/float[]… original, int from, int to);
6.比较两个数组是否相同:equals(int[],int[]);
7.将数组变为集合:List asList(T[]);
public class Arrays {
private static final int MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN = 1 << 13;
private Arrays() {}
static final class NaturalOrder implements Comparator<Object> {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public int compare(Object first, Object second) {
return ((Comparable<Object>)first).compareTo(second);
}
static final NaturalOrder INSTANCE = new NaturalOrder();
}
private static void rangeCheck(int arrayLength, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
if (fromIndex > toIndex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"fromIndex(" + fromIndex + ") > toIndex(" + toIndex + ")");
}
if (fromIndex < 0) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(fromIndex);
}
if (toIndex > arrayLength) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(toIndex);
}
}
public static void sort(int[] a) {
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, a.length - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void sort(int[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void sort(long[] a) {
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, a.length - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void sort(long[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void sort(short[] a) {
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, a.length - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void sort(short[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void sort(char[] a) {
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, a.length - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void sort(char[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void sort(byte[] a) {
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, a.length - 1);
}
public static void sort(byte[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1);
}
public static void sort(float[] a) {
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, a.length - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void sort(float[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void sort(double[] a) {
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, a.length - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void sort(double[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {//1.8
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void parallelSort(byte[] a) {//1.8
int n = a.length, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, n - 1);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJByte.Sorter
(null, a, new byte[n], 0, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(byte[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {//1.8
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
int n = toIndex - fromIndex, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJByte.Sorter
(null, a, new byte[n], fromIndex, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(char[] a) {//1.8
int n = a.length, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, n - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJChar.Sorter
(null, a, new char[n], 0, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(char[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {//1.8
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
int n = toIndex - fromIndex, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJChar.Sorter
(null, a, new char[n], fromIndex, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(short[] a) {//1.8
int n = a.length, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, n - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJShort.Sorter
(null, a, new short[n], 0, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(short[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {//1.8
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
int n = toIndex - fromIndex, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJShort.Sorter
(null, a, new short[n], fromIndex, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(int[] a) {//1.8
int n = a.length, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, n - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJInt.Sorter
(null, a, new int[n], 0, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(int[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {//1.8
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
int n = toIndex - fromIndex, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJInt.Sorter
(null, a, new int[n], fromIndex, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(long[] a) {//1.8
int n = a.length, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, n - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJLong.Sorter
(null, a, new long[n], 0, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(long[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {//1.8
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
int n = toIndex - fromIndex, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJLong.Sorter
(null, a, new long[n], fromIndex, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(float[] a) {//1.8
int n = a.length, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, n - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJFloat.Sorter
(null, a, new float[n], 0, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(float[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {//1.8
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
int n = toIndex - fromIndex, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJFloat.Sorter
(null, a, new float[n], fromIndex, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(double[] a) {//1.8
int n = a.length, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, n - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJDouble.Sorter
(null, a, new double[n], 0, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(double[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {//1.8
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
int n = toIndex - fromIndex, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJDouble.Sorter
(null, a, new double[n], fromIndex, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> void parallelSort(T[] a) {//1.8
int n = a.length, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
TimSort.sort(a, 0, n, NaturalOrder.INSTANCE, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJObject.Sorter<T>
(null, a,
(T[])Array.newInstance(a.getClass().getComponentType(), n),
0, n, 0, ((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g, NaturalOrder.INSTANCE).invoke();
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>>
void parallelSort(T[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {//1.8
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
int n = toIndex - fromIndex, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
TimSort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex, NaturalOrder.INSTANCE, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJObject.Sorter<T>
(null, a,
(T[])Array.newInstance(a.getClass().getComponentType(), n),
fromIndex, n, 0, ((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g, NaturalOrder.INSTANCE).invoke();
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T> void parallelSort(T[] a, Comparator<? super T> cmp) {//1.8
if (cmp == null)
cmp = NaturalOrder.INSTANCE;
int n = a.length, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
TimSort.sort(a, 0, n, cmp, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJObject.Sorter<T>
(null, a,
(T[])Array.newInstance(a.getClass().getComponentType(), n),
0, n, 0, ((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g, cmp).invoke();
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T> void parallelSort(T[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
Comparator<? super T> cmp) {//1.8
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
if (cmp == null)
cmp = NaturalOrder.INSTANCE;
int n = toIndex - fromIndex, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
TimSort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex, cmp, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJObject.Sorter<T>
(null, a,
(T[])Array.newInstance(a.getClass().getComponentType(), n),
fromIndex, n, 0, ((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g, cmp).invoke();
}
//Sorting of complex type arrays.
static final class LegacyMergeSort {
private static final boolean userRequested =
java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(
new sun.security.action.GetBooleanAction(
"java.util.Arrays.useLegacyMergeSort")).booleanValue();
}
public static void sort(Object[] a) {
if (LegacyMergeSort.userRequested)
legacyMergeSort(a);
else
ComparableTimSort.sort(a, 0, a.length, null, 0, 0);
}
private static void legacyMergeSort(Object[] a) {
Object[] aux = a.clone();
mergeSort(aux, a, 0, a.length, 0);
}
public static void sort(Object[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
if (LegacyMergeSort.userRequested)
legacyMergeSort(a, fromIndex, toIndex);
else
ComparableTimSort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex, null, 0, 0);
}
private static void legacyMergeSort(Object[] a,
int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
Object[] aux = copyOfRange(a, fromIndex, toIndex);
mergeSort(aux, a, fromIndex, toIndex, -fromIndex);
}
private static final int INSERTIONSORT_THRESHOLD = 7;
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes"})
private static void mergeSort(Object[] src,
Object[] dest,
int low,
int high,
int off) {
int length = high - low;
if (length < INSERTIONSORT_THRESHOLD) {
for (int i=low; i<high; i++)
for (int j=i; j>low &&
((Comparable) dest[j-1]).compareTo(dest[j])>0; j--)
swap(dest, j, j-1);
return;
}
int destLow = low;
int destHigh = high;
low += off;
high += off;
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
mergeSort(dest, src, low, mid, -off);
mergeSort(dest, src, mid, high, -off);
if (((Comparable)src[mid-1]).compareTo(src[mid]) <= 0) {
