一、集合框架概述
集合概述
集合、数组都是对多个数据进行存储操作的结构,简称Java容器。
数组在存储多个数据方面的特点
一方面
- 一旦初始化以后,其长度就确定了。
- 数组一旦定义好,其元素的类型也就确定了。我们也就只能操作指定类型的数据了。
- 如:String[] arr; int[] arr1; Object[] arr2;
另一方面
- 一旦初始化以后,其长度就不可修改。
- 数组中提供的方法非常有限,对于添加、删除、插入数据等操作,非常不便,同时效率不高。
- 没有现成的属性或方法获取数组中实际元素的个数。
数组存储数据的特点:有序、可重复。对于无序、不可重复的需求,不能满足。
集合框架
Collection接口:单列集合,用来存储一个一个的对象
- List接口:存储有序的、可重复的数据。(“动态”数组)
- ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector
- Set接口:存储无序的、不可重复的数据。(类似数学中的集合)
- HashSet、LinkedHashSet、TreeSet
- List接口:存储有序的、可重复的数据。(“动态”数组)
Map接口:双列集合,用来存储一对一对的数据(key-value)
HashMap、LinkedHashMap、TreeMap、HashTable、Properties
二、Collection接口常用方法
常用方法
```java @Test // Collection接口中声明的方法测试 public void test1() { Collection collection = new ArrayList();
// 1.add():添加元素 collection.add(“AA”); collection.add(“BB”); collection.add(123); collection.add(new Date());
// 2.size():获取添加的元素的个数 System.out.println(“size of collection —> “ + collection.size());
// 3.addAll():将collection集合中的元素添加到当前的集合中 Collection collection_01 = new ArrayList(); collection_01.add(456); collection_01.add(“CC”); collection_01.addAll(collection);
// 4.clear():清空集合元素 collection.clear();
// 5.isEmpty():判断当前集合是否为空 System.out.println(“is Empty ? —> “ + collection.isEmpty());
// 6.contains():是否包含,比较对象时使用equals方法 collection.add(new String(“Tom”)); collection.add(new Person(“Jerry”,20)); boolean contains = collection.contains(123); System.out.println(“contains 123 ? —> “ + contains); contains = collection.contains(new Person(“Jerry”,20)); System.out.println(“contains Person ? —> “ + contains);
// 7.containsAll(Collection c):判断形参c中的所有元素是否都存在于当前集合中 Collection c = Arrays.asList(123, 456); System.out.println(“contaionsAll ? —> “ + collection.containsAll(c));
// 8.remove(Object obj): System.out.println(“before remove: “ + collection); collection.remove(“Tom”); System.out.println(“after remove: “ + collection);
// 9.removeAll(Collection c):从当前集合中移除c中所有的元素 collection.add(123); collection.add(456); collection.add(“Tom”); System.out.println(“before removeAll: “ + collection); collection.removeAll(Arrays.asList(456,789)); System.out.println(“after removeAll: “ + collection);
// 10.retainAll(Collection c):保留当前集合和集合c的交集, collection.retainAll(collection_01); System.out.println(“after retainAll: “ + collection);
// 11.equals(Object obj):要想返回true,需要当前集合和形参集合的元素都相同。 System.out.println(“equals? —> “ + collection.equals(collection_01));
// 12.hashCode():返回当前对象的哈希值 System.out.println(“hashCode: “ + collection.hashCode());
// 13.toArray():集合—>数组 Object[] array = collection.toArray(); System.out.println(“Array:”); for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) { System.out.println(array[i]); }
// else: asList() 数组—>集合:调用Arrays类的静态方法 List list = Arrays.asList(new String[]{“AA”,”BB”,”CC”}); System.out.println(list);
List list1 = Arrays.asList(new int[]{123, 456}); System.out.println(list1.size());
List list2 = Arrays.asList(new Integer[]{123, 456}); System.out.println(list2.size());
}
输出结果:<br />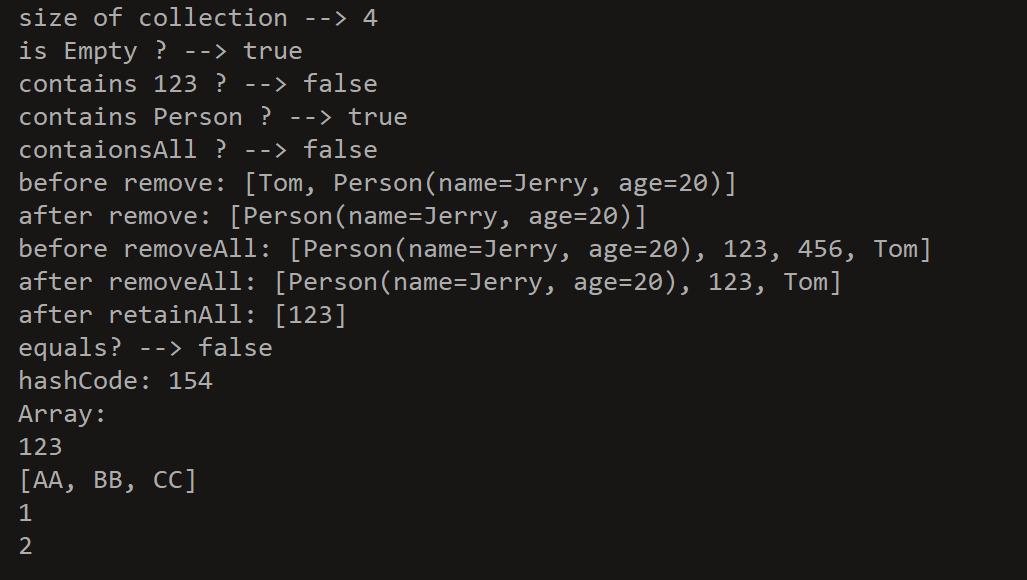<a name="QgiaS"></a>## Iterator接口与foreach循环```java@Test // 集合元素遍历public void IteratorTest() {Collection collection = new ArrayList();collection.add(123);collection.add(456);collection.add("Tom");collection.add(new Person("Jerry",17));Iterator iterator = collection.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()) {System.out.println(iterator.next());}// jdk5.0新增foreach循环,用于遍历集合、数组System.out.println("===========foreach============");for (Object o : collection) {System.out.println(o);}for (int i : new int[]{1,2,3}) {System.out.println(i);}}@Test // 增强for循环与普通for循环public void forTest() {String[] arr = new String[]{"MM","MM","MM"};// 普通for循环for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {arr[i] = "GG";}// 增强for循环for (String s : arr) {s = "GG";}for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {System.out.println(arr[i]);}}
