概述
@ConfigurationProperties注解大家应该在项目中都使用过,主要用来绑定属性中的值到我们的对象中。那大家对于怎么进行属性绑定的原理知道吗?
ConfigurationProperties使用
注解介绍
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD })@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Documented@Indexedpublic @interface ConfigurationProperties {// 配置的前缀, 和prefix一样@AliasFor("prefix")String value() default "";// 配置的前缀,和value一样@AliasFor("value")String prefix() default "";// 绑定时是否忽视无效字段,比如字段的类型错误等,默认falseboolean ignoreInvalidFields() default false;// 绑定时是否忽视没有的字段,默认trueboolean ignoreUnknownFields() default true;}
例子
定义Bean, 使用
@ConfigurationProperties@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "bsfit.user")@Componentpublic class User {private String userName;private Integer age;public String getUserName() {return userName;}public void setUserName(String userName) {this.userName = userName;}public Integer getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(Integer age) {this.age = age;}}
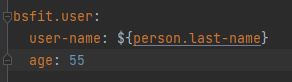
配置文件添加如下配置
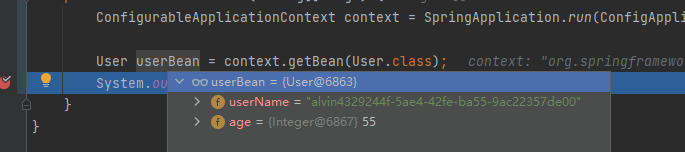
- 执行查看Bean的结果
注意点
- 被注释对象必须被注册为一个Bean, 可以通过以下几种方式
- 通过
@Component、@Service注解,参考上面的例子 通过
@Bean的方式,在方法上添加@Bean@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "bsfit.user")public User newUser() {return new User();}
通过
@EnableConfigurationProperties(value = User.class)方式- 通过
@ConfigurationPropertiesScan()的方式
属性的用中横线分隔和驼峰的方式都可以和Bean的字段映射
bsfit.user:## user-name等价于userName使用user-name: ${person.last-name}age: 55
源码解析
@ConfigurationProperties读取配置主要是通过ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessor配置绑定bean初始化后置处理器来实现的,它是在Bean初始化前后执行的。TODO执行主流程
首先我们看下
ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization方法,它是在Bean初始化前调用。// Bean初始化前调用postProcessBeforeInitialization方法@Overridepublic Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {//1. ConfigurationPropertiesBean.get(this.applicationContext, bean, beanName)方法根据 Bean 解析出一个 ConfigurationPropertiesBean 对象,包含Bean和相关的注解信息//2. 调用bind方法为对象添加属性bind(ConfigurationPropertiesBean.get(this.applicationContext, bean, beanName));//3.返回填充了配置属性的对象return bean;}
ConfigurationPropertiesBean#get(this.applicationContext, bean, beanName)方法如下:public static ConfigurationPropertiesBean get(ApplicationContext applicationContext, Object bean, String beanName) {// 1.找到这个beanName对应的工厂方法,例如@Bean标注的方法就是一个工厂方法,不是@Bean的话这里为空Method factoryMethod = findFactoryMethod(applicationContext, beanName);// 2.创建一个 ConfigurationPropertiesBean 对象,包含了这个 Bean 的@ConfigurationProperties注解信息return create(beanName, bean, bean.getClass(), factoryMethod);}
我们看下创建的
ConfigurationPropertiesBean对象都有哪些属性。public final class ConfigurationPropertiesBean {/*** Bean 的名称*/private final String name;/*** Bean 的实例对象*/private final Object instance;/*** Bean 的 `@ConfigurationProperties` 注解*/private final ConfigurationProperties annotation;/*** `@Bean` 对应的方法资源对象,包括实例对象和注解信息*/private final Bindable<?> bindTarget;/*** `@Bean` 对应的方法*/private final BindMethod bindMethod;}
调用关键方法
bind对属性进行绑定private void bind(ConfigurationPropertiesBean bean) {//1. 如果bean为空或者bean采用构造器绑定,直接返回,构造器方式绑定注解暂时不讨论,用的相对较小if (bean == null || hasBoundValueObject(bean.getName())) {return;}Assert.state(bean.getBindMethod() == BindMethod.JAVA_BEAN, "Cannot bind @ConfigurationProperties for bean '"+ bean.getName() + "'. Ensure that @ConstructorBinding has not been applied to regular bean");try {// 通过属性绑定器ConfigurationPropertiesBinder进行属性的绑定this.binder.bind(bean);}catch (Exception ex) {throw new ConfigurationPropertiesBindException(bean, ex);}}
通过属性绑定器