System.arraycopy(src, low, dest, destLow, length);
return;
}
for(int i = destLow, p = low, q = mid; i < destHigh; i++) {
if (q >= high || p < mid && ((Comparable)src[p]).compareTo(src[q])<=0)
dest[i] = src[p++];
else
dest[i] = src[q++];
}
}
private static void swap(Object[] x, int a, int b) {
Object t = x[a];
x[a] = x[b];
x[b] = t;
}
public static <T> void sort(T[] a, Comparator<? super T> c) {
if (c == null) {
sort(a);
} else {
if (LegacyMergeSort.userRequested)
legacyMergeSort(a, c);
else
TimSort.sort(a, 0, a.length, c, null, 0, 0);
}
}
private static <T> void legacyMergeSort(T[] a, Comparator<? super T> c) {
T[] aux = a.clone();
if (c==null)
mergeSort(aux, a, 0, a.length, 0);
else
mergeSort(aux, a, 0, a.length, 0, c);
}
public static <T> void sort(T[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
Comparator<? super T> c) {
if (c == null) {
sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex);
} else {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
if (LegacyMergeSort.userRequested)
legacyMergeSort(a, fromIndex, toIndex, c);
else
TimSort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex, c, null, 0, 0);
}
}
private static <T> void legacyMergeSort(T[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
Comparator<? super T> c) {
T[] aux = copyOfRange(a, fromIndex, toIndex);
if (c==null)
mergeSort(aux, a, fromIndex, toIndex, -fromIndex);
else
mergeSort(aux, a, fromIndex, toIndex, -fromIndex, c);
}
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes", "unchecked"})
private static void mergeSort(Object[] src,
Object[] dest,
int low, int high, int off,
Comparator c) {
int length = high - low;
if (length < INSERTIONSORT_THRESHOLD) {
for (int i=low; i<high; i++)
for (int j=i; j>low && c.compare(dest[j-1], dest[j])>0; j--)
swap(dest, j, j-1);
return;
}
int destLow = low;
int destHigh = high;
low += off;
high += off;
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
mergeSort(dest, src, low, mid, -off, c);
mergeSort(dest, src, mid, high, -off, c);
if (c.compare(src[mid-1], src[mid]) <= 0) {
System.arraycopy(src, low, dest, destLow, length);
return;
}
for(int i = destLow, p = low, q = mid; i < destHigh; i++) {
if (q >= high || p < mid && c.compare(src[p], src[q]) <= 0)
dest[i] = src[p++];
else
dest[i] = src[q++];
}
}
// Parallel prefix
public static <T> void parallelPrefix(T[] array, BinaryOperator<T> op) {//1.8
Objects.requireNonNull(op);
if (array.length > 0)
new ArrayPrefixHelpers.CumulateTask<>
(null, op, array, 0, array.length).invoke();
}
public static <T> void parallelPrefix(T[] array, int fromIndex,
int toIndex, BinaryOperator<T> op) {//1.8
Objects.requireNonNull(op);
rangeCheck(array.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
if (fromIndex < toIndex)
new ArrayPrefixHelpers.CumulateTask<>
(null, op, array, fromIndex, toIndex).invoke();
}
public static void parallelPrefix(long[] array, LongBinaryOperator op) {//1.8
Objects.requireNonNull(op);
if (array.length > 0)
new ArrayPrefixHelpers.LongCumulateTask
(null, op, array, 0, array.length).invoke();
}
public static void parallelPrefix(long[] array, int fromIndex,
int toIndex, LongBinaryOperator op) {//1.8
Objects.requireNonNull(op);
rangeCheck(array.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
if (fromIndex < toIndex)
new ArrayPrefixHelpers.LongCumulateTask
(null, op, array, fromIndex, toIndex).invoke();
}
public static void parallelPrefix(double[] array, DoubleBinaryOperator op) {//1.8
Objects.requireNonNull(op);
if (array.length > 0)
new ArrayPrefixHelpers.DoubleCumulateTask
(null, op, array, 0, array.length).invoke();
}
public static void parallelPrefix(double[] array, int fromIndex,
int toIndex, DoubleBinaryOperator op) {//1.8
Objects.requireNonNull(op);
rangeCheck(array.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
if (fromIndex < toIndex)
new ArrayPrefixHelpers.DoubleCumulateTask
(null, op, array, fromIndex, toIndex).invoke();
}
public static void parallelPrefix(int[] array, IntBinaryOperator op) {//1.8
Objects.requireNonNull(op);
if (array.length > 0)
new ArrayPrefixHelpers.IntCumulateTask
(null, op, array, 0, array.length).invoke();
}
public static void parallelPrefix(int[] array, int fromIndex,
int toIndex, IntBinaryOperator op) {//1.8
Objects.requireNonNull(op);
rangeCheck(array.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
if (fromIndex < toIndex)
new ArrayPrefixHelpers.IntCumulateTask
(null, op, array, fromIndex, toIndex).invoke();
}
// Searching
public static int binarySearch(long[] a, long key) {
return binarySearch0(a, 0, a.length, key);
}
public static int binarySearch(long[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
long key) {//1.6
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
return binarySearch0(a, fromIndex, toIndex, key);
}
private static int binarySearch0(long[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
long key) {
int low = fromIndex;
int high = toIndex - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
long midVal = a[mid];
if (midVal < key)
low = mid + 1;
else if (midVal > key)
high = mid - 1;
else
return mid; // key found
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found.
}
public static int binarySearch(int[] a, int key) {
return binarySearch0(a, 0, a.length, key);
}
public static int binarySearch(int[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
int key) {//1.6
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
return binarySearch0(a, fromIndex, toIndex, key);
}
private static int binarySearch0(int[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
int key) {
int low = fromIndex;
int high = toIndex - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
int midVal = a[mid];
if (midVal < key)
low = mid + 1;
else if (midVal > key)
high = mid - 1;
else
return mid; // key found
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found.
}
public static int binarySearch(short[] a, short key) {
return binarySearch0(a, 0, a.length, key);
}
public static int binarySearch(short[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
short key) {//1.6
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
return binarySearch0(a, fromIndex, toIndex, key);
}
private static int binarySearch0(short[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
short key) {
int low = fromIndex;
int high = toIndex - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
short midVal = a[mid];
if (midVal < key)
low = mid + 1;
else if (midVal > key)
high = mid - 1;
else
return mid; // key found
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found.
}
public static int binarySearch(char[] a, char key) {
return binarySearch0(a, 0, a.length, key);
}
public static int binarySearch(char[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
char key) {//1.6
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
return binarySearch0(a, fromIndex, toIndex, key);
}
// Like public version, but without range checks.
private static int binarySearch0(char[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
char key) {
int low = fromIndex;
int high = toIndex - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
char midVal = a[mid];
if (midVal < key)
low = mid + 1;
else if (midVal > key)
high = mid - 1;
else
return mid; // key found
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found.
}
public static int binarySearch(byte[] a, byte key) {
return binarySearch0(a, 0, a.length, key);
}
public static int binarySearch(byte[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
byte key) {//1.6
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
return binarySearch0(a, fromIndex, toIndex, key);
}
private static int binarySearch0(byte[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
byte key) {
int low = fromIndex;
int high = toIndex - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
byte midVal = a[mid];
if (midVal < key)
low = mid + 1;
else if (midVal > key)
high = mid - 1;
else
return mid; // key found
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found.
}
public static int binarySearch(double[] a, double key) {
return binarySearch0(a, 0, a.length, key);
}
public static int binarySearch(double[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
double key) {//1.6
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
return binarySearch0(a, fromIndex, toIndex, key);
}
private static int binarySearch0(double[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
double key) {
int low = fromIndex;
int high = toIndex - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
double midVal = a[mid];
if (midVal < key)
low = mid + 1; // Neither val is NaN, thisVal is smaller
else if (midVal > key)
high = mid - 1; // Neither val is NaN, thisVal is larger
else {
long midBits = Double.doubleToLongBits(midVal);
long keyBits = Double.doubleToLongBits(key);
if (midBits == keyBits) // Values are equal
return mid; // Key found
else if (midBits < keyBits) // (-0.0, 0.0) or (!NaN, NaN)
low = mid + 1;
else // (0.0, -0.0) or (NaN, !NaN)
high = mid - 1;
}
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found.
}
public static int binarySearch(float[] a, float key) {
return binarySearch0(a, 0, a.length, key);
}
public static int binarySearch(float[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
float key) {//1.6
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
return binarySearch0(a, fromIndex, toIndex, key);
}
private static int binarySearch0(float[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
float key) {
int low = fromIndex;
int high = toIndex - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
float midVal = a[mid];
if (midVal < key)
low = mid + 1; // Neither val is NaN, thisVal is smaller
else if (midVal > key)
high = mid - 1; // Neither val is NaN, thisVal is larger
else {
int midBits = Float.floatToIntBits(midVal);
int keyBits = Float.floatToIntBits(key);
if (midBits == keyBits) // Values are equal
return mid; // Key found
else if (midBits < keyBits) // (-0.0, 0.0) or (!NaN, NaN)
low = mid + 1;
else // (0.0, -0.0) or (NaN, !NaN)
high = mid - 1;
}
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found.
