Django中的ORM查询一般就是使用filter、exclude以及get三个方法来实现。我们可以在调用这些方法的时候,传递不同的参数来实现查询需求。在ORM层面,这些查询条件都是使用field__condition的方式来使用的。
常用查询条件
exact
- 精确查找,相当于SQL语句中的
=符号; 如果提供的是一个
None,那么在SQL层面就是被解释为NULL。article = Article.objects.get(id__exact=14) # 相当于直接id=14article = Article.objects.get(id__exact=None)
以上的两个查找翻译为SQL语句:
select * from article where id=14;select * from article where id IS NULL;
获取SQL语句
article.query:仅可以作用于QuerySet对象上- filter查询到的即为QuerySet类型
connection.queries:可以得到所有get查询的sql语句。模糊查找,相当于SQL语句中的like;
- 但没有使用%%,也属于精确匹配。 ```python article = Article.objects.filter(title__iexact=’hello world’)
以上的查询等价于以下的SQL语句:
select * from article where title like ‘hello world’;
**注意:**- **iexact**相当于SQL语句中的like,但是如果没有携带通配符%(不算模糊匹配),**也是精确匹配**;- exact和iexact的区别LIKE和=的区别,在大部分collation=utf8_general_ci情况下都是一样的(collation是用来对字符串比较的);<a name="Opdz5"></a>### contains- 大小写敏感,模糊查询;- 判断某个字段是否包含了某个数据。```pythonarticles = Article.objects.filter(title__contains='hello')# 以上等同于以下SQL语句:binary意为区分大小写select * where title like binary '%hello%';
注意:
- 在使用contains时,翻译成的sql语句左右两边是有百分号的,意味着使用的是模糊查询。
- 而exact翻译成sql语句左右两边是没有百分号的,意味着使用的是精确的查询。
icontains
大小写不敏感的模糊匹配查询。
articles = Article.objects.filter(title__icontains='hello')# 翻译成SQL语句如下:select * where title like '%hello%';
in
- 判断给定的field的值是否在给定的容器中。
- 容器可以为list、tuple或者任何一个可以迭代的对象,包括QuerySet对象。
- 如果是QuerySet对象,则默认将其中对象的主键提取出来在列表中,进行in判断
```python articles = Article.objects.filter(id__in=[1,2,3])
翻译成SQL语句如下:
select * from articles where id in (1,2,3)
查找标题为hello的文章分类
articles = Article.objects.filter(title__icontains=”hello”)
反向引用 - article
category = Category.objects.filter(article__in=articles) # 传递一个QuerySet对象
将以上两行合并后如下:
categories = Category.object.filter(articletitleicontains=”hello”)
查找文章ID为1,2,3的文章分类
category = Category.objects.filter(articleidin=[1,2,3])
**注意**:- django中定义了外键的话,会自动创建一个和flask中backref一样的**反向引用,名为模型名(类名)的小写**(也可通过related_name=xxx指定名称),所谓反向引用可理解为:在主表中进行查询时,可以通过反向引用,来使用从表的字段进行判断;- 当反向引用后面没跟字段时,代表**默认为从表的主键字段**;- ORM通过反向引用查找,使用的是SQL联合查询语句**inner join...on...** (on后面跟的条件相等才会查询出来)关于related_name 和 related_query_name区别:<br />[https://www.dazhuanlan.com/2020/02/26/5e5646ef86611/](https://www.dazhuanlan.com/2020/02/26/5e5646ef86611/)<a name="4hFVc"></a>### startswith/endswith查询以*** **开头,或结尾****<a name="a901ca81"></a>### first/last**查询第一条数据或最后一条数据**<a name="EtVLL"></a>### 根据关联的表进行查询想要获取文章标题中包含"hello"的所有的分类。```pythoncategories = Category.object.filter(article__title__contains="hello")# 拆分上面的命令如下:articles = Article.objects.filter(title__icontains="hello")# 反向引用 - articlecategories = Category.objects.filter(article__in=articles) # 传递一个QuerySet对象
比较运算
gt
某个field的值要大于给定的值。
# 将所有id大于4的文章全部都找出来。articles = Article.objects.filter(id__gt=4)# 翻译成以下SQL语句:select * from articles where id > 4;
gte
lt
lte
小于等于
range
判断某个field的值是否在给定的区间中。
