委托 Delegate的定义
typedef int(*Calc)(int a, int b);//函数指针。 //声明有两个int形参,返回类型为int的函数指针类型 int Add(int a, int b) { int result = a + b; return result; }
int Sub(int a, int b) { int result = a - b; return result; }
int main() { int x = 100; int y = 200; int z = 0;
Calc funPoint1 = &Add;Calc funPoint2 = ⋐z = funPoint1(x, y); //间接调用函数printf("%d+%d=%d\n", x, y, z);z = Sub(x, y); //直接调用函数printf("%d+%d=%d\n", x, y, z);system("pause"); //暂停程序运行,等待下一步操作执行结束return 0;
}
- **一切皆地址**- 变量(数据)是以某个地址为起点的一段内存中所存储的值- 函数(算法)是以某个地址为起点的一段内存中所存储的一组机器语言指令- **直接调用与间接调用**- 直接调用:通过函数名来调用函数,CPU 通过函数名直接获得函数所在地址并开始执行->返回- 间接调用:通过函数指针来调用函数,CPU通过读取函数指针存储的值获得函数所在地址并开始执行->返回<a name="Java"></a>## JavaJava 语言由 C++ 发展而来,为了提高应用安全性,Java 语言禁止程序员直接访问内存地址。即 Java 语言把 C++ 中所有与指针相关的内容都舍弃掉了。- **Java中没有与委托相对应的功能实体**<a name="3c299cc6"></a>## 委托实例 Action 与 Func- **委托的简单使用**- Action委托- Func委托Action 和 Func 是 C# 内置的委托实例,它们都有很多重载以方便使用。```cusing System;using System.Collections.Generic;namespace DelegateExample{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Calculator calculator = new Calculator();Action action = new Action(calculator.Report);calculator.Report();action.Invoke();action();Func<int, int, int> func1 = new Func<int, int, int>(calculator.Add);//委托Func<int, int, int> func2 = new Func<int, int, int>(calculator.Sub);int x = 100;int y = 200;int z = 0;z = func1.Invoke(x, y); //间接调用Console.WriteLine(z);z = func2(x, y); //指针类写法,效果不变Console.WriteLine(z);}}class Calculator{public void Report(){Console.WriteLine("I have 3 Methods.");}public int Add(int a,int b){int result = a + b;return result;}public int Sub(int a, int b){int result = a - b;return result;}}}
委托的声明(自定义委托)
- 委托是一种类(class) , 类是数据类型所以委托也是一种数据类型
- 它的声名方式与一般的类不同,主要是为了照顾可读性和C/C++传统
- 注意声明委托的位置
- 避免写错地方结果声明成嵌套类型
- 委托与所封装的方法必需”类型兼容”

返回值的数据类型一致
参数列表在个数和数据类型上一致(参数名不需要一样)
委托是一种类:
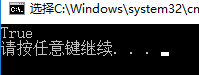
static void Main(string[] args){Type t = typeof(Action);Console.WriteLine(t.IsClass);}
委托是类,所以声明位置是和 class 处于同一个级别。但 C# 允许嵌套声明类(一个类里面可以声明另一个类),所以有时也会有 delegate 在 class 内部声明的情况。
实例:
public delegate double Calc(double x, double y);class Program{static void Main(string[] args){var calculator = new Calculator();var calc1 = new Calc(calculator.Mul);Console.WriteLine(calc1(5, 6));}}class Calculator{public double Mul(double x, double y){return x * y;}public double Div(double x, double y){return x / y;}}
委托的一般使用
- 实例:把方法当作参数传给另一个方法
- 正确使用1:模板方法,“借用”指定的外部方法来产生结果
- 相当于”填空题”
- 常位于代码中部
- 委托有返回值
- 正确使用2:回调(callback) 方法, 调用指定的外部方法
- 相当于”流水线”
- 常位于代码末尾
- 委托无返回值
- 正确使用1:模板方法,“借用”指定的外部方法来产生结果
注意:难精通+易使用+功能强大东西,一旦被滥用则后果非常严重
- 缺点1:这是一种方法级别的紧耦合,现实工作中要慎之又慎
- 缺点2:使可读性下降、debug的难度增加
- 缺点3:把委托回调、异步调用和多线程纠缠在一起,会让代码变得难以阅读和维护
-
模板方法
利用模板方法,提高代码复用性。
下例中 Product、Box、WrapFactory 都不用修改,只需要在 ProductFactory 里面新增不同的 MakeXXX 然后作为委托传入 WrapProduct 就可以对其进行包装。class Program{static void Main(string[] args){ProductFactory productFactory = new ProductFactory();WarpFactory warpFactory = new WarpFactory();Func<Product> fun1 =new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakePizza);//封装制作Pizza方法Func<Product> fun2 =new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakeToyCar);//封装制作Toy Car方法Func<Product> fun3 = new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakeUmbrella);//调用模板方法Box box1 = warpFactory.WarpProduct(fun1);Box box2 = warpFactory.WarpProduct(fun2);Box box3 = warpFactory.WarpProduct(fun3);//打印输出Console.WriteLine(box1.Product.Name);Console.WriteLine(box2.Product.Name);Console.WriteLine(box3.Product.Name);}}class