}
public static int binarySearch(Object[] a, Object key) {
return binarySearch0(a, 0, a.length, key);
}
public static int binarySearch(Object[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
Object key) {//1.6
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
return binarySearch0(a, fromIndex, toIndex, key);
}
private static int binarySearch0(Object[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
Object key) {
int low = fromIndex;
int high = toIndex - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
Comparable midVal = (Comparable)a[mid];
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
int cmp = midVal.compareTo(key);
if (cmp < 0)
low = mid + 1;
else if (cmp > 0)
high = mid - 1;
else
return mid; // key found
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found.
}
public static <T> int binarySearch(T[] a, T key, Comparator<? super T> c) {
return binarySearch0(a, 0, a.length, key, c);
}
public static <T> int binarySearch(T[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
T key, Comparator<? super T> c) {//1.6
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
return binarySearch0(a, fromIndex, toIndex, key, c);
}
private static <T> int binarySearch0(T[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
T key, Comparator<? super T> c) {
if (c == null) {
return binarySearch0(a, fromIndex, toIndex, key);
}
int low = fromIndex;
int high = toIndex - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
T midVal = a[mid];
int cmp = c.compare(midVal, key);
if (cmp < 0)
low = mid + 1;
else if (cmp > 0)
high = mid - 1;
else
return mid; // key found
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found.
}
// Equality Testing
public static boolean equals(long[] a, long[] a2) {
if (a==a2)
return true;
if (a==null || a2==null)
return false;
int length = a.length;
if (a2.length != length)
return false;
for (int i=0; i<length; i++)
if (a[i] != a2[i])
return false;
return true;
}
public static boolean equals(int[] a, int[] a2) {
if (a==a2)
return true;
if (a==null || a2==null)
return false;
int length = a.length;
if (a2.length != length)
return false;
for (int i=0; i<length; i++)
if (a[i] != a2[i])
return false;
return true;
}
public static boolean equals(short[] a, short a2[]) {
if (a==a2)
return true;
if (a==null || a2==null)
return false;
int length = a.length;
if (a2.length != length)
return false;
for (int i=0; i<length; i++)
if (a[i] != a2[i])
return false;
return true;
}
public static boolean equals(char[] a, char[] a2) {
if (a==a2)
return true;
if (a==null || a2==null)
return false;
int length = a.length;
if (a2.length != length)
return false;
for (int i=0; i<length; i++)
if (a[i] != a2[i])
return false;
return true;
}
public static boolean equals(byte[] a, byte[] a2) {
if (a==a2)
return true;
if (a==null || a2==null)
return false;
int length = a.length;
if (a2.length != length)
return false;
for (int i=0; i<length; i++)
if (a[i] != a2[i])
return false;
return true;
}
public static boolean equals(boolean[] a, boolean[] a2) {
if (a==a2)
return true;
if (a==null || a2==null)
return false;
int length = a.length;
if (a2.length != length)
return false;
for (int i=0; i<length; i++)
if (a[i] != a2[i])
return false;
return true;
}
public static boolean equals(double[] a, double[] a2) {
if (a==a2)
return true;
if (a==null || a2==null)
return false;
int length = a.length;
if (a2.length != length)
return false;
for (int i=0; i<length; i++)
if (Double.doubleToLongBits(a[i])!=Double.doubleToLongBits(a2[i]))
return false;
return true;
}
public static boolean equals(float[] a, float[] a2) {
if (a==a2)
return true;
if (a==null || a2==null)
return false;
int length = a.length;
if (a2.length != length)
return false;
for (int i=0; i<length; i++)
if (Float.floatToIntBits(a[i])!=Float.floatToIntBits(a2[i]))
return false;
return true;
}
public static boolean equals(Object[] a, Object[] a2) {
if (a==a2)
return true;
if (a==null || a2==null)
return false;
int length = a.length;
if (a2.length != length)
return false;
for (int i=0; i<length; i++) {
Object o1 = a[i];
Object o2 = a2[i];
if (!(o1==null ? o2==null : o1.equals(o2)))
return false;
}
return true;
}
// Filling
public static void fill(long[] a, long val) {
for (int i = 0, len = a.length; i < len; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(long[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex, long val) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
for (int i = fromIndex; i < toIndex; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(int[] a, int val) {
for (int i = 0, len = a.length; i < len; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(int[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex, int val) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
for (int i = fromIndex; i < toIndex; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(short[] a, short val) {
for (int i = 0, len = a.length; i < len; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(short[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex, short val) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
for (int i = fromIndex; i < toIndex; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(char[] a, char val) {
for (int i = 0, len = a.length; i < len; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(char[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex, char val) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
for (int i = fromIndex; i < toIndex; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(byte[] a, byte val) {
for (int i = 0, len = a.length; i < len; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(byte[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex, byte val) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
for (int i = fromIndex; i < toIndex; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(boolean[] a, boolean val) {
for (int i = 0, len = a.length; i < len; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(boolean[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
boolean val) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
for (int i = fromIndex; i < toIndex; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(double[] a, double val) {
for (int i = 0, len = a.length; i < len; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(double[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,double val){
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
for (int i = fromIndex; i < toIndex; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(float[] a, float val) {
for (int i = 0, len = a.length; i < len; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(float[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex, float val) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
for (int i = fromIndex; i < toIndex; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(Object[] a, Object val) {
for (int i = 0, len = a.length; i < len; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(Object[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex, Object val) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
for (int i = fromIndex; i < toIndex; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
// Cloning
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T> T[] copyOf(T[] original, int newLength) {//1.6
return (T[]) copyOf(original, newLength, original.getClass());
}
public static <T,U> T[] copyOf(U[] original, int newLength, Class<? extends T[]> newType) {//1.6
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T[] copy = ((Object)newType == (Object)Object[].class)
? (T[]) new Object[newLength]
: (T[]) Array.newInstance(newType.getComponentType(), newLength);
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static byte[] copyOf(byte[] original, int newLength) {//1.6
byte[] copy = new byte[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static short[] copyOf(short[] original, int newLength) {//1.6
short[] copy = new short[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static int[] copyOf(int[] original, int newLength) {//1.6