# 提取所有创建时间在2020/7/27 10:00到2020/7/28 00:00之间的书籍。from datetime import datetimesdate = datetime(year=2020, month=7, day=27, hour=10)edate = datetime(year=2020, month=7, day=28)book = Book.objects.filter(create_time__range=(sdate, edate))print(book)print(book.query)# 翻译成SQL语句:SELECT `book_book`.`id`, `book_book`.`name`, `book_book`.`author`, `book_book`.`price`, `book_book`.`create_time`, `book_book`.`category_id` FROM `book_book` WHERE `book_book`.`create_time` BETWEEN 2020-07-27 10:00:00 AND 2020-07-28 00:00:00
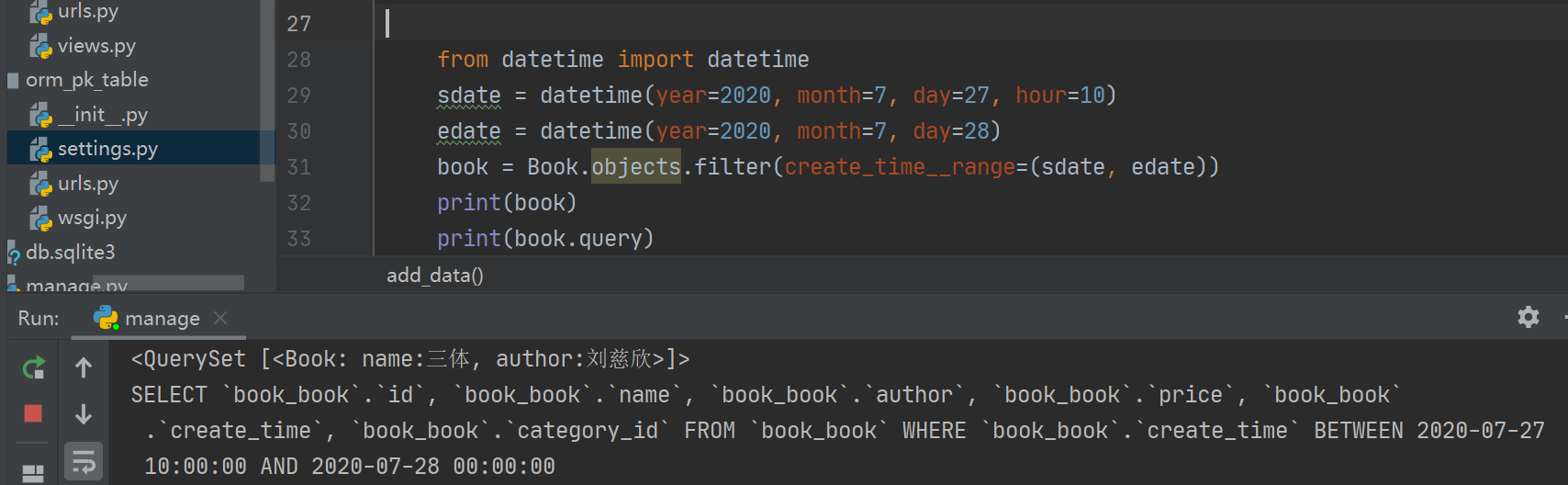
注意:setting.py中时区需设置如下:
TIME_ZONE = 'Asia/Shanghai'USE_TZ = False
date
针对某些date或者datetime类型的字段,可以指定date的范围。并且这个时间过滤,还可以使用链式调用。
def find_book(request):# book = Book.objects.get(pk=2)books = Book.objects.filter(create_time__date=datetime(year=2020, month=8, day=6))# books = Book.objects.filter(create_time__date='2020-08-06')# books = Book.objects.filter(create_time__date_gte=datetime(year=2020, month=8, day=1))print(books.query)# books = Book.objects.all()for book in books:print(book.name, book.author, book.price, book.create_time)return HttpResponse('查询图书数据')# 翻译成SQL语句:SELECT `books`.`id`, `books`.`name`, `books`.`author`, `books`.`price`, `books`.`create_time`, `books`.`category_id` FROM `books` WHERE DATE(`books`.`create_time`) = 2020-08-06
year
根据年份进行查找。
articles = Article.objects.filter(create_time__year=2018)articles = Article.objects.filter(create_time__year__gte=2017)# 翻译成SQL语句为如下:select ... where create_time between '2018-01-01' and '2018-12-31';select ... where create_time >= '2017-01-01';
time
根据时间进行查找。
articles = Article.objects.filter(create_time__time=time(hour=15, minute=21, second=10))# 以上的代码是获取每一天中15点21分10秒发表的所有文章。# 查询10秒到11秒之间的start_date = time(hour=17,minute=21,second=10)end_date = time(hour=17,minute=21,second=11)date_test = Article.objects.filter(create_time__time__range = (start_date, end_date))
聚合函数
如果用原生SQL,则可以使用聚合函数来提取数据。比如提取某个商品销售的数量,那么可以使用Count,如果想要知道商品销售的平均价格,那么可以使用Avg。
聚合函数是通过aggregate方法来实现的。
from django.db import modelsclass Author(models.Model):"""作者模型"""name = models.CharField(max_length=100)age = models.IntegerField()email = models.EmailField()class Meta:db_table = 'author'class Publisher(models.Model):"""出版社模型"""name = models.CharField(max_length=300)class Meta:db_table = 'publisher'class Book(models.Model):"""图书模型"""name = models.CharField(max_length=300)pages = models.IntegerField()price = models.FloatField()rating = models.FloatField()author = models.ForeignKey(Author,on_delete=models.CASCADE)publisher = models.ForeignKey(Publisher, on_delete=models.CASCADE)class Meta:db_table = 'book'class BookOrder(models.Model):"""图书订单模型"""book = models.ForeignKey("Book",on_delete=models.CASCADE)price = models.FloatField()class Meta:db_table = 'book_order'
聚合函数的使用
- Avg:求平均值。
想要获取所有图书的价格平均值,那么可以使用以下代码实现:
from django.db.models import Avgfrom django.db import connectionresult = Book.objects.aggregate(Avg('price'))print(connection.queries) # 打印SQL语句print(result)以上的打印结果是:{"price__avg":23.0}其中price__avg的结构是根据field__avg规则构成的。如果想要修改默认的名字,那么可以将Avg赋值给一个关键字参数。result = Book.objects.aggregate(my_avg=Avg('price'))print(result)那么以上的结果打印为:{"my_avg":23}