ConfigurationPropertiesBinder#bind方法对属性进行绑定BindResult<?> bind(ConfigurationPropertiesBean propertiesBean) {//1. 获取这个 Bean 的 Bindable 对象(包含了 @ConfigurationProperties、@Validated 配置信息和这个 Bean)Bindable<?> target = propertiesBean.asBindTarget();//2.获取这个 Bean 的 @ConfigurationProperties注解信息ConfigurationProperties annotation = propertiesBean.getAnnotation();//3. 获取属性绑定处理器,此处用了装饰器模式,提供了一些回调接口处理额外的逻辑,比如执行Validated校验等BindHandler bindHandler = getBindHandler(target, annotation);//4. 通过getBinder()方法new一个绑定器Binder对象,里面包括了配置属性对象列表、配置属性解析器、类型转换器等//5. 调用Binder的bind方法进行属性设置return getBinder().bind(annotation.prefix(), target, bindHandler);}
最关键的是
Binder#bind方法 ```java publicBindResult bind(String name, Bindable target, BindHandler handler) { //1. ConfigurationPropertyName.of(name)根据传入的name构造出ConfigurationPropertyName对象//2. 调用重载的方法bindreturn bind(ConfigurationPropertyName.of(name), target, handler);
}
public
private
private
- `ConfigurationPropertyName`: 由点分隔的元素组成的配置属性名称。用户创建的名称可以包含“a-z”“0-9”)和“-”,必须为小写,且首字符必须为字母和数字。“-”纯粹用于格式化,即。“foo-bar”和“foobar”被认为是等价的。5. 我们看下核心方法`Binder#bindObject````javaprivate <T> Object bindObject(ConfigurationPropertyName name, Bindable<T> target, BindHandler handler,Context context, boolean allowRecursiveBinding) {// 1. 根据属性名name从配置文件等source中遍历查找对应的结果ConfigurationProperty property = findProperty(name, target, context);// 2. 如果属性为空且不是第一层节点且不包含子节点,直接返回,否则继续遍历if (property == null && context.depth != 0 && containsNoDescendantOf(context.getSources(), name)) {return null;}//3. 处理聚合的绑定,比如List, Map等AggregateBinder<?> aggregateBinder = getAggregateBinder(target, context);if (aggregateBinder != null) {return bindAggregate(name, target, handler, context, aggregateBinder);}// 如果属性不为空, 直接绑定数据到属性上if (property != null) {try {//return bindProperty(target, context, property);}catch (ConverterNotFoundException ex) {// We might still be able to bind it using the recursive bindersObject instance = bindDataObject(name, target, handler, context, allowRecursiveBinding);if (instance != null) {return instance;}throw ex;}}// 绑定对象数据return bindDataObject(name, target, handler, context, allowRecursiveBinding);}
关注下核心方法
Binder#bindDataObjectprivate Object bindDataObject(ConfigurationPropertyName name, Bindable<?> target, BindHandler handler,Context context, boolean allowRecursiveBinding) {if (isUnbindableBean(name, target, context)) {return null;}Class<?> type = target.getType().resolve(Object.class);if (!allowRecursiveBinding && context.isBindingDataObject(type)) {return null;}// 1. 构造属性绑定器,比如用于绑定我们user对象的userName// DataObjectPropertyBinder是一个接口,最终执行的是Binder中的bind方法DataObjectPropertyBinder propertyBinder = (propertyName, propertyTarget) -> bind(name.append(propertyName),propertyTarget, handler, context, false, false);// 2. 相对比较复杂,调用Binder上下文对象Context的withDataObjectreturn context.withDataObject(type, () -> {for (DataObjectBinder dataObjectBinder : this.dataObjectBinders) {Object instance = dataObjectBinder.bind(name, target, context, propertyBinder);if (instance != null) {return instance;}}return null;});}
看下
Context.withDataObject方法 ```java privateT withDataObject(Class<?> type, Supplier supplier) { // 向栈中推入当前正在绑定的对象this.dataObjectBindings.push(type);try {// 深入属性绑定return withIncreasedDepth(supplier);}finally {this.dataObjectBindings.pop();}}
private
8. 我们看下传入的Supperlier方法如下```java() -> { // 遍历dataObjectBinders, 有两个,一个是构造函数绑定器,一个是JavaBeanBinder,也就是Set方法绑定,我们重点关注该绑定器for (DataObjectBinder dataObjectBinder : this.dataObjectBinders) {// 调用数据对象绑定器DataObjectBinder的bind方法Object instance = dataObjectBinder.bind(name, target, context, propertyBinder);if (instance != null) {return instance;}}return null;}
- 关注在
JavaBeanBinder#bind方法 ```java privateboolean bind(DataObjectPropertyBinder propertyBinder, Bean bean, BeanSupplier beanSupplier,
}Context context) {boolean bound = false;// 遍历Bean的属性列表for (BeanProperty beanProperty : bean.getProperties().values()) {// 调用bind方法绑定属性bound |= bind(beanSupplier, propertyBinder, beanProperty);context.clearConfigurationProperty();}return bound;
private