int[] copy = new int[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static long[] copyOf(long[] original, int newLength) {//1.6
long[] copy = new long[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static char[] copyOf(char[] original, int newLength) {//1.6
char[] copy = new char[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static float[] copyOf(float[] original, int newLength) {//1.6
float[] copy = new float[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static double[] copyOf(double[] original, int newLength) {//1.6
double[] copy = new double[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static boolean[] copyOf(boolean[] original, int newLength) {//1.6
boolean[] copy = new boolean[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T> T[] copyOfRange(T[] original, int from, int to) {//1.6
return copyOfRange(original, from, to, (Class<? extends T[]>) original.getClass());
}
public static <T,U> T[] copyOfRange(U[] original, int from, int to, Class<? extends T[]> newType) {//1.6
int newLength = to - from;
if (newLength < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(from + " > " + to);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T[] copy = ((Object)newType == (Object)Object[].class)
? (T[]) new Object[newLength]
: (T[]) Array.newInstance(newType.getComponentType(), newLength);
System.arraycopy(original, from, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length - from, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static byte[] copyOfRange(byte[] original, int from, int to) {//1.6
int newLength = to - from;
if (newLength < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(from + " > " + to);
byte[] copy = new byte[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, from, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length - from, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static short[] copyOfRange(short[] original, int from, int to) {//1.6
int newLength = to - from;
if (newLength < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(from + " > " + to);
short[] copy = new short[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, from, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length - from, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static int[] copyOfRange(int[] original, int from, int to) {//1.6
int newLength = to - from;
if (newLength < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(from + " > " + to);
int[] copy = new int[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, from, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length - from, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static long[] copyOfRange(long[] original, int from, int to) {//1.6
int newLength = to - from;
if (newLength < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(from + " > " + to);
long[] copy = new long[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, from, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length - from, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static char[] copyOfRange(char[] original, int from, int to) {//1.6
int newLength = to - from;
if (newLength < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(from + " > " + to);
char[] copy = new char[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, from, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length - from, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static float[] copyOfRange(float[] original, int from, int to) {//1.6
int newLength = to - from;
if (newLength < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(from + " > " + to);
float[] copy = new float[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, from, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length - from, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static double[] copyOfRange(double[] original, int from, int to) {//1.6
int newLength = to - from;
if (newLength < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(from + " > " + to);
double[] copy = new double[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, from, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length - from, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static boolean[] copyOfRange(boolean[] original, int from, int to) {//1.6
int newLength = to - from;
if (newLength < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(from + " > " + to);
boolean[] copy = new boolean[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, from, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length - from, newLength));
return copy;
}
// Misc
@SafeVarargs
@SuppressWarnings("varargs")
public static <T> List<T> asList(T... a) {
return new ArrayList<>(a);
}
private static class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements RandomAccess, java.io.Serializable
{//成员内部类
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2764017481108945198L;
private final E[] a;
ArrayList(E[] array) {
a = Objects.requireNonNull(array);
}
@Override
public int size() {
return a.length;
}
@Override
public Object[] toArray() {
return a.clone();
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
int size = size();
if (a.length < size)
return Arrays.copyOf(this.a, size,
(Class<? extends T[]>) a.getClass());
System.arraycopy(this.a, 0, a, 0, size);
if (a.length > size)
a[size] = null;
return a;
}
@Override
public E get(int index) {
return a[index];
}
@Override
public E set(int index, E element) {
E oldValue = a[index];
a[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
@Override
public int indexOf(Object o) {
E[] a = this.a;
if (o == null) {
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
if (a[i] == null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
if (o.equals(a[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
@Override
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) != -1;
}
@Override
public Spliterator<E> spliterator() {
return Spliterators.spliterator(a, Spliterator.ORDERED);
}
@Override
public void forEach(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
for (E e : a) {
action.accept(e);
}
}
@Override
public void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<E> operator) {
Objects.requireNonNull(operator);
E[] a = this.a;
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
a[i] = operator.apply(a[i]);
}
}
@Override
public void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) {
Arrays.sort(a, c);
}
}
public static int hashCode(long a[]) {//1.5
if (a == null)
return 0;
int result = 1;
for (long element : a) {
int elementHash = (int)(element ^ (element >>> 32));
result = 31 * result + elementHash;
}
return result;
}
public static int hashCode(int a[]) {//1.5
if (a == null)
return 0;
int result = 1;
for (int element : a)
result = 31 * result + element;
return result;
}
public static int hashCode(short a[]) {//1.5
if (a == null)
return 0;
int result = 1;
for (short element : a)
result = 31 * result + element;
return result;
}
public static int hashCode(char a[]) {//1.5
if (a == null)
return 0;
int result = 1;
for (char element : a)
result = 31 * result + element;
return result;
}
public static int hashCode(byte a[]) {//1.5
if (a == null)
return 0;
int result = 1;
for (byte element : a)
result = 31 * result + element;
return result;
}
public static int hashCode(boolean a[]) {//1.5
if (a == null)
return 0;
int result = 1;
for (boolean element : a)
result = 31 * result + (element ? 1231 : 1237);
return result;
}
public static int hashCode(float a[]) {//1.5
if (a == null)
return 0;
int result = 1;
for (float element : a)
result = 31 * result + Float.floatToIntBits(element);
return result;
}
public static int hashCode(double a[]) {//1.5
if (a == null)
return 0;
int result = 1;
for (double element : a) {
long bits = Double.doubleToLongBits(element);
result = 31 * result + (int)(bits ^ (bits >>> 32));
}
return result;
}
public static int hashCode(Object a[]) {//1.5
if (a == null)
return 0;
int result = 1;
for (Object element : a)
result = 31 * result + (element == null ? 0 : element.hashCode());
return result;
}
public static int deepHashCode(Object a[]) {//1.5
if (a == null)
return 0;
int result = 1;