Product{public string Name { get; set; }}class Box{public Product Product { get; set; }}//使用模板方法提高复用性class WarpFactory//模板方法逻辑{public Box WarpProduct(Func<Product> getProduct ){Box box = new Box();Product Product = getProduct.Invoke();box.Product = Product;return box;}}//书写成模板格式,Product、Box、WarpFactory都不需要改动,仅需要更改ProdcutFactory类class ProductFactory{public Product MakePizza(){Product product = new Product();product.Name = "Pizza";return product;}public Product MakeToyCar(){Product product = new Product();product.Name = "Toy Car";return product;}public Product MakeUmbrella(){Product product = new Product();product.Name = "Umbrella";return product;}}
Reuse,重复使用,也叫“复用”。代码的复用不但可以提高工作效率,还可以减少 bug 的引入。
良好的复用结构是所有优秀软件所追求的共同目标之一。回调方法(Hollywood方法)
回调方法是通过委托类型参数传入主调方法的被调用方法,主调方法根据自己的逻辑决定是否调用这个方法。 ```csharp using System; using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace DelegateExample { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { var productFactory = new ProductFactory();
// Func 前面是传入参数,最后一个是返回值,所以此处以 Product 为返回值Func<Product> func1 = new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakePizza);Func<Product> func2 = new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakeToyCar);var wrapFactory = new WrapFactory();Logger logger = new Logger();// Action 只有传入参数,所以此处以 Product 为参数Action<Product> log = new Action<Product>(logger.Log);Box box1 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(func1, log);Box box2 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(func2, log);Console.WriteLine(box1.Product.Name);Console.WriteLine(box2.Product.Name);}}class Logger//记录程序运行状态{public void Log(Product product){// Now 是带时区的时间,存储到数据库应该用不带时区的时间 UtcNow。Console.WriteLine("Product '{0}' created at {1}.Price is {2}", product.Name, DateTime.UtcNow, product.Price);}}class Product{public string Name { get; set; }public double Price { get; set; }}class Box{public Product Product { get; set; }}class WrapFactory{// 模板方法,提高复用性public Box WrapProduct(Func<Product> getProduct, Action<Product> logCallBack)//没有返回值的委托使用action<>{var box = new Box();Product product = getProduct.Invoke();// 只 log 价格高于 50 的if (product.Price >= 50){logCallBack(product);}box.Product = product;return box;}}class ProductFactory{public Product MakePizza(){var product = new Product{Name = "Pizza",Price = 12};return product;}public Product MakeToyCar(){var product = new Product{Name = "Toy Car",Price = 100};return product;}}
}
<a name="Pb3nc"></a>## 注意委托滥用恐怖的委托滥用示例,基本上工作在这段代码上的人,三个月内就离职了。 <br />以后技术上去了,记得回看这段代码,警示自己。:::danger**错误示范代码**:::```csharpusing System;using System.Collections.Generic;namespace DelegateExample{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Operation opt1=new Operation();Operation opt2=new Operation();Operation opt3=new Operation();opt3.InnerOperation = opt2;opt2.InnerOperation = opt1;opt3.Operate(new object(), null, null);//问题1:如果传入的两个参数为null, 失败和成功的效果是什么?答:内层的操作会调用外层的回调!//问题2:如果传入的两个参数不为null, 会出现什么情况?答:所有默认callback都被"穿透性"屏蔽}}class Operation//Operation包含一些对订单的操作{public Action DefaultSuccessCallback { get; set; }//默认成功回调public Action DefaultFailureCallback { get; set; }//默认失败回调public Operation InnerOperation { get; set; }//Operation类里面还有Operation,即可以套娃public object Operate(object input,Action successCallback,Action failureCallback){//两次判断作用为潘丹传入回调是否为空,为空就是用默认回调替代传入的回调if(successCallback==null){successCallback=this.DefaultSuccessCallback;}if(failureCallback==null){failureCallback=this.DefaultFailureCallback;}//由于不清楚上面传入的回调是否被替代,try...catch...内传入innnerOperation的回调难以确认object result = null;try{result = this.InnerOperation.Operate(input,successCallback,failureCallback);}catch{failureCallback.Invoke();}successCallback.Invoke();return result;}}}