三、Collection子接口:List
1、存储特点
存储有序的、可重复的数据。(注意:所在的类要重写equals方法)
2、常用方法
- 增:add(Object obj)
- 删:remove(int index) / remove(Object obj)
- 改:set(int index, Object ele)
- 查:get(int index)
- 插:add(int index, Object ele)
- 长度:size()
遍历
ArrayList:作为List接口的主要实现类;线程不安全,效率高;底层使用Object[] elementData存储
- LinkedList:对于频繁的插入、删除操作,使用此类效率比ArrayList高;底层使用双向链表存储
- Vector:作为List接口的古老实现类;线程安全,效率低;底层使用Object[] elementData存储
4、源码分析
ArrayList源码分析:
jdk1.7版本
```java // 存储元素的数组 private transient Object[] elementData;
// 空参构造器,默认容量为10 public ArrayList() { this(10); }
//根据给定容量创建数组 public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) { super(); if (initialCapacity < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException(“Illegal Capacity: “+initialCapacity); this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity]; }
// 添加元素 public boolean add(E e) { // 确认容量 ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); elementData[size++] = e; return true; }
// 确认容量大小,不够则扩容 private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) { // 修改次数 modCount++; // 如果容量不够,则扩容 if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) grow(minCapacity); }
// 扩容 private void grow(int minCapacity) { // 获取旧的容量大小 int oldCapacity = elementData.length; // 新的容量为原来的1.5倍 int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); // 如果1.5倍容量不够,则直接设置为传入容量大小 if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) newCapacity = minCapacity; // 容量上限 if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); // 生成新的数组 elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); }
<a name="s47Kh"></a>#### jdk1.8版本```java// 默认初始化容量private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;//空元素数组private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};// 默认初始化为空数组private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};// 非private简化内部类访问transient Object[] elementData;// 初始化为{}public ArrayList() {this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;}public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {if (initialCapacity > 0) {this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;} else {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+initialCapacity);}}private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));}// 添加元素时初始容量为10或更大private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) {if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);}return minCapacity;}
小结
jdk7中ArrayList的对象的创建类似于单例的饿汉式,而jdk8中的对象创建类似于单例的懒汉式,延迟了数组的创建,节省内存。
LinkedList源码分析:
元素用双链表结构存储
// 头结点transient Node<E> first;// 尾结点transient Node<E> last;public LinkedList() {}public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {this();addAll(c);}// 结点内部类private static class Node<E> {E item;Node<E> next;Node<E> prev;Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {this.item = element;this.next = next;this.prev = prev;}}// 添加结点public boolean add(E e) {linkLast(e);return true;}void linkLast(E e) {final Node<E> l = last;final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);last = newNode;if (l == null)first = newNode;elsel.next = newNode;size++;modCount++;}
Vector源码分析:
与ArrayList类似,但Vector是线程安全的
// 方法中都添加了synchronized关键字public synchronized boolean add(E e) {modCount++;ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);elementData[elementCount++] = e;return true;}// 扩容方面默认是原来的两倍private void grow(int minCapacity) {// overflow-conscious codeint oldCapacity = elementData.length;int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)newCapacity = minCapacity;if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);}