for (Object element : a) {
int elementHash = 0;
if (element instanceof Object[])
elementHash = deepHashCode((Object[]) element);
else if (element instanceof byte[])
elementHash = hashCode((byte[]) element);
else if (element instanceof short[])
elementHash = hashCode((short[]) element);
else if (element instanceof int[])
elementHash = hashCode((int[]) element);
else if (element instanceof long[])
elementHash = hashCode((long[]) element);
else if (element instanceof char[])
elementHash = hashCode((char[]) element);
else if (element instanceof float[])
elementHash = hashCode((float[]) element);
else if (element instanceof double[])
elementHash = hashCode((double[]) element);
else if (element instanceof boolean[])
elementHash = hashCode((boolean[]) element);
else if (element != null)
elementHash = element.hashCode();
result = 31 * result + elementHash;
}
return result;
}
public static boolean deepEquals(Object[] a1, Object[] a2) {//1.5
if (a1 == a2)
return true;
if (a1 == null || a2==null)
return false;
int length = a1.length;
if (a2.length != length)
return false;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
Object e1 = a1[i];
Object e2 = a2[i];
if (e1 == e2)
continue;
if (e1 == null)
return false;
// Figure out whether the two elements are equal
boolean eq = deepEquals0(e1, e2);
if (!eq)
return false;
}
return true;
}
static boolean deepEquals0(Object e1, Object e2) {
assert e1 != null;
boolean eq;
if (e1 instanceof Object[] && e2 instanceof Object[])
eq = deepEquals ((Object[]) e1, (Object[]) e2);
else if (e1 instanceof byte[] && e2 instanceof byte[])
eq = equals((byte[]) e1, (byte[]) e2);
else if (e1 instanceof short[] && e2 instanceof short[])
eq = equals((short[]) e1, (short[]) e2);
else if (e1 instanceof int[] && e2 instanceof int[])
eq = equals((int[]) e1, (int[]) e2);
else if (e1 instanceof long[] && e2 instanceof long[])
eq = equals((long[]) e1, (long[]) e2);
else if (e1 instanceof char[] && e2 instanceof char[])
eq = equals((char[]) e1, (char[]) e2);
else if (e1 instanceof float[] && e2 instanceof float[])
eq = equals((float[]) e1, (float[]) e2);
else if (e1 instanceof double[] && e2 instanceof double[])
eq = equals((double[]) e1, (double[]) e2);
else if (e1 instanceof boolean[] && e2 instanceof boolean[])
eq = equals((boolean[]) e1, (boolean[]) e2);
else
eq = e1.equals(e2);
return eq;
}
public static String toString(long[] a) {//1.5
if (a == null)
return "null";
int iMax = a.length - 1;
if (iMax == -1)
return "[]";
StringBuilder b = new StringBuilder();
b.append('[');
for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
b.append(a[i]);
if (i == iMax)
return b.append(']').toString();
b.append(", ");
}
}
public static String toString(int[] a) {//1.5
if (a == null)
return "null";
int iMax = a.length - 1;
if (iMax == -1)
return "[]";
StringBuilder b = new StringBuilder();
b.append('[');
for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
b.append(a[i]);
if (i == iMax)
return b.append(']').toString();
b.append(", ");
}
}
public static String toString(short[] a) {//1.5
if (a == null)
return "null";
int iMax = a.length - 1;
if (iMax == -1)
return "[]";
StringBuilder b = new StringBuilder();
b.append('[');
for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
b.append(a[i]);
if (i == iMax)
return b.append(']').toString();
b.append(", ");
}
}
public static String toString(char[] a) {//1.5
if (a == null)
return "null";
int iMax = a.length - 1;
if (iMax == -1)
return "[]";
StringBuilder b = new StringBuilder();
b.append('[');
for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
b.append(a[i]);
if (i == iMax)
return b.append(']').toString();
b.append(", ");
}
}
public static String toString(byte[] a) {//1.5
if (a == null)
return "null";
int iMax = a.length - 1;
if (iMax == -1)
return "[]";
StringBuilder b = new StringBuilder();
b.append('[');
for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
b.append(a[i]);
if (i == iMax)
return b.append(']').toString();
b.append(", ");
}
}
public static String toString(boolean[] a) {//1.5
if (a == null)
return "null";
int iMax = a.length - 1;
if (iMax == -1)
return "[]";
StringBuilder b = new StringBuilder();
b.append('[');
for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
b.append(a[i]);
if (i == iMax)
return b.append(']').toString();
b.append(", ");
}
}
public static String toString(float[] a) {//1.5
if (a == null)
return "null";
int iMax = a.length - 1;
if (iMax == -1)
return "[]";
StringBuilder b = new StringBuilder();
b.append('[');
for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
b.append(a[i]);
if (i == iMax)
return b.append(']').toString();
b.append(", ");
}
}
public static String toString(double[] a) {//1.5
if (a == null)
return "null";
int iMax = a.length - 1;
if (iMax == -1)
return "[]";
StringBuilder b = new StringBuilder();
b.append('[');
for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
b.append(a[i]);
if (i == iMax)
return b.append(']').toString();
b.append(", ");
}
}
public static String toString(Object[] a) {//1.5
if (a == null)
return "null";
int iMax = a.length - 1;
if (iMax == -1)
return "[]";
StringBuilder b = new StringBuilder();
b.append('[');
for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
b.append(String.valueOf(a[i]));
if (i == iMax)
return b.append(']').toString();
b.append(", ");
}
}
public static String deepToString(Object[] a) {//1.5
if (a == null)
return "null";
int bufLen = 20 * a.length;
if (a.length != 0 && bufLen <= 0)
bufLen = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(bufLen);
deepToString(a, buf, new HashSet<Object[]>());
return buf.toString();
}
private static void deepToString(Object[] a, StringBuilder buf,
Set<Object[]> dejaVu) {
if (a == null) {
buf.append("null");
return;
}
int iMax = a.length - 1;
if (iMax == -1) {
buf.append("[]");
return;
}
dejaVu.add(a);
buf.append('[');
for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
Object element = a[i];
if (element == null) {
buf.append("null");
} else {
Class<?> eClass = element.getClass();
if (eClass.isArray()) {
if (eClass == byte[].class)
buf.append(toString((byte[]) element));
else if (eClass == short[].class)
buf.append(toString((short[]) element));
else if (eClass == int[].class)
buf.append(toString((int[]) element));
else if (eClass == long[].class)
buf.append(toString((long[]) element));
else if (eClass == char[].class)
buf.append(toString((char[]) element));
else if (eClass == float[].class)
buf.append(toString((float[]) element));
else if (eClass == double[].class)
buf.append(toString((double[]) element));
else if (eClass == boolean[].class)
buf.append(toString((boolean[]) element));
else { // element is an array of object references
if (dejaVu.contains(element))
buf.append("[...]");
else
deepToString((Object[])element, buf, dejaVu);
}
} else { // element is non-null and not an array
buf.append(element.toString());
}
}
if (i == iMax)
break;
buf.append(", ");
}
buf.append(']');
dejaVu.remove(a);
}
public static <T> void setAll(T[] array, IntFunction<? extends T> generator) {//1.8
Objects.requireNonNull(generator);
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++)
array[i] = generator.apply(i);
}
public static <T> void parallelSetAll(T[] array, IntFunction<? extends T> generator) {//1.8
Objects.requireNonNull(generator);
IntStream.range(0, array.length).parallel().forEach(i -> { array[i] = generator.apply(i); });
}
public static void setAll(int[] array, IntUnaryOperator generator) {//1.8
Objects.requireNonNull(generator);
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++)
array[i] = generator.applyAsInt(i);
}
public static void parallelSetAll(int[] array, IntUnaryOperator generator) {//1.8
Objects.requireNonNull(generator);
IntStream.range(0, array.length).parallel().forEach(i -> { array[i] = generator.applyAsInt(i); });
}
public static void setAll(long[] array, IntToLongFunction generator) {//1.8
Objects.requireNonNull(generator);
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++)
array[i] = generator.applyAsLong(i);
}
public static void parallelSetAll(long[] array, IntToLongFunction generator) {//1.8
Objects.requireNonNull(generator);