委托的高级使用
多播(multicast)委托
多播委托即一个委托内部封装不止一个方法。
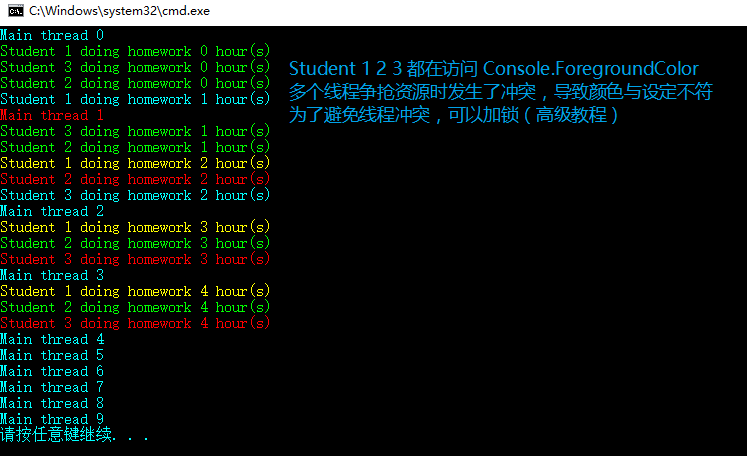
using System;using System.Threading;namespace DelegateExample{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){student stu1 = new Student{} { ID = 1, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow };student stu2 = new Student{} { ID = 2, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Green };student stu3 = new Student{} { ID = 3, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Red };action action1 = new Action(stu1.DoHomework);action action2 = new Action(stu2.DoHomework);action action3 = new Action(stu3.DoHomework);// 单播委托//action1.Invoke();//action2.Invoke();//action3.Invoke();// 多播委托action1 += action2;action1 += action3;action1.Invoke();}}class Student{public int ID { get; set; }public ConsoleColor PenColor { get; set; }public void DoHomework(){for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){Console.ForegroundColor = this.PenColor;Console.WriteLine("Student {0} doing homework {1} hour(s)", ID, i);Thread.Sleep(1000);}}}}
隐式异步调用
同步与异步的简介
- 中英文的语言差异
- 同步:你做完了我(在你的基础上)接着做
- 异步:咱们两个同时做(相当于汉语中的”同步进行”)
异步互不相干: 这里说的“互不相干”指的是逻辑上,而现实工作当中经常会遇到多个线程共享(即同时访问)同一个资源(比如某个变量)的情况,这时候如果处理不当就会产生线程间争夺资源的冲突。
同步调用与异步调用的对比
- 每一个运行的程序是一个进程(process)
- 每个进程可以有一个或者多个线程(thread)
- 同步调用是在同一线程内
- 异步调用的底层机理是多线程
- 串行==同步==单线程,并行==异步==多线程
三种同步调用
```csharp using System; using System.Threading;
namespace DelegateExample { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Student stu1 = new Student { ID = 1, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow }; Student stu2 = new Student { ID = 2, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Green }; Student stu3 = new Student { ID = 3, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Red };
// 直接同步调用//stu1.DoHomework();//stu2.DoHomework();//stu3.DoHomework();Action action1 = new Action(stu1.DoHomework);Action action2 = new Action(stu2.DoHomework);Action action3 = new Action(stu3.DoHomework);// 间接同步调用//action1.Invoke();//action2.Invoke();//action3.Invoke();// 多播委托,同步调用action1 += action2;action1 += action3;action1.Invoke();// 主线程模拟在做某些事情。for (var i = 0; i < 10; i++){Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Cyan;Console.WriteLine("Main thread {0}", i);Thread.Sleep(1000);}}}class Student{public int ID { get; set; }public ConsoleColor PenColor { get; set; }public void DoHomework(){for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){Console.ForegroundColor = PenColor;Console.WriteLine("Student {0} doing homework {1} hour(s)", ID, i);Thread.Sleep(1000);}}}
}
三种同步调用的结果一样:<br />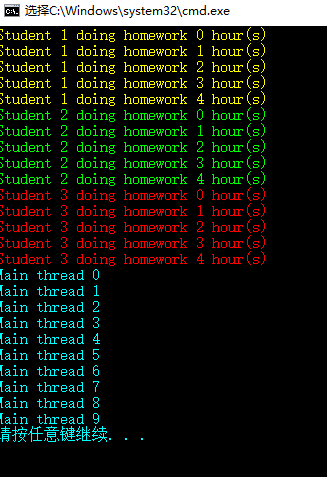<a name="MdhlN"></a>### 隐式多线程v.S.显式多线程- 直接同步调用:使用方法名- 间接同步调用:使用单播/多播委托的Invoke方法- 隐式异步调用:使用委托的Begin Invoke- 显式斤步调用:使用Thread或Task<a name="NiEbA"></a>#### 使用委托进行隐式异步调用 BeginInvoke```csharpusing System;using System.Threading;namespace DelegateExample{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Student stu1 = new Student { ID = 1, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow };Student stu2 = new Student { ID = 2, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Green };Student stu3 = new Student { ID = 3, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Red };Action action1 = new Action(stu1.DoHomework);Action action2 = new Action(stu2.DoHomework);Action action3 = new Action(stu3.DoHomework);// 使用委托进行隐式异步调用。