- Count:获取指定的对象的个数。
```python from django.db.models import Count result = Book.objects.aggregate(book_num=Count(‘id’)) 以上的result将返回Book表中总共有多少本图书。
Count类中,还有另外一个参数叫做distinct,默认是等于False,如果是等于True,那么将去掉那些重复的值。
比如要获取作者表中所有的不重复的邮箱总共有多少个。 from djang.db.models import Count result = Author.objects.aggregate(count=Count(‘email’,distinct=True))
统计每本图书的销量
result = Book.objects.annotate(book_nums=Count(“bookorder”)) for book in result: print(“%s/%s”%(book.name,book.book_nums))
- Max和Min:获取指定对象的最大值和最小值。<br />比如想要获取Author表中,最大的年龄和最小的年龄分别是多少:<br />```pythonfrom django.db.models import Max,Minresult = Author.objects.aggregate(Max('age'),Min('age'))如果最大的年龄是88,最小的年龄是18。那么以上的result将为:{"age__max":88,"age__min":18}# 统计每本售卖图书的最大值和最小值request = Book.objects.annotate(max=Max("bookorder__price"),min=Min("bookorder__price"))print(request)
- Sum:求指定对象的总和。
求图书的销售总额:
from djang.db.models import Sumresult = Book.objects.aggregate(total=Sum("price"))# 每一本图书的销售总额result = Book.objects.annotate(total=Sum("bookorder__price"))# 统计2019年,销售总额result = BookOrder.objects.filter(create_time__year=2019).aggregate(total=Sum("price"))
aggregate和annotate的区别
- aggregate:返回使用聚合函数后的字段和值。
- annotate:在原来模型字段的基础之上添加一个使用了聚合函数的字段,并且在使用聚合函数的时候,会使用当前这个模型的主键进行分组(group by)。
```python求每一本图书销售的平均价格
result = Book.objects.aggregate(avg=Avg(“bookorder__price”)) print(result) print(connection.queries)
result = Book.objects.annotate(avg=Avg(“bookorder__price”)) print(result)
<a name="a305adbf"></a>## F表达式和Q表达式<a name="d7a3ca51"></a>### F表达式F表达式是用来优化ORM操作数据库的。比如我们要将公司所有员工的薪水都增加1000元,如果按照正常的流程,应该是先从数据库中提取所有的员工工资到Python内存中,然后使用Python代码在员工工资的基础之上增加1000元,最后再保存到数据库中。<br />这里面涉及的流程就是,首先从数据库中提取数据到Python内存中,然后在Python内存中做完运算,之后再保存到数据库中。<br />```pythonemployees = Employee.objects.all()for employee in employees:employee.salary += 1000employee.save()
而我们的F表达式就可以优化这个流程,它可以不需要先把数据从数据库中提取出来,计算完成后再保存回去,他可以直接执行SQL语句,就将员工的工资增加1000元。
from djang.db.models import FEmployee.objects.update(salary=F("salary")+1000)F表达式并不会马上从数据库中获取数据,而是在生成SQL语句的时候,动态的获取传给F表达式的值。
比如如果想要获取作者中,name和email相同的作者数据。如果不使用F表达式。
authors = Author.objects.all()for author in authors:if author.name == author.email:print(author)如果使用F表达式,那么一行代码就可以搞定。示例代码如下:from django.db.models import Fauthors = Author.objects.filter(name=F("email"))
Q表达式
如果想要实现所有价格高于100元,并且评分达到9.0以上评分的图书。
books = Book.objects.filter(price__gte=100,rating__gte=9)
以上这个案例是一个并集查询,可以简单的通过传递多个条件进去来实现。
但是如果想要实现一些复杂的查询语句,比如要查询所有价格低于10元,或者是评分低于9分的图书。那就没有办法通过传递多个条件进去实现了。这时候就需要使用Q表达式来实现了。
from django.db.models import Qbooks = Book.objects.filter(Q(price__lte=10) | Q(rating__lte=9))
以上是进行或运算,当然还可以进行其他的运算,比如有&和~(非)等。
from django.db.models import Q# 获取id等于3的图书books = Book.objects.filter(Q(id=3))# 获取id等于3,或者名字中包含文字"传"的图书books = Book.objects.filter(Q(id=3)|Q(name__contains="传"))# 获取价格大于100,并且书名中包含"传"的图书books = Book.objects.filter(Q(price__gte=100)&Q(name__contains="传"))# 获取书名包含"传",但是id不等于3的图书books = Book.objects.filter(Q(name__contains='传') & ~Q(id=3))