IntStream.range(0, array.length).parallel().forEach(i -> { array[i] = generator.applyAsLong(i); });
}
public static void setAll(double[] array, IntToDoubleFunction generator) {//1.8
Objects.requireNonNull(generator);
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++)
array[i] = generator.applyAsDouble(i);
}
public static void parallelSetAll(double[] array, IntToDoubleFunction generator) {//1.8
Objects.requireNonNull(generator);
IntStream.range(0, array.length).parallel().forEach(i -> { array[i] = generator.applyAsDouble(i); });
}
public static <T> Spliterator<T> spliterator(T[] array) {//1.8
return Spliterators.spliterator(array,
Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.IMMUTABLE);
}
public static <T> Spliterator<T> spliterator(T[] array, int startInclusive, int endExclusive) {//1.8
return Spliterators.spliterator(array, startInclusive, endExclusive,
Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.IMMUTABLE);
}
public static Spliterator.OfInt spliterator(int[] array) {//1.8
return Spliterators.spliterator(array,
Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.IMMUTABLE);
}
public static Spliterator.OfInt spliterator(int[] array, int startInclusive, int endExclusive) {//1.8
return Spliterators.spliterator(array, startInclusive, endExclusive,
Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.IMMUTABLE);
}
public static Spliterator.OfLong spliterator(long[] array) {//1.8
return Spliterators.spliterator(array,
Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.IMMUTABLE);
}
public static Spliterator.OfLong spliterator(long[] array, int startInclusive, int endExclusive) {//1.8
return Spliterators.spliterator(array, startInclusive, endExclusive,
Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.IMMUTABLE);
}
public static Spliterator.OfDouble spliterator(double[] array) {//1.8
return Spliterators.spliterator(array,
Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.IMMUTABLE);
}
public static Spliterator.OfDouble spliterator(double[] array, int startInclusive, int endExclusive) {//1.8
return Spliterators.spliterator(array, startInclusive, endExclusive,
Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.IMMUTABLE);
}
public static <T> Stream<T> stream(T[] array) {//1.8
return stream(array, 0, array.length);
}
public static <T> Stream<T> stream(T[] array, int startInclusive, int endExclusive) {//1.8
return StreamSupport.stream(spliterator(array, startInclusive, endExclusive), false);
}
public static IntStream stream(int[] array) {//1.8
return stream(array, 0, array.length);
}
public static IntStream stream(int[] array, int startInclusive, int endExclusive) {//1.8
return StreamSupport.intStream(spliterator(array, startInclusive, endExclusive), false);
}
public static LongStream stream(long[] array) {//1.8
return stream(array, 0, array.length);
}
public static LongStream stream(long[] array, int startInclusive, int endExclusive) {//1.8
return StreamSupport.longStream(spliterator(array, startInclusive, endExclusive), false);
}
public static DoubleStream stream(double[] array) {//1.8
return stream(array, 0, array.length);
}
public static DoubleStream stream(double[] array, int startInclusive, int endExclusive) {//1.8
return StreamSupport.doubleStream(spliterator(array, startInclusive, endExclusive), false);
}
}
序列化
序列化:将对象写入到IO流中
反序列化:从IO流中恢复对象
意义:序列化机制允许将实现序列化的Java对象转换位字节序列,这些字节序列可以保存在磁盘上,或通过网络传输,以达到以后恢复成原来的对象。序列化机制使得对象可以脱离程序的运行而独立存在。
使用场景:所有可在网络上传输的对象都必须是可序列化的,比如RMI(remote method invoke,即远程方法调用),传入的参数或返回的对象都是可序列化的,否则会出错;所有需要保存到磁盘的java对象都必须是可序列化的。通常建议:程序创建的每个JavaBean类都实现Serializeable接口。
从 JVM 的角度看,Serializeable就是一个标记接口而已。
public interface Serializable {//1.1
}
序列化使用方式:实现Serializable接口,显示的定义serialVersionUID
Java的序列化机制是通过在运行时判断类的serialVersionUID来验证版本一致性的。在进行反序列化时,JVM会把传来的字节流中的serialVersionUID与本地相应实体(类)的serialVersionUID进行比较,如果相同就认为是一致的,可以进行反序列化,否则就会出现序列化版本不一致的异常。(InvalidCastException)
拷贝
1.java的类型分为两大类,一类为primitive,如int,另一类为引用类型,如String,Object等等。java的引用类型都是存储在堆上的。
primitive类型的拷贝的确能做到相等且隔离。引用类型的拷贝相对复杂,分浅拷贝(shallow clone)和深拷贝(deep clone)。
2.浅拷贝是指拷贝对象时仅仅拷贝对象本身和对象中的基本变量,以及它所包含的所有对象的引用地址,而不拷贝对象包含的引用指向的对象(这是 java 中的浅拷贝,其他语言的浅拷贝貌似是直接拷贝引用,即新引用和旧引用指向同一对象)。
3.深拷贝不仅拷贝对象本身和对象中的基本变量,而且拷贝对象包含的引用指向的所有对象,简单来说,即复制原型中对象的内存copy。
有名的GoF设计模式里有一个模式为原型模式,用原型实例指定创建对象的种类,并且通过拷贝这些原型创建新的对象。简单的说就是clone一个对象实例。使得clone出来的copy和原有的对象一模一样。
注意:对于常量池方式创建的 String 类型,会针对原值克隆,不存在引用地址一说,对于其他不可变类,如 LocalDate,也是一样
clone 方法定义在 Object 类中:
protected native Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException;
1. 声明实现Cloneable接口。从 JVM 的角度看,Cloneable 就是一个标记接口而已。
public interface Cloneable {//1.0
}
2. 如果父类的clone实现没有问题的话,调用super.clone拿到一个对象,在该对象的内存存储中,所有父类定义的field都已经clone好了,该类中的primitive和不可变类型引用也克隆好了,可变类型引用都是浅copy;如果父类的clone实现有问题,覆写一个新的clone逻辑。
3. 把浅copy的引用指向原型对象新的克隆体。
缺点· 手工维护clone的调用链;· 如果class的field是个final的可变类,第三步没有办法做了。
异常
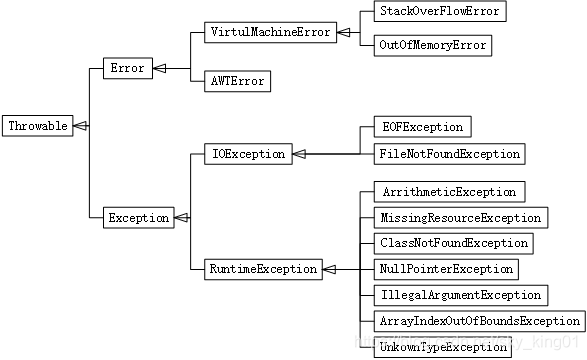
public class Throwable implements Serializable {
/** use serialVersionUID from JDK 1.0.2 for interoperability */
private static final long serialVersionUID = -3042686055658047285L;
private transient Object backtrace;//本机代码在此插槽中保存了一些堆栈回溯的指示
private String detailMessage;
private static class SentinelHolder {
public static final StackTraceElement STACK_TRACE_ELEMENT_SENTINEL =
new StackTraceElement("", "", null, Integer.MIN_VALUE);
public static final StackTraceElement[] STACK_TRACE_SENTINEL =
new StackTraceElement[] {STACK_TRACE_ELEMENT_SENTINEL};
}
private static final StackTraceElement[] UNASSIGNED_STACK = new StackTraceElement[0];//空栈的共享值
private Throwable cause = this;//1.4,当前对象为cause
private StackTraceElement[] stackTrace = UNASSIGNED_STACK;//1.4
private static final List<Throwable> SUPPRESSED_SENTINEL =
Collections.unmodifiableList(new ArrayList<Throwable>(0));//设置此静态字段会引入一个可接受的值,对一些java.util类的初始化依赖
private List<Throwable> suppressedExceptions = SUPPRESSED_SENTINEL;//1.7,
private static final String NULL_CAUSE_MESSAGE = "Cannot suppress a null exception.";//尝试抑制空异常的消息。
private static final String SELF_SUPPRESSION_MESSAGE = "Self-suppression not permitted";//试图压抑自己的讯息。
private static final String CAUSE_CAPTION = "Caused by: ";//标记原因异常堆栈跟踪的标题
private static final String SUPPRESSED_CAPTION = "Suppressed: ";//用于标记抑制的异常堆栈跟踪的标题
public Throwable() {
fillInStackTrace();
}
public Throwable(String message) {
fillInStackTrace();
detailMessage = message;
}
public Throwable(String message, Throwable cause) {//1.4
fillInStackTrace();
detailMessage = message;
this.cause = cause;
}
public Throwable(Throwable cause) {//1.4
fillInStackTrace();
detailMessage = (cause==null ? null : cause.toString());
this.cause = cause;
}
protected Throwable(String message, Throwable cause,
boolean enableSuppression,
boolean writableStackTrace) {//1.7
if (writableStackTrace) {
fillInStackTrace();
} else {
stackTrace = null;
}
detailMessage = message;
this.cause = cause;
if (!enableSuppression)
suppressedExceptions = null;
}
public String getMessage() {//返回此 throwable 的详细消息字符串
return detailMessage;
}
public String getLocalizedMessage() {//1.1,创建此 throwable 的本地化描述
return getMessage();
}
public synchronized Throwable getCause() {//1.4,返回此 throwable 的 cause;如果 cause 不存在或未知,则返回 null。
return (cause==this ? null : cause);
}
public synchronized Throwable initCause(Throwable cause) {//1.4,将此 throwable 的 cause 初始化为指定值
if (this.cause != this)
throw new IllegalStateException("Can't overwrite cause with " +
Objects.toString(cause, "a null"), this);
if (cause == this)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Self-causation not permitted", this);
this.cause = cause;
return this;
}
public String toString() {//返回此 throwable 的简短描述。
String s = getClass().getName();
String message = getLocalizedMessage();
return (message != null) ? (s + ": " + message) : s;
}
public void printStackTrace() {//将此 throwable 及其追踪输出至标准错误流
printStackTrace(System.err);
}
public void printStackTrace(PrintStream s) {//将此 throwable 及其追踪输出到指定的输出流
printStackTrace(new WrappedPrintStream(s));
}
private void printStackTrace(PrintStreamOrWriter s) {
// Guard against malicious overrides of Throwable.equals by
// using a Set with identity equality semantics.