// BeginInvoke 自动生成分支线程,并在分支线程内调用方法。action1.BeginInvoke(null, null);action2.BeginInvoke(null, null);action3.BeginInvoke(null, null);// 主线程模拟在做某些事情。for (var i = 0; i < 10; i++){Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Cyan;Console.WriteLine("Main thread {0}", i);Thread.Sleep(1000);}}}class Student{public int ID { get; set; }public ConsoleColor PenColor { get; set; }public void DoHomework(){for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){Console.ForegroundColor = PenColor;Console.WriteLine("Student {0} doing homework {1} hour(s)", ID, i);Thread.Sleep(1000);}}}}
使用 Thread 与 Task 进行异步调用
using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Threading;using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace DelegateExample{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Student stu1 = new Student { ID = 1, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow };Student stu2 = new Student { ID = 2, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Green };Student stu3 = new Student { ID = 3, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Red };// 老的显式异步调用方式 ThreadThread thread1 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(stu1.DoHomework));Thread thread2 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(stu2.DoHomework));Thread thread3 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(stu3.DoHomework));thread1.Start();thread2.Start();thread3.Start();// 使用 TaskTask task1 = new Task(new Action(stu1.DoHomework));Task task2 = new Task(new Action(stu2.DoHomework));Task task3 = new Task(new Action(stu3.DoHomework));/*当未引用名称空间时,使用“Ctrl+.”+Enter进行引用*/task1.Start();task2.Start();task3.Start();// 主线程模拟在做某些事情。for (var i = 0; i < 10; i++){Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Cyan;Console.WriteLine("Main thread {0}", i);Thread.Sleep(1000);}}}class Student{public int ID { get; set; }public ConsoleColor PenColor { get; set; }public void DoHomework(){for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){Console.ForegroundColor = PenColor;Console.WriteLine("Student {0} doing homework {1} hour(s)", ID, i);Thread.Sleep(1000);}}}}
设计模式常识:适时地使用接口(interface)取代委托
Java 完全使用接口取代了委托功能。
以前面的模板方法举列,通过接口也能实现方法的可替换。
using System;namespace DelegateExample{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){IProductFactory pizzaFactory = new PizzaFactory();IProductFactory toyCarFactory = new ToyCarFactory();var wrapFactory = new WrapFactory();Box box1 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(pizzaFactory);Box box2 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(toyCarFactory);Console.WriteLine(box1.Product.Name);Console.WriteLine(box2.Product.Name);}}interface IProductFactory{Product Make();}class PizzaFactory : IProductFactory{public Product Make(){var product = new Product();product.Name = "Pizza";return product;}}class ToyCarFactory : IProductFactory{public Product Make(){var product = new Product();product.Name = "Toy Car";return product;}}class Product{public string Name { get; set; }}class Box{public Product Product { get; set; }}class WrapFactory{// 模板方法,提高复用性public Box WrapProduct(IProductFactory productFactory){var box = new Box();Product product = productFactory.Make();box.Product = product;return box;}}}