Set<Throwable> dejaVu =
Collections.newSetFromMap(new IdentityHashMap<Throwable, Boolean>());
dejaVu.add(this);
synchronized (s.lock()) {
// Print our stack trace
s.println(this);
StackTraceElement[] trace = getOurStackTrace();
for (StackTraceElement traceElement : trace)
s.println("\tat " + traceElement);
// Print suppressed exceptions, if any
for (Throwable se : getSuppressed())
se.printEnclosedStackTrace(s, trace, SUPPRESSED_CAPTION, "\t", dejaVu);
// Print cause, if any
Throwable ourCause = getCause();
if (ourCause != null)
ourCause.printEnclosedStackTrace(s, trace, CAUSE_CAPTION, "", dejaVu);
}
}
private void printEnclosedStackTrace(PrintStreamOrWriter s,
StackTraceElement[] enclosingTrace,
String caption,
String prefix,
Set<Throwable> dejaVu) {
assert Thread.holdsLock(s.lock());
if (dejaVu.contains(this)) {
s.println("\t[CIRCULAR REFERENCE:" + this + "]");
} else {
dejaVu.add(this);
// Compute number of frames in common between this and enclosing trace
StackTraceElement[] trace = getOurStackTrace();
int m = trace.length - 1;
int n = enclosingTrace.length - 1;
while (m >= 0 && n >=0 && trace[m].equals(enclosingTrace[n])) {
m--; n--;
}
int framesInCommon = trace.length - 1 - m;
// Print our stack trace
s.println(prefix + caption + this);
for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++)
s.println(prefix + "\tat " + trace[i]);
if (framesInCommon != 0)
s.println(prefix + "\t... " + framesInCommon + " more");
// Print suppressed exceptions, if any
for (Throwable se : getSuppressed())
se.printEnclosedStackTrace(s, trace, SUPPRESSED_CAPTION,
prefix +"\t", dejaVu);
// Print cause, if any
Throwable ourCause = getCause();
if (ourCause != null)
ourCause.printEnclosedStackTrace(s, trace, CAUSE_CAPTION, prefix, dejaVu);
}
}
public void printStackTrace(PrintWriter s) {//1.1,将此 throwable 及其追踪输出到指定的 PrintWriter
printStackTrace(new WrappedPrintWriter(s));
}
private abstract static class PrintStreamOrWriter {
/** Returns the object to be locked when using this StreamOrWriter */
abstract Object lock();
/** Prints the specified string as a line on this StreamOrWriter */
abstract void println(Object o);
}
private static class WrappedPrintStream extends PrintStreamOrWriter {
private final PrintStream printStream;
WrappedPrintStream(PrintStream printStream) {
this.printStream = printStream;
}
Object lock() {
return printStream;
}
void println(Object o) {
printStream.println(o);
}
}
private static class WrappedPrintWriter extends PrintStreamOrWriter {
private final PrintWriter printWriter;
WrappedPrintWriter(PrintWriter printWriter) {
this.printWriter = printWriter;
}
Object lock() {
return printWriter;
}
void println(Object o) {
printWriter.println(o);
}
}
public synchronized Throwable fillInStackTrace() {
if (stackTrace != null ||
backtrace != null /* Out of protocol state */ ) {
fillInStackTrace(0);
stackTrace = UNASSIGNED_STACK;
}
return this;
}
private native Throwable fillInStackTrace(int dummy);//在异常堆栈跟踪中填充。
public StackTraceElement[] getStackTrace() {//1.4,提供编程访问由 printStackTrace() 输出的堆栈跟踪信息。
return getOurStackTrace().clone();
}
private synchronized StackTraceElement[] getOurStackTrace() {
// Initialize stack trace field with information from
// backtrace if this is the first call to this method
if (stackTrace == UNASSIGNED_STACK ||
(stackTrace == null && backtrace != null) /* Out of protocol state */) {
int depth = getStackTraceDepth();
stackTrace = new StackTraceElement[depth];
for (int i=0; i < depth; i++)
stackTrace[i] = getStackTraceElement(i);
} else if (stackTrace == null) {
return UNASSIGNED_STACK;
}
return stackTrace;
}
public void setStackTrace(StackTraceElement[] stackTrace) {//1.4,设置将由 getStackTrace() 返回,并由 printStackTrace() 和相关方法输出的堆栈跟踪元素。
// Validate argument
StackTraceElement[] defensiveCopy = stackTrace.clone();
for (int i = 0; i < defensiveCopy.length; i++) {
if (defensiveCopy[i] == null)
throw new NullPointerException("stackTrace[" + i + "]");
}
synchronized (this) {
if (this.stackTrace == null && // Immutable stack
backtrace == null) // Test for out of protocol state
return;
this.stackTrace = defensiveCopy;
}
}
native int getStackTraceDepth();
native StackTraceElement getStackTraceElement(int index);
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream s)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
s.defaultReadObject(); // read in all fields
if (suppressedExceptions != null) {
List<Throwable> suppressed = null;
if (suppressedExceptions.isEmpty()) {
// Use the sentinel for a zero-length list
suppressed = SUPPRESSED_SENTINEL;
} else { // Copy Throwables to new list
suppressed = new ArrayList<>(1);
for (Throwable t : suppressedExceptions) {
// Enforce constraints on suppressed exceptions in
// case of corrupt or malicious stream.
if (t == null)
throw new NullPointerException(NULL_CAUSE_MESSAGE);
if (t == this)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(SELF_SUPPRESSION_MESSAGE);
suppressed.add(t);
}
}
suppressedExceptions = suppressed;
} // else a null suppressedExceptions field remains null
if (stackTrace != null) {
if (stackTrace.length == 0) {
stackTrace = UNASSIGNED_STACK.clone();
} else if (stackTrace.length == 1 &&
// Check for the marker of an immutable stack trace
SentinelHolder.STACK_TRACE_ELEMENT_SENTINEL.equals(stackTrace[0])) {
stackTrace = null;
} else { // Verify stack trace elements are non-null.
for(StackTraceElement ste : stackTrace) {
if (ste == null)
throw new NullPointerException("null StackTraceElement in serial stream. ");
}
}
} else {
stackTrace = UNASSIGNED_STACK.clone();
}
}
private synchronized void writeObject(ObjectOutputStream s)
throws IOException {
getOurStackTrace();
StackTraceElement[] oldStackTrace = stackTrace;
try {
if (stackTrace == null)
stackTrace = SentinelHolder.STACK_TRACE_SENTINEL;
s.defaultWriteObject();
} finally {
stackTrace = oldStackTrace;
}
}
public final synchronized void addSuppressed(Throwable exception) {//1.7
if (exception == this)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(SELF_SUPPRESSION_MESSAGE, exception);
if (exception == null)
throw new NullPointerException(NULL_CAUSE_MESSAGE);
if (suppressedExceptions == null) // Suppressed exceptions not recorded
return;
if (suppressedExceptions == SUPPRESSED_SENTINEL)
suppressedExceptions = new ArrayList<>(1);
suppressedExceptions.add(exception);
}
private static final Throwable[] EMPTY_THROWABLE_ARRAY = new Throwable[0];
public final synchronized Throwable[] getSuppressed() {//1.7
if (suppressedExceptions == SUPPRESSED_SENTINEL ||
suppressedExceptions == null)
return EMPTY_THROWABLE_ARRAY;
else
return suppressedExceptions.toArray(EMPTY_THROWABLE_ARRAY);
}
}
Java异常栈
看Exception异常的时候,发生异常的方法会在最上层,中间还有其他的调用层次,main方法会在最下层。这其实是栈的结构,先进后出的。
Java异常中的Error
Error一般表示编译时或者系统错误,虚拟机相关的错误,系统崩溃(例如:我们开发中有时会遇到的OutOfMemoryError)等。这种错误无法恢复或不可捕获,将导致应用程序中断,通常应用程序无法处理这些错误,因此也不应该试图用catch来进行捕获。
Java异常中的Exception
public class Exception extends Throwable {
static final long serialVersionUID = -3387516993124229948L;
public Exception() {
super();
}
public Exception(String message) {
super(message);
}
public Exception(String message, Throwable cause) {//1.4
super(message, cause);
}
public Exception(Throwable cause) {//1.4
super(cause);
}
protected Exception(String message, Throwable cause,
boolean enableSuppression,
boolean writableStackTrace) {//1.7
super(message, cause, enableSuppression, writableStackTrace);
}
}
1.Java中的受检查异常
写IO操作的代码,对File或者Stream进行操作的时候一定需要使用try-catch包起来,否则编译会失败,这是因为这些异常类型是受检查的异常类型。编译器在编译时,对于受检异常必须进行try…catch或throws处理,否则无法通过编译。常见的受检查异常包括:IO操作、ClassNotFoundException、线程操作等,以及自定义业务异常。
2.Java中的非受检查异常(运行时异常)
RuntimeException及其子类都统称为非受检查异常,例如:NullPointExecrption、NumberFormatException(字符串转换为数字)、ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(数组越界)、ClassCastException(类型转换错误)、ArithmeticException(算术错误)等。
Java的异常处理
throws关键字 方法层,捕捉,不处理
throw关键字 逻辑层,捕捉,处理
try{
///可能会抛出异常的代码
}catch(Exception e1){
//处理Type1类型异常的代码
}catch(Exception e2){
//处理Type2类型异常的代码
}finally{
//资源关闭代码(一定会被执行),除内存以外的资源恢复到它们的初始状态
}
泛型
泛型的出现,为了在编译时提供更严格的类型检查,并支持泛型编程,解决了类型安全问题。泛型具有以下优点:
1.编译时的强类型检查
泛型要求在声明时指定实际数据类型,Java 编译器在编译时会对泛型代码做强类型检查,并在代码违反类型安全时发出告警。早发现,早治理,把隐患扼杀于摇篮,在编译时发现并修复错误所付出的代价远比在运行时小。
2.避免了类型转换
3.泛型编程可以实现通用算法
通过使用泛型,程序员可以实现通用算法,这些算法可以处理不同类型的集合,可以自定义,并且类型安全且易于阅读。
通过设定不同的类型,可以往集合里面存储不同类型的数据类型(而且只能存储设定的数据类型,这是泛型的优势之一)。“泛型”简单的意思就是泛指的类型(参数化类型)。最典型的的例子就是ArrayList,这个集合我们无论传递什么数据类型,它都能很好的工作,主要有泛型接口、泛型类、泛型方法
类型擦除
Java 泛型是使用类型擦除来实现的,使用泛型时,任何具体的类型信息都被擦除了。
1.把泛型中的所有类型参数替换为 Object,如果指定类型边界,则使用类型边界来替换。因此,生成的字节码仅包含普通的类,接口和方法。
2.擦除出现的类型声明,即去掉 <> 的内容。比如 T get() 方法声明就变成了 Object get() ;List< String> 就变成了 List。如有必要,插入类型转换以保持类型安全。
3.生成桥接方法以保留扩展泛型类型中的多态性。类型擦除确保不为参数化类型创建新类;因此,泛型不会产生运行时开销。
泛型不能用于显式地引用运行时类型的操作之中,例如:转型、instanceof 操作和 new 表达式。因为所有关于参数的类型信息都丢失了。正是由于泛型是基于类型擦除实现的,所以,泛型类型无法向上转型(用子类实例去初始化父类,这是面向对象中多态的重要表现)。比如,List< Interger> 却并非继承了 List< Object>。这是因为,泛型类并没有自己独有的 Class 类对象,并不存在 List< Object>.class 或是 List< Interger>.class,Java 编译器会将二者都视为 List.class。
泛型通配符(?)
类型边界可以对泛型的类型参数设置限制条件
上界通配符缩小类型参数的类型范围,<? extends Number>
下界通配符将未知类型限制为该类型的特定类型或超类类型。<? super Number>
无界通配符有两种应用场景:1.可以使用 Object 类中提供的功能来实现的方法。2.使用不依赖于类型参数的泛型类中的方法。<?>
泛型不能向上转型。但是,我们可以通过使用通配符来向上转型。
使用泛型的建议
1.消除类型检查告警
2.List 优先于数组
3.优先考虑使用泛型来提高代码通用性
4.优先考虑泛型方法来限定泛型的范围
5.利用有限制通配符来提升 API 的灵活性
6.优先考虑类型安全的异构容器
反射
1.一种 动态(运行时)访问、检测 & 修改它本身的能力
2.动态(运行时)获取类的完整结构信息(变量和方法) & 调用对象的方法
静态编译:在编译时确定类型 & 绑定对象。如常见的使用new关键字创建对象
动态编译:运行时确定类型 & 绑定对象。动态编译体现了Java的灵活性、多态特性 & 降低类之间的藕合性
3.反射机制的实现 主要通过 操作java.lang.Class类 ,步骤如下:
· 获取目标类型的Class对象;
· 通过 Class 对象分别获取Constructor类对象、Method类对象 和 Field 类对象;
· 通过 Constructor类对象、Method类对象 和 Field类对象分别获取类的构造函数、方法&属性的具体信息,并进行后续操作。
注解
注解不是必须的,但了解注解有助于我们深入理解某些第三方框架(比如,Lombok),提高工作效率。
注解定义
Java注解又称为标注,是Java从1.5开始支持加入源码的特殊语法元数据;Java中的类、方法、变量、参数、包都可以被注解。这里提到的元数据是描述数据的数据,和业务逻辑无关,所以当你查看注解类时,发现里面没有任何逻辑处理
注解的逻辑实现是元数据的用户来处理的,注解仅仅提供它定义的属性(类/方法/变量/参数/包)的信息,注解的用户来读取这些信息并实现必要的逻辑。
· 当使用java中的注解(比如@Override、@Deprecated、@SuppressWarnings)。JVM就是用户,它在字节码层面工作。
· 如果是自定义的注解。比如,第三方框架ActiveAndroid,它的用户是每个使用注解的类,所有使用注解的类都需要继承Model.java,在Model.java的构造方法中通过反射来获取注解类中的每个属性。
1.注解仅仅是元数据,和业务逻辑无关,所以当你查看注解类时,发现里面没有任何逻辑处理;
2.javadoc中的@author、@version、@param、@return、@deprecated、@hide、@throws、@exception、@see是标记,并不是注解;
注解的作用
1.格式检查:告诉编译器信息,比如被@Override标记的方法如果不是父类的某个方法,IDE会报错;
2.减少配置:运行时动态处理,得到注解信息,实现代替配置文件的功能;
3.减少重复工作:比如第三方框架xUtils,通过注解@ViewInject减少对findViewById的调用,类似的还有(JUnit、ActiveAndroid等);
内部类
定义在另一个类中的类
内部类存在主要原因
1.内部类方法可以访问该类定义所在作用域中的数据,包括被 private 修饰的私有数据
2.内部类可以对同一包中的其他类隐藏起来
3.内部类可以实现 java 单继承的缺陷
4.当我们想要定义一个回调函数却不想写大量代码的时候我们可以选择使用匿名内部类来实现
· 创建内部类的时刻并不依赖于外部类的创建
· 内部类是一个相对独立的实体,与外部类不是is-a关系
内部类分类
1.静态内部类、非静态内部类(成员内部类)
2.局部内部类(方法里边的内部类)
· 局部内类不允许使用访问权限修饰符 public private protected 均不允许
· 局部内部类对外完全隐藏,除了创建这个类的方法可以访问它其他的地方是不允许访问的。
· 局部内部类与成员内部类不同之处是他可以引用成员变量,但该成员必须声明为 final,内部不允许修改基本数据类型变量的值,内部不允许修改引用指向的对象(对象本身是可以被就修改的)。
3.匿名内部类(方法里边,没有类名的内部类)
· 匿名内部类是没有访问修饰符的。
· 匿名内部类必须继承一个抽象类或者实现一个接口
· 匿名内部类中不能存在任何静态成员或方法
· 匿名内部类是没有构造方法的,因为它没有类名。
· 与局部内部相同匿名内部类也可以引用局部变量。此变量也必须声明为 final(匿名内部类是没有访问修饰符的。)

